Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Science PT
Uploaded by
John Mc Raven NazarioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth Science PT
Uploaded by
John Mc Raven NazarioCopyright:
Available Formats
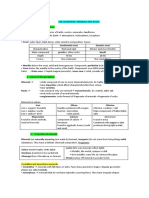
Mineral in Action
11 - Marangal
Nazario
Niar
Earth Science Teacher Palomaria Emilio Aguinaldo College
Sir Mark Sinatad Cavite Campus
1. Phone
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
1. Silica Sand -Silica Sand- -Silicon- -Sphalerite-
The silica minerals when pure are Exists as a solid at room is found hydrothermal activity
2. Silicon
colorless and transparent and temperature and pressure. And or contacts metamorphism has
3. Sphalerite have a vitreous luster. They are is very brittle. brought hot, acidic, zinc
nonconductors of electricity and bearing fluids in contact with
are diamagnetic. carbonated rocks
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Silica Sand - Unlike construction sands, which are used Silica Sand - construction materials like ceramic and
for their physical properties alone, silica sands are valued glass making. Silica sand is a primary ingredient in glass
for a combination of chemical and physical properties. industry
Silicon - This mineral is one of the most useful element in
Silicon - Elemental silicon is produced commercially by
humankind. This is a major constituent in ceramics and
reducing sand with carbon in an electric furnace.
bricks.
Sphalerite - This mineral is also used as a gemstone... in
Sphalerite - is found where hydrothermal activity or
phone it conducts electricity battery, display, circuitry
contact metamorphism has brought hot, acidic, zinc-
etc.
bearing fluids in contact with carbonate rocks.
2. Clock
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
1. Iron -Iron- -Nickel- -Silica-
Iron is a lustrous, ductile, and Nickel is a hard, silver-white The silica minerals when pure
2. Nickel
malleable silver-gray metal. It is metal that crystallizes into are colorless and transparent
3. Silica known to exist in four different cubic shapes. It has and have a vitreous lustre.
crystalline forms. Iron rusts in wet exceptional strength and
air but not in dry air. corrosion resistance,is
malleable, and ductile.
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Iron - Impurities and oxygen must be eliminated in order Iron - This mineral is needed to make alloy steels like
to transform iron ore into metallic iron. In order to liberate carbon steels with additives such as nickel, chromium,
the oxygen from the ore, this procedure needs heat and a vanadium, tungsten, and manganese.
reducing agent, which mixes with oxygen.
Nickel - Nickel resists corrosion and is used to plate
Nickel - nickel oxide is removed by reduction furnace
other metals to protect them. It is, however, mainly used
which also greatly reduces the chemical bound water.
in making alloys such as stainless steel.
Resulting in a 75% pure form of nickel.
Silica - use as a food additive, anti-caking agent, as a
Silica - It is formed when silicon is exposed to oxygen. It means to clarify beverages, control viscosity, as an anti-
has a covalent bond and is a superior electric insulator. foaming agent, dough modifier, and as an excipient in
drugs and vitamins.
3. Paper
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
1. Bentonite -Bentonite- -Kaolin- -Talc-
presents strong colloidal This mineral appears as This mineral is extremely soft,
2. Kaolin
properties and increases its odorless white to yellowish or colorless, color in white, pale
3. Talc volume several times when grayish powder. Kaolin to dark green, or yellowish to
coming into contact with water, contains mainly the clay brown.
creating a gelatinous and viscous mineral Kaolinite, a hydrous
substance. Its specific properties aluminosilicate.
include swelling, water
absorption, viscosity, and
thixotropy.
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Bentonite - This mineral is derived from the alteration, Bentonite - The main uses of bentonite are in drilling mud
over geological time periods, of glassy material emitted and as a binder, purifier, absorbent, and carrier for
from volcanoes, or from the alteration of silica bearing fertilizers or pesticides.
rocks such as granite and basalt.
Kaolin - Kaolin is both dry-and-wet-processed. The dry
Kaolin - This mineral is a layered silicate mineral. Kaolin is
process is simpler and produces a lower quality product
used in ceramics, medicine, as a food additive etc.
than the wet process. Dry-processed Kaolin is used
mainly in the rubber industry, and to lesser extent, for
paper filling and to produce fiberglass and sanitary ware.
