Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Nicole Blanch Buenavista0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
311 views2 pagesOriginal Title
99292871-Drug-Study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
311 views2 pagesDrug Study
Uploaded by
Nicole Blanch BuenavistaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
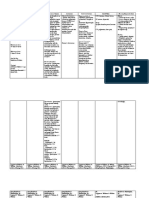
DRUG MECHANISM INDICATION/ SIDE EFFECTS/ NURSING
NAME OF ACTION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE CONSIDERATIONS
EFFECTS
Indications Contraindicati
on
1. Oral >Oral rehydration >For >Precise >Mild vomiting may >
Rehydration salts are given replacement of parenteral occur when oral
Salts orally to prevent or water and administration therapy has begun,
(Uphalyte) treat dehydration electrolyte of water and but therapy should be
due to acute loss associated electrolytes is continued with
Adults- ORS diarrhoea. Essential with diarrhoea recommended frequent, small
0.042(0.0425 water and salts are and vomiting. in the amounts of solution
) PO PRN lost in stools and following administered slowly.
vomitus, and conditions and Rarely, symptoms of
dehydration results the use of oral hypernatreamia
when blood volume rehydration (dizziness, fast
is decreased should not be heartbeat, high blood
because of fluid used except pressure, irritability,
loss from the under special muscle twitching,
extracellular fluid circumstances: restlessness,
compartment. seizures , swelling of
Preservation of the Anuria or feet or lower legs , or
facilitated glucose- oliguria, weakness) may be
sodium cotransport severe experienced.
system in the dehydration
small-bowel with
mucosa is the symptoms of
rationale of oral shock, severe
rehydration diarrhoea,
therapy. Glucose is inability to
actively absorbed drink, severe
in the normal and sustained
intestine and carries vomiting.
sodium with it in
about an equimolar Diarrhoea is
ration. Therefore, exacerbated
there is a greater and
net absorption of an dehydration
isotonic salt worsened
solution with when oral
glucose than one rehydration
without it. solutions are
Potassium given to
replacement during patients with
acute diarrhoea glucose
prevents below- malabsorption
normal serum ; volume of
concentrations of stool is greatly
potassium, increased and
especially in contains large
children, in whom amounts of
stool potassium glucose.
losses are higher Rehydration
than in adults. therapy should
Bicarbonates are be
effective in discontinued.
correcting the In patients
metabolic acidosis with intestinal
caused by diarrhoea obstruction,
and dehydration. paralytic ileus
or perforated
bowel,
delayed
passage of
carbohydrate
and
electrolytes
solution
through the
gastrointestina
l tract may
increase the
risk of
gastrointestina
l irritation.
You might also like
- The Borax Conspiracy How The Arthritis Cure Has Been StoppedDocument14 pagesThe Borax Conspiracy How The Arthritis Cure Has Been StoppedMilan Bogdanovic100% (7)
- Health Education HTPDocument4 pagesHealth Education HTPizelelelsNo ratings yet
- Oral Rehydration Solution: A Drug Study OnDocument7 pagesOral Rehydration Solution: A Drug Study OnRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Oxacillin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageOxacillin Nursing Considerationsnerissa_villanueva3523No ratings yet
- ORS Mechanism of Action and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesORS Mechanism of Action and Nursing ConsiderationsCyric Jyn Fadul Full100% (2)
- GlucoseDocument4 pagesGlucoseGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Vit EDocument2 pagesVit EkingpinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- DRUG ACTIONDocument3 pagesDRUG ACTIONGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie Angelica BilonoNo ratings yet
- Terramycin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTerramycin - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNo ratings yet
- PATIENT M.G.'S MEDICATIONS AND NURSING CONSIDERATIONSDocument5 pagesPATIENT M.G.'S MEDICATIONS AND NURSING CONSIDERATIONSGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAmikacin Drug StudyMark Angelo LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- OxacillinDocument2 pagesOxacillinSatinderSinghNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADocument3 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine ChampnessNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Nursing GuideDocument2 pagesCephalexin Nursing GuideKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Drugstudy PotassiumchlorideDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Potassiumchloridetrina412No ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument3 pagesDischarge PlanDranlie LagdamenNo ratings yet
- OxacillinDocument1 pageOxacillinSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanningSasa QuinaNo ratings yet
- Asian College of Science and Technology College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAsian College of Science and Technology College of Nursing Drug StudynizabangxNo ratings yet
- Ds OresolDocument2 pagesDs OresolShannie PadillaNo ratings yet
- Postop Drug2Document3 pagesPostop Drug2zbestgurlNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Glyburide Mechanism of Action, Side Effects and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesGlyburide Mechanism of Action, Side Effects and Nursing Responsibilitiesanne marieNo ratings yet
