Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02
Uploaded by
Julianne Maxine FloresCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02
Uploaded by
Julianne Maxine FloresCopyright:
Available Formats
PATEROS CATHOLIC SCHOOL
Senior High School Department
F. Imson St., San Pedro, Pateros, Metro Manila
SY 2020-2021
General Biology – 02
ACTIVITY TASK SHEET No. 1
Learning Competencies:
1.1. characterize compare and contrast the following processes in plants and animals: reproduction,
development, nutrition, gas exchange, transport/circulation, regulation of body fluids, chemical and
nervous control, immune systems, and sensory and motor mechanisms
Name of Student: Julianne Maxine G. Flores Grade and Section: _Grade 12 St. Dominic__
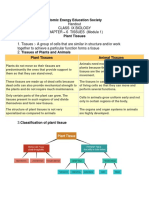
A. Plant Tissues and Reproduction
Today, there are more than 325,000 known plant species. Plants enabled other life-forms to
survive on land. For example, plants supply oxygen and are a key source of food for terrestrial animals.
Also, by their very presence, plants such as the trees of a forest physically create the habitats required
by animals and many other organisms.
1.Log on to the internet and visit the following website:
Genyolm.com – study the handout attached in your account about plant body parts
2.Answer the following:
I. Differentiate the Root and Shoot System of Plants in terms of:
Difference in: Root System Shoot System
Structures Root system grows The shoot system is an
beneath the ground, aerial and erect part of
Involved absorbing water and the plant which grows
minerals from the soil. It upwards.
is mainly composed of
roots, tubers, and
rhizomes.
Functions The root system absorbs The shoot system of a
water and minerals from plant functions as the
the soil while providing area where
support to the plant on photosynthesis,
the ground. It keeps the transportation and
ground intact in the reproduction occur.
ground.
PCS: MEN AND WOMEN OF NOBLE CHARACTER 1
II. Meristems: Differentiate the three types of meristematic tissue. Give its
importance and where they are located.
Apical Meristem Intercalary Lateral
Meristem Meristem
Importance These kind of The intercalary The lateral meristem
meristem tissues are meristem is used by helps in increasing the
immature cells with monocots for rapid thickness of the plants.
thin walls. A compact growth and regrowth It is part of secondary
arrangement can since these tissues are growth.
divide and from new capable of cell division.
cells. It can cause the
length of root and
stem to increase.
Another important use
of this meristem is the
asexual reproduction
of plants.
Location Apical Meristems can Intercalary meristems Lateral meristems are
be found just below are found in the leaves present on the lateral
the root cap in the and the internodes of side of the stem and
roots. It is a cluster of plants. roots of a plant.
densely packed and
undifferentiated cells.
III. Simple Tissues. What are simple tissues? Give their function.
- Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cell. It helps in the storage of food
and mechanical support. These are the types of Simple Tissues and their functions:
1. Dermal Tissues
- Also known as protective tissues, they are formed in the outer covering of plant
parts like the stem, roots, fruits, and flowers.
o Stomata
Stomata are specialized pores that allow gas exchange through holes
in the cuticle.
o Trichomes
Trichomes are either unicellular or multicellular structures that
develop from epidermal cells in above-ground plant tissues. Some
examples are leaf hairs.
o Root Hairs
Root hairs function as the protectors of plants, it covers and protects
the plant as well as controlling gas exchange and water absorption.
2. Ground Tissues
- Ground tissues are neither dermal nor vascular. It consists of the majority of cells
that perform basic survival processes such as growth, photosynthesis, and storage.
It is made up of three types of cells called:
PCS: MEN AND WOMEN OF NOBLE CHARACTER
2
o Parenchyma
It is a spherical, oval or polygonal cell. Its cell wall is made from
glucose and may or may not have an intracellular space. The main
function of this cell is to perform photosynthesis, storage, or
transport.
o Collenchyma
It is made of elongated living cells with unevenly thick primary walls.
The function of this cell is to provide support, structure and flexibility
to the plant.
o Sclerenchyma
It has thick lignified secondary walls and usually die when it gets to
its mature state. The primary function of this cell is to provide support
to the plant.
IV. Complex Tissues. What are complex tissues? Give their function.
- Complex tissues distribute water and nutrients throughout the body of the plant.
There are two types of vascular tissues:
o Xylem
It is a major component of vascular tissues.
