Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sunday, 3 April 2022 2:22 PM
Uploaded by
Fatima Aliana Mautante0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesdhfjdhfis kajdiscn
Original Title
idek
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdhfjdhfis kajdiscn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSunday, 3 April 2022 2:22 PM
Uploaded by
Fatima Aliana Mautantedhfjdhfis kajdiscn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Math
Sunday, 3 April 2022
2:22 pm
1st slide:
"Probability of Independent Events, Conditional Probability, Probability of Dependent Events"
Group 3 (Dawis, Baal, Olarte, Baguio, Mautante, Cagabcabon)
2nd slide:
Probability of Independent Events
o The probability of two independent events A and B is equals to the product of their
individual probabilities P(A) and P(B).
P (A ∩ B) = P(A) ∙ P(B)
3rd slide:
Example:
o A coin is tossed and a die is rolled. Find the probability of landing on the head side of the
coin and rolling a 6 on the die.
4th slide:
Solution:
o Let C1 = event of landing on the head side of the coin
D1 = event of rolling a 6 on the die
o C = {H, T}, n(C) = 2
o C1 = {H}, n(C1) = 1
o D = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, n(D) = 6
o D1 = {6}, n(D1) = 1
P (C1 ∩ D1) = P(C1 ) ∙ P(D1)
= (C1 / C) ∙ (D1 / D)
= (1/2) ∙ (1/6)
= 1/12 <--- Answer
5th slide:
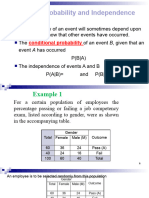
Conditional Probability
o The conditional probability of event B occurring given that event A has occurred is
P(B | A) = P(A∩B) / P(A), wherein P(A) ≠ 0
6th slide:
Example:
o In a group of 100 sports car buyers, 40 bought alarm systems, 30 purchased bucket
seats, and 20 purchased an alarm system and bucket seats. If a car buyer is chosen at
random bought an alarm system, what is the probability they also bought bucket seats?
7th slide:
Solution:
o Event A = sports car buyers who bought alarm systems
o Event B = sports car buyers who purchased bucket seats
o P(A∩B) = probability of joint occurrence of both A and B
P(A) = 40/100 = 2/5 or 0.4
P(A∩B) = 20/100 = 1/5 or 0.2
P(B | A) = P(A∩B) / P(A)
= 0.2 / 0.4
= 0.5 or 50% <--- Answer
8th slide:
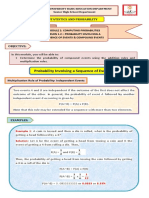
Probability of Dependent Events
o The probability of two dependent events A and B, with P(A) > 0 and P(B) > 0 is
P(A∩B) = P(A) ∙ P(B | A)
9th slide:
Example:
o If we randomly select two marbles from a box that has 3 blue marbles and 7 green
marbles, what is the probability of drawing a green marble and then a blue marble,
without replacement?
10th slide:
Solution:
o P(A) = 7/10
o P(B | A) = 3/9
P(A∩B) = P(A) ∙ P(B | A)
= (7/10) ∙ (3/9)
= 21/90 or 7/30 <--- Answer
You might also like
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Probability 1Document64 pagesProbability 1Deepak Kumar Arora100% (3)
- 52 Tips For Texas Hold em Poker - Barry ShulmanDocument70 pages52 Tips For Texas Hold em Poker - Barry Shulmanwacko_ro100% (1)
- Six Long Shot FactorsDocument10 pagesSix Long Shot FactorsManuel Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Tips, Strategies For Numerical Tests, Psychometric, Aptitude TestsDocument11 pagesTips, Strategies For Numerical Tests, Psychometric, Aptitude Testscorporateboy36596100% (3)
- Betting Track2 21 AdvancedDocument74 pagesBetting Track2 21 AdvancedNanaKarikariMintahNo ratings yet
- Free Horse Racing Systems: The Outsiders SystemDocument2 pagesFree Horse Racing Systems: The Outsiders SystemomikamiNo ratings yet
- The Football FormulaDocument56 pagesThe Football FormulaCiprian Dobrescu100% (7)
- Forex Price Action Scalping by Bob Volman 200 359Document160 pagesForex Price Action Scalping by Bob Volman 200 359sapthanhtien100% (1)
- Chapter 3.1 Conditional ProbabilityDocument22 pagesChapter 3.1 Conditional ProbabilityFauzi TwojitNo ratings yet
- UK ARMY Technical Selection TestsDocument9 pagesUK ARMY Technical Selection Testsusernamexi100% (9)
- PPT-2 of Chapter 2 Multiplication Rule, Conditional Probability and Bayes TheoremDocument17 pagesPPT-2 of Chapter 2 Multiplication Rule, Conditional Probability and Bayes TheoremDmddldldldlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ProbabilityDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To ProbabilityAbdul Azis Zaenal MustopaNo ratings yet