Talc - Used as a filler in ceramics, paint, paper, roofing
Talc - This mineral is formed by hydrothermal alteration of materials, plastic and many more.
ultrabasic rocks, or low grade thermal metamorphism of
siliceous dolomites. Talc is an important industrial mineral.
4. Laptop
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
1. Magnetite -Magnetite- -Galena- -Quartz-
Crystal Form - Octahedron Crystal Form - Cubes and Crystal Form - Prism
2. Galena
Crystal Habit - Granular Octahedra Crystal Habit - Prismatic
3. Quartz Cleavage - None Crystal Habit - Granular Cleavage - None
Luster - Metallic Cleavage - Perfect and cubic Luster - Non-metallic
Color - Black to silvery gray Luster - Metallic Color - White, gray, purple,
Streak - Black Color - Lead gray and silvery yellow, brown, black, pink,
Hardness - 5 to 6.5 Streak - Lead gray green, red, clear.
Hardness - 2.5+ Streak - Colorless
Hardness - 7
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Magnetite - First, the Magnetite was gathered where it Magnetite - Magnetite yields iron ore that helps in
was put into a crusher. After the mineral was crushed, it making steel. Steel is then used to many things such as
was pressurized then was processed to separate iron from laptops, vehicles, and appliances.
it where it'd transform into an acceptable product.
Galena - First, the ore was mined where then it'd be
Galena - Lead came from Galena, wherein Lead is used in
concentrated. There, it will be filtered to collect the
paint, gasoline, and batteries.
important ores in it. Afterwards, it will be smelted,
refined, and there, a lead is formed.
Quartz - First, the quartz is crushed then it would be Quartz - Quartz is most commonly used for manufacturing
scrubbed to remove unwanted stuff. Next, it'd undergo glass, which a lot of things around you have.
wet screening to classify oversize particles. Lastly, it'd go
sand dewatering to make it clean.
5. Television
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
-Galena- -Quartz- -Sphalerite-
Crystal Form - Cubes and Crystal Form - Prism Crystal Form - Complex
1. Galena
Octahedra Crystal Habit - Prismatic Crystal Habit - Granular
2. Quartz
Crystal Habit - Granular Cleavage - None Cleavage - Perfect perfect
3. Sphalerite Cleavage - Perfect and cubic Luster - Non-metallic Luster - Non-metallic
Luster - Metallic Color - White, gray, purple, Color - Yellow, light to dark
Color - Lead gray and silvery yellow, brown, black, pink, brown, black, red-brown,
Streak - Lead gray green, red, clear. colorless, light blue, and
Hardness - 2.5+ Streak - Colorless green.
Hardness - 7 Streak - Pale yellow to brown.
Hardness - 3.5 to 4
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Galena - First, the ore was mined where then it'd be Galena - Lead came from Galena, wherein Lead is used in
concentrated. There, it will be filtered to collect the paint, gasoline, and batteries.
important ores in it. Afterwards, it will be smelted,
refined, and there, a lead is formed.
Quartz - First, the quartz is crushed then it would be Quartz - Quartz is most commonly used for manufacturing
scrubbed to remove unwanted stuff. Next, it'd undergo glass, which a lot of things around you have.
wet screening to classify oversize particles. Lastly, it'd go
sand dewatering to make it clean.
Sphalerite - Just like other minerals, it was first gathered Sphalerite - Sphalerite contains Zinc, where it was used
and concentrated. Next, the mineral is roasted to be as construction materials.
reduced to powder. It is then neutralized and the
contaminants are removed by filtration. The Zinc then
reaches its final form in a foundry.