The primary function of this tissue is to transport water and solutes
from the plant to soil interface to the stems and leaves. It also
functions as a storage and support.
o Phloem
It is made up of living cells.
Phloem transports carbohydrates from sites where they are produced
to their storage sites.
There are pipelines that supports the transportation of carbohydrates,
it is called sieve tubes. The sieve tubes are stacks of living cells that
are connected to perforated sieve plates.
PCS: MEN AND WOMEN OF NOBLE CHARACTER
3
V. Plant Reproductive System. What is the reproductive organ of the plant? Draw
and differentiate the male and female sex organs.
Sexual production in plants is the sole function of flowers. A plant’s reproductive part is
the flower’s stamen (if a male), and the pistil (if female), or both. There are also
accessory parts such as sepals, petals, and nectar glands.
PCS: MEN AND WOMEN OF NOBLE CHARACTER
4
You might also like
- Plant Cell Type and Its FunctionDocument36 pagesPlant Cell Type and Its Functionlamberto revecheNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Types and Functions Explained in DetailDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue Types and Functions Explained in DetailBhawan malhiNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)Document22 pagesBiology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)AbdoNo ratings yet
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDocument3 pagesSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23Document4 pagesClass 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23collins thomasNo ratings yet
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissue DifferencesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissue DifferencesPrathmesh NamanNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity A) How The Plant Kingdom EvolvedDocument15 pagesPlant Diversity A) How The Plant Kingdom EvolvedAkhmad AkhmadNo ratings yet
- Storage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESDocument14 pagesStorage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESdubeymaya153No ratings yet
- Botany Module 2.1Document11 pagesBotany Module 2.1Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: How Plants SurviveDocument9 pagesEarth & Life Science: How Plants Survivejames bonfNo ratings yet
- Meristematic Tissue: Cell Modifications and Specialization I. Plant Cells and TissuesDocument6 pagesMeristematic Tissue: Cell Modifications and Specialization I. Plant Cells and TissuesBigsmile PhotoboothNo ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- GS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsDocument9 pagesGS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsChary Johanne MenesesNo ratings yet
- Green Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation TemplateDocument22 pagesGreen Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation Templatelyka garcia100% (1)
- General Biology Module 3Document12 pagesGeneral Biology Module 3reyloyd tabontabonNo ratings yet
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Plant Roots Written ReportDocument3 pagesPlant Roots Written ReportAshlee JornadalNo ratings yet
- A Plant's Organ Systems and Their FunctionsDocument1 pageA Plant's Organ Systems and Their FunctionsMariel KhoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument19 pagesKingdom PlantaeDanny DonNo ratings yet
- Plant tissues and their functionsDocument9 pagesPlant tissues and their functionsArjun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part - 1Document4 pagesTissues Part - 1Monika Mehan100% (2)
- Plant Form and FunctionsDocument2 pagesPlant Form and FunctionsJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class Ix NotesDocument19 pagesTissues Class Ix Notesjrheisenberg5No ratings yet
- Asgn 5974128103Document7 pagesAsgn 5974128103rappycatNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues WordDocument5 pagesPlant Tissues WordJeannie de leonNo ratings yet
- Tissues - YTDocument94 pagesTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- Plant PrintsDocument11 pagesPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 5 NotesDocument20 pagesBio Form 5 NotesNithyamathi KalimuthuNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument32 pagesPlant TissuesVikneswaran Gunahlan Nesh100% (2)
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8sheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues Lateral Meristems Increase The Girth orDocument3 pagesPlant Tissues Lateral Meristems Increase The Girth orWennie Fe MartinezNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologysakthilogi123No ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemDocument123 pagesPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- Chapter TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter TissuesAarti JainNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant CellsDocument26 pagesTypes of Plant CellsJustin BiboNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 10Document60 pagesBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument9 pagesTissues NotesPrathiba AugustineNo ratings yet
