Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obligation and Contracts
Uploaded by
Ma. Gemille Noprada0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesThis document provides an outline of the key topics and subtopics that will be covered in a syllabus on Obligations and Contracts law. The major sections include Obligations with a Period, Alternative and Facultative Obligations, Joint and Solidary Obligations, Divisible and Indivisible Obligations, Obligations with a Penal Clause, Extinguishment of Obligation through Payment/Performance, Loss of the Thing Due, Condonation or Remission of Debt, Confusion or Merger of Rights, Compensation, Novation, General Provisions on Contracts, Essential Requisites of Contracts including Consent and Object, Forms of Contracts, Reformation of Instruments, Interpretation
Original Description:
Original Title
OBLIGATION-AND-CONTRACTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an outline of the key topics and subtopics that will be covered in a syllabus on Obligations and Contracts law. The major sections include Obligations with a Period, Alternative and Facultative Obligations, Joint and Solidary Obligations, Divisible and Indivisible Obligations, Obligations with a Penal Clause, Extinguishment of Obligation through Payment/Performance, Loss of the Thing Due, Condonation or Remission of Debt, Confusion or Merger of Rights, Compensation, Novation, General Provisions on Contracts, Essential Requisites of Contracts including Consent and Object, Forms of Contracts, Reformation of Instruments, Interpretation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesObligation and Contracts
Uploaded by
Ma. Gemille NopradaThis document provides an outline of the key topics and subtopics that will be covered in a syllabus on Obligations and Contracts law. The major sections include Obligations with a Period, Alternative and Facultative Obligations, Joint and Solidary Obligations, Divisible and Indivisible Obligations, Obligations with a Penal Clause, Extinguishment of Obligation through Payment/Performance, Loss of the Thing Due, Condonation or Remission of Debt, Confusion or Merger of Rights, Compensation, Novation, General Provisions on Contracts, Essential Requisites of Contracts including Consent and Object, Forms of Contracts, Reformation of Instruments, Interpretation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
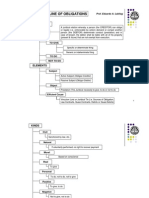
OBLIGATION AND CONTRACTS SYLLABUS
EDITED BY: RENE STEVE A. GARBO, JD
OBLIGATIONS WITH A PERIOD (Art. 1193-1198)
1. Meaning;
2. Effect;
3. A day certain meaning;
4. Suspensive vs. Resolutory Condition
5. Effect of loss, deterioration, or improvement before arrival of period
6. Effect of Payment before arrival of the period
7. Rule on the power of the court to fix period
8. Instances when the debtor lose every right of period
ALTERNATIVE AND FACULTATIVE OBLIGATIONS (Art. 1199-1206)
1. Alternative vs. Facultative
2. Right of choice
a. Debtor
b. creditor
3. Effect of notice of choice
4. When the debtor lose the right of choice
5. Effect if all the things which are alternatively the object of the obligation
have been lost or the compliance becomes impossible
JOINT AND SOLIDARY OBLIGATION (Art. 1207-1222)
1. Joint vs. solidary obligation
a. General Rule;
b. Exception/s
2. Rule in joint indivisible obligation
3. Indivisibility vs. solidarity
4. Art. 1211
5. Art. 1212
6. Art. 1213
7. Rule on pay to solidary creditors
8. Liability of solidary creditors in case of novation, compensation, confusion,
or remission
9. Rule on the demand of the creditor against solidary debtor
10.Effects of payment by a solidary debtor
11. Effect of payment after obligation has prescribed or become illegal
12. Effect of remission of share after payment
13. Rule in case the thing has been lost or if the prestation has become
impossible without the fault of the solidary debtors
DIVISIBLE AND INDIVISIBLE OBLIGATION (Art. 1223-1225)
1. Divisible vs. Indivisible Obligation
2. Effect of non-compliance by a debtor in a joint indivisible obligation
3. Art. 1225
OBLIGATIONS WITH PENAL CLAUSE (Art. 1226-1230)
1. Meaning
2. Purpose
3. Enforceability of penalty
4. Art. 1227
5. Art. 1228
6. Nullity of penal clause vs. nullity of principal obligation
EXTINGUISHMENT OF OBLIGATION
PAYMENT/PERFORMANCE (Art. 1232-1261)
1. Meaning;
2. When debt is considered paid
3. Payment/performance by third person
4. Payment made by one who does not have the capacity to dispose
5. To whom payment be made
6. Creditor cannot be compel to receive a different thing
7. Dation in payment / dation en pago
8. Rule in the delivery of an indeterminate thing
9. Rule on partial payment
10.Art. 1249
11. Inflation and deflation
12. Place of payment
13. Application of payments
a. Art. 1253
b. Art. 1254
14. Payment by cession
15. Tender of payment and consignation
a. Art. 1257 - 1261
LOSS OF THE THING DUE (Art. 1262-1269)
1. Art. 1262
2. Loss of generic thing
3. Effect of partial loss
4. Effect of impossibility of performance
5.
