Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pi Is 0140673622010637
Uploaded by
Mariel Loayza OlazabalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pi Is 0140673622010637
Uploaded by
Mariel Loayza OlazabalCopyright:
Available Formats
Correspondence
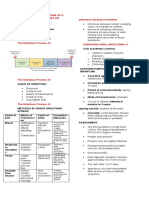
Guidelines for pregnant Pregnant individual with suspected monkeypox exposure
• Travelled to an affected country within the previous 21 days
individuals with • Close contact with a confirmed case of monkeypox (ie, living together, sexual contact, or contact with
body fluids and contaminated linen)
Published Online
monkeypox virus • Exposure to unusual or exotic pets
June 21, 2022
https://doi.org/10.1016/
exposure Clinical examination (including skin, vagina, and oral mucosa)
S0140-6736(22)01063-7
Airborne and contact PPE during patient evaluation
On May 21, 2022, WHO reported
an emerging global outbreak of For more on the 2022
monkeypox virus infection, with monkeypox outbreak see
Asymptomatic Symptomatic https://www.who.int/
documented community transmission • Skin rash*, genital lesions emergencies/disease-outbreak-
among people in contact with • Fever >38°C, headache, lymphadenopathy news/item/2022-DON385
• Sore throat, mouth or throat lesions
symptomatic cases in non-endemic
countries.
The likelihood of infection in Monkeypox real-time PCR Monkeypox real-time PCR
Oropharyngeal swab (blood, vaginal fluid, or urine Swabs of any suspicious skin or mucosal lesion
pregnant women is high because of can be considered) (surface or exudate)
post-COVID-19 border reopening
and travel among countries presently
experiencing an outbreak. Monkeypox negative Monkeypox positive Monkeypox negative Monkeypox positive
Human infections with monkeypox
and smallpox (a closely related
Isolation at home for 21 days Isolation at home for 21 days
orthopoxvirus) can carry a high • No visitors • No visitors
risk of severe congenital infection, • Clinical self-monitoring (temperature • Clinical self-monitoring
and rash) • Rule out other potential causes†
pregnancy loss, and maternal • Discuss orthopox vaccine (best within • If symptoms persist: retest
morbid i ty and mortality. 1 Of 4 days of exposure but can be up to
14 days in the absence of symptoms)
four pregnant women from the
Democratic Republic of the Congo
infected with monkey p ox virus Ultrasound fetal surveillance Hospitalisation in a tertiary or designated
centre (if clinically indicated)
(probably with the central African • Growth and umbilical artery Doppler
scans monthly WHO clinical severity score
clade of the virus) between 2007 and • Discuss amniocentesis if signs of • Mild (<25 skin lesions)
2011, two had spontaneous early hydrops or hepatomegaly • Moderate (25–99 skin lesions)
• Severe (100–250 skin lesions)
miscarriages, and one had a second- • Grave (>250 skin lesions)
trimester loss at 18 weeks’ gestation.2 Maternal surveillance
The stillborn fetus had a generalised Stop monitoring Recovery
• Temperature, heart rate, blood pressure
(3–4 times per day), plus supportive care and
skin rash, and monkeypox virus DNA pain management
detected in fetal tissue, umbilical • Antibiotics (systemic amoxicillin,
chloramphenicol via eye drops) to prevent
cord, and placenta, confirming bacterial superinfection
vertical transmission of monkeypox • Tecovirimat, vaccinia immune globulin, and
orthopox vaccine
virus. Genomic sequencing data • Cidofovir considered only in critically ill pregnant
suggest the west African clade of women (teratogen)
Fetal
monkeypox virus is responsible for • Fetal assessment (FHR) and corticosteroid use
the current outbreak; although it for fetal lung maturation depending on
gestational age
is associated with milder disease
and a lower case fatality rate in
Delivery (high risk of preterm birth)
• On site or IRNP
• Caesarean section probably not superior to
vaginal delivery, except if genital lesions present
Figure: Clinical management algorithm for • Consider monkeypox viral load assessment from
suspected monkeypox virus exposure during umbilical cord blood and placenta
pregnancy Newborn
FHR=fetal heart rate. IRNP=isolation room with • Early cleaning of the newborn
negative pressure. PPE=personal protective • Newborn monitoring in IRNP
equipment. *Higher suspicion if skin rash is • Monkeypox real-time PCR of the newborn (any
suspicious mucocutaneous lesions, or: eye,
concentrated over the genitals, face, and extremities. Submissions should be
nasopharynx, mouth, rectum, perineal area,
†PCR should be done from a vesicle or genital lesion. made via our electronic
and infant/umbilical cord blood)
We also suggest PCR for herpes simplex virus, • Depending on local policy, infant separation submission system at
varicella zoster virus, and syphilis to rule out other should be discouraged where possible http://ees.elsevier.com/
causes of vesiculopustular rash in pregnancy. thelancet/
www.thelancet.com Vol 400 July 2, 2022 21
Correspondence
non-pregnant people, the effects of and tecovirimat can be used in the University Hospital (CHUV), 1011 Lausanne,
this clade in pregnancy are unknown. USA under an expanded access Switzerland (DB)
Here, we propose a clinical Investigational New Drug protocol for 1 Nishiura H. Smallpox during pregnancy and
maternal outcomes. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;
management algorithm for pregnant the empirical treatment of non-variola 12: 1119–21.