- Biology Ls 6Document14 pagesBiology Ls 6KhatrasNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm For Exit ExamDocument166 pagesAngiosperm For Exit Examgeorge manNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Remove watermark with VeryDOC converterDocument8 pagesRemove watermark with VeryDOC converterNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Tissue NotesDocument4 pagesTissue NotesRoopaNo ratings yet
- Biology Presentation Class 7Document11 pagesBiology Presentation Class 7binu biju100% (2)
- Chapter-6 BioDocument18 pagesChapter-6 BioDevansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tissue 9 PDFDocument5 pagesTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument23 pagesThe Nature and Composition of PlantsAndrea Nicole BalaresNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument38 pagesPlant KingdomjuliankobieplaysNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyDocument4 pagesPlant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Edu246 Botany 2Document8 pagesEdu246 Botany 2ANNE MARGUERITE BARETENo ratings yet
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- Tissues 9thDocument15 pagesTissues 9thANKIT RAJNo ratings yet
- Crop Plant Parts and FunctionsDocument11 pagesCrop Plant Parts and FunctionsJetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument19 pagesKingdom PlantaeJoralyn Compuesto-Francisco TañanNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Friedrich MohsDocument7 pagesFriedrich MohsJohnMadeNo ratings yet
- Anuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)Document1 pageAnuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- BNMNS B370205Document8 pagesBNMNS B370205James PerianayagamNo ratings yet
- 4-26 MDC - Tongue CancerDocument3 pages4-26 MDC - Tongue CancerCLUSTER 5 PGINo ratings yet
- Worksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1Document4 pagesWorksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1AreebNo ratings yet
- Methods of Canal Maintenance in The Netherlands: J - HebbinkDocument17 pagesMethods of Canal Maintenance in The Netherlands: J - HebbinkMarko BabicNo ratings yet
- Impact of Yeast-Handling Procedures On Beer Flavour Development During FermentationDocument7 pagesImpact of Yeast-Handling Procedures On Beer Flavour Development During FermentationMayra Schmidt RechsteinerNo ratings yet
- Uses and Abuses of Mathematics in BiologyDocument4 pagesUses and Abuses of Mathematics in Biologymuhammad sami ullah khanNo ratings yet
- Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis 2014Document27 pagesEarly-Onset Neonatal Sepsis 2014Ninde Rivera GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources in The Province of SiquijorDocument8 pagesMineral Resources in The Province of SiquijorGabrielle Troy A. CuevasNo ratings yet
- Grade-10-IM-Inventory - RODGEDocument10 pagesGrade-10-IM-Inventory - RODGEPaul AniceteNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology GCSE - Homeostasis MechanismsDocument4 pagesAQA Biology GCSE - Homeostasis MechanismsMareeb ShahNo ratings yet
- Seeds & FruitDocument26 pagesSeeds & Fruitricabaloyo2002No ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland Functions and StructureDocument6 pagesPituitary Gland Functions and StructureaparnaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Friday 24 May 2019: Biology BDocument24 pagesFriday 24 May 2019: Biology BAyaNo ratings yet
- Collecting Objective DataDocument3 pagesCollecting Objective DataJasmine MayeNo ratings yet
- Appn H Column Cleaning RegenerationDocument3 pagesAppn H Column Cleaning RegenerationducngoctrinhNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Microbial SpeciesDocument11 pagesThe Concept of Microbial SpeciesRin ChanNo ratings yet
- Crush Step 1 ErrataDocument2 pagesCrush Step 1 ErrataAbd SamadNo ratings yet
- Food Science and NutritionDocument5 pagesFood Science and NutritionJostynaNo ratings yet
- PVA Nanoparticles for Protein DeliveryDocument10 pagesPVA Nanoparticles for Protein DeliverySandeep GargNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering NotesDocument52 pagesGenetic Engineering NotesBulan PutriNo ratings yet
- Xiaoyu Yang Asms2020 PresentationDocument20 pagesXiaoyu Yang Asms2020 PresentationoceanpinkNo ratings yet
- Culture Media CombinedDocument131 pagesCulture Media CombinedEmit Rosary PenetranteNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 TGDocument100 pagesGeneral Biology 2 TGKaren Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- 04a Springer-Nature Ejournals Title-ListDocument57 pages04a Springer-Nature Ejournals Title-ListYaamini Rathinam K RNo ratings yet
- Banasthali Vidyapith: Internal Research SupervisorsDocument10 pagesBanasthali Vidyapith: Internal Research SupervisorsasanyogNo ratings yet
- Making The Most of WBDDDocument42 pagesMaking The Most of WBDDsiaofongting1No ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA UNTUK PENELITIAN HIPERTENSI DAN IKAN ZEBRADocument7 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA UNTUK PENELITIAN HIPERTENSI DAN IKAN ZEBRAVivin MuLaNo ratings yet