Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Recursion
Uploaded by
Ashish ShuklaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Recursion
Uploaded by
Ashish ShuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
Recursive function
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Outline
• Recursion
• Examples of recursion
– Finding factorial of a number
– Finding Fibonacci series up to nth term
• Recursion Vs Iteration
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion
• Recursive functions
– Functions that call themselves
– Can only solve a base case
– Divide a problem up into
• What it can do
• What it cannot do
– What it cannot do resembles original
problem
– The function launches a new copy of itself
(recursion step) to solve what it cannot do
– Eventually base case gets solved
• Gets plugged in, works its way up and
solves whole problem
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (factorial)
• Factorial of a number in mathematics
– 5! = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1
• Another method we have studied is
Values returned
– For 5!, we write 5! = 5 * 4! 120
– Then for 4!, 4! = 4 * 3!
24
– Then for 3!, 3! = 3 * 2!
– Then for 2!, 2! = 2 * 1! 6
2
– Then for 1!, 1! = 1 * 0!
1
– And if its comes to 0,
– 0!=1
– Solve base case (1! = 0! = 1)
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (factorial)
Fin a l va lue = 120
5! 5!
5! = 5 * 24 = 120 is re turn ed
5 * 4! 5 * 4!
4! = 4 * 6 = 24 is re turne d
4 * 3! 4 * 3!
3! = 3 * 2 = 6 is re tu rn e d
3 * 2! 3 * 2!
2! = 2 * 1 = 2 is re turne d
2 * 1! 2 * 1!
1 re turne d
1 1
( a ) Se q u en c e o f re c ursive c a lls. ( b ) Va lue s re turne d fro m e a c h re cu rsive c a ll.
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (factorial code)
This function
calculates
factorial of
first 10
numbers
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (factorial code)
This
function
calculates
factorial of
first 10
numbers
1! = 1
2!
3!
=
=
2
6
output
4! = 24
5! = 120
6! = 720
7! = 5040
8! = 40320
9! = 362880
10! = 3628800
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (fibonacci)
• What is Fibonacci series: …??
• 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8...
– Each number is the sum of the previous two
– Can be solved recursively:
• fib( n ) = fib( n - 1 ) + fib( n – 2 )
– Code for the fibonacci function
long fibonacci( long n )
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1) // base case
return n;
else
return fibonacci( n - 1)+fibonacci( n – 2 );
}
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
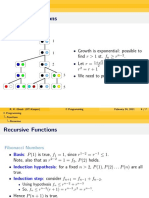
Recursion example (fibonacci)
• Set of recursive calls to fibonacci() function
f( 3 )
return f( 2 ) + f( 1 )
return f( 1 ) + f( 0 ) return 1
return 1 return 0
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (fibonacci code)
This function
calculates
fibonacci
number of
any given
position
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion example (fibonacci code)
This function
calculates
fibonacci
number of
any given
position
Enter an integer: 0
Fibonacci( 0 ) = 0
or
Enter an integer: 1 output
Fibonacci( 1 ) = 1
or
Enter an integer: 20
Fibonacci( 20 ) = 6765
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Recursion vs. Iteration
• Repetition
– Iteration: explicit loop(for,while)
– Recursion: repeated function calls
• Termination
– Iteration: loop condition fails
– Recursion: base case reached
• Both can have infinite loops
• Balance
– Choice between performance (iteration) and good
software engineering (recursion)
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
Rules for recursive function
1. In recursion, it is essential to call a function itself
2. Only the user defined function can be involved in the
recursion. Library function cannot be involved in
recursion because their source code cannot be
viewed
3. A recursive function can be invoked by itself or by
other function.
4. To stop recursive function, it is necessary to base
recursion on some condition, and proper termination
statement such as exit() or return
5. The user defined function main() can be invoked
recursively.