women with suspected monkeypox orthopoxvirus infections, including 2 Mbala PK, Huggins JW, Riu-Rovira T, et al.
virus exposure (figure). Clinicians monkeypox. The US Food and Drug Maternal and fetal outcomes among pregnant
women with human monkeypox infection in
must maintain a high index of Administration (FDA) prescribing the Democratic Republic of Congo. J Infect Dis
suspicion for monkeypox virus in any information for tecovirimat confirms 2017; 216: 824–28.
3 Vouga M, Musso D, Mieghem TV, Baud D. CDC
pregnant woman presenting with that no embryotoxic and teratogenic guidelines for pregnant women during the
lymphadenopathy and vesiculopustular effects have been detected in animal Zika virus outbreak. Lancet 2016; 387: 843–44.
rash—including rash localised to the studies. Furthermore, the US Centers 4 US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccinia (smallpox) vaccine: recommendations
genital or perianal region—even if for Disease Control and Prevention4 of the Advisory Committee on Immunization
there are no apparent epidemiological permits the emergency use of the Practices (ACIP), 2001. MMWR Recomm Rep
2001; 50: 1–26.
links. Diagnosis is confirmed by live smallpox vaccine ACAM2000,
5 UK Health Security Agency. Recommendations
nucleic acid amplification testing which confers 85% cross-protective for the use of pre and post exposure
with real-time or conventional PCR immunity against monkeypox, if high- vaccination during a monkeypox incident.
June 6 2022. https://www.gov.uk/
for monkeypox virus from vesicles or risk exposure to monkeypox virus government/publications/monkeypox-
genital lesions; additionally, we advise occurs in pregnancy. Patients must, vaccination (accessed June 15, 2022).
ruling out varicella, herpes simplex, however, be counselled on the rare 6 Panchaud A, Favre G, Pomar L, et al.
An international registry for emergent
and syphilis, as these might resemble risk of fetal vaccinia from ACAM2000, pathogens and pregnancy. Lancet 2020; 395:
monkeypox in pregnancy. Fetal which can result in preterm delivery, 1483–84.
ultrasound monitoring is required stillbirth, neonatal death, and potential
in cases of maternal monkeypox adverse maternal reactions. MVA-BN,
virus infection, and subsequent a third-generation smallpox vaccine Monkeypox genomic
management should be based on the recently approved in the USA, Canada, surveillance will
presence of ultrasound anomalies such and the EU, is possibly safer because it
as fetal hepatomegaly or hydrops. contains non-replicating virus and has challenge lessons learned
Monkeypox can have considerable not demonstrated adverse pregnancy from SARS-CoV-2
risks to the fetus, so we also suggest outcomes.5 Finally, we encourage the
testing asymptomatic pregnant reporting of all cases of monkeypox The emergence of a series of
women with significant monkeypox virus in pregnancy to WHO and an epidemiologically connected monkey
virus exposure to identify those who international registry for emerging pox virus infections around the world,
require fetal ultrasound follow-up. pathogens.6 with ongoing human-to-human
The sensitivity of molecular detection These recommendations should transmission (as of June 15, 2022,
of monkeypox virus in the amniotic be adapted to local guidelines and 2103 confirmed cases, one probable
fluid is unknown. By analogy with updated as more information arises. case, and one death have been
For WHO’s monkeypox cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, We declare no competing interests. reported to WHO from 42 countries),
outbreak situation update see and Zika virus infections, it is likely raises concerns of a long-apprehended
https://www.who.int/ Pradip Dashraath,
emergencies/disease-outbreak-
that monkeypox virus is shed in the Karin Nielsen-Saines, Citra Mattar, comeback of a human-adapted
news/item/2022-DON393 amniotic fluid only once the fetal Didier Musso, Paul Tambyah, orthopoxvirus related to variola virus,
kidneys produce sufficient urine (ie, *David Baud the aetiological agent of smallpox.
