Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sepsis
Uploaded by
Charlie LeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sepsis
Uploaded by
Charlie LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
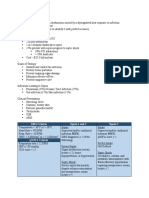
SEPSIS & SIRS
DEFINITIONS
Bacteraemia | viable bacteria in the blood.
Sepsis | life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by dysregulated host
response to infection.
Septic shock | subset of sepsis—profound circulatory, cellular, and metabolic
abnormalities are associated with increased risk of mortality.
SIRS vs Sepsis Most common sources
of infection leading to
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) is a bodily response causing sepsis are respiratory
>2 of the following. tract infections and
urinary tract infections.
• Temp. < 36 C OR > 38.3 C • BG > 7.7 mmol/L
• HR > 90 bpm • WBC < 4 OR > 12
RISK FACTORS
• RR > 20 bpm
• Advanced age
• Immunosuppressed
• Recent surgery/
hospitalization
ANTIBIOTICS
SEPSIS 6 in 1 Hour
Respiratory Tract
Give Take
• Oxygen (94-98% SpO2 or 88-92% COPD) • Blood cultures • Penicillin V (calvipen)
• Amoxicillin
• IV Antibiotics • Lactate and FBC
• Clarithromycin
• Fluids (500 mL bolus; 30mL/kg max) in 15 min. • Urine output & culture • Doxycycline
!
RED FLAGS Urinary Tract
Sepsis progresses to septic shock when… • Trimethoprim
• Nitrofurintoin
• SBP < 90 mmHg • AVPU response of V or P • Cephalexin
• HR > 120 bpm • Supplemental O2 for > 92% • Fosfomycin
• RR > 25 bpm • Lactate > 2 mmol/L
Cellulitis
If hypotension unresponsive to fluids (MAP < 65 or SBP <90)
• Trimethoprim
• Doxycycline
• Flucloxacillin
Fluid replace + vasopressors. • Lymecycline
Vasopressors
1) Norepinephrine (1-10 mcg/min) Fluid Overload:
2) Unresponsive? Add vasopressin (0.04 units/min). S&S of jugular venous
distention, chest
q-SOFA crepitations, &
Bedside score for mortality risk for patients with organs failure & sepsis. decreased pulse O2
Score >2 is high indicator of poor outcome. readings. Stop all IV
1) Altered mental 2) RR >22 bpm 3) SPB < 100 mmHg fluids until no longer
status overloaded.
You might also like
- SEPSIS Early DetectionDocument35 pagesSEPSIS Early DetectionKomang_JananuragaNo ratings yet
- Kegiatan 3 - Refreshment Lecture Diagnosis Dan Tatalaksana Sepsis Juli 2022Document36 pagesKegiatan 3 - Refreshment Lecture Diagnosis Dan Tatalaksana Sepsis Juli 2022Agnes Irene ZagotoNo ratings yet
- Acute Chest SyndromeDocument28 pagesAcute Chest SyndromeJohn OkidiNo ratings yet
- Sepsis UpdatedDocument4 pagesSepsis Updatedapi-535481376No ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan Bidang Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: I.Penyakit Dalam - MIC/ICU FK - UNPAD - RS DR - Hasan Sadikin BandungDocument47 pagesKegawatdaruratan Bidang Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: I.Penyakit Dalam - MIC/ICU FK - UNPAD - RS DR - Hasan Sadikin BandungEfa FathurohmiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Resuscitation in SepsisDocument68 pagesFluid Resuscitation in SepsisRonald Ariyanto WiradirnataNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: ManagementDocument50 pagesSepsis: Managementer bcmNo ratings yet
- 13.30 DR Arunraj Navaratnarajah - The Septic PatientDocument49 pages13.30 DR Arunraj Navaratnarajah - The Septic PatientagusNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Document4 pagesShanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: DR Unnikrishnan P / CcuDocument53 pagesSepsis: DR Unnikrishnan P / CcupaanarNo ratings yet
- 418 Septic Shock Sirs and ModsDocument51 pages418 Septic Shock Sirs and ModsApril Ann HortilanoNo ratings yet
