Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Position
Position
Uploaded by
jer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThe document defines position and displacement in physics. It explains that position refers to where an object is located relative to a reference frame, such as describing a professor's position relative to a whiteboard. Displacement is defined as the change in an object's position, represented by the symbol Δx and defined mathematically as the final position minus the initial position. Displacement is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, represented by an arrow pointing from the initial to final position.
Original Description:
Original Title
position
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines position and displacement in physics. It explains that position refers to where an object is located relative to a reference frame, such as describing a professor's position relative to a whiteboard. Displacement is defined as the change in an object's position, represented by the symbol Δx and defined mathematically as the final position minus the initial position. Displacement is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, represented by an arrow pointing from the initial to final position.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesPosition
Position
Uploaded by
jerThe document defines position and displacement in physics. It explains that position refers to where an object is located relative to a reference frame, such as describing a professor's position relative to a whiteboard. Displacement is defined as the change in an object's position, represented by the symbol Δx and defined mathematically as the final position minus the initial position. Displacement is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, represented by an arrow pointing from the initial to final position.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
What does position mean?
In physics, we love to precisely describe the motion of an object.
Seriously, the first few chapters of basically every physics textbook are
devoted to teaching people how to precisely describe motion since it is so
important to everything else we do in physics.
But to describe an object's motion, we have to first be able to describe its
position—where it is at any particular time. More precisely, we need to
specify its position relative to a convenient reference frame. Earth is often
used as a reference frame, and we often describe the position of an object
as it relates to stationary objects in that reference frame. For example, a
professor’s position could be described in terms of where she is in relation
to the nearby white board (Figure 1). In other cases, we use reference
frames that are not stationary but rather are in motion relative to Earth. To
describe the position of a person in an airplane, for example, we use the
airplane, not Earth, as the reference frame (Figure 2).
The variable xxx is often used to represent the horizontal position. The
variable yyy is often used to represent the vertical position.
[What about z?]
What does displacement mean?
If an object moves relative to a reference frame—for example, if a
professor moves to the right relative to a whiteboard, or a passenger moves
toward the rear of an airplane—then the object’s position changes. This
change in position is known as displacement. The word displacement
implies that an object has moved, or has been displaced.
Displacement is defined to be the change in position of an object. It can
be defined mathematically with the following equation:
\text{Displacement}=\Delta x=x_f-x_0Displacement=Δx=xf
−x0start text, D, i, s, p, l, a, c, e, m, e, n, t, end text, equals, delta, x,
equals, x, start subscript, f, end subscript, minus, x, start subscript, 0, end
subscript
x_fxfx, start subscript, f, end subscript refers to the value of the final
position.
x_0x0x, start subscript, 0, end subscript refers to the value of the initial
position.
\Delta xΔxdelta, x is the symbol used to represent displacement.
[What does the triangle symbol mean?]
Displacement is a vector. This means it has a direction as well as a
magnitude and is represented visually as an arrow that points from the
initial position to the final position. For example, consider the professor
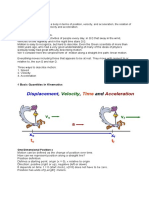
that walks relative to the whiteboard in Figure 1.
Figure 1: A professor paces left and right while lecturing. The +2.0\
text{ m}+2.0 mplus, 2, point, 0, start text, space, m, end text displacement
of the professor relative to the whiteboard is represented by an arrow
pointing to the right. (Image credit: Openstax College Physics)
You might also like
- The Pyramid Star Identification TechniqueDocument21 pagesThe Pyramid Star Identification Techniquesat_rinsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Physics - Arihant Aiimsneetshortnotes1Document464 pagesHandbook of Physics - Arihant Aiimsneetshortnotes1VinayNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesForce and Pressure Notesmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Linearalgebra BookDocument212 pagesLinearalgebra BookMarina XuNo ratings yet
- Momentum and CollisionsDocument27 pagesMomentum and CollisionsBeverly Carballo - MoguelNo ratings yet