after 18–21 weeks’ gestation).3 At david.baud@chuv.ch Since variola virus had no natural
delivery, we recommend assessing reservoir other than humans, the
Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Department of
viral load in umbilical cord blood and Obstetrics and Gynecology, National University eradication of the virus by use of
placenta and real-time PCR analysis of Hospital, Singapore (PD, CM); Yong Loo Lin School of highly effective vaccines against
Medicine, National University of Singapore,
specimens obtained from the neonate. orthopoxviruses was irreversible. 1
Singapore (PD, CM, PT); Division of Infectious
For treatment, tecovirimat and Diseases, Department of Medicine, National However, other orthopoxviruses have
vaccinia immune globulin can be University Hospital, Singapore (PT); Division of reservoirs in wildlife, such as cowpox
considered for pregnant women Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Department of virus (in voles), taterapox virus (in
Pediatrics, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA,
who are severely ill. Tecovirimat is Los Angeles, CA, USA (KN-S); Aix Marseille Université, African gerbils), and monkeypox
an inhibitor of the orthopoxvirus IRD, AP-HM, SSA, VITROME, IHU – Méditerranée virus (in small mammals), do have
VP37 envelope wrapping protein. infection, Marseille, France (DM); Laboratoire the potential to spill into the human
Eurofins Labazur Guyane, French Guiana (DM);
The European Medicines Agency has Materno-fetal and Obstetrics Research Unit, population and facilitate a restart of
approved tecovirimat for monkeypox, Department Woman-Mother-Child, Lausanne the genetic adaptation of the virus to
22 www.thelancet.com Vol 400 July 2, 2022
You might also like
- Legal Aspects of Healthcare Administration AssignmentDocument7 pagesLegal Aspects of Healthcare Administration Assignmentjossy MulingeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenDocument20 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenMark oliver Gonzales100% (1)
- ST Interview GuideDocument79 pagesST Interview GuideElena Marinaki100% (4)
- Downtime Procedures For NextGenDocument6 pagesDowntime Procedures For NextGenmanntarNo ratings yet
- Monkey PoxDocument29 pagesMonkey PoxMalavika A GNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox RA and MX 27 Mei 2022Document45 pagesMonkeypox RA and MX 27 Mei 2022alfonso de albuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Interim Guidelines On Monkeypox Management in Malaysia 2022Document40 pagesInterim Guidelines On Monkeypox Management in Malaysia 2022Hadinur JufriNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox Webinar 2022 Materi 1Document34 pagesMonkeypox Webinar 2022 Materi 1Devi PurnamayantiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Sexually Transmitted Infections & PregnancyDocument24 pages1.2 Sexually Transmitted Infections & Pregnancyyen.nursing02No ratings yet
- Fungal Infections of HumansDocument22 pagesFungal Infections of HumansJhara100% (2)
- Communication Kit - MonkeypoxDocument52 pagesCommunication Kit - MonkeypoxVanessa ChickNo ratings yet
- CYRUSSDocument13 pagesCYRUSSRienna Marie HentoloroNo ratings yet
- Chang AnDocument36 pagesChang AnErrol LlanesNo ratings yet
- Monkey Pox XCovidDocument57 pagesMonkey Pox XCovidKrenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- Monkey Pox-FinalDocument23 pagesMonkey Pox-FinalnirmalaspandagaleNo ratings yet
- CDC Updates For Monkey PoxDocument4 pagesCDC Updates For Monkey PoxMohammed AbdillahiNo ratings yet
- Block 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Document29 pagesBlock 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Sabelo VictorNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Management of Monkeypox DiseaseDocument23 pagesGuidelines For Management of Monkeypox DiseaseMinerva Medical Treatment Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyBeyins TiuNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Affecting The Reproductive SystemDocument49 pagesCommunicable Diseases Affecting The Reproductive SystemJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Sexual Transmitted DiseaseDocument109 pagesSexual Transmitted DiseaseFRANCISCO, QUENNIE MARIE D.No ratings yet
- Smallpox A Dead DiseaseDocument42 pagesSmallpox A Dead DiseasefarigNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea 1Document26 pagesGonorrhea 1Alessandra Franchesca CortezNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox Guidelines 01 June 2023 V1.4Document39 pagesMonkeypox Guidelines 01 June 2023 V1.4Talaat OmranNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Monkeypox in 2022 - JAMADocument2 pages2022 - Monkeypox in 2022 - JAMArudy sanabriaNo ratings yet