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- CetirizineDocument2 pagesCetirizineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJan DeeNo ratings yet
- Isoxsuprine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesIsoxsuprine HydrochloridePatricia Mae MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocument6 pagesDrug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- DRUG+STUDY NaprexDocument2 pagesDRUG+STUDY NaprexJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopancen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- VITAMIN K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVITAMIN K Drug StudyMarl DumiligNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Pedia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesGentamicin Pedia Drug StudyGong AllenaNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate Supplement GuideDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Supplement GuidezjoshuacNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument1 pageRanitidineliza sian100% (1)
- GI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDocument3 pagesGI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug StudyCath Bril100% (1)
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAnn AquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Ferrous Sulfate - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFerrous Sulfate - Drug StudyElla Musk100% (1)
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ParacetamolNE TdrNo ratings yet
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- Sample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYDocument8 pagesSample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYSherina BolosNo ratings yet
- ORS Package InsertDocument1 pageORS Package InsertwhothehellisarcticmonkeysNo ratings yet
- KCL 2Document2 pagesKCL 2Hoseña, Kathea Khyll BSN3No ratings yet
- EntrestoDocument39 pagesEntrestonikhilNo ratings yet
- Prakriti TestDocument4 pagesPrakriti TestSubramanya RaoNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry: AnalgesicsDocument6 pagesMedicinal Chemistry: AnalgesicsAlishba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- CleftlipandpalateDocument134 pagesCleftlipandpalatePARIJAT CHAKRABORTY100% (1)
- Exploratory EssayDocument3 pagesExploratory Essayapi-251189694No ratings yet
- Reversible Dementia and DeliriumDocument65 pagesReversible Dementia and Deliriummpm8471No ratings yet
- Adrenal Vein SamplingDocument8 pagesAdrenal Vein SamplingsirrfsNo ratings yet
- Untitled 25Document530 pagesUntitled 25Tony ChangNo ratings yet
- Super 108 DR LalDocument8 pagesSuper 108 DR Lalarkaprava paulNo ratings yet
- Final Intervention Protocol 1Document5 pagesFinal Intervention Protocol 1api-333354952No ratings yet
- Self Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisDocument57 pagesSelf Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisHarby Ongbay Abellanosa100% (1)
- Hydrotherap Y: Anna Ria R. Balaladia, PTRPDocument20 pagesHydrotherap Y: Anna Ria R. Balaladia, PTRPFloriza de LeonNo ratings yet
- Community Nursing Diagnosis and PrioritizingDocument12 pagesCommunity Nursing Diagnosis and Prioritizingsanty27No ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument16 pagesBlood CirculationMesyawallaNo ratings yet
- 10 Surprising Health Benefits of HoneyDocument5 pages10 Surprising Health Benefits of Honeykarina chaswinNo ratings yet
- A Clinician's Guide to Treating X-Linked HypophosphatemiaDocument9 pagesA Clinician's Guide to Treating X-Linked HypophosphatemiaFreddy ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- How To Get Appointed Ocn370397207Document46 pagesHow To Get Appointed Ocn370397207api-241896162No ratings yet
- Fact Shett - OSHADocument2 pagesFact Shett - OSHALuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- Statement Letter For Offline Final ParticipationDocument3 pagesStatement Letter For Offline Final ParticipationDina RovivahNo ratings yet
- Health Problems Vocabulary and PhrasesDocument17 pagesHealth Problems Vocabulary and PhrasesMartha Bazan PazNo ratings yet
- Anti-Dopamine D2 Receptor Antibody Ab30743 Anti-Dopamine D2 Receptor Antibody Ab30743Document3 pagesAnti-Dopamine D2 Receptor Antibody Ab30743 Anti-Dopamine D2 Receptor Antibody Ab30743Michael DaleyNo ratings yet
- Nama-Nama Obat PrekurDocument2 pagesNama-Nama Obat PrekurWatini Daiman Fii QolbyNo ratings yet
- Fibrous Protein or ScleroproteinDocument4 pagesFibrous Protein or ScleroproteinMia DimagibaNo ratings yet
- MCQ OphthalmoDocument62 pagesMCQ Ophthalmosafasayed100% (1)
- Rca CheckDocument34 pagesRca CheckBhella Guntoro100% (1)
- 9 Exercise Physiology Handout 2011Document20 pages9 Exercise Physiology Handout 2011maraj687No ratings yet
- Phần 3: Viết - Vstep: You should spend about 20 minutes on this taskDocument16 pagesPhần 3: Viết - Vstep: You should spend about 20 minutes on this taskTạ Đình TuấnNo ratings yet
- Sleep, Dreams, & More (: Exploring Consciousness)Document46 pagesSleep, Dreams, & More (: Exploring Consciousness)Sheila G. DolipasNo ratings yet
- Rachel Catratin (20711194) & Marshanda Bayu (20711161) - Penugasan STARDDocument30 pagesRachel Catratin (20711194) & Marshanda Bayu (20711161) - Penugasan STARDRACHEL CATRATIN NADANo ratings yet