Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem Guide 01
Uploaded by
Ahmed Sayed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views27 pagesThe document discusses the properties and applications of various thermoplastics and elastomers used in plumbing systems, including ABS, CPVC, and PVC. ABS is resistant to a wide range of chemicals and temperatures from -40°F to 180°F, making it suitable for residential drain, waste and vent systems. CPVC has similar properties to PVC but better chemical resistance up to 210°F, so it is used for hot water distribution systems handling corrosive liquids. PVC is resistant to acids, alkalis and salts, with applications in potable water distribution from 0°F to 140°F.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the properties and applications of various thermoplastics and elastomers used in plumbing systems, including ABS, CPVC, and PVC. ABS is resistant to a wide range of chemicals and temperatures from -40°F to 180°F, making it suitable for residential drain, waste and vent systems. CPVC has similar properties to PVC but better chemical resistance up to 210°F, so it is used for hot water distribution systems handling corrosive liquids. PVC is resistant to acids, alkalis and salts, with applications in potable water distribution from 0°F to 140°F.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views27 pagesChem Guide 01
Uploaded by
Ahmed SayedThe document discusses the properties and applications of various thermoplastics and elastomers used in plumbing systems, including ABS, CPVC, and PVC. ABS is resistant to a wide range of chemicals and temperatures from -40°F to 180°F, making it suitable for residential drain, waste and vent systems. CPVC has similar properties to PVC but better chemical resistance up to 210°F, so it is used for hot water distribution systems handling corrosive liquids. PVC is resistant to acids, alkalis and salts, with applications in potable water distribution from 0°F to 140°F.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
1
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
2
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
3
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
4
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
5
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
6
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
7
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
8
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
9
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
10
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
11
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
12
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
13
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
14
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
15
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
16
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
17
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
18
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
19
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
20
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
21
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
22
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
23
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
24
Connexion Developments Ltd + Solenoid Valves (UK) Ltd
Unit 3, Rainbow Court, Armstrong Way, Great Western Business Park, Yate, Bristol, BS37 5NG, England
Tel: 01454 334990 Fax: 01454 326390 www.solenoidvalvesuk.com
25
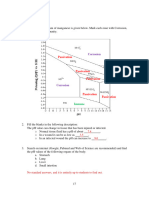
THERMOPLASTICS & ELASTOMERS
ABS — Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Class 32222 conforming to ASTM D3965 is a time-proven material. The smooth inner surface and
superior resistance to deposit formation makes ABS drain, waste, and vent material ideal for residential and commercial sanitary systems. The
residential DWV system can be exposed in service to a wide temperature span. ABS-DWV has proven satisfactory for use from -40°F to 180°F.
These temperature variations can occur due to ambient temperature or the discharge of hot liquids into the system. ABS-DWV is very resistant
to a wide variety of materials ranging from sewage to commercial household chemical formulations. ABS-DWV is joined by solvent cementing or
threading and can easily be connected to steel, copper, or cast iron through the use of transition fittings.
CPVC — Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride Class 23447 conforming to ASTM D1784, has physical properties at 73°F similar to those of PVC, and its
chemical resistance is similar to or generally better than that of PVC. CPVC, with a design stress of 2000 psi and maximum service temperature
of 210°F, has proven to be an excellent material for hot corrosive liquids, hot or cold-water distribution, and similar applications above the
temperature range of PVC. CPVC is joined by solvent cementing, threading or flanging.
PP (Polypropylene) — Polypropylene is a polyolefin, which is lightweight and generally high in chemical resistance. Although polypropylene is
slightly lower in physical properties compared to PVC, it is chemically resistant to organic solvents as well as acids and alkalis. Generally,
polypropylene should not be used in contact with strong oxidizing acids, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and aromatics. With a
design stress of 1000 psi at 73° F, polypropylene has gained wide acceptance where its resistance to sulfur-bearing compounds is particularly
useful in salt water disposal lines, crude oil piping, and low pressure gas gathering systems. Polypropylene has also proved to be an excellent
material for laboratory and industrial drainage where mixtures of acids, bases, and solvents are involved. Polypropylene is joined by the heat
fusion process, threading or flanging. At 180°F, or when threaded, PP should be used for drainage only at a pressure not exceeding
20 psi.
