Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE 318 - Digital Signal Processing
Uploaded by
Pentester 01Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 318 - Digital Signal Processing
Uploaded by
Pentester 01Copyright:
Available Formats
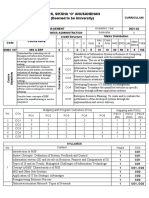
National Institute of Technology Meghalaya CURRICULUM
An Institute of National Importance
Programme Bachelor of Technology in Electrical and Electronics Engineering Year of Regulation 2019-20
Department Electrical Engineering Semester VI
Course Credit Structure Marks Distribution
Course Name
Code L T P C INT MID END Total
EE318 Digital Signal processing 3 0 0 3 50 50 100 200
After the completion of the course, the student should be able to:
use concepts of trigonometry, complex algebra, Fourier series,
To make students familiar with the DSP concepts and aware about the
implications of the properties of systems and signals.
CO1 transform and properties, z-transform to analyze the
operations on signals and acquire knowledge about Systems.
select proper tools, methods, processes, techniques for time
To learn time domain and frequency domain analysis CO2 domain and frequency domain evaluation.
To learn the different frequency transform techniques and apply on the design, implement, analyses and compare digital filters for
Course Course CO3
digital filter design techniques processing of discrete time signals
Objectives Outcomes
integrate computer-based tools, hardware knowledge
To learn the implementation techniques of digital filter and analyze its
characteristics based on different conditions.
CO4 components and their operation effects for engineering
applications
employ signal processing strategies at multidisciplinary team
CO5 activities.
Mapping with Program Outcomes (POs) Mapping with PSOs
No. COs
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 PSO1 PSO2 PSO3
1 CO1 1 2 1 2 2 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0
2 CO2 2 1 1 2 2 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 2 1 1
3 CO3 2 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 2 3 3
4 CO4 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 2 3 3
5 CO5 1 2 3 2 2 2 0 0 1 1 0 1 2 1 1
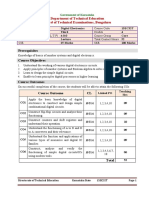
SYLLABUS
No. Content Hours COs
Unit 1: Review of Discrete-Time Signals and Systems CO1
I 06
Discrete - Time Signals, Signal Classification, Discrete - Time System And Analysis Of Discrete - Time Linear
Time Invariant Systems, Correlation Of Discrete - Time Signals.
CO2
Unit 2: Fast Fourier Transform
Introduction, Direct Evolution Of DFT, The Fast Fourier Transform, Decimation-In-Time Algorithm, Summary Of
II 07
Steps Of Radix-2 DIT-FFT Algorithm, Decimation-In-Frequency Algorithm, Summary Of Steps Of Radix-2 DIF-
FFT Algorithm.
Unit 3: Finite Impulse Response Filters CO3
Causality And Its Implications, Linear Phase FIR Filters, Frequency Response Of Linear Phase FIR Filters,
III Location Of The Zeros Of Linear Phase FIR Filters, The Fourier Series Method Of Designing FIR Filters, Design 05
Of FIR Filter Using Windows, Digital Differentiator, Hilbert Transformers, Frequency Sampling Method Of
Designing FIR Filters, Optimum Equi-ripple Approximation Of FIR Filters.
Unit 4: Infinite Impulse Response Filters CO3
Introduction, Frequency Selective Filter, Design Of Digital Filter From Analog Filter, Analog Low Pass Filter
Design, Analog Low Pass Butterworth Filter, Analog Low Pass Chebyshev Filter, Comparison Between
IV Butterworth Filter And Chebyshev Filter, Frequency Transformation In Analog Domain, Design Of High Pass, 06
Bandpass And Bandstop Filters, Design Of IIR Filters From Analog Filters, Approximation Of Derivatives,
Design Of IIR Filter Using Impulse Invariance Technique, Design of IIR Filter Using Bilinear Transformation,
Frequency Transformation In Digital Domain
CO4
Unit 5: Finite Word Length Effects in Digital Filters
Floating Point Numbers, Block Floating Point Numbers, Quantization Noise, Input Quantization Error, Product
V 04
Quantization Error, Coefficient Quantization Error, and Quantization In Floating Point Realization Of IIR Digital
Filters, Finite Word Length Effect In FIR Digital Filters
Unit 6: Realization of Digital Filter CO4
Realization of FIR Filters, Transversal Structure, Linear Phase Realization, Lattice Structure Of An FIR Filter,
Polyphase Realization of FIR Filter, Realization of Digital Filter, Direct Form-I Realization, Direct Form-11
VI 04
Realization, Signal Flow Graph, Transposition Theorem And Transposed Structure, Cascade Form, 6 Parallel
Form Structure, Lattice Structure Of IIR System, Comb Filter, All Pass Filter, Minimum Phase, Maximum Phase
And Non-minimum Phase Systems.