- Statistics, Problem Solving, and Decision Making: Week 3: Dr. Edwin Setiawan NugrahaDocument20 pagesStatistics, Problem Solving, and Decision Making: Week 3: Dr. Edwin Setiawan NugrahaJocelyn Beatrice MihardjaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Statistics and Probability STA 201 S M Rajib Hossain MNS, BRAC University Lecture-9 & 10Document15 pagesElements of Statistics and Probability STA 201 S M Rajib Hossain MNS, BRAC University Lecture-9 & 10pritom.biswas.niloyNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability Exercise 13.2Document13 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability Exercise 13.2ilakiyamuruganandhamNo ratings yet
- Basic Probability RulesDocument5 pagesBasic Probability RulesAbdulrahman SerhalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document16 pagesLecture 2Hossam Mohamed Ahmed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Probability p3Document27 pagesProbability p3Hana ElfarNo ratings yet
- QM Unit - 2 Probability MCQ SYBBA SEM-4Document15 pagesQM Unit - 2 Probability MCQ SYBBA SEM-4BKC EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- Statically MathDocument22 pagesStatically Math21142467No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture 4Document21 pagesChapter 2 Lecture 4mariammaged981No ratings yet
- Probabilistic MethodDocument12 pagesProbabilistic MethodShàhzád ÀñsärìNo ratings yet
- Ms. Sana Tahir at Giki: Engineering Statistics ES-202Document16 pagesMs. Sana Tahir at Giki: Engineering Statistics ES-202Zain AshfaqNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths Exemplar Chapter 13 PDFDocument29 pages12 Maths Exemplar Chapter 13 PDFMohammed IrshadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-3Document41 pagesChapter 2-3Riaz Hussain JunejoNo ratings yet
- Math1905 l7-8Document22 pagesMath1905 l7-8edmond1200No ratings yet
- Ms. Sana Tahir at Giki: Engineering Statistics ES-202Document16 pagesMs. Sana Tahir at Giki: Engineering Statistics ES-202Zain AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Prob U2 t3 Act - Int8 Word 01Document9 pagesProb U2 t3 Act - Int8 Word 01makicamps11No ratings yet
- Addition and Multiplication Laws of Probability: PrerequisitesDocument17 pagesAddition and Multiplication Laws of Probability: PrerequisitespangbattaNo ratings yet
- 3 ProbabilityDocument24 pages3 ProbabilitySaad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument100 pagesStatistics and Probabilitykamaraabdulrahman547No ratings yet
- 35 3 Addn Mult Laws ProbDocument15 pages35 3 Addn Mult Laws Probfatcode27No ratings yet
- HW3 11 SolDocument5 pagesHW3 11 SolShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Probability MCQDocument26 pagesProbability MCQMariyappan RNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Conditional ProbabilityDocument3 pages2.3 Conditional ProbabilityKumar Gaurab JhaNo ratings yet
- Probability, Lec 2Document16 pagesProbability, Lec 2tarqtito4390No ratings yet
- HW1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHW1 SolutionsRey TangNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 - ProbabilityDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 9 - ProbabilityAhmad Naqiuddin0% (1)
- Ass # 4, SE (Solution)Document2 pagesAss # 4, SE (Solution)Malaika saleemNo ratings yet
- Probability: Counting TechniquesDocument54 pagesProbability: Counting Techniquesمحمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- The Axiomatic Approach: P (A) Be Assigned. Then, P (A) Is The Probability of Event A, If The Following AxiomsDocument9 pagesThe Axiomatic Approach: P (A) Be Assigned. Then, P (A) Is The Probability of Event A, If The Following AxiomsMragankNo ratings yet
- Additive Rule of ProbabilityDocument7 pagesAdditive Rule of ProbabilityJohn Ismael MoralNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Basic Probability & Its ApplicationsDocument25 pagesTopic 2 - Basic Probability & Its ApplicationsAmin ZaquanNo ratings yet
- Chapter+1 Recorded-1Document41 pagesChapter+1 Recorded-1doug johnsonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (M) CourseworkDocument16 pagesMathematics (M) CourseworkCHIA SENG YEE MoeNo ratings yet
- Conditional & Independent EventsDocument15 pagesConditional & Independent EventsCYNo ratings yet
- 505 Review Problems For Final SolutionsDocument6 pages505 Review Problems For Final SolutionsGabe GuerrierNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Engr. Muhammad Amin Qureshi: Probability & Statistics Week 10Document30 pagesPrepared By: Engr. Muhammad Amin Qureshi: Probability & Statistics Week 10Muhammad YahyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Jay MenonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Prob & Stat Lecture Notes 5Document10 pagesEngineering Prob & Stat Lecture Notes 5EICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- ProbaDocument51 pagesProbaapi-3756871100% (1)