PVC — Polyvinyl Chloride Class 12454 conforming to ASTM D1784. PVC is the most frequently specified of all thermoplastic materials. It has
been used successfully for over 40 years in such areas as chemical processing, industrial plating, chilled water distribution, de-ionised water
lines, chemical drainage, and irrigation systems. PVC is characterized by high physical properties and resistance to corrosion and chemical
attack by acids, alkali’s, salt solutions, and many other chemicals. It is attacked, however, by polar solvents such as ketones, some chlorinated
Hydrocarbons and aromatics. The maximum service temperature of PVC is 140°F. With a design stress of 2000 psi, PVC has the highest long-
term hydrostatic strength at 73°F of any of the major thermoplastics being used for piping systems. PVC is joined by solvent cementing,
threading, or flanging.
PVDF — Polyvinylidene Fluoride is a strong, tough and abrasion resistant fluorocarbon material. It resists distortion and retains most of its
strength to 280°F. It is chemically resistant to most acids, bases, and organic solvents and is ideally suited for handling wet or dry chlorine,
26
bromine and other halogens. No other solid thermoplastic piping components can approach the combination of strength, chemical resistance
and working temperatures of PVDF. PVDF is joined by the heat fusion process, threading or flanging.
EPDM — EPDM is a terpolymer elastomer made from ethylene propylene diene monomer. EPDM has good abrasion and tear
resistance and offers excellent chemical resistance to a variety of acids and alkalines. It is susceptible to attack by oils and is not
recommended for applications involving petroleum oils, strong acids, or strong alkalines. It has good ozone resistance.
It is fairly good with ketones and alcohols and has an excellent temperature range from -20°F to 250°F.
POLYCHLOROPRENE (CR) — Polychloroprenes were one of the first synthetic rubbers developed. Polychloroprene is an all-purpose
polymer with many desirable characteristics and features high resiliency with low compression set, flame resistance, and is animal and
vegetable oil resistant. Polychloroprene is principally recommended for food and beverage service. Generally, Polychloroprene is not affected by
moderate chemicals, fats, greases, and many oils and solvents. Polychloroprene is attacked by strong oxidizing acids, most
chlorinated solvents, esters, ketones, aromatic hydrocarbons, and hydraulic fluids. Polychloroprene has a moderate
temperature range of
-20°F to 160°F.
NITRILE (NBR) — BUNA-N is a general purpose oil-resistant polymer known as nitrile rubber. Nitrile is a copolymer of butadiene and
acrylonitrile and has a moderate temperature range of 20°F to 180°F. Nitrile has good solvent, oil, water, and hydraulic fluid resistance. It
displays good compression set, abrasion resistance and tensile strength. Nitrile should not be used in highly polar solvents such as
acetone and methyl ethyl ketone, nor should it be used in chlorinated hydrocarbons, ozone or nitro hydrocarbons.
FLUOROCARBON (FKM) — Fluorocarbon elastomers are inherently compatible with a broad spectrum of chemicals. Because of this extensive
chemical compatibility, which spans considerable concentration and temperature ranges, fluorocarbon elastomers have gained wide acceptance
as a material of construction for butterfly valve o-rings and seats. Fluorocarbon elastomers can be used in most applications involving mineral
acids, salt solutions, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and petroleum oils. They are particularly good in hydrocarbon service. Fluorocarbon elastomers
have one of the broadest temperature ranges of any of the elastomers, -20°F to 300°F; however, they are not suited for steam service.
PTFE — Polytetrafluoroethylene has outstanding resistance to chemical attack by most chemicals and solvents. PTFE has a temperature rating
of -20°F to 400°F in valve applications. PTFE, a self-lubricating compound, is used as a seat material in ball valves.
GRAPHITE — Graphite is the packing and seal material of choice for most fire-rated products, primarily because of its high temperature rating
of approximately 2000°F. Graphite has excellent chemical resistance, can retain compressibility at all temperatures and has a low coefficient of
friction. Graphite is not recommended for use in strong oxidizing atmospheres.
