Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VLAN Trunk Protocols (VTP) One Picture Summary
Uploaded by
Jumput Purnomo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesSwitch
Original Title
VTP and DTP Summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSwitch
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesVLAN Trunk Protocols (VTP) One Picture Summary
Uploaded by
Jumput PurnomoSwitch
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
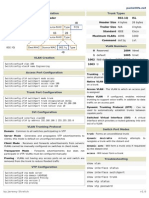
VLAN Trunk Protocols (VTP) One Picture Summary
What is VTP? Subnet adv:
How VLAN database is stored:
VTP uses lay 2 multicast frames on Native VLAN (VLAN 1) to IOS switch in Server & Client mode: VLAN databases into Response to request from client, includes detailed info for
synchronize VLAN information among a group of switches in vlan.dat file in Flash, to clear all configurations, you need specific vlan.
the same VTP domain. to delete the vlan.dat file in flash after command “erase
VTP versions: startup-config”.
VTP version 1&2: only support VLAN ID range 1-1005, in IOS switch in Transparent mode: VLAN database is stored
which VLAN 1, 1002-1005 are set aside for dedicated in configuration file in NVRAM, thus “erase
use. In order to support extended-range VLANs (1-4094), startup-config” will clear all VLANs.
the only way for VTP version 1&2 node is to enable VTP CatOS switch: VLAN database stored in memory. VLAN
Transparent mode. database disappears after reloading and configuration
VTP version 3: natively supports extended-range VLANs. version becomes 0.
However, it can be enabled only on CatOS based VTP Pruning:
switches. It makes more efficient use of Trunk link BW.
VTP version 1 is by default enabled, and switching the Broadcast and unknown unicast frames on a VLAN are
whole VTP domain to VTP Ver 2 only requires you to forwarded over a trunk link only if the receiving switch
enable VTP ver 2 on VTP Server mode switch. currently has active port on that VLAN.
Note that SVI of a VLAN will also be shutdown Adv Request from client:
How does VTP works? automatically if there is no Active port on that VLAN. Request updates when higher config version number in
summary adv is heard.
VTP mechanism relies on 3 VTP Roles (Server / Client /
Transparent; and 3 VTP Advertisement (Summary / Request / Basic Operational Parameters
Response). Layer-2 multicast address: 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC
VTP Operation VLAN range: Vlan 1 to 1005
VTP Server: VTP message Interval: 5 mins
Originate VTP Summary adv every 300 secs, but never
forward VTP Summary adv.
VTP version change on VTP server will automatically VTP Advertisement Types
propagate throughout the whole domain.
VTP Client: Summary adv:
Every 300 secs, and change triggered. Configuration Commands
Originate VTP Summary adv every 300 secs, and also
forward VTP Summary adv originated from other VTP Switch(config)# vtp version {1 | 2}
Server Nodes. Switch(config)# vtp mode server
VTP Transparent: Switch(config)# vtp domain Enterprise
Configuration version value always equals 0. Switch(config)# vtp password cisco
Only forwards VTP Advertisements but never originates, Switch(config)# vtp pruning
and its local VLAN database is never overwritten Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk pruning vlan {none |
according to VTP Advertisements. {add | except | remove (vlan-list)} }
Normally used to clear all local VLAN Information.
Troubleshooting
Switch# show vtp status
Switch# show vtp counters
Switch# show vlan brief
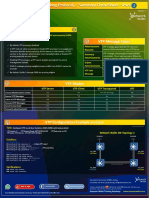
Dynamic Trunking Protocols (DTP) One Picture Summary
Basic Concepts
Default Behaviors
What is DTP?
Cisco proprietary point-to-point protocol that negotiates Default Configuration on Trunk port:
whether a link should be a trunk link, and whether ISL or Switch(config)# interface fa0/1
802.1Q should be used for encapsulation Switch(config-if)# switchport mode dynamic desirable
How does it work? Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation
DTP frames are sent out per 30 secs to keep informing negotiate
neighbor of its link mode, regardless of which trunk ISL is preferred over 802.1Q.
mode (trunk | dynamic desirable | dynamic auto) the In case of 802.1Q, Native VLAn is 1 by default.
switchport is on. By default, all VLANs (1-4094) are allowed on trunk.
The only way to disable these DTP frames exchange is
“switch(config-if)# switchport nonegotiate”.
A trunk negotiation only happens between two switches DTP Configuration
who belong to the same VTP domain or if one or both Switch(config)# interface fa0/1
switches have not defined their VTP domain (that is, the Switch(config-if)# switchport
NULL domain). Switch(config-if)# switchport mode {trunk | dynamic
(desirable | auto)}
Types of switchport mode Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation {isl |
dot1q | negotiate}
Switchport mode trunk: Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan (vlan-id)
Place port in permanent trunking mode unconditionally, Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan {vlan-list |
regardless all other configs (VTP domain, etc). However, all | (add | except | remove) vlan-list}
DTP frames is still sent out.
