Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Coverage Funda
Uploaded by
Glory Neri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThis document discusses medications and drug administration. It defines key terms like generic names, trade names, prescription, and routes of administration. It outlines the parts of a legal doctor's order and discusses principles of administering medications correctly, like following the seven rights. The document also covers types of doctor's orders, effects of drugs, and different routes of administration like oral, topical, sublingual, and others. It stresses the importance of reporting any medication errors.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses medications and drug administration. It defines key terms like generic names, trade names, prescription, and routes of administration. It outlines the parts of a legal doctor's order and discusses principles of administering medications correctly, like following the seven rights. The document also covers types of doctor's orders, effects of drugs, and different routes of administration like oral, topical, sublingual, and others. It stresses the importance of reporting any medication errors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesFinal Coverage Funda
Uploaded by
Glory NeriThis document discusses medications and drug administration. It defines key terms like generic names, trade names, prescription, and routes of administration. It outlines the parts of a legal doctor's order and discusses principles of administering medications correctly, like following the seven rights. The document also covers types of doctor's orders, effects of drugs, and different routes of administration like oral, topical, sublingual, and others. It stresses the importance of reporting any medication errors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
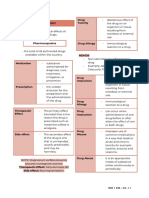
MEDICATIONS: Parts of Legal Doctor’s Order addiction ----- it is due to biochemical changes in
body tissues, esp. the nervous system .
Medication ----- is a substance administered for the Name of the patient
habituation ---- it is the emotional reliance on a
diagnosis, cure, treatment, or relief of a symptom or for Date and time
drug to maintain a sense of well being
prevention of disease. name of drug
accompanied by feelings of need or cravings
dose of drug of the drug.
drug ---- are illicitly obtained substance such as heroin,
route of administration synergism ----- the combined effects of drug is
cocaine, amphetamines.
time of frequency greater than the sum of each individual agent
prescription ----- the written direction for the signature of the physician acting independently
administration of a drug.
Effects of the Drug Therapeutic actions of drugs
four kinds of names in drugs;
Therapeutic effect ---- the primary effects 1. palliative ----- relieves the symptoms of a
1. generic name------ used throughout the drug’s intended, that is the reason the drug is disease but not affect the disease itself e.g.
lifetime prescribed. also called desired effect. antineoplastic agents for cancer.
2. trade name or brand name----- is the name side effect ---- the effect of the drug that is 2. curative ---- treats the disease condition… e.g.
given by the drug manufacturer and identifies it unintended also called the secondary effect. antibiotic for infection.
aa property of that company. drug allergy --- the immunologic reaction of the 3. supportive ---- sustains body functions until
3. official name---- is the name under which a drug drug. other treatment of the body’s response can
is listed in one of the official publication. anaphylactic reaction -----a severe allergic take over. e.g mannitol to reduce ICP (intra
4. chemical name. ----- is the name by which a reaction which usually occurs immediately cranial pressure) in a clients for surgery due to
chemist knows it, this name describes the following the administration of the drug. brain tumor.
constituents of the drug. drug tolerance ----- a deceased physiologic 4. substitutive --- replaces body fluids or
Pharmacology ----- is the study of the effect of drugs on response to the repeated doses of a drug that substances… e.g insulin injection for diabetes
living organisms. occurs when the rate of administration exceeds mellitus.
the rate of the metabolism or excretion. 5. chemotherapeutic ----- destroys malignant cells .
cumulative effect ----- it is the increasing e.g cyclophosphamide for cancer of the prostate
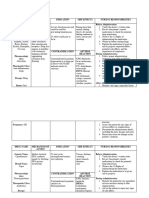
Types of Doctors Order response to the repeated doses of a drug that gland.
occurs when the rate of administration exceeds 6. restorative ---- returns the body health. e.g
1. Standing order ----- it is carried out until the the rate of metabolism or excretion. multivitamins
specified period of time or until it is idiosyncratic effect ----- it is the unexpected
discontinued by another order. peculiar response to the drug either
2. Single order -- it is carried out for one time overresponse , under response, different Principles in Administering Medication
only. response than expected.
3. STAT ORDER -----it is carried out at once or drug abuse ---- inappropriate intake of a 1. Observe the “7 rights” of drug administration.
immediately. substance, either continually or periodically. Right drug …… read the label three times.
4. PRN Order ----- it is carried out as the patient drug dependence ----- it is a person’s reliance to Right dose ---- know the usual dose of the drug..
requires. take a drug or substance. calculate the correct amount.