METALS USED IN VALVES & FITTINGS
COPPER — Among the most important properties of wrot copper materials are their thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion
resistance, wear resistance, and ductility. Wrot copper performs well in high temperature applications and is easily joined by soldering or
brazing. Wrot copper is exclusively used for fittings.
BRONZE — One of the first alloys developed in the bronze age is generally accepted as the industry standard for pressure-rated
bronze valves and fittings. Bronze has a higher strength than pure copper, is easily cast, has improved machinability, and is very easily joined
by soldering or brazing. Bronze is very resistant to pitting corrosion, with general resistance to most chemicals less than that of pure copper.
SILICONE BRONZE — Silicone bronze has the ductility of copper but much more strength. The corrosion resistance of silicon bronze is equal
to or greater than that of copper. Commonly used as stem material in pressure-rated valves, silicon bronze has greater resistance to stress
corrosion cracking than common brasses.
ALUMINUM BRONZE — The most widely accepted disc material used in butterfly valves, aluminum bronze is heat treatable and has the
strength of steel. Formation of an aluminum oxide layer on exposed surfaces makes this metal very corrosion resistant. Not recommended
for high pH wet systems.
BRASS — Generally, brass has good corrosion resistance. Susceptible to de-zincification in specific applications; excellent
machinability. Primary uses for wrot brass are for ball valve stems and balls, and iron valve stems. A forging grade of brass is used in ball valve
bodies and end pieces.
GRAY IRON — An alloy of iron, carbon and silicon, gray iron is easily cast, and has good pressure tightness in the as-cast condition. Gray iron
has excellent dampening properties and is easily machined. It is standard material for bodies and bonnets of Class 125 and 250 iron body
valves. Gray iron has corrosion resistance that is better than steel in certain environments.
DUCTILE IRON — Ductile iron has composition similar to gray iron. Special treatment modifies metallurgical structure, which yields higher
mechanical properties; some grades are heat-treated to improve ductility. Ductile iron has the strength properties of steel using similar casting
techniques to that of gray iron.
CARBON STEEL — Carbon steel has very good mechanical properties and is resistant to stress corrosion and sulfides. Carbon
steel has high and low temperature strength, is very tough and has excellent fatigue strength. Mainly used in gate, globe, and check valves for
applications up to 850°F, and in one-, two-, and three-piece ball valves.
3% NICKEL IRON — 3% Nickel iron has improved corrosion resistance over gray and ductile iron. Higher temperature corrosion
resistance and mechanical properties. Very resistant to oxidizing atmospheres.
NICKEL-PLATED DUCTILE IRON — Nickel coatings have received wide acceptance for use in chemical processing. These coatings have very
high tensile strength, 50 to 225 psi. To some extent, the hardness of a material is indicative of its resistance to abrasion and wear
characteristics. Nickel plating is widely specified as a disc coating for butterfly valves.
400 SERIES STAINLESS STEEL — An alloy of iron, carbon, and chromium, 400 series stainless steel is normally magnetic due to
its martensitic structure and iron content. It is resistant to high temperature oxidation and has improved physical and mechanical
properties over carbon steel. Most 400 series stainless steels are heat-treatable. The most common applications in valves are for stem material
in butterfly valves and backseat bushings and wedges in cast steel valves.
316 STAINLESS STEEL — An alloy of iron, carbon, nickel, and chromium, 316 stainless steel is nonmagnetic with more ductility
than 400SS. Austinetic in structure, 316 stainless steel has very good corrosion resistance to a wide range of environments, is
not susceptible to stress corrosion cracking and is not affected by heat treatment. Most common uses in valves are stem, body
and ball materials.
630 STAINLESS STEEL — 630 stainless steel is a martensitic precipitation/age hardening stainless steel, offering high strength
and hardness. 630 SS withstands corrosive attack better than any of the 400 series stainless steels, and in most conditions
its corrosion resistance closely approaches that of 300 series stainless steel. 630 SS is primarily used as a stem material for butterfly and ball
valves.