In other words, setting up the trunk forcely, and DTP Disable unnecessary DTP frames: You should disable DTP
frames can be manually disabled in this mode. negotiation if a switch has a trunk link connected to a
Switchport mode dynamic desirable (default): non-trunking router or firewall interface because those devices
Proactively ask the far-end to setup the trunk link, and cannot participate in DTP negotiation.
will succeed when dynamic desirable or dynamic auto is
configured on the far-end. Troubleshooting
Switchport mode dynamic auto:
Switch# show interface fa0/0 trunk
Passively wait far-end to proactively attempt to setup
the trunk link when dynamic desirable is configured on
the far-end.
You might also like
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- 2.3 VTPDocument9 pages2.3 VTPSaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Ccna3 CommandsDocument54 pagesCcna3 CommandsDiatomspinalcordNo ratings yet
- Config VTP v3Document8 pagesConfig VTP v3Mustafa HussienNo ratings yet
- VTPDocument14 pagesVTPAmro GoneimNo ratings yet
- ICND2 v3 NotesDocument34 pagesICND2 v3 NotesAndrewNo ratings yet
- Week13 Data Communication and NetworkingDocument16 pagesWeek13 Data Communication and NetworkingMark Dhel VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN TrunkingDocument16 pagesLab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN TrunkingMoh diakNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Lab - Implement VTP - ILMDocument26 pages5.1.2 Lab - Implement VTP - ILMAndrei Petru PârvNo ratings yet
- Cisco VLAN Trunking ProtocolDocument3 pagesCisco VLAN Trunking ProtocolHe RoNo ratings yet
- VTP & STP TutorialDocument19 pagesVTP & STP TutorialsureshNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Lab - Implement VTP - ILMDocument26 pages5.1.2 Lab - Implement VTP - ILMgoodreziNo ratings yet
- VLAN Trunking Protocol VTP TutorialDocument6 pagesVLAN Trunking Protocol VTP TutorialSallie ChaitNo ratings yet
- Configuring VTP: Understanding How VTP WorksDocument12 pagesConfiguring VTP: Understanding How VTP WorksIamSajid JatoiNo ratings yet
- UnderStand VTP ModesDocument9 pagesUnderStand VTP Modesgjump0103No ratings yet
- 0.2 VTPv2 and v3Document4 pages0.2 VTPv2 and v3Kv142 KvNo ratings yet
- What Is VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)Document15 pagesWhat Is VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)Belete TilahunNo ratings yet
- Configuring VTPDocument16 pagesConfiguring VTPcatalinolopezNo ratings yet
- Configuring VTP, Vlans, Vlan Trunks, and VmpsDocument50 pagesConfiguring VTP, Vlans, Vlan Trunks, and VmpsapNo ratings yet
- SWVTPDocument18 pagesSWVTPAjith PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Vlan Trunks and Etherchannel Bundles: Instructor MaterialsDocument51 pagesChapter 5: Vlan Trunks and Etherchannel Bundles: Instructor MaterialsSaianbNo ratings yet
- Vlan 1Document31 pagesVlan 1hosamhamid20022020No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-1-Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP: TopologyDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-1-Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP: TopologySulayman AlwabelNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-1 VLAN-TRUNK-VTP STUDENTDocument20 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-1 VLAN-TRUNK-VTP STUDENTDarrenNo ratings yet
- VLAN and VTPDocument13 pagesVLAN and VTPرفال الجهنيNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 - Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP: TopologyDocument30 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-1 - Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP: Topologyandres gomezNo ratings yet
- VLAN NetlabDocument25 pagesVLAN Netlabphuc1231991100% (1)
- Configuring VTP: Finding Feature InformationDocument26 pagesConfiguring VTP: Finding Feature InformationBui Hong MyNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-1 VLAN-TRUNK-VTP STUDENT PDFDocument36 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-1 VLAN-TRUNK-VTP STUDENT PDFHollman JimenezNo ratings yet
- VLAN Trunking Protocol1Document2 pagesVLAN Trunking Protocol1Dara IsmailNo ratings yet
- Ccnpv7.1 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-Vtp InstructorDocument33 pagesCcnpv7.1 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-Vtp InstructorAustin GriffithNo ratings yet
- Configure DTP - VTPDocument2 pagesConfigure DTP - VTPDani EneNo ratings yet
- Understanding VTPDocument22 pagesUnderstanding VTPBurhan RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 2 - Labs: Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering - Ho Chi Minh City University of TechnologyDocument14 pagesComputer Networks 2 - Labs: Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering - Ho Chi Minh City University of Technologyquocdung89No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 - Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP: TopologyDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-1 - Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP: Topologyorlando cartagenaNo ratings yet