- Nzs 4219 2009Document114 pagesNzs 4219 2009fausto giovannardiNo ratings yet
- 9 Sci HCVerma 2 Describing Motion 2011 EditDocument49 pages9 Sci HCVerma 2 Describing Motion 2011 EditPramod Gupta60% (5)
- Mechanics NotesDocument220 pagesMechanics NotesPunit BadalNo ratings yet
- Derivative and Integration Applications For The Real LifeDocument11 pagesDerivative and Integration Applications For The Real LifeTabarak EbaidNo ratings yet
- KinamaticsDocument10 pagesKinamaticsChathur ChandrasooryaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Motion Force and Energy PDFDocument26 pagesUnit 2 Motion Force and Energy PDFMuhammad Ahsan Ali KharalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Live - Power SystemDocument27 pagesElectrical Live - Power SystemashishNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics MCQ QuestionsDocument116 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQ QuestionsMiral_Kagathra100% (2)
- KinematicsDocument58 pagesKinematicsdevendraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering - Reference Power Systems Protection HandbookDocument195 pagesElectrical Engineering - Reference Power Systems Protection Handbookfinolh0% (1)
- C2 - Lesson 3Document5 pagesC2 - Lesson 3Wild RiftNo ratings yet
- C2 - Lesson 4Document8 pagesC2 - Lesson 4Wild RiftNo ratings yet
- C2 - Lesson 5Document9 pagesC2 - Lesson 5Wild RiftNo ratings yet
- C2 - Lesson 2Document5 pagesC2 - Lesson 2Wild RiftNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement1Document3 pagesDistance and Displacement1Jazpearl Krisha LindaNo ratings yet
- P Week II Kinematics IxDocument17 pagesP Week II Kinematics IxSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- BA FisDas 1Document16 pagesBA FisDas 1bilqiszahra1708No ratings yet
- 6.7 Introduction Dynamics in Three Dimensions A. General PrinciplesDocument12 pages6.7 Introduction Dynamics in Three Dimensions A. General PrincipleselvyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Versus Geometric DynamicsDocument13 pagesFluid Flow Versus Geometric DynamicsDragos IsvoranuNo ratings yet
- Game Engine Programming 2 Week 3 Module 3Document25 pagesGame Engine Programming 2 Week 3 Module 3Dean LevyNo ratings yet
- Space-Time Structure, Newton's Laws and Galilean TransformationDocument18 pagesSpace-Time Structure, Newton's Laws and Galilean TransformationabhijeetNo ratings yet
- DisplacementDocument1 pageDisplacementHAROLD'S DIGESTNo ratings yet
- Overview of Classical Mechanics: 1 Ideas of Space and TimeDocument7 pagesOverview of Classical Mechanics: 1 Ideas of Space and TimeredcoatNo ratings yet
- Notas ComplementariasDocument39 pagesNotas ComplementariasLuis Vargas SanchezNo ratings yet
- FM3003 - Calculus III: Dilruk Gallage (PDD Gallage)Document31 pagesFM3003 - Calculus III: Dilruk Gallage (PDD Gallage)Dilruk GallageNo ratings yet
- Name: Nambio, Geraldine M. Physics I Student Number: 18B1010 Date: October 23, 2020 Section: BSES III-A KinematicsDocument8 pagesName: Nambio, Geraldine M. Physics I Student Number: 18B1010 Date: October 23, 2020 Section: BSES III-A KinematicsGeraldine NambioNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 TransformationDocument28 pagesTOPIC 2 Transformationjonathanmaithya9No ratings yet
- 1 Motion Along Straight LineDocument33 pages1 Motion Along Straight Lineumer iqbalNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 ADocument18 pagesLec 1 ASaad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3 1 Position Displacement and Average VelocityDocument6 pages3 1 Position Displacement and Average Velocitygenetamane6No ratings yet
- 1.partial DifferentiationDocument23 pages1.partial DifferentiationPratyush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Math Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesMath Investigatory ProjectKavinn100% (1)
- Physics in A NutshellDocument9 pagesPhysics in A NutshellAngel Angelique ApostolNo ratings yet
- Reading 04Document9 pagesReading 04Shehab Rawhan AlsanwyNo ratings yet
- 1855 PDF C04Document65 pages1855 PDF C04Leisy De La Hoz RomeroNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument9 pagesPhysicsE.LOKESH NAIKNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument2 pagesKinematicsShamsherNo ratings yet
- Physics 7Document12 pagesPhysics 7Raymond De AsisNo ratings yet
- Ross DeutscherDocument15 pagesRoss Deutschercarlino1963No ratings yet
- CG Unit-3 PDFDocument63 pagesCG Unit-3 PDFTechnical Kamal RajputNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument16 pagesKinematics in One DimensionApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Aerial Robotics Lecture 2A - 1 TransformationsDocument10 pagesAerial Robotics Lecture 2A - 1 TransformationsIain McCullochNo ratings yet
- 801-825 Differentiation Formulae (For Latex)Document14 pages801-825 Differentiation Formulae (For Latex)Muhammad ZainNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Modelling CPS With SysMLDocument2 pagesLab 2 - Modelling CPS With SysMLChioma Nkem-EzeNo ratings yet
- Ncert 0Document4 pagesNcert 0rajkmeena272No ratings yet
- MATH45061 Ch2Document26 pagesMATH45061 Ch2Faisal RahmanNo ratings yet
- P6 - 3 RevDocument10 pagesP6 - 3 RevShirsendu MondolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 1 PDFGabriel mongeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Kinematics of Fluid Motion: T X X TDocument15 pagesChapter 4 - The Kinematics of Fluid Motion: T X X THengNo ratings yet