27
You might also like
- A ZListingDocument18 pagesA ZListingterence.yong8466No ratings yet
- Telecoms - Roll - Out - Plan - 2010-11 in The London Borough of MertonDocument6 pagesTelecoms - Roll - Out - Plan - 2010-11 in The London Borough of MertonFuzzy_Wood_PersonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Companies in The MidelndsDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering Companies in The MidelndsJonathan ManningNo ratings yet
- Practical Tips For Selecting Residual Current Device RCD PDFDocument59 pagesPractical Tips For Selecting Residual Current Device RCD PDFSketch HolderNo ratings yet
- RB Metals Product Guide RBL0619mpgDocument100 pagesRB Metals Product Guide RBL0619mpgBoris Darío Peréz DuránNo ratings yet
- Encon Industrial Price List 2013Document84 pagesEncon Industrial Price List 2013Ferdie BautistaNo ratings yet
- 'A) 'B) CD CD "Document3 pages'A) 'B) CD CD "bansalrNo ratings yet
- BPF Industry Directory 2016Document36 pagesBPF Industry Directory 2016Trevor J. HutleyNo ratings yet
- Beama Guide To Arc Fault Detection Devices (Afdds) 1Document18 pagesBeama Guide To Arc Fault Detection Devices (Afdds) 1Andy FarleyNo ratings yet
- Garden+centers SlaneysideDocument72 pagesGarden+centers SlaneysideAiziel OrenseNo ratings yet
- Geoceptor CertDocument5 pagesGeoceptor CertWilliam MurrayNo ratings yet
- Foreign AffiliatedDocument1 pageForeign Affiliatedsmart crackerNo ratings yet
- Kent Waste Business GuideDocument14 pagesKent Waste Business Guidezkte009No ratings yet
- Uk Laptop StoresDocument2 pagesUk Laptop Storesbigben861223No ratings yet
- Chloride Power Lan Green 5 7 KvaDocument2 pagesChloride Power Lan Green 5 7 Kvafedericosanchez50% (2)
- NW295 25214 25215 25216 25217 UK DOC 文件Document2 pagesNW295 25214 25215 25216 25217 UK DOC 文件test.alanbdjNo ratings yet
- A Standard For Asphaltic Plug Joints2Document20 pagesA Standard For Asphaltic Plug Joints2kheang mengNo ratings yet
- Manual ELE Internacional Maquina de CompresionDocument33 pagesManual ELE Internacional Maquina de Compresionelieser7410No ratings yet
- TB Series TB Series: General InstructionsDocument1 pageTB Series TB Series: General InstructionsEric WangNo ratings yet
- SC-manual-R8 (EN+SMOKE) - 2013.06.14Document30 pagesSC-manual-R8 (EN+SMOKE) - 2013.06.14TharinSiriwardanaNo ratings yet
- Approved Service CentresDocument4 pagesApproved Service CentresOmar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Traders Directory UK: How To Make Big Savings And Maximise ProfitsFrom EverandTraders Directory UK: How To Make Big Savings And Maximise ProfitsNo ratings yet
- Find Your Local OfficeDocument1 pageFind Your Local Officef9zvxkvw5mNo ratings yet
- Roller Shutters BizHouse - UkDocument3 pagesRoller Shutters BizHouse - UkCata LinNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter-2019 EPCOMDocument4 pagesAuthorization Letter-2019 EPCOMjose carlos valencia valenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Contacts - STMicroelectronicsDocument179 pagesContacts - STMicroelectronicsDoni RandanuNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter-2025 EPCOMDocument4 pagesAuthorization Letter-2025 EPCOMMARIA FERNANDA GARCIA PEREZNo ratings yet
- Uni Birmingham SLDocument1 pageUni Birmingham SLOceanNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual: ADE 442NDocument64 pagesParts Manual: ADE 442NBassie100% (1)
- The RCD Handbook - Guide To The Selection and Application of Residual Current DevicesDocument42 pagesThe RCD Handbook - Guide To The Selection and Application of Residual Current DevicesRahim Bux100% (1)
- Polytek International Distributor ListDocument3 pagesPolytek International Distributor ListArieza PerdhanaNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: Sand Density Cone, 12" (305 MM)Document9 pagesOperating Instructions: Sand Density Cone, 12" (305 MM)luis VeramendiNo ratings yet