- From SIRS To Septic Shock (2022!01!22 00-25-28 UTC)Document1 pageFrom SIRS To Septic Shock (2022!01!22 00-25-28 UTC)Andrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument11 pagesSeptic Shockj.doe.hex_87100% (1)
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines For Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic ShockDocument27 pagesSurviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines For Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic ShockAgnes TanicNo ratings yet
- Lit 2. Sepsis-3 Abdul Hakeem Al Hashim, MD, FRCPCDocument76 pagesLit 2. Sepsis-3 Abdul Hakeem Al Hashim, MD, FRCPCKomang_JananuragaNo ratings yet
- Golden Period Septic ChildDocument32 pagesGolden Period Septic ChildcallNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Management: Runal Shah 1 Year Resident MEM, Kdah, MumbaiDocument18 pagesSepsis Management: Runal Shah 1 Year Resident MEM, Kdah, Mumbaibotet_2306No ratings yet
- Fluid Dss PKB - RsDocument39 pagesFluid Dss PKB - RsancillaagraynNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Dan Penanganan Syok Hemorrhagi. (Manajemen Dan Terapi Cairan)Document31 pagesDiagnosis Dan Penanganan Syok Hemorrhagi. (Manajemen Dan Terapi Cairan)Idea HouseNo ratings yet
- Syock & ManagementDocument34 pagesSyock & ManagementIndra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan: Sri Setiyarini, S.KP., M.Kes Keperawatan Kritis & Kegawatdaruratan Psik-Fk UgmDocument50 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan: Sri Setiyarini, S.KP., M.Kes Keperawatan Kritis & Kegawatdaruratan Psik-Fk Ugmmanna_aiyaNo ratings yet
- DR. DR Umar Zein, SP - PD DTM&H - New Generation Antibiotic in SepsisDocument27 pagesDR. DR Umar Zein, SP - PD DTM&H - New Generation Antibiotic in SepsisOlivia DwimaswastiNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan IDI 2016Document53 pagesTerapi Cairan IDI 2016Annisa VitrianiNo ratings yet
- KeynoteDocument45 pagesKeynoteJim RohnNo ratings yet
- 12 Internal BleedingDocument40 pages12 Internal BleedingNoval LiadyNo ratings yet
- HarrisonsDocument117 pagesHarrisonsEm TimbolNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock: Dr. Dr. Hori Hariyanto, Span, Kic, KMNDocument89 pagesSeptic Shock: Dr. Dr. Hori Hariyanto, Span, Kic, KMNPander MadonNo ratings yet
- Surat-2019 Septic Shock Clinical PolicyDocument49 pagesSurat-2019 Septic Shock Clinical PolicyBaronKornNo ratings yet
- New Format MasterDocument34 pagesNew Format MasterMuhammad FurqanNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Treatment of ShockDocument52 pagesRecent Advances in The Treatment of ShockasupicuNo ratings yet
- Contora, Isah TblrenalDocument7 pagesContora, Isah TblrenalisahNo ratings yet
- Surgery - PPT'sDocument172 pagesSurgery - PPT'sShreya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Symposium 2. Detection and Management of Distributive Shock (DR Yunita Widyastuti SpAn)Document80 pagesSymposium 2. Detection and Management of Distributive Shock (DR Yunita Widyastuti SpAn)Rafela Agatha ChristyNo ratings yet
- Shock and Its Management: Presented byDocument72 pagesShock and Its Management: Presented bysheme171150% (2)
- W2D3 DR - Yasa-Bacteremia Dan SepsisDocument54 pagesW2D3 DR - Yasa-Bacteremia Dan SepsisJaka BawaviNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument26 pagesSepsisWulan MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Askep Shock Sepsis, AnafilaktikDocument28 pagesAskep Shock Sepsis, AnafilaktikTomi KurniaNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSTICS (Student Copy)Document59 pagesDIAGNOSTICS (Student Copy)Abigail Mayled LausNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Prognosing Pneumonia - DR DanielDocument30 pagesAssessing and Prognosing Pneumonia - DR Danielibrahim sengajiNo ratings yet