- Correspondence: Evidence of Human-To-Dog Transmission of Monkeypox VirusDocument2 pagesCorrespondence: Evidence of Human-To-Dog Transmission of Monkeypox VirusYuri ChaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Community: Control of Communicable Diseases Instructional SlidesDocument46 pagesNursing Care of The Community: Control of Communicable Diseases Instructional SlidesJullienne Ysabelle AngNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox in Pregnancy - Dr. Lingga, SP - OGDocument20 pagesMonkeypox in Pregnancy - Dr. Lingga, SP - OGIndah KaDeNo ratings yet
- Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Cocci: Unit 3: Neisseriaceae and Moraxella CatarrhalisDocument18 pagesGram-Positive & Gram-Negative Cocci: Unit 3: Neisseriaceae and Moraxella CatarrhalisKathleen RodasNo ratings yet
- Metritis With Pelvic CellulitisDocument2 pagesMetritis With Pelvic CellulitisCleoGomezNo ratings yet
- Comment: Published June 27, 2022 S2214-109X (22) 00284-4Document2 pagesComment: Published June 27, 2022 S2214-109X (22) 00284-4Mariel Loayza OlazabalNo ratings yet
- IOG - National Clinical Guidelines - Monkeypox Guidelines - 2022Document9 pagesIOG - National Clinical Guidelines - Monkeypox Guidelines - 2022Maryam YasminNo ratings yet
- Scabies MITEDocument16 pagesScabies MITEIrul AnwarNo ratings yet
- Scabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanDocument16 pagesScabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanochaNo ratings yet
- Scabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanDocument16 pagesScabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanResti FadyaNo ratings yet
- A Primer On Monkeypox Virus For.7Document7 pagesA Primer On Monkeypox Virus For.7OMARNo ratings yet
- Monkey Pox FinalDocument35 pagesMonkey Pox FinalHiren patelNo ratings yet
- Human MonkeypoxDocument8 pagesHuman Monkeypoxlakshay kumarNo ratings yet
- PLAGUE in Ecuador. PesteDocument11 pagesPLAGUE in Ecuador. PesteConsuelo QuispeNo ratings yet
- PIIS014067362202075XDocument15 pagesPIIS014067362202075XOMARNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis (Inclusion) Vs Acute Bacterial ConjunctivitisDocument13 pagesConjunctivitis (Inclusion) Vs Acute Bacterial ConjunctivitisJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Epi#3Document19 pagesEpi#3JNo ratings yet
- Incursions Learning Objectives/Study Guide: EEDA/IAT Web-Based CourseDocument7 pagesIncursions Learning Objectives/Study Guide: EEDA/IAT Web-Based Coursevdcastillo13No ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument13 pagesScabiespompas pNo ratings yet
- Gusti Izza - English Medical ArticleDocument6 pagesGusti Izza - English Medical Articlenuna_idaNo ratings yet
- EpiC - Monkeypox - Fact Sheet - V5 - 08 - 03 - 22 - FinalDocument8 pagesEpiC - Monkeypox - Fact Sheet - V5 - 08 - 03 - 22 - FinalOmarNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox FAQDocument2 pagesMonkeypox FAQMaritza NunezNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox in The United States - What Clinicians Need To KnowDocument59 pagesMonkeypox in The United States - What Clinicians Need To KnowVladimir Sebastián Cruz RománNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesDocument4 pagesReviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesGeriel QuidesNo ratings yet
- Edited Monkeypox Facts 2022Document93 pagesEdited Monkeypox Facts 2022anghelmiguel07262016No ratings yet
- PDF Chapter 22 The Female Genital TractDocument59 pagesPDF Chapter 22 The Female Genital Tractsmian08No ratings yet
- 2.01 Gynecology Infections of The Genital TractDocument16 pages2.01 Gynecology Infections of The Genital TractAsela MirandaNo ratings yet
- CD-2 NotesDocument8 pagesCD-2 NotesRika MaeNo ratings yet
- ChikungunyaDocument38 pagesChikungunyaasgarmNo ratings yet
- F.06 STD and Infections in Pregnancy (Dr. Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 1)Document5 pagesF.06 STD and Infections in Pregnancy (Dr. Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 1)Dasha VeeNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseaseBrianna ValerioNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Reference: Chapter 23 Comprehensive Gynecology 7Th EDITION PAGES 548-562Document19 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease: Reference: Chapter 23 Comprehensive Gynecology 7Th EDITION PAGES 548-562Nica-Ann SantosNo ratings yet