- WSM Tool Automatik enDocument6 pagesWSM Tool Automatik enmuthusamyeeeNo ratings yet
- Spring ManufacturersDocument25 pagesSpring ManufacturersVinay GundappaNo ratings yet
- PM B35C B40CR B40CM 6 Speed MkiiDocument436 pagesPM B35C B40CR B40CM 6 Speed MkiiPieter Botha100% (1)
- Purchase Order: 4502245629: Invoice CustomerDocument1 pagePurchase Order: 4502245629: Invoice Customerupkumar871No ratings yet
- Approved Suppliers 2012Document7 pagesApproved Suppliers 2012Afeez AzizNo ratings yet
- Contact Addresses For OIL RIGSDocument47 pagesContact Addresses For OIL RIGSDancinos100% (1)
- ProductDocument2 pagesProductYassir ElsafiNo ratings yet
- Impinjet ScrubbersDocument3 pagesImpinjet ScrubbersLinus RidgeNo ratings yet
- ENF Recycling Directory SampleDocument40 pagesENF Recycling Directory SampleKishore Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Progressive Reference Form-1Document2 pagesProgressive Reference Form-1Freddie Asiedu LarbiNo ratings yet
- Nuts Bolts BizHouse - UkDocument3 pagesNuts Bolts BizHouse - UkAlex BekeNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual: Daimlerchrysler Om 442Document67 pagesParts Manual: Daimlerchrysler Om 442Bassie100% (2)
- Niaic SN (Ni) 1998 60Document3 pagesNiaic SN (Ni) 1998 60ahmed_galal_waly1056No ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument162 pagesAir ConditioningAdemola Olakunle Ajayi100% (1)
- Web Page Skip Company Approved List Details As of 19th June 2020Document2 pagesWeb Page Skip Company Approved List Details As of 19th June 2020Perched AboveNo ratings yet
- SOLO Detector 16392Document2 pagesSOLO Detector 16392Oleksandr100% (1)
- Appendix 3 Equipment SuppliersDocument16 pagesAppendix 3 Equipment SuppliersaegosmithNo ratings yet
- Crane Company ExampleDocument4 pagesCrane Company ExamplethilakNo ratings yet
- 01 B30C 6x6 MkII Rev 01 February 2001Document405 pages01 B30C 6x6 MkII Rev 01 February 2001philippe gravierNo ratings yet
- Injection MouldingDocument16 pagesInjection Mouldingramesh.rao3192No ratings yet
- Racecar Engineering 2005.07Document100 pagesRacecar Engineering 2005.07Arsenij KroptyaNo ratings yet
- List of Chambers of Commerce in ScotlandDocument3 pagesList of Chambers of Commerce in Scotlandmike100% (1)
- Understanding Lightning and Lightning Protection: A Multimedia Teaching GuideFrom EverandUnderstanding Lightning and Lightning Protection: A Multimedia Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- How to Find Out in Iron and Steel: The Commonwealth and International Library: Libraries and Technical Information DivisionFrom EverandHow to Find Out in Iron and Steel: The Commonwealth and International Library: Libraries and Technical Information DivisionNo ratings yet
- Network neutrality: From policy to law to regulationFrom EverandNetwork neutrality: From policy to law to regulationNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Response To Bauxite Mining and Rehabili - 2017 - Journal of HydroloDocument15 pagesHydrological Response To Bauxite Mining and Rehabili - 2017 - Journal of HydroloAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Age Determination Using 85Kr and Multiple A - 2017 - Journal of HydrDocument16 pagesGroundwater Age Determination Using 85Kr and Multiple A - 2017 - Journal of HydrAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Salinization in Graciosa and Pico Island - 2017 - Journal of HydroloDocument19 pagesGroundwater Salinization in Graciosa and Pico Island - 2017 - Journal of HydroloAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Capability of Meteorological Drought Indices For - 2017 - Journal of HydrologyDocument17 pagesCapability of Meteorological