Right time ---- standard time may be followed 12. preoperative medications are usually elixir --- alcohol based liquid medication
by the institution. discontinued during the post operative period
2. Sublingual ----- a drug that is placed under the
Right route ---- check the route of the unless ordered to be continued.
tongue, where it dissolves.
administration
13. When a medication error is made, report it
Right patient ---- identify patient by; checking 3. buccal ---- a medication is held in the mouth against
immediately to the nurse in charge or physician. To
the ID band, asking him to state his name. the mucous membranes of the cheek until the drug it
implement necessary measures immediately. This
Right recording ----- sign medication sheet dissolves.
may prevent any adverse effects of the drug.
immediately after the administration of the
4. topical ---- application of medications to a
drug. 14. When a medication error is made, report
circumscribed area of the body .
right approach immediately to the nurse in charge or physician. to
2. Practice asepsis ---- wash hands before and implement necessary measures immediately. This a. dermatologic ---- includes lotions, liniments and
after preparing medications. may prevent any adverse effects of the drug. ointments.
3. Nurses who administer medications are
responsible for their own actions. question any b. ophthalmic ---- includes instillations and irrigations.
order that you consider incorrect (may be Routes of Drug Administration: 1. instillations ----to provide an eye medication that the
unclear or inappropriate) 1. Oral client requires.
4. Be knowledgeable about the medications that Advantages:
you administer. a. most convenient 2. irrigation ---- to clear the eye of noxious or other
5. keep narcotics in a locked place. b. usually less expensive foreign material.
6. Use medication that are in clearly labeled c. safe, does not break skin barrier c. otic ---- includes instillations and irrigations
containers. relabelling of drugs is the
responsibility of the pharmacist. d. nasal --- nasal instillations usually are instilled for
7. Return liquid that are cloudy in color he disadvantagesor other alkaline substances their astringent effect (to shrink swollen mucous
pharmacy. a. inappropriate for client with nausea and vomiting membrane), to loosen secretions and facilitate
8. Before administering the medication , identify b. drugs may have unpleasant taste or odor drainage or treat infections.
the client correctly. c. inappropriate if client cannot swallow and if GIT has e. inhalation --- use of nebulizers, metered dose
reduced motility. inhalers
9. Do not leave the medication at the bedside. d. drug may discolor the teeth
stay with the client until he actually takes the e. drug may be aspirated by seriously ill patient. f. vaginal ---
medications. Drug forms for oral administration:
5. rectal ---- can be used when the drug has
1. solid --- tablet, capsule, pill, powder
10. The nurse who prepares the drug administers it. objectionable taste or odor.
2. liquid ---- syrup, suspension, emulsion, elixir, milk
only the nurse who prepared the drug knows what
syrup --- sugar based liquid medication 6. parenteral ---- the administration of medication by a
the drug is. do not accept endorsement of
needle
medications. suspension --- water based liquid medication. shake the
bottle before use of medication to property mix it. a. intradermal --- under the epidermis
11. If the client vomits after taking the medication,
report this to the nurse in charge or physician. emulsion ---- oil based liquid medication b. subcutaneous ---- into the subcutaneous tissues
c. intramuscular ---- in the muscle
d. intravenous ---- into the vein
e. intra arterial ---- into the artery
f. intraosseous --- Into the bone
1. intradermal -----the administration of a drug into the
dermal layer of the skin beneath the epidermis.
You might also like
- Frontal LobesDocument275 pagesFrontal LobesSilvia Eugenia100% (7)
- Child Abuse and NeglectDocument16 pagesChild Abuse and NeglectStephanie Arum Devyana100% (1)
- Trans 1 Medication Administration 1Document23 pagesTrans 1 Medication Administration 1Germin CesaNo ratings yet
- Biological Self Sexual Self ?Document70 pagesBiological Self Sexual Self ?Glory NeriNo ratings yet
- Kemper, Ed - 2004Document7 pagesKemper, Ed - 2004abhinav_asokhNo ratings yet
- Study Guide-Pharmacology-PrelimDocument20 pagesStudy Guide-Pharmacology-Prelimcath payotNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication NotesDocument9 pagesAdministering Medication NotesCyriel DicoNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2Document4 pagesNCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2christyl necesitoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1 4Document61 pagesPharmacology 1 4Emily BernatNo ratings yet
- Medicationpart1 110202192115 Phpapp02Document10 pagesMedicationpart1 110202192115 Phpapp02Jessamine Rochelle Reyes Esberto100% (1)
- Social Determinants of HealthDocument27 pagesSocial Determinants of HealthDensearn Seo100% (5)
- Challenges of Drugs Abuse in YouthDocument65 pagesChallenges of Drugs Abuse in YouthJoseph Ssemujju Olson67% (3)