6. Refrigerator
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
-Chromite- -Hematite- -Galena-
Crystal Form - Octahedron Crystal Form - Complex Crystal Form - Cubes and
1. Chromite
Crystal Habit - Granular Crystal Habit - Fibrous Octahedra
2. Hematite
Cleavage - None Cleavage - None Crystal Habit - Granular
3. Galena Luster - Metallic Luster - Metallic Cleavage - Perfect and cubic
Color - Black to brownish Color - Metallic Gray Luster - Metallic
black; brown to brownish Streak - Red Color - Lead gray and silvery
black Hardness - 5 to 6 Streak - Lead gray
Streak - Brown Hardness - 2.5+
Hardness - 5.5 to 6
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Chromite - The Chromite is mined and was smelted for it Chromite - Chromite contains chromium that is mainly
to be converted into alloys. used for stainless steel. Some uses of stainless steel are
used in cookware and surgical tools.
Hematite - Hematite goes through a lot of process but
first, it is crushed and grinded. Afterwards iron was
extracted through many means like flotation or magnetic Hematite - Hematite is used in producing pigment and
separation. Lastly, the hematite is concentrated and dried radiation shielding.
to get the high-quality iron powders.
Galena - First, the ore was mined where then it'd be Galena - Lead came from Galena, wherein Lead is used in
concentrated. There, it will be filtered to collect the paint, gasoline, and batteries.
important ores in it. Afterwards, it will be smelted,
refined, and there, a lead is formed.
7. Earphone
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
-Chalcopyrite- -Chalcopyrite- -Quartz-
Crystal Form - Octahedron Crystal Form - Complex Crystal Form - Prism
1. Chalcopyrite
Crystal Habit - Botryoidal Crystal Habit - Granular Crystal Habit - Prismatic
2. Limonite
Cleavage - Poor Cleavage - None Cleavage - None
3. Quartz Luster - Metallic Luster - Non-metallic Luster - Non-metallic
Color - Brass yellow Color - Yellowish brown to Color - White, gray, purple,
Streak - Greenish black brown to black yellow, brown, black, pink,
Hardness - 3.5 to 4 Streak - Yellowish brown green, red, clear.
Hardness - 1 to 5 Streak - Colorless
Hardness - 7
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Chalcopyrite - Chalcopyrite is processed by the means Chalcopyrite - Chalcopyrite contains copper that is used
of hydrometallurgical or the process of conducting a mostly for electrical devices.
separation and extraction of metals using chemicals.
Limonite - Blast furnace is used to extract Limonite. Limonite - Just like Magnetite, this contains iron that is
used in making steel.
Quartz - First, the quartz is crushed then it would be
scrubbed to remove unwanted stuff. Next, it'd undergo Quartz - Quartz is most commonly used for manufacturing
wet screening to classify oversize particles. Lastly, it'd go glass, which a lot of things around you have.
sand dewatering to make it clean.
8. Battery
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
-Nickel- -Cobalt- -Graphite-
It is a good conductor of heat •it is a hard ferromagnetic, A good conductor of
1. Nickel
and electricity silver-white, lustrous, brittle electricity( Due to the
2. Cobalt
element. presence of free electrons) and
3. Graphite •It is stable in air and does not good conductor of heat.
react with water.
•Like other metals, it can also
be magnetized.
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Nickel - Nickel - Most mined nickel derives from two
Nickel - The most crucial use of this element is that it is
types of ore deposits that form in very different geological
used to make coins. It is used in making wires.
environments: magmatic sulfide deposits, where the
principal ore mineral is pentlandite, and laterites, where Cobalt - Cobalt is used in many alloys (super alloys for
the principal ore minerals are nickeliferous limonite and parts in gas turbine aircraft engines, corrosion resistant
garnierit alloys, high-speed steels, cemented carbides), in
Cobalt - Cobalt - Most cobalt is formed as a by-product magents and magnetic recording media, as catalysts for
of nickel refining. A huge reserve of several transition the petroleum and chemical industries, as drying agents
metals (including cobalt) can be found in strange nodules
for paints and inks.
on the floors of the deepest oceans.