Unit 7: Multirate Signal Processing
Introduction, Down Sampling, Spectrum of The Down Sampled Signal, Up Sampling Spectrum Of The Up-
VII Sampled Signal, Anti-Imaging Filter, Cascading Sample Rate Converters, Efficient Transversal Structure For 04 CO5
Decimator, Efficient Transversal Structure For Interpolator, Polyphase Structure Of Decimator, Polyphase
Decimation Using The Z- Transform, Polyphase Structure Of Interpolator
Total Hours 36
Essential Readings
1. Sanjit K. Mitra, “Digital Signal Processing: A Computer Based Approach,” Tata McGraw-Hill, 4th Edition, 2013.
2. J. G. Proakis and D. G. Manolakis, “Digital Signal Processing: Principles, Algorithms and Applications,” Pearson Education, 4th Edition, 2007.
3. A. V. Oppenhein and R. W. Shafer, “Discrete-Time Signal Processing,” Pearson Education India, 4th Edition, 2007.
4. Tarun Kumar Rawat, “Digital Signal Processing,” Oxford University Press, 5th Edition, 2015.
Supplementary Readings
1. K. Padmanabhan, S. Ananthi, R. Vijayarajeswaran, “A Practical Approach to Digital Signal Processing,” New Age International, 2nd Edition,
2013.
You might also like
- Plain English Part 2Document18 pagesPlain English Part 2ابو ريمNo ratings yet
- Stonehell Dungeon 1 Down Night Haunted Halls (LL)Document138 pagesStonehell Dungeon 1 Down Night Haunted Halls (LL)some dude100% (9)
- Enrico Fermi Pioneer of The at Ted GottfriedDocument156 pagesEnrico Fermi Pioneer of The at Ted GottfriedRobert Pérez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Comm Sys Lab Manual PDFDocument110 pagesComm Sys Lab Manual PDFSaidatul kamarudinNo ratings yet
- Taoist Master Zhang 张天师Document9 pagesTaoist Master Zhang 张天师QiLeGeGe 麒樂格格100% (2)
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesFrom EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lect2 - 1151 - Grillage AnalysisDocument31 pagesLect2 - 1151 - Grillage AnalysisCheong100% (1)
- U19EC416 DSP Lab SyllabusDocument2 pagesU19EC416 DSP Lab SyllabusRamesh MallaiNo ratings yet
- Adc Lab-19et6dladc - 2022Document45 pagesAdc Lab-19et6dladc - 2022Pavan ParameshwarNo ratings yet
- Don Bosco Institute of Technology: Course Syllabi With CO'sDocument2 pagesDon Bosco Institute of Technology: Course Syllabi With CO'sprashantgeminiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Networks and SecurityDocument14 pagesPresentation On Networks and SecurityheraldNo ratings yet
- Bcse2370 DCN LabDocument27 pagesBcse2370 DCN LabJATIN KUMAR SHARMA 22SCSE1012203No ratings yet
- IV-Semester Syllabus On 20.12.23Document21 pagesIV-Semester Syllabus On 20.12.23Karthikeyan RVNo ratings yet
- QP ArchDocument1 pageQP ArchsubhamNo ratings yet
- 1.cs Lab Manual Original (1,2,4,5,9,10,11,12)Document113 pages1.cs Lab Manual Original (1,2,4,5,9,10,11,12)I AM A PROGRAMMERNo ratings yet
- CCN Lab Manual Ecl77Document121 pagesCCN Lab Manual Ecl77Manasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation-Electronics EnggDocument5 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation-Electronics Enggneo viktorNo ratings yet
- ADE LAB UPDATED Manual-Draft 22 SCHEME - 23-24Document87 pagesADE LAB UPDATED Manual-Draft 22 SCHEME - 23-24Harish G CNo ratings yet
- 20EE3602Document2 pages20EE3602RithwakNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Ece PG Commn Sys2013 14Document49 pagesSYLLABUS Ece PG Commn Sys2013 14Ashwin RajaratnamNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab ManualDocument59 pagesADE Lab ManualShreevas NandanNo ratings yet
- Subject CO-PO Mapping DSSDocument1 pageSubject CO-PO Mapping DSSAnonymous J2Dd0nUNo ratings yet
- Rns Institute of Technology: Advanced Communication Laboratory ManualDocument74 pagesRns Institute of Technology: Advanced Communication Laboratory ManualharshithaysNo ratings yet
- MOBILE COMPUTING - Academic Plan (2020-21)Document17 pagesMOBILE COMPUTING - Academic Plan (2020-21)Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Ibcs, Siksha O' Anusandhan (Deemed To Be University) : CurriculumDocument2 pagesIbcs, Siksha O' Anusandhan (Deemed To Be University) : CurriculumSwagat PraharajNo ratings yet
