Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics - Application and Interpretation - Command Terms and Notation
Uploaded by
Ranveer RatraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics - Application and Interpretation - Command Terms and Notation
Uploaded by
Ranveer RatraCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendices
Glossary of command terms
Command terms for Mathematics: applications
and interpretation
Students should be familiar with the following key terms and phrases used in examination questions, which
are to be understood as described below. Although these terms will be used frequently in examination
questions, other terms may be used to direct students to present an argument in a specific way.
Command term Definition
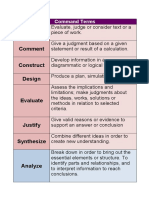
Calculate Obtain a numerical answer showing the relevant stages in the working.
Comment Give a judgment based on a given statement or result of a calculation.
Compare Give an account of the similarities between two (or more) items or
situations, referring to both (all) of them throughout.
Compare and contrast Give an account of similarities and differences between two (or more) items
or situations, referring to both (all) of them throughout.
Construct Display information in a diagrammatic or logical form.
Contrast Give an account of the differences between two (or more) items or
situations, referring to both (all) of them throughout.
Deduce Reach a conclusion from the information given.
Demonstrate Make clear by reasoning or evidence, illustrating with examples or practical
application.
Describe Give a detailed account.
Determine Obtain the only possible answer.
Differentiate Obtain the derivative of a function.
Distinguish Make clear the differences between two or more concepts or items.
Draw Represent by means of a labelled, accurate diagram or graph, using a pencil.
A ruler (straight edge) should be used for straight lines. Diagrams should be
drawn to scale. Graphs should have points correctly plotted (if appropriate)
and joined in a straight line or smooth curve.
Estimate Obtain an approximate value.
Explain Give a detailed account including reasons or causes.
Find Obtain an answer showing relevant stages in the working.
Hence Use the preceding work to obtain the required result.
Hence or otherwise It is suggested that the preceding work is used, but other methods could
also receive credit.
Identify Provide an answer from a number of possibilities.
Integrate Obtain the integral of a function.
90 Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide
Glossary of command terms
Command term Definition
Interpret Use knowledge and understanding to recognize trends and draw
conclusions from given information.
Investigate Observe, study, or make a detailed and systematic examination, in order to
establish facts and reach new conclusions.
Justify Give valid reasons or evidence to support an answer or conclusion.
Label Add labels to a diagram.
List Give a sequence of brief answers with no explanation.
Plot Mark the position of points on a diagram.
Predict Give an expected result.
Prove Use a sequence of logical steps to obtain the required result in a formal way.
Show Give the steps in a calculation or derivation.
Show that Obtain the required result (possibly using information given) without the
formality of proof. “Show that” questions do not generally require the use of
a calculator.
Sketch Represent by means of a diagram or graph (labelled as appropriate). The
sketch should give a general idea of the required shape or relationship, and
should include relevant features.
Solve Obtain the answer(s) using algebraic and/or numerical and/or graphical
methods.
State Give a specific name, value or other brief answer without explanation or
calculation.
Suggest Propose a solution, hypothesis or other possible answer.
Verify Provide evidence that validates the result.
Write down Obtain the answer(s), usually by extracting information. Little or no
calculation is required. Working does not need to be shown.
Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide 91
Appendices
Notation list
There are various systems of notation in use, and the IB has chosen to adopt a system of notation based on
the recommendations of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This notation is used in
the examination papers for this course without explanation. If forms of notation other than those listed in
this guide are used on a particular examination paper, they are defined within the question in which they
appear.
Because students are required to recognize, though not necessarily use, IB notation in examinations, it is
recommended that teachers introduce students to this notation at the earliest opportunity. Students are
not allowed access to information about this notation in the examinations.
Students must always use correct mathematical notation, not calculator notation.
SL and HL
ℕ the set of positive integers and zero, {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
ℤ the set of integers, {0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3, ...}
ℤ+ the set of positive integers, {1, 2, 3, ...}
ℚ the set of rational numbers
ℚ+ the set of positive rational numbers, {x | x ∈ ℚ, x > 0}
ℝ the set of real numbers
ℝ+ the set of positive real numbers, {x | x ∈ ℝ, x > 0}
x1, x2, … the set with elements x1, x2, ...
