Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HYGIENE
Uploaded by
Nicole NipasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HYGIENE
Uploaded by
Nicole NipasCopyright:
Available Formats
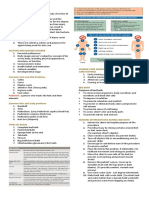
HYGIENE Lack of physical energy
Loss of dexterity
FROM THE GREEK WORD “HYGIES” MEANING
“HEALTHY, SOUND” KNOWLEDGE ABOUT IMPORTANCE OF
HYGIENE
WHAT IS PERSONAL HYGIENE?
PROVIDING SCHEDULED HYGIENE
REGULAR ROUTINE OF PERSONAL CARE
WASHING AND GROOMING Early morning
Morning care
YOUR HAIR Afternoon care (PM care)
YOUR FACE HS care
YOUR SKIN PRN care
YOUR TEETH
PURPOSE OF THE PATIENT'S HYGIENE
YOUR EARS
YOUR HANDS 1. Cleanses skin
YOUR NAILS 2. Skin conditioner
YOUR FEET 3. Relaxes patient
4. Promotes circulation
NURSING KNOWLEDGE BASE 5. Exercise
PERSONAL PREFERENCES FOR 6. Stimulates respirations
HYGIENE 7. Comfort
HYGIENE CARE IS NEVER ROUTINE 8. Sensory input
9. Improves self-image
DURING HYGIENE
10. Establish rapport
1. Assess physical status and limitations
11. Physical assessment
2. Assess client’s readiness to learn
12. Health teaching
3. Provide privacy
4. Foster physical well being BED BATHS
SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE BASE Provide supplies
Good physical hygiene is necessary for Provide privacy
comfort, safety, and well-being. Provide Mirror
Ill clients require assistance with personal Assist as necessary
hygiene. BATHING AND SKIN CARE
Several factors influence a client’s hygiene
practices. TUB OR SHOWER
FACTORS INFLUENCING HYGIENE More thorough than bed bath
BODY IMAGE COMPLETE BED BATH
A person’s subjective concept of their For clients who are dependent and require total
appearance hygienic care
SOCIAL PRACTICES PARTIAL BED BATH
Social groups and family practices Involves bathing only those parts that would
cause discomfort or odor if left unbathed
SOCIOECONOMICS
ORAL CARE
CULTURAL VARIABLES
Supply equipment for self-care
PERSONAL PREFERENCES Provide care or assistance as necessary
Frequency
Preferred products
ORAL CARE
Involves cleanliness, comfort, and
PHYSICAL CONDITION moisturizing the mouth
Unconscious client 3. Tones muscle
Flossing and brushing Hair Care
Denture care 1. Brush or comb hair
2. May need to shampoo hair
CLEANING THE EYES
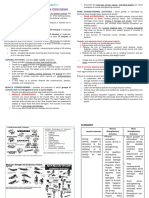
SKIN HYGIENE
No soap
Clean wash cloth FUNCTIONS OF SKIN:
Water runs away from eyes Protection
Clean inside to outside Regulation of Body Temperature
HAIR CARE Sensation
Production of Vitamin D
Shampoo requires a doctor’s order Secretes Sebum
Wash as often as necessary
MAINTAINING COMFORT NEEDS (Cleanliness
PERINEAL CARE of the Patient’s Environment)
Always proceed from least contaminated area PATIENT OUTCOME ACHIEVEMENT
to most
1. Females – front to back Level of patient participation in hygiene
2. Males – wash tip of penis and then program
down shaft Elimination of, reduction in, or compensation
Turn patient over and clean anal area for factors interfering with independent
execution of hygiene measures
PERINEAL CARE Changes related to specific skin problems
Part of the bed bath
Clients most in need are those with secretions
or Foley catheters and following rectal surgery
Be alert to discharge, skin irritation, and odors
Good perineal care prevents skin irritation and
breakdown
NURSING PROCESS: ASSESSMENT
Nursing history to determine:
1. Self-care practices
2. Self-care abilities
3. Past or current problems
4. Identification of clients at risk for
developing impairment
Physical assessment
FOCUS OF SELF-CARE DEFICIT DIAGNOSES
Self-Care Deficit : Bathing/Hygiene
Self-Care Deficit : Dressing/Grooming
Self-Care Deficit : Toileting
Self-Care Deficit : Feeding
NURSING INTERVENTION (Meeting Personal
Hygiene Needs: Bathing a Patient)
MEETING ADDITIONAL HYGIENE NEEDS
Backrub
1. Promotes relaxation & Comfort
2. Stimulates circulation
You might also like
- Client Bed BathDocument6 pagesClient Bed BathLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security and SanitationDocument2 pagesRisk Management As Applied To Safety, Security and SanitationCynthia AyadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Personal HygieneDocument12 pagesLesson Plan On Personal HygieneD Dimpy ThakurNo ratings yet
- HTP FinalDocument3 pagesHTP Finalאורזלין לנזוןNo ratings yet
- Personal HygieneDocument10 pagesPersonal HygieneNie SernadillaNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines For Skin CareDocument4 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Skin CareDaesungNo ratings yet
- Personal Hygiene: Didik S AtmojoDocument25 pagesPersonal Hygiene: Didik S AtmojoRetno BeniNo ratings yet