- A Sample STRIPS ProblemDocument3 pagesA Sample STRIPS Problemmonica pNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - VELOCITY VS. TIME AND ACCELERATION VS. TIME GRAPHDocument26 pagesLesson 11 - VELOCITY VS. TIME AND ACCELERATION VS. TIME GRAPHJasmine PrimaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Kinematics - Boundless PhysicsDocument68 pagesBasics of Kinematics - Boundless PhysicsAvirup RayNo ratings yet
- AIML - Unit 3Document71 pagesAIML - Unit 3TEST ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- DerivativeDocument3 pagesDerivativeElizabeth ColeNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Prof C. S. Upadhyay Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument27 pagesFinite Element Method Prof C. S. Upadhyay Department of Mechanical EngineeringabimanaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicDocument66 pagesEngineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicNefer PitouNo ratings yet
- On Classical Dynamics of Af F Inely-Rigid Bodies Subject To The Kirchhof F-Love ConstraintsDocument12 pagesOn Classical Dynamics of Af F Inely-Rigid Bodies Subject To The Kirchhof F-Love ConstraintsBayer MitrovicNo ratings yet
- The DerivativeDocument14 pagesThe DerivativeBiancaMihalacheNo ratings yet
- 01 KinematicsDocument69 pages01 KinematicsChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Note 10 Rotational Motion I: Sections Covered in The Text: Chapter 13Document9 pagesNote 10 Rotational Motion I: Sections Covered in The Text: Chapter 13nalliminiNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Kinematics: How To Describe A Moving Object Without Considering The Forces InvolvedDocument19 pagesWeek 1: Kinematics: How To Describe A Moving Object Without Considering The Forces Involvedanola prickNo ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument22 pagesLinear MotionbobNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line PDFDocument26 pagesMotion in A Straight Line PDFsujit21in4376100% (1)
- What Is Electron MicrosDocument2 pagesWhat Is Electron MicrosjerNo ratings yet
- Velocity MeaningDocument3 pagesVelocity MeaningjerNo ratings yet
- History of MicrosDocument2 pagesHistory of MicrosjerNo ratings yet
- Distance and DisplacementDocument3 pagesDistance and DisplacementjerNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document18 pagesTutorial 2Miguel MartinNo ratings yet
- 5轴资料Document136 pages5轴资料jiabang liuNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Two and Three Dimensional Motion: Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo)Document4 pagesKinematics: Two and Three Dimensional Motion: Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo)RALPH ANDREW ESPERONNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Kinetics of A Particle-Impulse and MomentumDocument72 pagesModule 4 Kinetics of A Particle-Impulse and MomentumHuy VũNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Force SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 2. Force SystemNadjer C. AdamNo ratings yet
- MATH 2023 Spring 2015-16 Multivariable Calculus Problem Set #0 Dot and Cross Products (Review) RDocument8 pagesMATH 2023 Spring 2015-16 Multivariable Calculus Problem Set #0 Dot and Cross Products (Review) RToby ChengNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science Jagannath University, DhakaDocument129 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Faculty of Science Jagannath University, DhakaRockSamNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PHY 101 U2Document14 pagesGravitation PHY 101 U2Rashmi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document19 pagesLec 2Smita TungNo ratings yet
- Kom NotesDocument15 pagesKom NoteselangandhiNo ratings yet
- The Magnetic FieldDocument40 pagesThe Magnetic Fieldyuliantoriski19No ratings yet
- Vector Data RepresentationDocument16 pagesVector Data RepresentationAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- MSG322 Note 1Document11 pagesMSG322 Note 1Chong Cherng WongNo ratings yet
- Animation Maths: Ivo de Pauw Bieke MasselisDocument20 pagesAnimation Maths: Ivo de Pauw Bieke MasselisLil Iced heartNo ratings yet
- The City SchoolDocument8 pagesThe City Schoolalfredo pastaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stripline-Fed Slot-Coupled Patch Antennas With Vias For Parallel-Plate Mode SuppressionDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Stripline-Fed Slot-Coupled Patch Antennas With Vias For Parallel-Plate Mode SuppressionnaranjitoNo ratings yet
- Topic 05 One Dimensional Kinematics NotesDocument28 pagesTopic 05 One Dimensional Kinematics NotesRukiezillaNo ratings yet
- MIT8 02SC Challenge Prob19Document7 pagesMIT8 02SC Challenge Prob19Olman VargasNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Unit 3 Sura English Medium GuideDocument30 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Unit 3 Sura English Medium GuideAakaash C.K.29% (7)
- JOSA (1997) - New Formulation of The Fourier Modal Method For Crossed Surface-Relief GratingsDocument10 pagesJOSA (1997) - New Formulation of The Fourier Modal Method For Crossed Surface-Relief GratingspythonicangNo ratings yet
- Velociity : Junior Kalam CampusDocument3 pagesVelociity : Junior Kalam CampusSubrahmanyam SanaNo ratings yet