©LPU CSE101 C Programming
You might also like
- Ion-Valve Oscillators and Ion-Valve Converters Technologies (Who's Who in Free Energy)Document74 pagesIon-Valve Oscillators and Ion-Valve Converters Technologies (Who's Who in Free Energy)ernieespells1jtkl56100% (19)
- Excel Ch. 3 in The Lab 1Document5 pagesExcel Ch. 3 in The Lab 1Jemelia StewartNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - Liebherr WR - Lube SCDocument1 pageData Sheet - Liebherr WR - Lube SChoi0% (1)
- CSE101 Lec 15Document14 pagesCSE101 Lec 15Amulya RajNo ratings yet
- ©LPU CSE101 C ProgrammingDocument14 pages©LPU CSE101 C ProgrammingSharath SaiNo ratings yet
- CSE101Recrusive FunctionDocument21 pagesCSE101Recrusive FunctionAkshay ArebellyNo ratings yet
- RECUSSIONDocument14 pagesRECUSSIONSai GunturNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 11recursion and Mathematical Functions in CDocument25 pagesLecture - 11recursion and Mathematical Functions in CSumant YadavNo ratings yet
- Recursive FunctionDocument13 pagesRecursive FunctionSuresh Reddy PolinatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Recursion and Mathematical Functions in CDocument25 pagesLecture - Recursion and Mathematical Functions in CHome TvNo ratings yet
- 09 RecursionDocument13 pages09 Recursionamramr.elbrns78No ratings yet
- L29 L30 Recursive FunctionsDocument25 pagesL29 L30 Recursive FunctionsIshank PatelNo ratings yet
- Recurs IonsDocument47 pagesRecurs IonsKing Shah 673No ratings yet
- Math Library Functions: by Pundreekaksha Sharma Assistant Professor CSEDocument29 pagesMath Library Functions: by Pundreekaksha Sharma Assistant Professor CSEAkshay ArebellyNo ratings yet
- T5 RepititionDocument34 pagesT5 Repititionsiyu chenNo ratings yet
- Recursive Functions: Fibonacci NumbersDocument9 pagesRecursive Functions: Fibonacci NumbersKESHAV SINGHALNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem, ITP, Lecture 11-Algorithms & ComputingDocument12 pages1st Sem, ITP, Lecture 11-Algorithms & ComputingM KhattakNo ratings yet
- CS1010S-Lec-03 Recursion, IterationDocument70 pagesCS1010S-Lec-03 Recursion, IterationAkane YoriNo ratings yet
- Cat 2 Question Bank With All Part PDFDocument32 pagesCat 2 Question Bank With All Part PDFJJNo ratings yet
- Recursion: Intro, Recursive Functions Recursion Vs IterationDocument12 pagesRecursion: Intro, Recursive Functions Recursion Vs IterationSourabh ShekharNo ratings yet
- CSE101 - Lec 6 PART 2 (Looping or Iterative Statement)Document33 pagesCSE101 - Lec 6 PART 2 (Looping or Iterative Statement)Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Alg Ch1 Part2Document24 pagesAlg Ch1 Part2yarajehadrabNo ratings yet
- CSE101 LoopsDocument33 pagesCSE101 LoopsVedanth PradhanNo ratings yet
- Recursion PDFDocument19 pagesRecursion PDFذیشان چودھریNo ratings yet
- CSE101 - Lec 5 PART 1 (Operators)Document29 pagesCSE101 - Lec 5 PART 1 (Operators)Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming NotesDocument4 pagesComputer Programming NotesstaceyNo ratings yet
- Bscs-402 Data Structure Lab 1Document8 pagesBscs-402 Data Structure Lab 1Muhammad Anas RashidNo ratings yet
- RecursionDocument18 pagesRecursionWong YNo ratings yet
- Recursion: CS 367 - Introduction To Data StructuresDocument20 pagesRecursion: CS 367 - Introduction To Data Structuresscet 315No ratings yet
- Ds NotesDocument65 pagesDs Notesuma sNo ratings yet
- Cse L5 (Operators)Document45 pagesCse L5 (Operators)abhiNo ratings yet
- Recursion in CDocument20 pagesRecursion in CSamyak AnandNo ratings yet
- Lecture25 RecursionDocument36 pagesLecture25 Recursionabc xyzNo ratings yet
- RecursionDocument35 pagesRecursionvarun.chintatiNo ratings yet
- Iteration and Recursion: CPE222 - Discrete StructuresDocument10 pagesIteration and Recursion: CPE222 - Discrete StructuresAhmed SaidNo ratings yet
- Recursion C++Document39 pagesRecursion C++MateoCaCeNo ratings yet
- Recursion: - Definition of Factorial: ! 1 2 2 1 - Recursive Definition: !, 0 1, 0Document11 pagesRecursion: - Definition of Factorial: ! 1 2 2 1 - Recursive Definition: !, 0 1, 0ankit kumarNo ratings yet
- CSE101 Lec#8Document36 pagesCSE101 Lec#8Debatulya MandalNo ratings yet
- Program Control: OutlineDocument29 pagesProgram Control: OutlineSyhr AlydrsNo ratings yet
- CSE101-Lec#13: Math Library FunctionsDocument24 pagesCSE101-Lec#13: Math Library FunctionsVikas MishraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 33Document15 pagesLesson 33Jason UchennnaNo ratings yet
- Recursion: Mirza Mohammad Lutfe ElahiDocument36 pagesRecursion: Mirza Mohammad Lutfe ElahiFahad Rahman AmikNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Unit - 1 1. AlgorithmDocument64 pagesData Structures Unit - 1 1. Algorithmuma sNo ratings yet
- 6.006 Introduction To Algorithms: Mit OpencoursewareDocument5 pages6.006 Introduction To Algorithms: Mit Opencoursewareraw.junkNo ratings yet