nA the number of elements in the finite set A
x| the set of all x such that
∈ is an element of
∉ is not an element of
∅ the empty (null) set
U the universal set
∪ union
∩ intersection
A′ the complement of the set A
a1/2, a 1
a to the power , square root of a (if a ≥ 0 then a ≥ 0)
2
a1/n, n a 1
a to the power of , nth root of a (if a ≥ 0 then n a ≥ 0)
n
1 a to the power of …n, reciprocal of an
a…n =
an
92 Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide
Notation list
x the modulus or absolute value of x, that is
x for x ≥ 0, x ∈ ℝ
…x for x < 0, x ∈ ℝ
≈ is approximately equal to
> is greater than
≥ is greater than or equal to
< is less than
≤ is less than or equal to
≯ is not greater than
≮ is not less than
⇒ implies
un the nth term of a sequence or series
d the common difference of an arithmetic sequence
r the common ratio of a geometric sequence
Sn the sum of the first n terms of a sequence, u1 + u2 + ... + un
n u1 + u2 + … + un
∑ ui
i=1
f x the image of x under the function f
f …1 the inverse function of the function f
dy the derivative of y with respect to x
dx
f′ x the derivative of f (x) with respect to x
∫y d x the indefinite integral of y with respect to x
the definite integral of y with respect to x between the limits x = a
∫
b
ydx
a and x = b
ex the exponential function of x
loga x the logarithm to the base a of x
lnx the natural logarithm of x, loge x
sin, cos, tan the circular functions
A x, y the point A in the plane with Cartesian coordinates x and y
AB the line segment with end points A and B
AB the length of [AB]
AB the line containing points A and B
^ the angle at A
A
^ the angle between [CA] and [AB]
CAB
△ ABC the triangle whose vertices are A, B and C
PA probability of event A
Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide 93
Notation list
P A′ probability of the event “not A”
P A|B probability of the event A given B
x1, x2, … observations
f 1, f 2, … frequencies with which the observations x1, x2, ... occur
EX the expected value of the random variable X
μ population mean
σ2 population variance
σ population standard deviation
x̄ the sample mean of a set {x1, x2, ..., xn} of n observations
PX=x the probability that the random variable X takes the value x
B n, p binomial distribution with parameters n and p
N μ, σ 2 normal distribution with mean μ and variance σ 2
X~B n, p the random variable X has a binomial distribution with parameters
n and p
X~N μ, σ 2 the random variable X has a normal distribution with mean μ and
variance σ 2
r Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient
rs Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient
v number of degrees of freedom
χ2 chi-squared distribution
2 the chi-squared test statistic
χcalc
H0 the null hypothesis
H1 the alternative hypothesis
HL only
ℂ the set of complex numbers, {a + bi | a , b ∈ ℝ}
i …1 where i2 = … 1
z a complex number
z* the complex conjugate of z
z the modulus of z
arg z the argument of z
Re z the real part of z
Im z the imaginary part of z
cisθ cosθ + isinθ
eiθ Euler/exponential form of a complex number
⇐ is implied by
94 Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide
Notation list
⇔ implies and is implied by
a, b the closed interval a ≤ x ≤ b
]a, b[ the open interval a < x < b
S∞ the sum to infinity of a sequence, u1 + u2 + …
n! n n … 1 n … 2 …3 × 2 × 1
Δ The discriminant of a quadratic equation, Δ = b2 … 4ac
f: A → B f is a function under which each element of set A has an image in set B
f ∘g the composite function of f and g
lim f x the limit of f (x) as x tends to a
x→a
d2y the second derivative of y with respect to x
dx2
f″ x the second derivative of f (x) with respect to x
ẋ the first derivative of f (x) with respect to time (t)
ẍ the second derivative of f (x) with respect to time (t)
arcsin, sin…1 the inverse circular functions
arccos, cos…1
arctan, tan…1
v the vector v
→ the vector represented in magnitude and direction by the directed line
AB
segment from A to B
a →
the position vector OA
i, j, k unit vectors in the directions of the Cartesian coordinate axes
a the magnitude of a
→ →
AB the magnitude of AB
v·w the scalar product of v and w
v×w the vector product of v and w
A the matrix A
A…1 the inverse of the non-singular matrix A
detA the determinant of the square matrix A
I the identity matrix
0 the zero matrix
s0 an initial state matrix
T a transition matrix
AG the adjacency matrix of a graph G
P a matrix of eigenvectors
D a diagonal matrix of eigenvalues
Var X the variance of the random variable X
Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide 95
Notation list
sn2 sample variance
sn standard deviation of the sample
sn2 − 1 unbiased estimate of the population variance
Pο m Poisson distribution with mean m
X~Po m the random variable X has a Poisson distribution with mean m
ρ Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient for the population
SSres the sum of square residuals
R2 the coefficient of determination
kn a complete graph with n vertices
96 Mathematics: applications and interpretation guide
You might also like
- ESS Booklet Topic 1 PDF PDFDocument27 pagesESS Booklet Topic 1 PDF PDFTushar MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Geometry Ubd Stages 1 2 3 - Edu 223 - 9 12 - Aurora TurmelleDocument7 pagesGeometry Ubd Stages 1 2 3 - Edu 223 - 9 12 - Aurora Turmelleapi-434662376No ratings yet
- IE505 Final Exam (Take Home) : 1 Basic Concepts (15 Points)Document3 pagesIE505 Final Exam (Take Home) : 1 Basic Concepts (15 Points)Daninson CamachoNo ratings yet
- Command Terms IB Maths AA SLDocument2 pagesCommand Terms IB Maths AA SLPraggu SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- Command TermsDocument2 pagesCommand TermsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Command Terms DPDocument4 pagesCommand Terms DPMaría Sofía Sánchez EscobarNo ratings yet
- Command - Terms - For - Mathematics IB Math AADocument3 pagesCommand - Terms - For - Mathematics IB Math AAkhushbir kaur basraNo ratings yet
- Command Terms in Sciences PDFDocument2 pagesCommand Terms in Sciences PDFchethansharmaNo ratings yet
- MYP Command Terms For Sciences: AppendicesDocument2 pagesMYP Command Terms For Sciences: AppendicesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- ESS Booklet Topic 1Document34 pagesESS Booklet Topic 1Tara HasanNo ratings yet
- Command terms for IB Chemistry explainedDocument3 pagesCommand terms for IB Chemistry explainedSarah AmroNo ratings yet
- Biology Command TermsDocument2 pagesBiology Command TermsKumutha ChelliahNo ratings yet
- Glossary of IB Biology Command TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary of IB Biology Command TermsElaine LiNo ratings yet
- IB - Command - Terms Physics 2016 13t7wngDocument2 pagesIB - Command - Terms Physics 2016 13t7wngamukrishNo ratings yet
- Ibmyp Command TermsDocument3 pagesIbmyp Command TermsMensah GbeassorNo ratings yet
- CS Command TermsDocument2 pagesCS Command TermsMai AbdouNo ratings yet
- Past PaperDocument3 pagesPast PapermiraamerabdallahNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Command Terms: Objective 1Document2 pagesIB Biology Command Terms: Objective 1sahasraNo ratings yet
- IB Command Terms For Chemistry PDFDocument2 pagesIB Command Terms For Chemistry PDFMichaelAnthonyNo ratings yet
- ESS Command TermsDocument39 pagesESS Command TermsSecond VynilNo ratings yet
- MYP Maths E-Assessment Support Material Interactive NotebookDocument22 pagesMYP Maths E-Assessment Support Material Interactive NotebookKarthikeya ShukklaNo ratings yet
- DP BIOLOGY COMMAND TERMS Students - Docx 1 PDFDocument3 pagesDP BIOLOGY COMMAND TERMS Students - Docx 1 PDFRoberto David Herrera RosilloNo ratings yet
- Command Words in Questions: Add/LabelDocument2 pagesCommand Words in Questions: Add/LabelDelosh TNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Command Terms: Objective 1Document1 pageIB Biology Command Terms: Objective 1loveis1020No ratings yet
- Myp - Fpip - Command TermsDocument3 pagesMyp - Fpip - Command Termsapi-207781408No ratings yet
- Ib Command Terms For ChemistryDocument2 pagesIb Command Terms For ChemistryMichaelAnthonyNo ratings yet
- IB Command TermsDocument1 pageIB Command TermsMbeeNo ratings yet
- Myp Command TermsDocument2 pagesMyp Command Termsapi-401098405No ratings yet
- Break Down in Order To Bring Out The Essential Elements or StructureDocument52 pagesBreak Down in Order To Bring Out The Essential Elements or StructureMai AbdouNo ratings yet
- Command Terms for Analyzing Academic DocumentsDocument6 pagesCommand Terms for Analyzing Academic DocumentsCicy IrnaNo ratings yet
- 18 Command Terms From The International Baccalaureate January 15-16 Workshop PDFDocument4 pages18 Command Terms From The International Baccalaureate January 15-16 Workshop PDFvictormwongNo ratings yet
- PPTs - Set Theory & Probability (L-1 To L-6)Document49 pagesPPTs - Set Theory & Probability (L-1 To L-6)Daksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ess Command TermsDocument1 pageEss Command TermsAnalía CalderónNo ratings yet