- VTP NotesDocument3 pagesVTP Notessainipreetpal0% (1)
- Ccnpv7 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-VtpDocument20 pagesCcnpv7 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-VtpKevin KimNo ratings yet
- VTPDocument14 pagesVTPMuhammad AZibNo ratings yet
- Creación de VLANSDocument4 pagesCreación de VLANSAgustin SarriaNo ratings yet
- VlansDocument1 pageVlansopexxx100% (1)
- VLANs 221112 111736Document2 pagesVLANs 221112 111736nguyenbaviet89No ratings yet
- VLANsDocument1 pageVLANsWA LidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 - VLAN and TrunkingDocument35 pagesChapter 08 - VLAN and TrunkingtrietbuivienNo ratings yet
- Cisco VTP Notes Part 2 Cheat Sheet Network WalksDocument1 pageCisco VTP Notes Part 2 Cheat Sheet Network WalksJon Carlo R. ChavezNo ratings yet
- Bridging Content: CCNA Routing & Switching 6.0 BridgingDocument53 pagesBridging Content: CCNA Routing & Switching 6.0 BridgingJorge Luis Adco CcahuayNo ratings yet
- Vlans, Trunking and VTPDocument55 pagesVlans, Trunking and VTPAbdelkader MechiNo ratings yet
- Switching by MohandDocument11 pagesSwitching by MohandMorad AlabsyNo ratings yet
- CCNP3 Lab 2 1 enDocument17 pagesCCNP3 Lab 2 1 enCarlos LopezNo ratings yet
- Ccnav3.3 308Document32 pagesCcnav3.3 308Tung HoangNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)Document36 pagesUnderstanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)Raj100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - LAN Switching TechnologiesDocument65 pagesLesson 4 - LAN Switching TechnologiestvdanNo ratings yet
- Configure VTP Server and Client in SwitchDocument4 pagesConfigure VTP Server and Client in SwitchPerbz JayNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Scaling VLANs PDFDocument37 pagesWeek 2 - Scaling VLANs PDFJacob Satorious ExcaliburNo ratings yet
- 4.2.1 Default VTP ConfigurationsDocument9 pages4.2.1 Default VTP ConfigurationsmmasliniaNo ratings yet
- Vlans, Trunking and VTPDocument73 pagesVlans, Trunking and VTPAbdelkader MechiNo ratings yet
- Trunking Operation PDFDocument7 pagesTrunking Operation PDFDenis MsusaNo ratings yet
- Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) : Document ID: 10558 This Document Contains Flash AnimationDocument8 pagesUnderstanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) : Document ID: 10558 This Document Contains Flash AnimationCesar A. Romero CarranzaNo ratings yet
- VTP Interview Questions and Answers (VLAN Trunking Protocol) - Networker InterviewDocument2 pagesVTP Interview Questions and Answers (VLAN Trunking Protocol) - Networker InterviewBhanu SainiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Hcia DatacoDocument44 pagesQuiz Hcia DatacoJumput Purnomo100% (1)
- Isr4331 k9 DatasheetDocument5 pagesIsr4331 k9 DatasheetJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Huawei Voucher Order Guide V1 0Document5 pagesHuawei Voucher Order Guide V1 0Jumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Silver Peak TrainingDocument5 pagesSilver Peak TrainingJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Cisco 3800 Series Integrated Services RoutersDocument17 pagesCisco 3800 Series Integrated Services RoutersJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- 7606 VPN+ k9 DatasheetDocument1 page7606 VPN+ k9 DatasheetJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Hybrid InterfacesDocument4 pagesHybrid InterfacesJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Switch StackingDocument9 pagesSwitch StackingJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Configure A Basic WLAN On The WLC: Addressing TableDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer - Configure A Basic WLAN On The WLC: Addressing TableRaul Sebastian BuriNo ratings yet
- Day1a DHCP NAT PAT RevDocument26 pagesDay1a DHCP NAT PAT RevJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Ether ChannelsDocument6 pagesEther ChannelsJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Day1 LabDocument9 pagesDay1 LabJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About OSPFDocument20 pagesAll You Need To Know About OSPFJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- BGP Short NotesDocument23 pagesBGP Short NotesJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- IS-IS ProtocolDocument17 pagesIS-IS ProtocolJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Halabi Bgp4 Case Studies TutorialDocument100 pagesHalabi Bgp4 Case Studies Tutorialjanaksundhar85No ratings yet
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) One Picture SummaryDocument2 pagesHot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) One Picture SummaryNameNo ratings yet
- AWS Services Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument21 pagesAWS Services Cheat Sheet: by ViaDigambar S TatkareNo ratings yet