CONDONATION OR REMISSION OF DEBT (Art. 1270-1274)
1. Meaning;
CONFUSION OR MERGER OF RIGHTS (Art. 1275-77)
1. meaning
COMPENSATION (Art. 1278-1290)
1. Meaning
2. Requisites
NOVATION (Art. 1291-1304)
1. Meaning
2. Requisites
3. Kinds
4. Effect owhere the new obligation is void
PART II
CONTRACTS
(Art. 1305 - 1422)
GENERAL PROVISION (Art. 1305-1317)
1. Meaning of contracts
2. Art. 1306
3. Mutuality of contracts
4. Relativity of contracts
5. Perfection of contracts
6. Unauthorized contracts
ESSENTIAL REQUISITES OF CONTRACTS (Art. 1319-1355)
1. Consent
a. Art. 1319
b. Offer made through an agent
c. When offer becomes ineffective
d. Option contract
e. Persons who cannot give consent
f. Contracts entered during lucid interval
g. Vices of consent
h. Mistake
i. Violence
j. Undue influence
k. Fraud
2. Object
a. Art. 1347
b. Impossible things
c. Requisites
3. Cause of Contracts
a. Art. 1350
b. Requisites
FORMS OF CONTRACTS (Art. 1356-1358)
REFORMATION OF INSTRUMENTS (Art. 1359-1369)
INTERPRETATION OF CONTRACTS (Art. 1370-1378)
DEFECTIVE CONTRACTS (Art. 1380-1422)
1. Rescissible Contracts
2. Voidable Contracts
3. Unenforceable Contracts
4. Void or inexistent contracts
xxx
You might also like
- OBLIGATIONS and Contracts SyllabusDocument4 pagesOBLIGATIONS and Contracts SyllabusAnne Aguilar ComandanteNo ratings yet
- Elements of Obligation:: Obligations: SummaryDocument5 pagesElements of Obligation:: Obligations: Summarycheska maguadNo ratings yet
- Buslaw 1 - SyllabusDocument9 pagesBuslaw 1 - SyllabusStephanie Head AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Course Schedule Session 1Document7 pagesCourse Schedule Session 1Jeferson Villalobos AlcarazNo ratings yet
- ObliCon Review 2017Document87 pagesObliCon Review 2017Lyndonn SantosNo ratings yet
- Business Law SyllabusDocument24 pagesBusiness Law SyllabusMK GrospeNo ratings yet
- Oblicon-Prelims-Answer KeyDocument4 pagesOblicon-Prelims-Answer KeyKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (2007) PDFDocument39 pagesChapter 4 (2007) PDFPatricia LargoNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts OutlineDocument3 pagesObligations and Contracts OutlineJames Robert AdoanNo ratings yet
- Law On Obligations and ContractsDocument6 pagesLaw On Obligations and Contractswatanabe200412No ratings yet
- Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument6 pagesExtinguishment of ObligationsAndrea TabulaoNo ratings yet
- OBLICON - Topic SyllabusDocument14 pagesOBLICON - Topic SyllabusKenneth Bryan Tegerero TegioNo ratings yet
- ObliCon Article 1169 To 1178Document6 pagesObliCon Article 1169 To 1178Soojoo Hong100% (2)
- Oblicon OutlineDocument8 pagesOblicon OutlineFred AbisNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Nature and Effects of Obligations 2021Document12 pagesModule 3. Nature and Effects of Obligations 2021Valdez, Jeremie A.No ratings yet
- Business Law: Obligations & ContractsDocument20 pagesBusiness Law: Obligations & ContractsMAWIIINo ratings yet
- OBLICONDocument7 pagesOBLICONBryan Arias100% (1)
- Oblicon Diagrams - LabitagDocument74 pagesOblicon Diagrams - LabitagDigoy Esguerra100% (3)
- Oblicon - Course Outline PDFDocument4 pagesOblicon - Course Outline PDFEarl John PajaroNo ratings yet
- 1231 1267Document22 pages1231 1267Thea BacsaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon (Working Reviewer)Document5 pagesOblicon (Working Reviewer)cheska maguadNo ratings yet
- 2SF - ObliConDocument1 page2SF - ObliConJana MiaNo ratings yet
- Breach of Contract and Remedies For BreachDocument15 pagesBreach of Contract and Remedies For BreachThandie ChirambaNo ratings yet
- Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument29 pagesExtinguishment of Obligationst2691153No ratings yet
- REQUISITESDocument7 pagesREQUISITESReinalyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Laws 1230Document8 pagesLaws 1230marvinreboquioNo ratings yet
- 1167 1176Document11 pages1167 1176Aryan LeeNo ratings yet
- OBLICON REVIEWER EditedDocument6 pagesOBLICON REVIEWER EditedGiedizel LizarondoNo ratings yet
- CIV2 Tip SheetDocument23 pagesCIV2 Tip Sheetdenbar15No ratings yet
- Module 2Document13 pagesModule 2MARITES M. CUYOSNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Course SyllabusDocument6 pagesOblicon Course SyllabusRitchie John Distor BolañoNo ratings yet