- Slu Bedbath NursingDocument13 pagesSlu Bedbath NursingGabeNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching On Personal Hygiene PDF HygieDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching On Personal Hygiene PDF Hygieroseline vinodiNo ratings yet
- MARY GRACE (CHN) Final Presentation For FNCPDocument6 pagesMARY GRACE (CHN) Final Presentation For FNCPMary grace VirayNo ratings yet
- SLAYT FUNDAMENTALS - KopyaDocument40 pagesSLAYT FUNDAMENTALS - KopyaIlker AlpçetinNo ratings yet
- LRPD InglesDocument5 pagesLRPD InglesYuleika Zulema Pachas MachaNo ratings yet
- Personal hygiene..H.EDocument6 pagesPersonal hygiene..H.EJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Notes On Health AssessmentDocument6 pagesNotes On Health AssessmentApril Grace CanasaNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale: Nursing TheoriesDocument27 pagesFlorence Nightingale: Nursing TheoriesVanessa Bullecer100% (1)
- Handouts in HYGIENE Hygiene - Is The Science of Health and Its MaintenanceDocument9 pagesHandouts in HYGIENE Hygiene - Is The Science of Health and Its MaintenanceTweetie Borja DapogNo ratings yet
- Funda Notes Compilation Lecture and SkillsDocument21 pagesFunda Notes Compilation Lecture and SkillsmysterioushumaneNo ratings yet
- Rle Week 7 Bed Bath DocsDocument2 pagesRle Week 7 Bed Bath DocsCHRISTINE KEITH NEPOMUCENONo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan FormatDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan FormatGlem BernardoNo ratings yet
- Material On: Rajkumari Amrit Kaur College of NursingDocument34 pagesMaterial On: Rajkumari Amrit Kaur College of NursingAswathy AswathyNo ratings yet
- Mark Norriel CelisDocument2 pagesMark Norriel CelisMark Norriel CajandabNo ratings yet
- TimeframeDocument1 pageTimeframeShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- Bed BathDocument11 pagesBed Bathramtenki sreelekha100% (1)
- Develop Positive Attitude Towards The Concept of Medical Hand WashingDocument5 pagesDevelop Positive Attitude Towards The Concept of Medical Hand WashingJohn R. AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Hygiene CareDocument45 pagesHygiene Careenam professorNo ratings yet
- Triptico de La Higiene PersonalDocument2 pagesTriptico de La Higiene PersonalxiomaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes HWDocument16 pagesLesson Notes HWNlida LieydaNo ratings yet
- Three Major Categories: "The Twenty-One NursingDocument5 pagesThree Major Categories: "The Twenty-One NursingmrcupNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer 2Document1 pageQuestion and Answer 2Jaja BookNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Procedure of Bed BathDocument7 pagesLesson Plan On Procedure of Bed BathSaritha SvNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan: Objectives Identified Problems/Concerns Activities Evaluation Student Nurse Client/Family MemberDocument5 pagesTeaching Plan: Objectives Identified Problems/Concerns Activities Evaluation Student Nurse Client/Family MemberRaine SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bed BathDocument10 pagesBed BathVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- CHN Homevisit-FNCPDocument17 pagesCHN Homevisit-FNCPSachi Reuel BernateNo ratings yet
- UNIT5 HealthDocument13 pagesUNIT5 HealthMy everyday LifeeeNo ratings yet
- EPP 4 HE Lesson 1 Caring For OneselfDocument11 pagesEPP 4 HE Lesson 1 Caring For Oneselfmarjorie rochaNo ratings yet
- PriorityDocument13 pagesPriorityKristen NateNo ratings yet
- Geria Week 3Document4 pagesGeria Week 3Sam PothNo ratings yet
- LOréalDocument5 pagesLOréalDiana MihaelaNo ratings yet
- The ABC Towards Proper Personal Care: Always Be Clean!: Presented By: Balita, Gamboa, Lejero, Sulit, TenorioDocument31 pagesThe ABC Towards Proper Personal Care: Always Be Clean!: Presented By: Balita, Gamboa, Lejero, Sulit, TenorioAngelou RosalesNo ratings yet
- Hygiene and Bed Bath ModuleDocument18 pagesHygiene and Bed Bath ModuleZhedriex EspirituNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories and History HandoutsDocument5 pagesNursing Theories and History Handoutsvinax89No ratings yet
- FNCP Poor HygieneDocument2 pagesFNCP Poor HygieneGian Carlo Quilantang50% (2)
- Shampooing Hair in Bed Procedure ChecklistDocument3 pagesShampooing Hair in Bed Procedure ChecklistGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Personal HygieneDocument23 pagesPersonal Hygieneksraghavan2000No ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN ON Hand Washing Procedure PPTX - Edited - PDF MergedDocument16 pagesLESSON PLAN ON Hand Washing Procedure PPTX - Edited - PDF MergedPeter MarshallNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN ON Hand Washing Procedure PPTX - Edited - EditedDocument19 pagesLESSON PLAN ON Hand Washing Procedure PPTX - Edited - EditedPeter MarshallNo ratings yet