- IB SEHS QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesIB SEHS QuestionnairechaaarrNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus Book 1 by David FearnleyDocument178 pagesAdvanced Calculus Book 1 by David FearnleyasdfghNo ratings yet
- ACTION VERBS AND THEIR DEFINITIONSDocument1 pageACTION VERBS AND THEIR DEFINITIONSPaul Benedict LeeNo ratings yet
- MYP Command TermsDocument3 pagesMYP Command TermsLennoxMeldrumNo ratings yet
- A Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionDocument10 pagesA Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionxcrunitccNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy, Costa's, and IB MYP Command Terms: A Concise ComparisonDocument1 pageBloom's Taxonomy, Costa's, and IB MYP Command Terms: A Concise ComparisonAhmed Helmi100% (1)
- Set Theory v1.3.1Document28 pagesSet Theory v1.3.1Marco RicardNo ratings yet
- Command Terms - An Exercise For Students: © Dr. Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingDocument2 pagesCommand Terms - An Exercise For Students: © Dr. Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingOmar HijaziNo ratings yet
- Command TermsDocument14 pagesCommand TermsThu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Command WordsDocument2 pagesCommand WordsHaya ZayedNo ratings yet
- Class Notes - CalculusDocument31 pagesClass Notes - CalculusRyan GilbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notation and DefinitionsDocument1 pageChapter 2 Notation and DefinitionschengpeckNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document7 pagesAlgebra 2api-262893996No ratings yet
- Appendix 7: Command Words Used in Examination PapersDocument2 pagesAppendix 7: Command Words Used in Examination PapersMagan AliNo ratings yet
- AQA Command WordsDocument3 pagesAQA Command Wordssanjana shettyNo ratings yet
- Calculate: Task Verbs Commonly Used in The Free-Response Questions in Ap PhysicsDocument5 pagesCalculate: Task Verbs Commonly Used in The Free-Response Questions in Ap PhysicsAndy Jun BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Putnam List of ToolsDocument2 pagesPre-Putnam List of ToolsGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Rational Number OperationsDocument4 pagesRational Number OperationsGreg WalkerNo ratings yet
- Plan, Produce, Check, Judge, Hypothesize, Critique, ExperimentDocument2 pagesPlan, Produce, Check, Judge, Hypothesize, Critique, ExperimentCicy Irna100% (1)
- BTEC National in Engineering Unit 01Document72 pagesBTEC National in Engineering Unit 01ayanaemairaNo ratings yet
- Command Terms IbDocument4 pagesCommand Terms Ibapi-316404287100% (1)
- CONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Document17 pagesCONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Jaysa Avila SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Academic Mathematics: Placement Study GuideDocument98 pagesAcademic Mathematics: Placement Study GuideAugustine DharmarajNo ratings yet
- BSA - PUT - SEM I - 21-22 SolutionDocument16 pagesBSA - PUT - SEM I - 21-22 SolutionRizwan SaifiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Introduction of Gen - Math1Document8 pagesLESSON 1 Introduction of Gen - Math1Ma RiaNo ratings yet
- Analysis II Lecture NotesDocument85 pagesAnalysis II Lecture NotesChandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Defining Common Exam Instruction WordsDocument7 pagesDefining Common Exam Instruction WordsifratsubhaNo ratings yet
- Authoritarian and Single Party States Hodder MurrayDocument361 pagesAuthoritarian and Single Party States Hodder Murraytracer29No ratings yet
- Authoritarian and Single Party States Hodder MurrayDocument361 pagesAuthoritarian and Single Party States Hodder Murraytracer29No ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 103.240.232.50 On Wed, 02 Nov 2022 03:41:04 UTCDocument39 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 103.240.232.50 On Wed, 02 Nov 2022 03:41:04 UTCRanveer RatraNo ratings yet
- PDF - Official Sat Study Guide Sample Reading Test QuestionsDocument32 pagesPDF - Official Sat Study Guide Sample Reading Test QuestionsPriya TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 - PDF - Official-Sat-Study-Guide-Sample-Writing-Language-Test-QuestionsDocument18 pagesChap 13 - PDF - Official-Sat-Study-Guide-Sample-Writing-Language-Test-QuestionsKriti NyatiNo ratings yet
- IBDP Math Application and Interpretation SyllabusDocument101 pagesIBDP Math Application and Interpretation SyllabusJeane MJANo ratings yet