Graphite - Graphite is used in pencils, lubricants,
Graphite - Graphite - Graphite is formed by the
crucibles, foundry facings, polishes, arc lamps, batteries,
metamorphosis of sediments containing carbonaceous
brushes for electric motors, and cores of nuclear reactors.
material, by the reaction of carbon compounds with
hydrothermal solutions or magmatic fluids, or possibly by It is mined extensively in China, India, Brazil, North Korea,
the crystallization of magmatic carbon. and Canada
9. Paint
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
-Asbestos- -Barites- -Calcite-
All forms of asbestos are resistant It has a high specific gravity of Calcite is number 3 on the Mohs
1. Asbestos
to heat, fire, chemical, and 4.50 g/cm3. Its Mohs hardness scale; thus, it can be
2. Barites biological break-down. Asbestos hardness is 3.0 to 3.5. Barite, scratched readily by a knife blade
3. Calcite does not dissolve in water or which may be found in a variety or geologic pick. It has a specific
evaporate. These properties mean of colors including yellow, gravity of 2.71. Three perfect
that asbestos fibres do not burn, brown, white, blue, gray, or cleavages give calcite its six-
do not undergo significant even colorless, typically has a sided polyhedrons with diamond-
reactions with most chemicals, vitreous to pearly luster. shaped faces; the angles defining
and do not break down the faces are 78° and 102°.
significantly in the environment.
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Asbestos - Contributing to asbestos formation is the Asbestos - Asbestos has also been used in a wide range
faulting and fracturing of these rocks with increased of manufactured goods, mostly in building materials
temperatures, pressures, and the presence of water.
Barytes - Barite is also used in a wide variety of other
applications including plastics, clutch pads, rubber mud
flaps, mold release compounds, radiation shielding,
Barytes - Some smaller mines utilize barite from veins,
which formed when barium sulphate precipitated from hot television and computer monitors, sound-deadening
subterranean waters. material in automobiles, traffic cones, brake linings, paint
and golf balls.
Calcite - Calcite crystal's properties make it one of the
Calcite - Calcite can form by direct precipitation from
most widely used minerals. It is used as a building
waters rich in calcium.
material, abrasive, agricultural soil treatment, construction
aggregate, pigment, pharmaceutical, and other
applications. It has more applications than nearly any
other mineral
10. Toaster
Minerals Present Properties of each mineral
-Nickel- -Chromium- -Iron-
It is a good conductor of heat and Chromium is a lustrous, brittle, Iron is a lustrous, ductile,
1. Nickel
electricity. hard metal. Its colour is silver-gray malleable, silver-gray metal
2. Chromium
and it can be highly polished. It (group VIII of the periodic table).
3. Iron does not tarnish in air, when It is known to exist in four distinct
heated it borns and forms the crystalline forms. Iron rusts in
green chromic oxide. Chromium is damp air, but not in dry air. It
unstable in oxygen, it immediately dissolves readily in dilute acids.
produces a thin oxide layer that is
impermeable to oxygen and
protects the metal below.
How these minerals are
formed and processed Uses of each minerals
Nickel - Most mined nickel derives from two types of ore Nickel - The most crucial use of this element is that it is
deposits that form in very different geological used to make coins. It is used in making wires.
environments: magmatic sulfide deposits, where the
principal ore mineral is pentlandite, and laterites, where
the principal ore minerals are nickeliferous limonite and Chromium - Chromium is used to harden steel, to
garnier it. manufacture stainless steel (named as it won't rust) and to
Chromium - Chromium metal is usually produced by produce several alloys.
reducing chromite with carbon in an electric-arc furnace,
or reducing chromium(III) oxide with aluminium or silicon.
Iron - Iron is used to make alloy steels like carbon steels
Iron - This iron was mainly in a reduced state (ferrous
with additives such as nickel, chromium, vanadium,
iron), and so when the Earth cooled and rain fell on these
tungsten, and manganese.
Hadean volcanic rocks, iron dissolved and was carried as
ferrous ions to the ocean.