- M. Tech - Communication Systems (Full Time) Curriculum & Syllabus (2015-2016 & Onwards)Document60 pagesM. Tech - Communication Systems (Full Time) Curriculum & Syllabus (2015-2016 & Onwards)Anonymous IjquQOmNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document107 pagesUnit 1Machindra GaikarNo ratings yet
- B.tech Cse VTR Uge2021 de SyllabusDocument4 pagesB.tech Cse VTR Uge2021 de SyllabusBOLLIGARLA MOHAN SAI AKASH,CSE2021 Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- CS Lab Manual FinalDocument40 pagesCS Lab Manual FinalYashwin.v YashuNo ratings yet
- 9 - 19ec213l Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument1 page9 - 19ec213l Analog and Digital CommunicationE.GANGADURAI AP-I - ECENo ratings yet
- DSP Lab ManualDocument57 pagesDSP Lab ManualPraveenNo ratings yet
- AC 09 Course Delivery Plan Practicals GCC Lab CDPDocument5 pagesAC 09 Course Delivery Plan Practicals GCC Lab CDPDeenadayalan ThanigaimalaiNo ratings yet
- Io TDocument2 pagesIo TPrasanth VarasalaNo ratings yet
- ECE 3-2 SyllabusDocument14 pagesECE 3-2 SyllabusRamcharan KadamNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem Octave - DSP ManualDocument68 pages5th Sem Octave - DSP ManualKuldeep KarmaNo ratings yet
- B.E III. Sem Curriculum & Syllabus 2020 Batch Pages 51 67Document17 pagesB.E III. Sem Curriculum & Syllabus 2020 Batch Pages 51 67Sharath Chandan SNo ratings yet
- B.E. EieDocument87 pagesB.E. EieBala SamNo ratings yet
- BXE SYLLABUS - TH and PRDocument5 pagesBXE SYLLABUS - TH and PRSakshi KhomaneNo ratings yet
- ME8791 Mechatronics - UNIT IIDocument52 pagesME8791 Mechatronics - UNIT IIUdamanNo ratings yet
- 2.6.1 Programme and Course Outcomes CIVIL Dept.Document76 pages2.6.1 Programme and Course Outcomes CIVIL Dept.PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Adhoc and Sensor NetworkDocument4 pagesAdhoc and Sensor NetworkVaishnavi BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 4.eee19ee3402-Digital Logic DesignDocument2 pages4.eee19ee3402-Digital Logic Designv.saigeetha lakshmiNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDocument26 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiSK BeharNo ratings yet
- M.E. Ece PDFDocument49 pagesM.E. Ece PDFmspriyarcNo ratings yet
- EC 205-Network Analysis and SynthesisDocument1 pageEC 205-Network Analysis and Synthesis224211No ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Switching Systems: Mapping of Course Outcomes To Program OutcomesDocument4 pagesAdvanced Digital Switching Systems: Mapping of Course Outcomes To Program OutcomesDatha KishorNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Computer Applications Semester - I (2019-22) : Subject Code Title L T P S CreditsDocument22 pagesBachelor of Computer Applications Semester - I (2019-22) : Subject Code Title L T P S CreditsRaghav DuggalNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument10 pagesElectronics & Communication EngineeringanuNo ratings yet
- Mtech-Syllabus-Data Science - Sem2Document18 pagesMtech-Syllabus-Data Science - Sem2reshmaitagiNo ratings yet
- 2.digital Electronics TheoryDocument15 pages2.digital Electronics TheoryYash KuncolienkerNo ratings yet
- ADS Lecture Plan 2022 23 ODDDocument6 pagesADS Lecture Plan 2022 23 ODD1SI20CS116 - Sunil Kumar B ANo ratings yet
- 15ec74 MMC Course ModulesDocument2 pages15ec74 MMC Course Modulesragavendra4No ratings yet
- AllSem23 MAKAUTDocument81 pagesAllSem23 MAKAUTAmit Bikram MishraNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Third Year Syllabus - EMBEDDED SYSTEMSDocument6 pagesB.Tech Third Year Syllabus - EMBEDDED SYSTEMSMAHESWARY SREENATH ECNo ratings yet
- Ac Lab Manual MainDocument59 pagesAc Lab Manual MainMnl KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Ec8381 Fundamentals of DS in C LaboratoryDocument112 pagesEc8381 Fundamentals of DS in C LaboratorysaraswathiNo ratings yet
- 3/2/1: High/Medium/LowDocument8 pages3/2/1: High/Medium/Lowaman singhNo ratings yet
- r14r WSN Fcar Final With Po Attainment 7oct 2018 KMR FelDocument11 pagesr14r WSN Fcar Final With Po Attainment 7oct 2018 KMR FelKommisetty MurthyrajuNo ratings yet
- Course Data Sheet-Cs LabDocument3 pagesCourse Data Sheet-Cs LabpoornimaNo ratings yet