- Practice Probability ProblemsDocument2 pagesPractice Probability ProblemsSaravanakumar VanniarajanNo ratings yet
- Probability of Event Intersections: Vietnamese-German UniversityDocument17 pagesProbability of Event Intersections: Vietnamese-German UniversityĐặng ThưNo ratings yet
- Additive Rule: - Applies To Unions of EventsDocument24 pagesAdditive Rule: - Applies To Unions of EventsPauline UmandapNo ratings yet
- One Marker ProbabilityDocument6 pagesOne Marker Probabilityamit gargNo ratings yet
- Video Conference Probability Theory: 16 September 2020Document36 pagesVideo Conference Probability Theory: 16 September 2020eirinneNo ratings yet
- Leep 213Document29 pagesLeep 213Koyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1743 Chapter 3 ProbabilityDocument21 pages1743 Chapter 3 ProbabilitySho Pin TanNo ratings yet
- STAT 112 Session 1B - MDocument36 pagesSTAT 112 Session 1B - MProtocol WonderNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Probability&Statics ECDocument27 pagesChap 4 Probability&Statics ECMidhun BabuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document19 pagesLecture 03Saad AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and Statistics Course ID:MA2203: Course Teacher: Dr. Manas Ranjan TripathyDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Probability and Statistics Course ID:MA2203: Course Teacher: Dr. Manas Ranjan TripathyGaurav Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Probability Involving A Sequence of Events & Compound EventsDocument5 pagesProbability Involving A Sequence of Events & Compound EventsÇhärlöttë Çhrístíñë Dë ÇöldëNo ratings yet
- Probability, Distributuion and Time SeriesDocument49 pagesProbability, Distributuion and Time Serieshodcommerceeve rkmvcNo ratings yet
- 3A - Conditional Probablility and IndependenceDocument17 pages3A - Conditional Probablility and IndependenceQwerty QwertyNo ratings yet
- Random Sampling & ProbabilityDocument54 pagesRandom Sampling & ProbabilityShaila LopezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Take Home Exam 6Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Take Home Exam 6Anthony Jay PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Paper-1: Amcat Quants Previous Years Question Paper BankDocument137 pagesPaper-1: Amcat Quants Previous Years Question Paper BankbhargaviNo ratings yet
- A MadurskaDocument98 pagesA MadurskaPatrick LangstromNo ratings yet
- RS Aggarwal Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Percentage Exersice 10ADocument9 pagesRS Aggarwal Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Percentage Exersice 10Ashahanakhn25No ratings yet
- 346 Chapter 13 HWSolutionsDocument17 pages346 Chapter 13 HWSolutionsSu4family0% (1)
- Advanced Macroeconomics 4th Edition Romer Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesAdvanced Macroeconomics 4th Edition Romer Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsahebmostwhatgr91100% (16)
- Work and Time ProbsDocument9 pagesWork and Time ProbsMuhammad Noor AmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 - 895241 Probability PDFDocument54 pagesChapter - 12 - 895241 Probability PDFJj SotoNo ratings yet
- Six Nations Friday Pacific RacingDocument1 pageSix Nations Friday Pacific RacingjoanalcarazNo ratings yet
- Simplification All ConceptsDocument70 pagesSimplification All ConceptsNilabja BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Examination in Math 10Document3 pages4th Quarter Examination in Math 10Enrico EusebioNo ratings yet
- TCS Set 2Document361 pagesTCS Set 2AbcdefNo ratings yet
- Maths Statistics & LR MockDocument11 pagesMaths Statistics & LR MockInnovation SkylineNo ratings yet
- Betting Short Guide:: Things That Most Know, But Few FollowDocument4 pagesBetting Short Guide:: Things That Most Know, But Few FollowFox BoxNo ratings yet
- Math Project Class 11 ProbabilityDocument18 pagesMath Project Class 11 ProbabilityMumita Teyung LimbuNo ratings yet
- Ultimatcher3 InstructionsDocument20 pagesUltimatcher3 InstructionsBruno Miguel Santos SIlva0% (1)
- GTA Cheat CodesDocument65 pagesGTA Cheat Codesantukara0% (1)
- LTD 1 1 Cheat Sheet Sports Trading LifeDocument14 pagesLTD 1 1 Cheat Sheet Sports Trading LifedavidtourraineNo ratings yet
- Math: What Is Probability: ? Grade 6Document16 pagesMath: What Is Probability: ? Grade 6Kelly ManganNo ratings yet
- Cheat CodesDocument75 pagesCheat CodesPranay BendreNo ratings yet
- 8.1, 8.2 & 8.3 Theoretical Probability: Probability of An Event OccurringDocument3 pages8.1, 8.2 & 8.3 Theoretical Probability: Probability of An Event OccurringEugenio CapielloNo ratings yet