Resources
https://geology.com/minerals/magnetite.shtml
http://webmineral.com/data/Galena.shtml#.YxxaUnZBzIUl
https://geology.com/minerals/galena.shtml
https://geologyscience.com/minerals/quartz/
http://www.madehow.com/Volume-2/Lead.html
https://geologyscience.com/minerals/sphalerite/
https://www.generalkinematics.com/blog/zinc-mining-processing-
everything-need-know/
https://www.mindat.org/min-1036.html
https://geology.com/minerals/chromite.shtml
https://www.minerals.net/mineral/hematite.aspx
https://geology.com/minerals/chalcopyrite.shtml#:~:text=The%20most%20ob
vious%20physical%20properties,a%20much%20higher%20specific%20gravity.
https://geology.com/minerals/limonite.shtml
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224905986_A_Review_on_Novel_
Techniques_for_Chalcopyrite_Ore_Processing#:~:text=Chalcopyrite%20ores%
20are%20usually%20processed,upsurge%20of%20interest%20in%20the
You might also like
- Earth Science MineralsDocument18 pagesEarth Science Mineralspaul mariscoteNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument15 pagesEarth Science ReviewerMonicaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Minerals RocksDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Minerals RocksMandora SGNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks emDocument8 pagesMinerals and Rocks empdiksha694No ratings yet
- Mineral FlashcardsDocument6 pagesMineral FlashcardsbudiNo ratings yet
- RAMOS Worksheet1Document7 pagesRAMOS Worksheet1Keirvin Cloi RamosNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesEarth ScienceJ-Flores StephanieNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 MIneral EarthScienceDocument4 pagesLesson3 MIneral EarthScienceSHANIA GWYNETH SUMALPONGNo ratings yet
- EarthLifeScience 2nd SessionDocument58 pagesEarthLifeScience 2nd SessionJohn Peter HuertaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Minerals and ResourcesDocument6 pagesEarth Science Minerals and ResourcesChristian Neri FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesEarth and Life ScienceKiyomi LabradorNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument85 pagesRocks and MineralsRowena LupacNo ratings yet
- Earthy Materials and ProcessesDocument5 pagesEarthy Materials and ProcessesAngèll RòseNo ratings yet
- ES Rocks and Minerals 3 LECTUREDocument50 pagesES Rocks and Minerals 3 LECTUREJailanie BacatanoNo ratings yet
- Abecia - PT#2 - Minerals in ActionDocument6 pagesAbecia - PT#2 - Minerals in ActionJAN JENIS NICOLE ABECIANo ratings yet
- Earth Sci. RevDocument2 pagesEarth Sci. RevI am WWGNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument8 pagesChem ReviewerJULLIANA KEI PINONo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument11 pagesEarth Sciencesalabsabhga0529No ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Earth Materials and ResourcesDocument11 pagesLesson 5: Earth Materials and Resources아지3No ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument50 pagesRocks and MineralsCzarina Bea SaberonNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Minerals and Its PropertiesDocument1 pageTopic 6 - Minerals and Its Propertieslesly AnneNo ratings yet
- ES1QPT2TAROGDocument11 pagesES1QPT2TAROGMuhammad AbdulNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mobile Phone:: Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) - Battery. Speaker. Circuit Board Electrical ConductorDocument7 pagesParts of Mobile Phone:: Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) - Battery. Speaker. Circuit Board Electrical ConductorBARTE CEEJAYNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Resources (Group 3 - Pasteur)Document12 pagesRocks and Minerals Resources (Group 3 - Pasteur)NathalieNo ratings yet
- Finding The Perfect Match: Name: CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesFinding The Perfect Match: Name: CharacteristicsMay BonitaNo ratings yet
- Minerals Products That Contain The MineralDocument6 pagesMinerals Products That Contain The MineralRodz QuinesNo ratings yet