- 03 - Special Clinical SituationsDocument32 pages03 - Special Clinical SituationsClaudia KosztelnikNo ratings yet
- SEPSİS ARDS Eng 2020Document70 pagesSEPSİS ARDS Eng 2020Sarper Hikmet TAZENo ratings yet
- Management of ShockDocument12 pagesManagement of ShockMuhamad HilmiNo ratings yet
- Management and Complications of Ascites SravaDocument26 pagesManagement and Complications of Ascites Sravasravan thatiNo ratings yet
- S1M3 Update Fluid Resuscitation Management in Emergency CasesDocument70 pagesS1M3 Update Fluid Resuscitation Management in Emergency Casesgriya medicaNo ratings yet
- NRNP 6566 Week 4 Knowledge CheckDocument7 pagesNRNP 6566 Week 4 Knowledge Checkmary011danielNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation in Retroperitoneal HaemorrhageDocument39 pagesResuscitation in Retroperitoneal Haemorrhagemark chrisatyaNo ratings yet
- (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) : Norepinephrine Vasopressin or DopamineDocument2 pages(Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) : Norepinephrine Vasopressin or DopaminejamesomooreNo ratings yet
- Clinical Learning Session-Acute Coronary Syndromes Acs - 1Document31 pagesClinical Learning Session-Acute Coronary Syndromes Acs - 1api-611918048No ratings yet
- Blood ProductDocument35 pagesBlood Productrajan kumar100% (3)
- Septic Shock: Supervisor: DR Ali Haedar, Sp. EM FAHA Dinisa Novaurahmah Nanin Aprilia PutriDocument42 pagesSeptic Shock: Supervisor: DR Ali Haedar, Sp. EM FAHA Dinisa Novaurahmah Nanin Aprilia PutriMutia Larasati AlbarNo ratings yet
- Shock: Bethelhem BerhanuDocument33 pagesShock: Bethelhem BerhanuAbdelrahman M. AlnweiriNo ratings yet
- Icu Journal ClubDocument19 pagesIcu Journal Clubapi-649066372No ratings yet
- Supervisor: Dr. Ali Haedar, Spem: Oleh: Fakhrina Nur F 170070201011030 Kurnia Auliana A.R 1700702010110Document54 pagesSupervisor: Dr. Ali Haedar, Spem: Oleh: Fakhrina Nur F 170070201011030 Kurnia Auliana A.R 1700702010110fakhrina nur fadhillahNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument4 pagesPharmacologyEmmanuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Dka NewDocument37 pagesDka NewMuhammad FurqanNo ratings yet
- Referat Sepsis Dan ARDS - Lea SichiliaDocument24 pagesReferat Sepsis Dan ARDS - Lea SichiliaLea SichiliaNo ratings yet
- 3.kuliah Sepsis Malaysia UsuDocument42 pages3.kuliah Sepsis Malaysia UsuBaran PalanimuthuNo ratings yet
- Icu Guidelines - 024219Document6 pagesIcu Guidelines - 024219M Hammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: Hugh Hemsley MD February 2011Document33 pagesSepsis: Hugh Hemsley MD February 2011Nhat NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Heart FailureDocument16 pagesPediatric Heart FailureCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument23 pagesPancreatitisCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument1 pageAtrial FibrillationCharlie Lee100% (1)
- Dermatology ImpetigoDocument2 pagesDermatology ImpetigoCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- OC-Ischemia Heart DiseaseDocument1 pageOC-Ischemia Heart DiseaseCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- OET Reading Test 13 Part ADocument6 pagesOET Reading Test 13 Part ATavi Nicolae100% (1)
- Hesi Exam Practice Pharmacology PDFDocument55 pagesHesi Exam Practice Pharmacology PDFAna Bienne100% (2)
- Soal Akm IngwaDocument11 pagesSoal Akm IngwaRivansyah Raditya100% (1)
- Thesis On Stroke in IndiaDocument7 pagesThesis On Stroke in Indialaurataylorsaintpaul100% (2)