- Huawei CloudEngine S5735-L Series Switches DatasheetDocument44 pagesHuawei CloudEngine S5735-L Series Switches DatasheetJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Linux Command LineDocument56 pagesLinux Command LinePranesh SathyanarayanNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree Protocols: Basic Operational ParametersDocument3 pagesSpanning Tree Protocols: Basic Operational ParametersJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Cisco NX-OS and Cisco IOS ComparisonDocument2 pagesCisco NX-OS and Cisco IOS ComparisonJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- OSPF Short NotesDocument12 pagesOSPF Short NotesJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Exel ShortcutsDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Exel ShortcutsAgung Dwi LaksonoNo ratings yet
- Azure FIREWALL Protection Real TimeDocument12 pagesAzure FIREWALL Protection Real TimeJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Audit Committee and Corporate Governance: CA Pragnesh Kanabar Sir's The Audit Academy-CA Final AuditDocument17 pagesAudit Committee and Corporate Governance: CA Pragnesh Kanabar Sir's The Audit Academy-CA Final AuditPULKIT MURARKANo ratings yet
- AR Financial StatementsDocument281 pagesAR Financial StatementsISHA AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- What On Earth Is A MainframeDocument132 pagesWhat On Earth Is A MainframeCarlos DantasNo ratings yet
- Why Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedDocument16 pagesWhy Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedFarooq SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Construction of Perimeter Fence of BFP NHQ PDFDocument133 pagesConstruction of Perimeter Fence of BFP NHQ PDFYalla ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Family History Timeline Rubric HonorsDocument1 pageFamily History Timeline Rubric Honorsapi-291510568No ratings yet
- A Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument65 pagesA Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofMadhavpokale100% (1)
- Catphan®604 ManualDocument34 pagesCatphan®604 ManualTold Told LeungNo ratings yet
- Interection 2 Reading Teacher's Book PDFDocument165 pagesInterection 2 Reading Teacher's Book PDFتركي الزهراني0% (1)
- Exam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)Document10 pagesExam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)SadishNo ratings yet
- Asme Bladder Accumulator DatasheetDocument3 pagesAsme Bladder Accumulator DatasheetSamad A BakarNo ratings yet
- Test Cases: Project Name: Virtual ClassroomDocument5 pagesTest Cases: Project Name: Virtual ClassroomTina HernandezNo ratings yet
- EHR StandardsIndia - August 2013-32630521Document54 pagesEHR StandardsIndia - August 2013-32630521kartiksinhNo ratings yet
- Management Glossary - Musa KamawiDocument50 pagesManagement Glossary - Musa KamawiKazi Nazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Procedures Involved in The Ansys ACP17.2Document10 pagesProcedures Involved in The Ansys ACP17.2Vijayanandh RNo ratings yet
- Sharp Product-Catalogue 2019 enDocument48 pagesSharp Product-Catalogue 2019 enMiki di KaprioNo ratings yet
- Program Logic FormulationDocument69 pagesProgram Logic FormulationIan OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Buy Wholesale China Popular Outdoor Football Boot For Teenagers Casual High Quality Soccer Shoes FG Ag Graffiti Style & FootballDocument1 pageBuy Wholesale China Popular Outdoor Football Boot For Teenagers Casual High Quality Soccer Shoes FG Ag Graffiti Style & Footballjcdc9chh8dNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseShaina MabborangNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaDocument15 pagesThe Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaAasvogel Felodese Carnivora64% (14)
- Claudio MonteverdiDocument2 pagesClaudio MonteverdiBrendan LynchNo ratings yet
- Ken Holt 06 The Secret of Hangman's InnDocument216 pagesKen Holt 06 The Secret of Hangman's InnPastPresentFuture100% (2)
- NCP81205Document1 pageNCP81205Tom TomNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Regional PlanningDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Regional Planningadeeba siddiquiNo ratings yet
- p1632 eDocument4 pagesp1632 ejohn saenzNo ratings yet
- Cyrille MATH INVESTIGATION Part2Document18 pagesCyrille MATH INVESTIGATION Part2Jessie jorgeNo ratings yet
- E Commerce and Its Influence in Changing in Purchasing Behavior of Modern ConsumersDocument13 pagesE Commerce and Its Influence in Changing in Purchasing Behavior of Modern ConsumersRichard VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review A2-B1Document5 pagesGrammar Review A2-B1Lena Silva SouzaNo ratings yet
- Sample Hum RepDocument21 pagesSample Hum RepPritam PiyushNo ratings yet
- VDRL - Press. GaugesDocument9 pagesVDRL - Press. GaugesSourav RayNo ratings yet