Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Cefaclor Isoxsuprine
Uploaded by
Jelly Ong 王金玉Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Cefaclor Isoxsuprine
Uploaded by
Jelly Ong 王金玉Copyright:
Available Formats
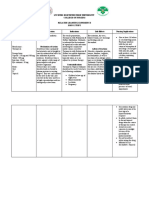
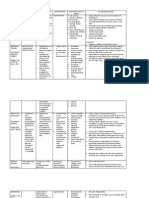
GENERIC / TRADE NAME CARBOCISTEINE
CLASSIFICATION Mucolytics
INDICATION Use for the treatment of disorders of the respiratory tract associated with excessive mucous.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated in active peptic ulcer.
SIDE EFFECTS Nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, palpitations and heartburn may occur. Caution must be exercised in patients with a history of gastric or duodenal ulcer. Gastrointestinal bleeding and skin rash may occur.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Assess cough for type, frequency, character. Tell patient to take with water and to drink plenty of fluids. Instruct patient to contact doctor if cough lasts more than 1 week. As appropriate, review all other significant adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the test mentioned above. Do not use more than the recommended dosage to prevent adverse reactions. The drug will make the sputum more liquid making it easier to cough up.
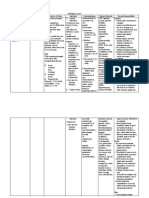
CEFACLOR
Antibiotic Cephalosporin (second generation)
Low respiratory tract infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, S. pyogenes URIs caused by S. pyogenes Dermatologic infections caused by Staphylococcus
Contraindicated with allergy to cephalosporins or penicillins. Use cautiously with renal failure, lactation, pregnancy.
CNS: Headache, dizziness, lethargy, paresthesias
Culture infection before drug therapy. Give drug with meals or food
GI: Nausea, to decrease GI discomfort. vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal Refrigerate suspension after pain, flatulence, reconstitution, and discard pseudomembranous
aureus, S. pyogenes UTIs caused by E. coli, P. mirabilis, Klebsiella, coagulase-negative staphylococci Otitis media caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, S. pyogenes, staphylococci ER tablets: Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, secondary infections of acute bronchitis, pharyngitis, and tonsilitis due to S. pyogenes; uncomplicated skin infections Unlabeled use: Acute uncomplicated UTI in select patients, single 2-g dose Peripheral and cerebral vascular insufficiency with spastic component showing symptoms: dizziness; forgetfulness; confusion; visual, auditory and speech abnormalities; coldness and numbness of limbs; color changes and ischemic ulcers; Raynaud s Disease
colitis, liver toxicity GU: Nephrotoxicity Hematologic: Bone marrow depression Hypersensitivity: Ranging from rash to fever to anaphylaxis; serum sickness reaction Other: Superinfections
after 14 days. Discontinue drug if hypersensitivity reaction occurs. Give patient yogurt or buttermilk in case of diarrhea. Arrange for oral vancomycin for serious colitis that fails to respond to discontinuation of drug.
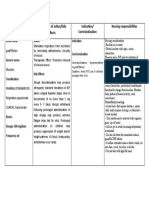
GENERIC NAME: ISOXSUPRINE BRAND NAME: DUVADILAN
Vasodilator
Hypersensitivity to isoxsuprine or any component of the formulation
Transient flushing Hypotension Rashes Gastrointestinal disturbances Maternal pulmonary edema
Assess patient s condition before therapy. Assess potential benefits from drug therapy. Monitor for possible drug induced adverse reactions. Inform patient about the possible side effects, adverse symptoms to report.
Arterial hemorrhage, heart disease, severe anemia Should not be administered
Uterine hypermotility disorders: threathened abortion; premature labor; dysmenorrheal
immediately in postpartum and premature labor
Tachycardia Transient palpitations Dizziness
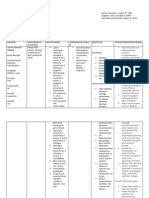
ACETAMINOPHEN Antipyretic Analgesic (nonopioid)
Analgesic-antipyretic in patients with aspirin allergy, hemostatic disturbances, bleeding diatheses, upper GI disease, gouty arthritis Arthritis and rheumatic disorders involving musculoskeletal pain (but lacks clinically significant antirheumatic and antiinflammatory effects) Common cold, flu, other viral and bacterial infections with pain and fever Unlabeled use: Prophylactic for children receiving DPT vaccination to reduce incidence of fever and pain
Contraindicated with allergy to acetaminophen. Use cautiously with impaired hepatic function, chronic alcoholism, pregnancy, lactation.
CNS: Headache CV: Chest pain, dyspnea, myocardial damage when doses of 58 g/day are ingested daily for several weeks or when doses of 4 g/day are ingested for 1 yr GI: Hepatic toxicity and failure, jaundice GU: Acute kidney failure, renal tubular necrosis Hematologic: Methemoglobinem iacyanosis; hemolytic
Do not exceed the recommended dosage. Consult physician if needed for children < 3 yr; if needed for longer than 10 days; if continued fever, severe or recurrent pain occurs (possible serious illness). Avoid using multiple preparations containing acetaminophen. Carefully check all OTC products. Give drug with food if GI upset occurs. Discontinue drug if hypersensitivity reactions occur. Treatment of overdose: Monitor serum levels regularly, N-acetylcysteine
anemia hematuria, anuria; neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypoglycemia Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever
should be available as a specific antidote; basic life support measures may be necessary.