- Non Re CursiveDocument52 pagesNon Re CursiveSathis KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 11 DSADocument12 pagesLab Manual 11 DSAinft18111035 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Lecture# 12-Recursive and Iterative AlgorithmsDocument17 pagesLecture# 12-Recursive and Iterative AlgorithmsShahzad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Recursion in C, C++Document16 pagesRecursion in C, C++sabarisriNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 6 23112021 114139amDocument6 pagesLab Manual 6 23112021 114139amQazi MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Programming Basics in MATLAB: September 7Document24 pagesLecture 2: Programming Basics in MATLAB: September 7adethroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document11 pagesTutorial 4213025 ktr.et.mech.15No ratings yet
- ITC LAB 11 - For LoopDocument4 pagesITC LAB 11 - For LooppathwayNo ratings yet
- Lec13 ReviewDocument70 pagesLec13 Reviewkayle1535No ratings yet
- Recursive Functions: 5.13 RecursionDocument7 pagesRecursive Functions: 5.13 RecursionOrinIslamRahaNo ratings yet
- Matlab PDFDocument34 pagesMatlab PDFAbhilash MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Control Statements in MATLAB: The Decision Making Control Statements Permit To Select andDocument34 pagesControl Statements in MATLAB: The Decision Making Control Statements Permit To Select andnarun9895152299No ratings yet
- Lab 7 Nov 15,16 (2PM), 17Document45 pagesLab 7 Nov 15,16 (2PM), 17melt.bonier.0zNo ratings yet
- 07 RecursionDocument38 pages07 RecursionUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- Slot07 08 09 RecursionDocument82 pagesSlot07 08 09 RecursionCông QuânNo ratings yet
- Week9 1Document9 pagesWeek9 1tanushaNo ratings yet
- Pydata SeattleDocument98 pagesPydata Seattlednn38hdNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Based Trajectory Optimization For UAVDocument23 pagesDeep Learning Based Trajectory Optimization For UAVSalil SharmaNo ratings yet
- WSZ ControllerDocument6 pagesWSZ ControllerAtiqur Rahman AtiqNo ratings yet
- TrakPro Lite Secure 6004404Document47 pagesTrakPro Lite Secure 6004404jinos13No ratings yet
- Determination of Amount of Vitamin C in A Commercial ProductDocument7 pagesDetermination of Amount of Vitamin C in A Commercial ProductNoel NeumanNo ratings yet
- Assign N LabDocument4 pagesAssign N LabMtende MosesNo ratings yet
- Formal Methods in Software Engineering: Propositional LogicDocument28 pagesFormal Methods in Software Engineering: Propositional LogicIzhar HussainNo ratings yet
- 610 SIdata SheetsDocument26 pages610 SIdata Sheetssjois_hsNo ratings yet
- Examination-Schedule BE-Arch-BCA-B.Sc .Env - Fall-2023 AllDocument4 pagesExamination-Schedule BE-Arch-BCA-B.Sc .Env - Fall-2023 Allsandhyakhadka909No ratings yet
- Q4 Module 2 Gathering and Organizing Data 2023 2024Document55 pagesQ4 Module 2 Gathering and Organizing Data 2023 2024orazajedediahNo ratings yet
- Crud Web Api Entity FrameworkDocument6 pagesCrud Web Api Entity FrameworkSaurabh Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Maxwell Transient ProblemDocument45 pagesMaxwell Transient ProblemConstantin DorinelNo ratings yet
- 543369Document57 pages543369Robert MacomberNo ratings yet
- Answer StepExercise Min EOLDocument2 pagesAnswer StepExercise Min EOLKamal SaravananNo ratings yet
- MIMO Channel CapacityDocument9 pagesMIMO Channel CapacityGendyNo ratings yet
- APC Back-UPS 400 CLII-9FCLHR - R0 - ENDocument2 pagesAPC Back-UPS 400 CLII-9FCLHR - R0 - ENPatrizia CudinaNo ratings yet
- Demister Beam Calculation - Final PDFDocument4 pagesDemister Beam Calculation - Final PDFGauravNo ratings yet
- PAHS 306: Session 5 - Simple CorrelationDocument14 pagesPAHS 306: Session 5 - Simple CorrelationSuhuyini GaribugliNo ratings yet
- Weirs Notch Report PDFDocument62 pagesWeirs Notch Report PDFMaxwell RejilNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Analysis Using Windows PowerShellDocument28 pagesIntrusion Analysis Using Windows PowerShellioqseNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Onventional Ncryption PrinciplesDocument35 pagesUnit - 2: Onventional Ncryption PrincipleshafeezaNo ratings yet
- Asist. Univ. Dr. Mihaela Popescu Catedra de Cardiologie Spitalul Universitar de Urgenta EliasDocument64 pagesAsist. Univ. Dr. Mihaela Popescu Catedra de Cardiologie Spitalul Universitar de Urgenta EliasAnonymous CQmrhq1O7No ratings yet
- Configuring DHCP Server On CentOS 7 With VLANDocument3 pagesConfiguring DHCP Server On CentOS 7 With VLANRui MaiéNo ratings yet
- Energy Monitoring With Ultrasonic Flow MetersDocument35 pagesEnergy Monitoring With Ultrasonic Flow MetersViswa NathanNo ratings yet
- Sizing of GeneratorDocument5 pagesSizing of GeneratorNiño Reanzares100% (1)
- Performance TablesDocument48 pagesPerformance Tablesdannyells_danielsNo ratings yet
- Project On Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of CellDocument11 pagesProject On Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of CellVeenaGupta60% (5)
- 001 Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Greiner Neise StockerDocument470 pages001 Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Greiner Neise StockerJose GuerraNo ratings yet