- RVWR Earth Science - W2L3-4Document3 pagesRVWR Earth Science - W2L3-4Gabrielle Mari Gratuito PerezNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 AND 4 Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesLESSON 3 AND 4 Earth SciencejojoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Characteristics of Soil ColloidsDocument4 pagesExercise 5 Characteristics of Soil ColloidslexiclesmcgeeNo ratings yet
- Minerals Cleavage - The Planes of Weak Bonding: Lesson 2: Minerals and RocksDocument4 pagesMinerals Cleavage - The Planes of Weak Bonding: Lesson 2: Minerals and RocksShiba MahesvaraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledMa’am Diana V.No ratings yet
- EARTH SCI REVIEWER Q1S2 (John Patrick Pagauitan)Document6 pagesEARTH SCI REVIEWER Q1S2 (John Patrick Pagauitan)timothybadiola99No ratings yet
- Talc and Pyrophylite GroupDocument21 pagesTalc and Pyrophylite Groupmap vitcoNo ratings yet
- LAS ES W2-LC6and7Document8 pagesLAS ES W2-LC6and7nana.No ratings yet
- Notes - MineralsDocument29 pagesNotes - Mineralsapi-243587006No ratings yet
- CASTANEDA Elements and CompoundDocument31 pagesCASTANEDA Elements and CompoundTito V. Bautista Jr.No ratings yet
- Justin Elle D. Pelpinosas Activity 4Document1 pageJustin Elle D. Pelpinosas Activity 4Justin Elle PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Minerals and RocksDocument30 pagesLesson 1 - Minerals and RocksBelle SevillenoNo ratings yet
- Mineral Sekunder: Mineralogi - 13Document24 pagesMineral Sekunder: Mineralogi - 13RosellaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of MetalsDocument31 pagesExtraction of MetalsTadiwa RylyNo ratings yet
- DAY#03Document35 pagesDAY#03jeonghany727No ratings yet
- Soil Colloids: Clay MineralsDocument16 pagesSoil Colloids: Clay MineralsPeter MukunzaNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials: Rocks and MineralsDocument12 pagesEarth Materials: Rocks and MineralsCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Q1.lesson 3. Minerals Chemical PropertiesDocument30 pagesQ1.lesson 3. Minerals Chemical PropertiesshusuishigakiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.1 Answer SheetDocument3 pagesLesson 4.1 Answer SheetSam PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Layers of The GeosphereDocument2 pagesLayers of The GeosphereParsel BlehNo ratings yet
- O Level Geography Chap Mineral Resources Full NotesDocument23 pagesO Level Geography Chap Mineral Resources Full NotesAmna Faisal73% (15)
- 2-Minerals and Rocks-4 Classes 2 - 2Document85 pages2-Minerals and Rocks-4 Classes 2 - 2Felix kabweNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Soc Sci Ac1Document3 pagesModule 2 Soc Sci Ac1Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- ResourcesDocument34 pagesResourcesRisa Rahmawati PurliantoroNo ratings yet
- KAZANDRA CASSIDY GARCIA - Assessment Task - MetalsDocument4 pagesKAZANDRA CASSIDY GARCIA - Assessment Task - MetalsKazandra Cassidy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 1 ShsDocument3 pagesEarth Science Quarter 1 Shscheryl dgalonNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesRocks and MineralsAditi AherNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Grade 11Document3 pagesEarth Science Grade 11Cherub DaramanNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11Document2 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11len100% (1)
- Earth Sci Classification of Rocks NotesDocument58 pagesEarth Sci Classification of Rocks NotesAriana LaynoNo ratings yet
- SiliconDocument1 pageSiliconAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Little Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksFrom EverandLittle Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- List of Revised Required Standards - 04 05 09Document11 pagesList of Revised Required Standards - 04 05 09Navnath TamhaneNo ratings yet
- Astm A153Document5 pagesAstm A153NhanNo ratings yet