- Gov - Uscourts.lawd.189520.301.0 1Document13 pagesGov - Uscourts.lawd.189520.301.0 1Susie MooreNo ratings yet
- Higado Graso No Alcoholico y Niveles de PCRDocument6 pagesHigado Graso No Alcoholico y Niveles de PCRperuliz19No ratings yet
- IUGRDocument10 pagesIUGRAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- OsteoporoseDocument54 pagesOsteoporoseJandui DinizNo ratings yet
- Fine-Needle Aspiration of Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell LymphomaDocument2 pagesFine-Needle Aspiration of Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell LymphomaMarta MudarraNo ratings yet
- Umar Muhammad Basalamah 22010112110188 Lap - KTI BAB 7Document25 pagesUmar Muhammad Basalamah 22010112110188 Lap - KTI BAB 7Sofila FilaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health Lectures 2009.student - ModifiedDocument68 pagesOccupational Health Lectures 2009.student - ModifiedAdewumi Ebenezer Oluwapelumi0% (1)
- Mina NotesDocument649 pagesMina Notestoobakhann23No ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Hyaline Membrane Disease)Document98 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Hyaline Membrane Disease)Miraf MesfinNo ratings yet
- Tropical MCQS: C. Visceral LeishmaniasisDocument29 pagesTropical MCQS: C. Visceral Leishmaniasisساره ابوالقاسمNo ratings yet
- 14 - INSIDA - Summary Sheet - ENGDocument4 pages14 - INSIDA - Summary Sheet - ENGRito Muzazaila MassuanganheNo ratings yet
- Elias, Adikwu, Et Al. 2014Document15 pagesElias, Adikwu, Et Al. 2014priya panaleNo ratings yet
- Resting and FastingDocument15 pagesResting and Fastingmark ignacioNo ratings yet
- Flaccid BladderDocument29 pagesFlaccid BladderphotosaurusrapNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of A Network ofDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of A Network ofrichardong lauNo ratings yet
- Handbook of DialysisDocument1 pageHandbook of DialysisSurafel KebedeNo ratings yet
- SciTech Writing II Basic StructureDocument4 pagesSciTech Writing II Basic Structureangelie.babasNo ratings yet
- Injury Report FormDocument2 pagesInjury Report FormFrank Abuda100% (2)
- Typhoid Fever AND Paratyphoid Fever: Guoli Lin Department of Infectious Diseases The Third Affiliated Hospital of SYSUDocument70 pagesTyphoid Fever AND Paratyphoid Fever: Guoli Lin Department of Infectious Diseases The Third Affiliated Hospital of SYSUDrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Lecture ENDOCRINE Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland DisordersDocument4 pagesNCM 116 Lecture ENDOCRINE Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland DisordersMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Contagion Movie Assessment 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Contagion Movie Assessment 1swathim123No ratings yet
- Autar DVT Risk Assessment ScaleDocument1 pageAutar DVT Risk Assessment ScaleRicky Virnardo0% (1)
- MANAGEMENT OF FEBRILE in ChildrenDocument12 pagesMANAGEMENT OF FEBRILE in ChildrenNur AiniNo ratings yet
- Haematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountDocument8 pagesHaematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountArun DheekshahNo ratings yet
- Prenatal and Neonatal Factors Related With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-Control Study in Banyumas, Central Java, IndonesiaDocument11 pagesPrenatal and Neonatal Factors Related With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-Control Study in Banyumas, Central Java, IndonesiaSilvia SalwaNo ratings yet
- Bank Robbery EssayDocument8 pagesBank Robbery Essayaaqvuknbf100% (2)