- Anxietate DepresieDocument18 pagesAnxietate Depresieandreea_zgrNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Chapter 35 MedicationsDocument4 pagesReviewer Chapter 35 MedicationsKeren GaciasNo ratings yet
- Medication AdministrationDocument99 pagesMedication AdministrationJoycee BoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: By: Nerissa Cabañero Laiza PinedaDocument121 pagesPharmacology: By: Nerissa Cabañero Laiza PinedaJacq CalaycayNo ratings yet
- Medication AdministrationDocument298 pagesMedication AdministrationOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- GRADE-4-CATCH-UP-FRIDAYS-ACTION-PLAN Final April 05Document3 pagesGRADE-4-CATCH-UP-FRIDAYS-ACTION-PLAN Final April 05Mary Rose Ramos86% (7)
- ABYIP of SK of Brgy. EspanaDocument7 pagesABYIP of SK of Brgy. EspanaCindy RoyoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Central Nervous System Depressant Drug Abuse And Addiction:: Implications for CounselingFrom EverandCentral Nervous System Depressant Drug Abuse And Addiction:: Implications for CounselingNo ratings yet
- DRUG EDUCATION AND VICE CONTROL NewDocument34 pagesDRUG EDUCATION AND VICE CONTROL NewDark MageNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PharmaDocument5 pagesReviewer PharmaRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument8 pagesPharmacologyJi-Han Abalo ImnidaNo ratings yet
- Finals 109 6Document202 pagesFinals 109 6JHOANA MARIE LOONo ratings yet
- Drug Education and Vice Control: Reviewer Notes inDocument10 pagesDrug Education and Vice Control: Reviewer Notes inJolly BelleNo ratings yet
- Cdi Lecture 1Document10 pagesCdi Lecture 1TJ del MarNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cdi 7 Drug Education and Vice ControlDocument11 pagesNotes On Cdi 7 Drug Education and Vice ControlDr.MontañoNo ratings yet
- Administration of MedicationDocument13 pagesAdministration of MedicationjoyceNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1Document7 pagesPharmacology 1Lorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- 05-Pharmacology NCLEX ExcerptDocument14 pages05-Pharmacology NCLEX ExcerptShiraishiNo ratings yet
- Introduction On DrugsDocument2 pagesIntroduction On DrugsAdya AeshaNo ratings yet
- Notes Funda SLDocument5 pagesNotes Funda SLPaguirigan, Louise AndreaNo ratings yet
- Vice and Drug Education and Control-RkDocument21 pagesVice and Drug Education and Control-RkROSES KISSES SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 1 NCM 106 Introduction To DrugsDocument8 pages1 NCM 106 Introduction To DrugscharmiemabaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction Definitions and Sources of DrugsDocument4 pagesIntroduction Definitions and Sources of Drugssindhu mNo ratings yet
- Review Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDocument6 pagesReview Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDela Cruz, Maria Roanne M.No ratings yet
- Drug - A Chemical Substance Used Drug Abuse - Is TheDocument6 pagesDrug - A Chemical Substance Used Drug Abuse - Is TheYam P BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1Document56 pagesPharmacology 1bsn1kgangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology TrancesDocument27 pagesPharmacology TrancesMAZON, DHANYCIA XYREENNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration RevDocument9 pagesMedication Administration RevIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- PcolDocument1 pagePcolYnah CelesteNo ratings yet
- Vice and Drug Education and ControlDocument7 pagesVice and Drug Education and ControlAimae Eata EalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing PharmacologyDocument4 pagesNursing PharmacologyAshley Jane MacapayadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyAdri Sinclaire100% (1)
- Unit #1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesUnit #1 IntroductionSaima VictorNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Introduction To PharmacologyDocument12 pagesWeek 1 Introduction To PharmacologyDino MicaNo ratings yet
- Unit #1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesUnit #1 IntroductionSaima VictorNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument7 pagesPharmacokineticsRonica MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - PrelimsDocument9 pagesPharmacology - PrelimsLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Quick TestDocument27 pagesPharmacology Quick TestAassh DcmbrNo ratings yet
- Midterm PharmacologyDocument8 pagesMidterm PharmacologyMae Ysobel HalangdonNo ratings yet
- Principles of Drug AdministrationDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Drug AdministrationEmman NuelleNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ortega ST., Iriga City, Philippines: University of Saint Anthony (Dr. Santiago G. Ortega Memorial)Document3 pagesDr. Ortega ST., Iriga City, Philippines: University of Saint Anthony (Dr. Santiago G. Ortega Memorial)Wilma BeraldeNo ratings yet
- Ncma216 PrelimDocument44 pagesNcma216 Prelimroldanmarygrace023No ratings yet
- Dangerous Drugs: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesDangerous Drugs: Learning OutcomesKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- 3 RdeditonDocument387 pages3 RdeditonHamza shoaib100% (1)
- MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION ReviewerDocument10 pagesMEDICATION ADMINISTRATION ReviewererlyncapaciteNo ratings yet
- NCM103 Medication&hygiene NotesDocument4 pagesNCM103 Medication&hygiene NotesAlexis Alyn CanoyNo ratings yet
- Responses To Drug Administration:: Factors Affecting Drug ResponseDocument4 pagesResponses To Drug Administration:: Factors Affecting Drug ResponseThea GonzalesNo ratings yet
- FNP - Oral Medication NotesDocument23 pagesFNP - Oral Medication NotesOliver DiamaeNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Midterm LectureDocument5 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Midterm LectureSana ChanNo ratings yet
- Medication AdministrationDocument298 pagesMedication AdministrationChristille Grace Basa MuchuelasNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ReviewerDocument24 pagesPharmacology ReviewergreinabelNo ratings yet
- General PharmacologyDocument8 pagesGeneral PharmacologysekarenthangavelNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument20 pagesPharmacologyKan JiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing PharmacologyDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Nursing PharmacologyMa. Isabel A. EnriquezNo ratings yet
- VdecDocument60 pagesVdecJustine yuNo ratings yet
- Druggggggg StudyDocument8 pagesDruggggggg StudyAcob, Jean LykaNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and Heredity: Alma Lou Ria Mae B. Castro, LPT 09264948991Document80 pagesNucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and Heredity: Alma Lou Ria Mae B. Castro, LPT 09264948991Glory NeriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice 1Document17 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice 1Glory NeriNo ratings yet
- SEMI Final Coverage Fundamentals of NursingDocument14 pagesSEMI Final Coverage Fundamentals of NursingGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument13 pagesFundamentals of NursingGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument24 pagesFundamentals of NursingGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module 2Document11 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 2Glory NeriNo ratings yet
- Cumulative College Blancia College Foundation IncorporatedDocument6 pagesCumulative College Blancia College Foundation IncorporatedGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Module 3 UtsDocument20 pagesModule 3 UtsGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept in Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Prepared By: Zyvel S. ZamoraDocument49 pagesBasic Concept in Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Prepared By: Zyvel S. ZamoraGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Journal 9Document18 pagesJournal 9ameraizahNo ratings yet
- HECAT Module AODDocument26 pagesHECAT Module AODririhenaNo ratings yet
- 04 Worksheet 1 (2) NSTPDocument2 pages04 Worksheet 1 (2) NSTPaby marieNo ratings yet
- Drug Addiction and YouthDocument3 pagesDrug Addiction and YouthHussain Mohi-ud-Din QadriNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Policies For The Poor and Uninsured Shelby Schroeder SW 4710 10/22/2015Document16 pagesMental Health Policies For The Poor and Uninsured Shelby Schroeder SW 4710 10/22/2015api-310782911No ratings yet
- Health 2 PDFDocument5 pagesHealth 2 PDFYen Pama RiveroNo ratings yet
- What Is Foxy? What Is Foxy? How Is Foxy Used? How Is Foxy Used?Document2 pagesWhat Is Foxy? What Is Foxy? How Is Foxy Used? How Is Foxy Used?losangelesNo ratings yet
- Form3 View New PDFDocument5 pagesForm3 View New PDFUMESH PATILNo ratings yet
- Sexual Assault - Males - PTSD - National Center For PTSDDocument3 pagesSexual Assault - Males - PTSD - National Center For PTSDEsioruname DanesiNo ratings yet
- Final DemoDocument16 pagesFinal DemoCaren DamasNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesInvestigatory ProjectSACHI KHIRENo ratings yet
- Banks or District Court Conditional Release Feb 2021Document7 pagesBanks or District Court Conditional Release Feb 2021KGW NewsNo ratings yet
- Introductory Handbook On The Prevention of Recidivism and The Social Reintegration of OffendersDocument166 pagesIntroductory Handbook On The Prevention of Recidivism and The Social Reintegration of Offendersyheal tolosaNo ratings yet
- JR Group ProposalDocument8 pagesJR Group Proposalapi-254132646100% (1)
- Adolescent Substance AbuseDocument5 pagesAdolescent Substance AbuseHamza DouichiNo ratings yet
- Substance Disorder QuizDocument3 pagesSubstance Disorder QuizmalindaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Drug Abuse Prevention and ControlDocument29 pagesModule 6 Drug Abuse Prevention and ControlAmon AmonNo ratings yet
- Binge Drinking Thesis StatementDocument6 pagesBinge Drinking Thesis Statementafbtegwly100% (2)
- Sociology Drug Addiction SlidesDocument47 pagesSociology Drug Addiction SlidesUmair MansoorNo ratings yet
- KKM Buku Vocational Examniation StandardDocument24 pagesKKM Buku Vocational Examniation StandardDr tangaraju waratarajuNo ratings yet
- My Dare ReportDocument2 pagesMy Dare Reportapi-260412202No ratings yet