- 89 Aristorod Rev4 ER120S GDocument2 pages89 Aristorod Rev4 ER120S Grusf123No ratings yet
- Uparatnas - Alternative Gems - Vedic Astrology Semi Precious StonesDocument1 pageUparatnas - Alternative Gems - Vedic Astrology Semi Precious StonesVastu VijayNo ratings yet
- Influence of Various Soluble Carbonates On The Hydration of Portland Cement Studied by X-Ray DiffractionDocument16 pagesInfluence of Various Soluble Carbonates On The Hydration of Portland Cement Studied by X-Ray DiffractionThanhNhựtNo ratings yet
- Bulk Flotation of Complex Copper Ore From Siocon, Zamboanga SibugayDocument70 pagesBulk Flotation of Complex Copper Ore From Siocon, Zamboanga SibugayAileen Insalada100% (2)
- Chitriki Rudrappa, Belavadi Ravi, P.Sharathkumar, Siregere Gopalkrishna Mahesh Patil, Prakash Naganoor and M.V.RudramuniyappaDocument6 pagesChitriki Rudrappa, Belavadi Ravi, P.Sharathkumar, Siregere Gopalkrishna Mahesh Patil, Prakash Naganoor and M.V.RudramuniyapparavibelavadiNo ratings yet
- Report Of: AnalysisDocument2 pagesReport Of: AnalysisAsdaRrNo ratings yet
- A.S.L. Pauls College of Engineering and Technology Coimbatore-109Document5 pagesA.S.L. Pauls College of Engineering and Technology Coimbatore-109vkesavakannan4722No ratings yet
- 1.8550 34cralni7 Ni50: Chemical CompositionDocument2 pages1.8550 34cralni7 Ni50: Chemical CompositionMichel PortalNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Singkapan Batuan: Kompetensi TujuanDocument2 pagesPraktikum Singkapan Batuan: Kompetensi Tujuanoctavira auliaNo ratings yet
- Slide Pack - Digestion Methods - Amanda StoltzeDocument62 pagesSlide Pack - Digestion Methods - Amanda StoltzeLeonor Patricia MEDINA SIFUENTESNo ratings yet
- Graphitization of Steels in Elevated-Temperature Service: Introduction and BackgroundDocument2 pagesGraphitization of Steels in Elevated-Temperature Service: Introduction and BackgroundMuhammad Noman ButtNo ratings yet
- Tungsten Electrodes PDFDocument1 pageTungsten Electrodes PDFtyeuqmaiNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Berrillium Copper C17200Document9 pagesData Sheet Berrillium Copper C17200Jonas TambunanNo ratings yet
- XPS TableDocument4 pagesXPS TableEki SetijadiNo ratings yet
- MI L"STD-1595A 26 February 1982 Superseding MIL-STD-1 595 26 July 1977Document72 pagesMI L"STD-1595A 26 February 1982 Superseding MIL-STD-1 595 26 July 1977Jay MillerNo ratings yet
- Special Steels SB4: For Cold Deformation and BearingsDocument1 pageSpecial Steels SB4: For Cold Deformation and BearingsRollpass DesignNo ratings yet
- Pure Nickel Special, Nuclear Grade: Never SeezDocument2 pagesPure Nickel Special, Nuclear Grade: Never SeezsekharsamyNo ratings yet
- Is 1875 1992Document7 pagesIs 1875 1992mukherjeeatanu100% (1)
- ASSAB Tool Steel Performance Comparison Chart PDFDocument1 pageASSAB Tool Steel Performance Comparison Chart PDFSophian Hakim WirajayaNo ratings yet
- Myb1 2015 Nicke PDFDocument18 pagesMyb1 2015 Nicke PDFakbar suhadaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Alloy Redraw Rods - For Electrical Purposes - SpecificationDocument6 pagesAluminium Alloy Redraw Rods - For Electrical Purposes - Specificationvenkat8eNo ratings yet
- 410 QDT Stainless Steel Bar - AISI 410 StandardDocument7 pages410 QDT Stainless Steel Bar - AISI 410 StandardchamaljsNo ratings yet
- NC-559-ASM, No-Clean Solder Paste: Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesNC-559-ASM, No-Clean Solder Paste: Product Data SheetAkhmad MukhsinNo ratings yet
- Kobelco Flux Coated Wires 2009Document28 pagesKobelco Flux Coated Wires 2009Uthanmalliah NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Metric - DIN - 6334 - Spec For Hexagonal Coupling NutDocument4 pagesMetric - DIN - 6334 - Spec For Hexagonal Coupling NutTuff qualityNo ratings yet
- Ripper Tip D11Document2 pagesRipper Tip D11Max SashikhinNo ratings yet
- CF8M VS CF8 Stainless Steel Casting - JC CastingDocument7 pagesCF8M VS CF8 Stainless Steel Casting - JC CastingSHivaprasad APITNo ratings yet