- 4832 Concept Map 1Document3 pages4832 Concept Map 1api-508452270No ratings yet
- SHIVIDocument15 pagesSHIVIShubham BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Building Your Immune System: What Is Healthy Eating? What Food Should I Eat?Document3 pagesBuilding Your Immune System: What Is Healthy Eating? What Food Should I Eat?Maria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Hygiene Is The Science of Health and Its: Types of Hygienic CareDocument12 pagesHygiene Is The Science of Health and Its: Types of Hygienic CareAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Improper HygieneDocument2 pagesImproper HygieneAllen Reyes SantosNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 NCM 100 Skills Hygiene ComfortDocument24 pagesTopic 6 NCM 100 Skills Hygiene ComfortPearl IbisateNo ratings yet
- Cleansing Bed BathDocument19 pagesCleansing Bed BathCherie BanzonNo ratings yet
- NCP QueDocument2 pagesNCP Quesecondacvalo123No ratings yet
- Bed BathDocument4 pagesBed BathAbegail FloresNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Procedure of Bed BathDocument9 pagesLesson Plan On Procedure of Bed BathVipin kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Tvl-Caregiving: Senior High School DepartmentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Tvl-Caregiving: Senior High School DepartmentJroybej BejonaNo ratings yet
- From The Coronavirus: 5 Ways To Protect YourselfDocument2 pagesFrom The Coronavirus: 5 Ways To Protect YourselfsumantonoNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN ON Hand Washing ProcedureDocument21 pagesLESSON PLAN ON Hand Washing ProcedurePeter MarshallNo ratings yet
- Principles of Skin Care: A Guide for Nurses and Health Care PractitionersFrom EverandPrinciples of Skin Care: A Guide for Nurses and Health Care PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System Assessment NCM 101 Health Assessment March 11, 2022 Clinical Instructor: Nomelita LoDocument10 pagesNeurologic System Assessment NCM 101 Health Assessment March 11, 2022 Clinical Instructor: Nomelita LoNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- DocuDocument6 pagesDocuNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Perineal CareDocument1 pagePerineal CareNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Shampooing Clients in BedDocument2 pagesShampooing Clients in BedNicole Nipas100% (1)
- Making Beds: PerformanceDocument2 pagesMaking Beds: PerformanceNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Daet, Camarines NorteDocument4 pagesDaet, Camarines NorteNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Report Chapter 20Document22 pagesReport Chapter 20Nicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Nicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument3 pagesVital SignsNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Osce WrittenDocument6 pagesOsce WrittenNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- CCPGroup 3Document5 pagesCCPGroup 3Nicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Normal Flora of The Human BodyDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Normal Flora of The Human BodyNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Phases of Drug Action: Pharmaceutic Pharmacokinetic PharmacodynamicDocument153 pagesPhases of Drug Action: Pharmaceutic Pharmacokinetic PharmacodynamicNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Nicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Bacterial Morphology: Murein Sacculus. MucopeptideDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Bacterial Morphology: Murein Sacculus. MucopeptideNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReportDocument31 pagesChapter 2 ReportNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Deontological EthicsDocument5 pagesLesson 5 Deontological EthicsNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Assessing Neurologic System: Mabini CollegesDocument25 pagesAssessing Neurologic System: Mabini CollegesNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Health Care PlanDocument19 pagesHealth Care PlanNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2Document6 pagesChapter 1,2Nicole NipasNo ratings yet
- General Properties of CestodesDocument42 pagesGeneral Properties of CestodesNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Assisting With PPADocument69 pagesAssisting With PPANicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Assessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistDocument7 pagesAssessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- GEC 5-Purposive Communication MODULE 1 Title: The Nature of LanguageDocument4 pagesGEC 5-Purposive Communication MODULE 1 Title: The Nature of LanguageNicole Nipas100% (1)