- PDF - Official Sat Study Guide Words ContextDocument6 pagesPDF - Official Sat Study Guide Words ContextAUSTRANo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Application and Interpretation - SyllabusDocument47 pagesMathematics - Application and Interpretation - SyllabusRanveer RatraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Application and Interpretation - SL Specimen Papers 1 and 2Document56 pagesMathematics - Application and Interpretation - SL Specimen Papers 1 and 2Ranveer RatraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Application and Interpretation - Assessment ObjectivesDocument5 pagesMathematics - Application and Interpretation - Assessment ObjectivesRanveer RatraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Application and Interpretation - Prior Learning TopicsDocument2 pagesMathematics - Application and Interpretation - Prior Learning TopicsRanveer RatraNo ratings yet
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 7th Edition Stoker Solutions ManualDocument13 pagesGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 7th Edition Stoker Solutions ManualJenniferCookabdqk100% (15)
- Geom 7.4 Guided NotesDocument2 pagesGeom 7.4 Guided NotesBarbie Custodio - MangulabnanNo ratings yet
- LACSAP Ia EriczhangDocument16 pagesLACSAP Ia Ericzhangz ericNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations of Fluid DynamicsDocument48 pagesPartial Differential Equations of Fluid DynamicsinsanNo ratings yet
- 20 Effective Math Teaching Strategies For Explicit LearningDocument13 pages20 Effective Math Teaching Strategies For Explicit LearningChristian Ranzel ExchaureNo ratings yet
- Sci Lab For NumericalDocument142 pagesSci Lab For NumericalbevNo ratings yet
- Short Tricks of Maths For Iit-JeeDocument38 pagesShort Tricks of Maths For Iit-JeePraveen Kaushik73% (51)
- Binomial DistributionDocument15 pagesBinomial DistributionNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- CIDAM General MathematicsDocument2 pagesCIDAM General MathematicsJeffrey Lavisores San DiegoNo ratings yet
- Pascal's Life and Contributions to Math, Science and PhilosophyDocument6 pagesPascal's Life and Contributions to Math, Science and Philosophycsulbstudent1No ratings yet
- John RainwaterDocument4 pagesJohn RainwaterAlHazredNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: GrowthDocument35 pagesChapter 4: GrowthJamaica JunioNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Linear Algebra: Specific ObjectivesDocument41 pagesLinear Equations in Linear Algebra: Specific ObjectivesGorkha's techNo ratings yet
- Exam Question OnlineTest2110 BQT1614Document9 pagesExam Question OnlineTest2110 BQT1614Syamala 29No ratings yet
- Aberlink 3D Faro PDFDocument173 pagesAberlink 3D Faro PDFluchot10No ratings yet
- Nearest Neighbor Classifier ExplainedDocument16 pagesNearest Neighbor Classifier ExplainedRam RoyalNo ratings yet
- Trial Mathematics SPM Perak 2012 AnswerDocument8 pagesTrial Mathematics SPM Perak 2012 AnswerwaichunkoNo ratings yet
- Math 110 - Chapters 4 and 5 Review Problems - Math 110 - Spring 2020, Spring 2020 - WebAssignDocument36 pagesMath 110 - Chapters 4 and 5 Review Problems - Math 110 - Spring 2020, Spring 2020 - WebAssignjosephalbert3141592gmail.comNo ratings yet
- TOS 3rdDocument8 pagesTOS 3rdMichelle Jacinto FajardoNo ratings yet
- QMT437 Group Project: Prepared byDocument21 pagesQMT437 Group Project: Prepared byIZATUN HAJAR MOHD NASIRNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics and Probability Whole Name HiddenDocument17 pagesCombinatorics and Probability Whole Name Hiddenapi-255303924No ratings yet
- Interview ProblemsDocument8 pagesInterview ProblemsDim X Mun100% (1)
- Calculating derivatives using implicit differentiationDocument8 pagesCalculating derivatives using implicit differentiationBryan SaligaoNo ratings yet
- A4 Prospectus 2024 260523Document15 pagesA4 Prospectus 2024 260523jaredNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (B.SC - II) Charpit's MethodDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 (B.SC - II) Charpit's MethodMohammadFaizan71% (7)
- Newton's Method and Its Extensions for Approximating RootsDocument17 pagesNewton's Method and Its Extensions for Approximating Rootsسعود يحيىNo ratings yet
- Lect#2 RegularExprAndAutomataDocument39 pagesLect#2 RegularExprAndAutomataبصمة إبداعNo ratings yet
- CSC479 Data Mining: Data Preprocessing (Ch # 3Document76 pagesCSC479 Data Mining: Data Preprocessing (Ch # 3iLikeCode 101No ratings yet