- Obligations AND Contracts: Atty. Amado R. Villegas, JRDocument26 pagesObligations AND Contracts: Atty. Amado R. Villegas, JRThea BacsaNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts Summary ReviewerDocument17 pagesObligations and Contracts Summary ReviewerJamie ToriagaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Ae01Document7 pagesModule 3 Ae01Edgielyn AlociljaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Finals ReviewerDocument4 pagesOblicon Finals ReviewerMaki CabuenaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon ReviewerDocument6 pagesOblicon ReviewerFatima Elaine AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Oblicon P1Document8 pagesAnswer Key Oblicon P1Sabbb VlscNo ratings yet
- What Are The Causes of Extinguishment of Obligation?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Causes of Extinguishment of Obligation?Sophia MilletNo ratings yet
- Section 4 Joint and Solidary ObligationsDocument28 pagesSection 4 Joint and Solidary ObligationscandolitamarianjyNo ratings yet
- Articles 1167 1170 SummaryDocument5 pagesArticles 1167 1170 SummaryKaila Clarisse CortezNo ratings yet
- IIVG Report - Articles 1231 1236Document3 pagesIIVG Report - Articles 1231 1236Dah Rin Cavan100% (1)
- Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument128 pagesExtinguishment of ObligationsVal Sanchez100% (1)
- Chapter2 ObligationsDocument48 pagesChapter2 ObligationsJames Russel RondillaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon - Final ReviewerDocument11 pagesOblicon - Final ReviewerKarenn GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Atty Ngo From ExtinguishmentDocument31 pagesReviewer Atty Ngo From ExtinguishmentPaulo TapallaNo ratings yet
- Nature-And-Effect-Of 20240213 070919 0000Document23 pagesNature-And-Effect-Of 20240213 070919 0000shenamaecordez.sccNo ratings yet
- OBLICON by Atty. Anselmo S. Rodiel IVDocument43 pagesOBLICON by Atty. Anselmo S. Rodiel IVAnselmo Rodiel IVNo ratings yet
- OBLICON - CHAPTER3 Different Kinds of An Obligations Part 1Document46 pagesOBLICON - CHAPTER3 Different Kinds of An Obligations Part 1Arvin Cain DiezNo ratings yet
- HRM Module 1 Week3 Page 7Document7 pagesHRM Module 1 Week3 Page 7oh may gadNo ratings yet
- Oblicontract 3 ObliMoraDocument7 pagesOblicontract 3 ObliMorajownathanjowstarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. - Rescissible ContractsDocument3 pagesChapter 6. - Rescissible ContractsMa Theresa MirandaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon ReviewerDocument10 pagesOblicon ReviewerGiedizel LizarondoNo ratings yet
- Civ2 QuizDocument13 pagesCiv2 QuizAce Roncalli Jereza Velasco100% (1)
- OBLICON SyllabusDocument4 pagesOBLICON SyllabusEveHailsNo ratings yet
- Law MadamiiiDocument4 pagesLaw MadamiiiJanna Katrina De TorresNo ratings yet
- The Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts and Sales Agreements for Non-Lawyers: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #5From EverandThe Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts and Sales Agreements for Non-Lawyers: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #5No ratings yet
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesFrom EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Named, Automatic and Additional Insureds in the CGL PolicyFrom EverandUnderstanding Named, Automatic and Additional Insureds in the CGL PolicyNo ratings yet
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesFrom EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PNC Application Form Irish Nicole L. NopradaDocument4 pagesPNC Application Form Irish Nicole L. NopradaMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Title II-3Document10 pagesLecture Title II-3Ma. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Christian Formation Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesChristian Formation Reaction PaperMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- A Tracer StudyDocument10 pagesA Tracer StudyMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- CHED Application FormDocument8 pagesCHED Application FormMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Cases For FinalsDocument10 pagesCases For FinalsMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Urban GenerationDocument2 pagesUrban GenerationMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation Chapter 4Document4 pagesInterpretation Chapter 4Ma. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- ISSUANCE OF DEVELOPMENT PERMIT DP Subdivision Memorial MPDCDocument18 pagesISSUANCE OF DEVELOPMENT PERMIT DP Subdivision Memorial MPDCMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- FernandezDocument6 pagesFernandezMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Prject ContextDocument1 pagePrject ContextMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Tracer Study NopradaQuiatchonTuyaySabaybayDocument36 pagesTracer Study NopradaQuiatchonTuyaySabaybayMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Final-Business-Plan SampleDocument64 pagesFinal-Business-Plan SampleMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Title I RPCDocument11 pagesLecture Title I RPCMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument30 pagesBusiness PlanMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Holder and Holder in Due CourseDocument6 pagesDifference Between Holder and Holder in Due Courseparveen mehtaNo ratings yet
- Cases 5th BatchDocument21 pagesCases 5th BatchPat RañolaNo ratings yet
- Law On: Negotiable InstrumentsDocument19 pagesLaw On: Negotiable InstrumentsCaryl BaylonNo ratings yet
- HB 3593 Anti-SLAPP BillDocument10 pagesHB 3593 Anti-SLAPP BillGabe PentecostesNo ratings yet
- Kamarulzaman Bin Omar & Ors V Yakub Bin HusiDocument21 pagesKamarulzaman Bin Omar & Ors V Yakub Bin HusievasopheaNo ratings yet
- STATCON - Constitutional Construction By: MartinDocument10 pagesSTATCON - Constitutional Construction By: Martincookiemonster1996No ratings yet
- Purpose of Arraignment and PleaDocument7 pagesPurpose of Arraignment and PleaClaudine Arrabis100% (1)
- Topic 10 - Contract TermsDocument20 pagesTopic 10 - Contract TermsSaravanan SekarNo ratings yet
- Case Digest ObliconDocument17 pagesCase Digest ObliconstrgrlNo ratings yet
- 13 SPOUSES TOH Vs SOLID BANK CORPORATIONDocument22 pages13 SPOUSES TOH Vs SOLID BANK CORPORATIONJem Cromwell S. GorospeNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Attachment Gma V. NTC Doctrine: Section 3, Part VI of The NTC Rules ofDocument11 pagesPreliminary Attachment Gma V. NTC Doctrine: Section 3, Part VI of The NTC Rules ofBrigette DomingoNo ratings yet
- VIDHYODAY - Law Revision ChartsDocument20 pagesVIDHYODAY - Law Revision Chartsshethdipati2100% (1)
- Legal Pedagogy: Types of Bills (Indian Polity)Document7 pagesLegal Pedagogy: Types of Bills (Indian Polity)Swag ka VikretaNo ratings yet
- Paradise International ComplaintDocument16 pagesParadise International ComplaintMatthew Seth SarelsonNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: Negotiable Instruments (Act 2031)Document9 pagesCourse Syllabus: Negotiable Instruments (Act 2031)Jessamine OrioqueNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Cancellation of Lis PendensDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Cancellation of Lis PendensR Ornopia & Associates100% (4)
- Atty. Uribe Transcribed by Atty. HYUGI SEMBRANODocument7 pagesAtty. Uribe Transcribed by Atty. HYUGI SEMBRANOHyugi Nicolae SembranoNo ratings yet
- (Of Plaintiff Angelina C. Feliciano) : Judicial AffidavitDocument5 pages(Of Plaintiff Angelina C. Feliciano) : Judicial AffidavitBetsy T. JavierNo ratings yet
- Trust DocsDocument25 pagesTrust Docsncwazzy93% (15)
- Property Law Assignment: "Voluntary Trust"Document4 pagesProperty Law Assignment: "Voluntary Trust"Sri MuganNo ratings yet
- Crocodile Int. Pte. Ltd. v. LacosteDocument6 pagesCrocodile Int. Pte. Ltd. v. Lacosteshruti guptaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument677 pagesUntitledMakeda DerrickNo ratings yet
- Case Digest SpecProDocument3 pagesCase Digest SpecPromarcialxNo ratings yet
- Judicial Interpretation AssignmentDocument13 pagesJudicial Interpretation AssignmentIshita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Negotiable Instruments ActDocument20 pagesThe Negotiable Instruments Actpooja guptaNo ratings yet
- Garrido Vs TortogoDocument2 pagesGarrido Vs Tortogo09367766284No ratings yet
- Avoid These Five Errors and Draft Your Best Legal WorkDocument3 pagesAvoid These Five Errors and Draft Your Best Legal WorkLuis ArangoNo ratings yet
- Affirmation Confirmation of DonationDocument3 pagesAffirmation Confirmation of DonationTerence Verona100% (4)
- Affidavit of Loss: Kappa Community Ministry, International, Inc. Kidapawan CityDocument1 pageAffidavit of Loss: Kappa Community Ministry, International, Inc. Kidapawan CityAngelica Branzuela Pagal Aninipot0% (1)
- CDA Omnibus Rules of ProcedureDocument106 pagesCDA Omnibus Rules of Procedureuclaw23No ratings yet