- Emerging Vector-Borne Diseases: Sioux Falls, South DakotaDocument7 pagesEmerging Vector-Borne Diseases: Sioux Falls, South DakotaHakiki Oksan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument41 pagesCommunicable DiseaseBasari OdalNo ratings yet
- Candida Albicans: Figure 1. Skin Smear Candida Albicans WWW - Meddean.luc - EduDocument38 pagesCandida Albicans: Figure 1. Skin Smear Candida Albicans WWW - Meddean.luc - EduFirda jihanNo ratings yet
- StdsDocument71 pagesStdsabel semuNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Skin and EyesDocument29 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Skin and EyesqueennieNo ratings yet
- Self-Care of The DoctorDocument2 pagesSelf-Care of The DoctorShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Situational Analysis 2Document3 pagesSituational Analysis 2Julienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- Faunce, NickDocument14 pagesFaunce, NickSWE BlaDeZNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument6 pagesDiarrhea in ChildrenAdeola AdegboyegaNo ratings yet
- Suicidal Behaviour in Children & Adolescents: Dr. Ajaz Ahmad SuhaffDocument21 pagesSuicidal Behaviour in Children & Adolescents: Dr. Ajaz Ahmad SuhaffdrsuhaffNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy, Unani, Naturopathy Lic InspectionDocument12 pagesHomeopathy, Unani, Naturopathy Lic InspectionBala Kiran GaddamNo ratings yet
- You Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeDocument2 pagesYou Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeWen Silver100% (1)
- Warm Sponging Versus Tepid Sponging in Febrile ChildrenDocument6 pagesWarm Sponging Versus Tepid Sponging in Febrile ChildrenkurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Trimester First Second ThirdDocument12 pagesTrimester First Second Thirdmacky sympranoNo ratings yet
- Clinic Management System With Scheduling For Cabuyao Animal Bite ClinicDocument200 pagesClinic Management System With Scheduling For Cabuyao Animal Bite ClinicvinNo ratings yet
- Pengkajian Pasien Menggunakan Four Score Coma Scale Di Ruang Perawatan Intensive Care Unit (Icu)Document5 pagesPengkajian Pasien Menggunakan Four Score Coma Scale Di Ruang Perawatan Intensive Care Unit (Icu)ArselBrooklynNo ratings yet
- Discrete Separation of Patients' Profiles For Chronical Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Context-Aware Healthcare Efficient SystemsDocument13 pagesDiscrete Separation of Patients' Profiles For Chronical Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Context-Aware Healthcare Efficient SystemsIAES IJAINo ratings yet
- MAFMHuman Serviceswspecializationin Addiction CounselingDocument3 pagesMAFMHuman Serviceswspecializationin Addiction CounselingmichelleflresmartinezNo ratings yet
- ImmunitationDocument2 pagesImmunitationahurtado017No ratings yet
- Weekly Nursing Care Plan 4Document13 pagesWeekly Nursing Care Plan 4api-673227957No ratings yet
- WEBINAR On PEDIATRIC TRAUMADocument44 pagesWEBINAR On PEDIATRIC TRAUMAGovindarajan HariharanNo ratings yet
- Hospice CareDocument33 pagesHospice CareEva YantiNo ratings yet
- B2 - Wcet - Inwocna 2017Document37 pagesB2 - Wcet - Inwocna 2017Anis SartikaNo ratings yet
- Preconceptional Counseling and CareDocument12 pagesPreconceptional Counseling and CareGaurav ThakurNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Health Assessment For Nursing Practice 6th Edition by WilsonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Health Assessment For Nursing Practice 6th Edition by Wilsonunhealth.foist8qrnn2100% (43)
- Collection of Subjective Data Throught InterviewDocument3 pagesCollection of Subjective Data Throught InterviewChuche Marie TumarongNo ratings yet
- Keywords:-Data Collection and Evaluation, UKGSDocument11 pagesKeywords:-Data Collection and Evaluation, UKGSInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Arbitration - Hospital (Mr. Chaudhary)Document2 pagesArbitration - Hospital (Mr. Chaudhary)Kunwarbir Singh lohatNo ratings yet
- Induced Abortion and Mental Health (Dec 2011)Document252 pagesInduced Abortion and Mental Health (Dec 2011)MichaelCookNo ratings yet
- Occupational Problems and Barriers Reported by Individuals With ObesityDocument10 pagesOccupational Problems and Barriers Reported by Individuals With ObesityGraciela SeveriniNo ratings yet
- Essential Nutrition Actions PDFDocument144 pagesEssential Nutrition Actions PDFAmany MokhtarNo ratings yet