- Funda Prelim ReviewerDocument7 pagesFunda Prelim ReviewerNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Human SexualityDocument40 pagesHuman SexualityNicole Nipas100% (1)
- NCM 101 Health Assessment The Eyes: Prepared byDocument28 pagesNCM 101 Health Assessment The Eyes: Prepared byNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Assessing Eye Structures and Visual Acuity Prepared By: Nomelita S. LoDocument3 pagesAssessing Eye Structures and Visual Acuity Prepared By: Nomelita S. LoNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- NCM IO3 Eye ExaminationDocument50 pagesNCM IO3 Eye ExaminationNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 NematodesDocument73 pagesChapter 15 NematodesNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Health and WellnessDocument5 pagesHealth and WellnessCordelia Marisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Team Sports - Games: Portfolio Prelim - FinalsDocument33 pagesTeam Sports - Games: Portfolio Prelim - FinalsLydia ElaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Continuous and Interval Training On Different Fitness Parameters in AthletesDocument4 pagesEffects of Continuous and Interval Training On Different Fitness Parameters in AthletesYared TegegneNo ratings yet
- Formative 2 - Ans KeyDocument39 pagesFormative 2 - Ans KeyDhine Dhine ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Natacha Oceane Cut KK Fit Workout GuideDocument97 pagesNatacha Oceane Cut KK Fit Workout GuideglebNo ratings yet
- Orem TheoryDocument3 pagesOrem TheoryLaverne CastroNo ratings yet
- 30 Days of Self-CareDocument19 pages30 Days of Self-CareAnas100% (3)
- Nres1dm-Chapter I and IIDocument35 pagesNres1dm-Chapter I and IImlmmandapNo ratings yet
- Wendler 5/3/1 Strength Program: Enter Desired Lifts, Then 1RM. Everything Fills in AutomaticallyDocument7 pagesWendler 5/3/1 Strength Program: Enter Desired Lifts, Then 1RM. Everything Fills in AutomaticallyBen RotkerNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale'S TheoryDocument40 pagesFlorence Nightingale'S TheoryJeff Raian BatongbakalNo ratings yet
- Septemberstarterworkout4weekbeginnerworkout PDFDocument1 pageSeptemberstarterworkout4weekbeginnerworkout PDFJonhatan GómezNo ratings yet
- First Year Instructional Home Modules - PHYSICAL EDUCATION 1 (Movement Enhancement) PrelimDocument13 pagesFirst Year Instructional Home Modules - PHYSICAL EDUCATION 1 (Movement Enhancement) PrelimJake CorañesNo ratings yet
- Fitness For Life-3Document496 pagesFitness For Life-3Frank LeggNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriestDocument79 pagesNursing TheoriestRichmond TanNo ratings yet
- Impact of The Canteen Management To The Health of Junior High School Students in Talipan National High SchoolDocument9 pagesImpact of The Canteen Management To The Health of Junior High School Students in Talipan National High SchoolMarlon PornasdoroNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory: Metaparadigm PersonDocument15 pagesFlorence Nightingale Environmental Theory: Metaparadigm PersonAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- AerobicsDocument8 pagesAerobicsIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- PortfolioDocument5 pagesPortfolioDafchen Villarin MahasolNo ratings yet
- 100 Workouts Vol3 PDFDocument211 pages100 Workouts Vol3 PDFpink lady100% (4)
- NP1Document25 pagesNP1Andrea Franchesca DelaCruz Descalzo100% (2)
- Nutri and Diet (Lab)Document12 pagesNutri and Diet (Lab)Mary Claire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 4Document8 pagesResearch Paper 4api-667053930No ratings yet
- 3 Complexes For Rapid Female Fat LossDocument13 pages3 Complexes For Rapid Female Fat LossVictor Horta100% (1)
- Physical Education and Health 11 (M1-M4)Document6 pagesPhysical Education and Health 11 (M1-M4)Mary Vhenn SamonteNo ratings yet
- PhysicalfitnessDocument31 pagesPhysicalfitnessFebi BelvisNo ratings yet
- Chloe Ting - 2020 Summer Shred Challenge - Free Workout ProgramDocument1 pageChloe Ting - 2020 Summer Shred Challenge - Free Workout ProgramCatalina Madariaga LeivaNo ratings yet
- Food Label Reading Knowledge and Understanding.5Document2 pagesFood Label Reading Knowledge and Understanding.5Miss'ElNo ratings yet
- Madbarz Routines Plan: Strength - AdvancedDocument18 pagesMadbarz Routines Plan: Strength - AdvancedJuan Sebastian AnguloNo ratings yet
- Health Behaviors Enhancing Vs CompromisingDocument7 pagesHealth Behaviors Enhancing Vs CompromisingumibrahimNo ratings yet
- 11 - Muscular FitnessDocument23 pages11 - Muscular FitnessRusu Alex100% (2)