- Understand - Grasp The Impact of - PN Junction and Junction Diodes. Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document41 pagesUnderstand - Grasp The Impact of - PN Junction and Junction Diodes. Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)TANISHQ CHANDRAVANSHINo ratings yet
- Assign - 1-ADCDocument3 pagesAssign - 1-ADCCHANDRAKANT TRIPATHI (RA2011053010028)No ratings yet
- Embedded Lab ManualDocument8 pagesEmbedded Lab ManualAlazmi Faleh50% (2)
- Soft Computing: Academic Year: 2018 - 2022 Course Code: CS604 Semester: Vi Branch: Cse & ItDocument4 pagesSoft Computing: Academic Year: 2018 - 2022 Course Code: CS604 Semester: Vi Branch: Cse & ItRaj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Updated - DSDV - BEC302 - LAB MANUAL123Document54 pagesUpdated - DSDV - BEC302 - LAB MANUAL123Harish G CNo ratings yet
- Using Artificial Neural Networks for Analog Integrated Circuit Design AutomationFrom EverandUsing Artificial Neural Networks for Analog Integrated Circuit Design AutomationNo ratings yet
- Boarding House Preferences by Middle Up Class Students in SurabayaDocument8 pagesBoarding House Preferences by Middle Up Class Students in Surabayaeditor ijeratNo ratings yet
- The Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (Document34 pagesThe Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (mark_schwartz_41No ratings yet
- Chief Complaint: History TakingDocument9 pagesChief Complaint: History TakingMohamad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- RECYFIX STANDARD 100 Tipe 010 MW - C250Document2 pagesRECYFIX STANDARD 100 Tipe 010 MW - C250Dadang KurniaNo ratings yet
- Multimedia System DesignDocument95 pagesMultimedia System DesignRishi Aeri100% (1)
- Advertisement: National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli - 620 015 TEL: 0431 - 2503365, FAX: 0431 - 2500133Document4 pagesAdvertisement: National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli - 620 015 TEL: 0431 - 2503365, FAX: 0431 - 2500133dineshNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: The University of Lahore (Islamabad Campus)Document3 pagesStrategic Marketing: The University of Lahore (Islamabad Campus)Sumaira IrshadNo ratings yet
- Data Network Unit 6 - UCDocument15 pagesData Network Unit 6 - UCANISHA DONDENo ratings yet
- 1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementDocument10 pages1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementrohaizadNo ratings yet
- 2023 Teacher Email ListDocument5 pages2023 Teacher Email ListmunazamfbsNo ratings yet
- Java Complete Collection FrameworkDocument28 pagesJava Complete Collection FrameworkkhushivanshNo ratings yet
- Women Are Better Managers Than MenDocument5 pagesWomen Are Better Managers Than MenCorazon ValdezNo ratings yet
- X - WORMWOOD EVENT IMMEDIATE - Paranormal - 4chanDocument7 pagesX - WORMWOOD EVENT IMMEDIATE - Paranormal - 4chanAnonymous dIjB7XD8ZNo ratings yet
- Community Architecture Concept PDFDocument11 pagesCommunity Architecture Concept PDFdeanNo ratings yet
- William Hallett - BiographyDocument2 pagesWilliam Hallett - Biographyapi-215611511No ratings yet
- PNP Ki in July-2017 AdminDocument21 pagesPNP Ki in July-2017 AdminSina NeouNo ratings yet
- IOT Architecture IIDocument29 pagesIOT Architecture IIfaisul faryNo ratings yet
- Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions Manualoutlying.pedantry.85yc100% (28)
- Notice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsDocument5 pagesNotice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Khairun nissaNo ratings yet
- The First Voyage Round The World by MageDocument405 pagesThe First Voyage Round The World by MageGift Marieneth LopezNo ratings yet
- Hannah Mancoll - Research Paper Template - 3071692Document14 pagesHannah Mancoll - Research Paper Template - 3071692api-538205445No ratings yet
- Presenters: Horace M. Estrella Jay Mart A. Lazana Princess Camille R. HipolitoDocument23 pagesPresenters: Horace M. Estrella Jay Mart A. Lazana Princess Camille R. HipolitoHorace EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Caradol sc48 08Document2 pagesCaradol sc48 08GİZEM DEMİRNo ratings yet
- Cosmopolitanism in Hard Times Edited by Vincenzo Cicchelli and Sylvie MesureDocument433 pagesCosmopolitanism in Hard Times Edited by Vincenzo Cicchelli and Sylvie MesureRev. Johana VangchhiaNo ratings yet