AZITHROMYCIN
Macrolide antibiotic
Treatment of lower respiratory infections: Acute bacterial exacerbations of COPD due to H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. pneumoniae; communityacquired pneumonia due to S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae Treatment of lower respiratory infections: Streptococcal pharyngitis and tonsillitis due to Streptococcus pyogenes in those who cannot take penicillins Treatment of uncomplicated skin
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to azithromycin, erythromycin, or any macrolide antibiotic. Use cautiously with gonorrhea or syphilis, pseudomembranou s colitis, hepatic or renal impairment, lactation.
CNS: Dizziness, headache, vertigo, somnolence, fatigue GI: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, dyspepsia, flatulence, vomiting, melena, pseudomembranou s colitis Other: Superinfections, angioedema, rash, photosensitivity, vaginitis
Culture site of infection before therapy. Administer on an empty stomach 1 hr before or 23 hr after meals. Food affects the absorption of this drug. Prepare Zmax by adding 60 mL water to bottle, shake well. Counsel patients being treated for STDs about appropriate precautions and additional therapy.
Instruct patient to take the full course prescribed. Do
infections due to Staphylococcus aureus, S. pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae Treatment of nongonococcal urethritis and cervicitis due to C. trachomatis; treatment of PID Treatment of acute sinusitis Treatment of otitis media caused by H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, S. pneumoniae in children > 6 mo Treatment of pharyngitis and tonsillitis in children > 2 yr who cannot use first-line therapy Prevention and treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) in patients with advanced AIDS Treatment of patients with
not take with antacids. Tablets and oral suspension can be taken with or without food. Prepare Zmax by adding 60 mL (1/4 cup) water to bottle, shake well, drink all at once. You may experience these side effects: Stomach cramping, discomfort, diarrhea; fatigue, headache (medication may help); additional infections in the mouth or vagina (consult with health care provider for treatment). Report severe or watery diarrhea, severe nausea or vomiting, rash or itching, mouth sores, vaginal sores.
mild to moderate acute bacterial sinusitis caused by H. influenzae, Moracellis catarrhalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae (Zmax) Treatment of mild to moderate communityacquired pneumonia caused by Chlamydophila pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (Zmax) Unlabeled uses: Uncomplicated gonococcal infections caused by N. gonorrhoeae; gonococcal pharyngitis caused by N. gonorrhoeae; chlamydial infections caused by C. trachomatis; prophylaxis after sexual attack
You might also like
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Isoxilan Generic Name: Isoxsuprine: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesIsoxilan Generic Name: Isoxsuprine: Drug StudyJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument6 pagesDrug Study NurseryPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- TerramycinDocument2 pagesTerramycinChoox PriiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- DS HydralazineDocument3 pagesDS HydralazineGe LoNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug Study PDFDocument2 pagesVit K Drug Study PDFA sisonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocument6 pagesDrug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Terramycin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTerramycin - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Cavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidDocument3 pagesCavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Nursing GuideDocument2 pagesCephalexin Nursing GuideKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Sample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYDocument8 pagesSample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYSherina BolosNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument1 pageMethergineCharissa Magistrado De Leon0% (1)
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcDocument9 pagesDRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcPatricia Reese YutiamcoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug Study DisudrinDocument1 pageDrug Study DisudrinGrant Kenneth Dumo AmigableNo ratings yet
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Document2 pagesSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- VITAMIN K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVITAMIN K Drug StudyMarl DumiligNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- VACCINES Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccine StudyDocument2 pagesVACCINES Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccine StudyCarlo AniagNo ratings yet
- IsoxsuprineDocument1 pageIsoxsuprineAndrean EnriquezNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEMelvz BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionJulia Shane Barrios100% (1)
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesTranexamic Acid Drug Studyswitchlers anneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 04-21-09Document2 pagesDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySa Dei100% (1)
- Pediatric Drug Study SummaryDocument13 pagesPediatric Drug Study SummaryAriane Rose Saria CedronNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa: An Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist for HypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa: An Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist for HypertensionJinnijinniNo ratings yet
- Cefprozil (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefprozil (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Vit EDocument2 pagesVit EkingpinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- Gatchalian Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGatchalian Drug StudyAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Silver SulfadiazineDocument1 pageDrug Study Silver SulfadiazineMaica Lectana100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNicole Blanch BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Mupirocin DSDocument2 pagesMupirocin DSArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan 4Document4 pagesNursing-Care-Plan 4Christine CornagoNo ratings yet
- GlucoseDocument4 pagesGlucoseGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- TergecefDocument2 pagesTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- HYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)Document1 pageHYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)wen_pilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Azithromycinkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for Metronidazole AdministrationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities for Metronidazole AdministrationKristine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument1 pageAzithromycinjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- HNBB Drug StudyDocument4 pagesHNBB Drug StudyYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Endorsement Week 9Document13 pagesEndorsement Week 9MICHELLE FACTONo ratings yet
- MeclizineDocument2 pagesMeclizineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)