Drought Indices For - 2017 - Journal of HydrologyAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Consistency Among Global Precipi - 2017 - Journal of HydrologyDocument14 pagesAssessment of The Consistency Among Global Precipi - 2017 - Journal of HydrologyAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Hydrological Variability Over The Volta - 2017 - Journal of HydroloDocument23 pagesAnalysis of Hydrological Variability Over The Volta - 2017 - Journal of HydroloAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 6511946Document88 pagesGrundfosliterature 6511946Ahmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Solenoidvalvesuk Chemical Resistance GuideDocument17 pagesSolenoidvalvesuk Chemical Resistance GuideAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Ch2c-Irrigation Water QualityDocument28 pagesCh2c-Irrigation Water QualityAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- CatalogDocument268 pagesCatalogAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- National Turf Industry Delivery Assessment Guides Final DrafDocument38 pagesNational Turf Industry Delivery Assessment Guides Final DrafAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- WpaDocument14 pagesWpaRusli NurdinNo ratings yet
- Excel Clean Room TechnologiesDocument9 pagesExcel Clean Room Technologiesxlcleantech100% (2)
- Hoffman JB Corrosion 4Document4 pagesHoffman JB Corrosion 4HJNo ratings yet
- General Requirements For Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and StripDocument24 pagesGeneral Requirements For Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and StripJeisson GómezNo ratings yet
- JSS 4210-18-2005Document25 pagesJSS 4210-18-2005Kaushik Sengupta100% (1)
- Over 500,000: Tooling ComponentsDocument84 pagesOver 500,000: Tooling ComponentsSamik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Concrete Lining Science DirectDocument17 pagesConcrete Lining Science DirectGilbert LimNo ratings yet
- Tools For Pipe Welding: W E L D T E C HDocument24 pagesTools For Pipe Welding: W E L D T E C HChano Hanok100% (1)
- Mock 8Document27 pagesMock 8Otob NitroNo ratings yet
- Morse ArchcatalogDocument74 pagesMorse ArchcatalogDerf ZednanrefNo ratings yet
- Materials Guideline Update: Preliminary Survey ResultsDocument44 pagesMaterials Guideline Update: Preliminary Survey ResultsmrinalkantibhaduriNo ratings yet
- Kerk Catalog 2008 PDFDocument74 pagesKerk Catalog 2008 PDFhexapodoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Insertos FresamentoDocument33 pagesCatalogo Insertos FresamentoClediliano André MirandaNo ratings yet
- E.M.C. QuestionsDocument38 pagesE.M.C. QuestionsJoshnewfound67% (3)
- BDL Project Supply Range and Specification For Piping Materials PDFDocument49 pagesBDL Project Supply Range and Specification For Piping Materials PDFhengki wibowoNo ratings yet
- 2012flagpoles1 BackupDocument12 pages2012flagpoles1 BackupmmflagsdonNo ratings yet
- Copy Obf PARTDocument62 pagesCopy Obf PARTGordan SanticNo ratings yet
- RCF GMDocument38 pagesRCF GMkr_ananthNo ratings yet
- Calpeda MXH - 2008 PumpDocument4 pagesCalpeda MXH - 2008 PumpMichael SetiaNo ratings yet
- MN 2Document52 pagesMN 2dbb2r6w8d5No ratings yet
- IE7 Chapter-IDocument15 pagesIE7 Chapter-ILUCAS AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Annex H API 650 - Earthing For IFRTDocument1 pageAnnex H API 650 - Earthing For IFRTAmul AmnajeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Pressure Vessel Design Models For CylindersDocument60 pagesChapter One: Pressure Vessel Design Models For Cylindersabiy balkewNo ratings yet
- Waste Cone Cla-ValDocument2 pagesWaste Cone Cla-ValRobertoNo ratings yet
- High Temperature CorrosionDocument2 pagesHigh Temperature CorrosionIlhamChaniefNo ratings yet
- Analyisis of en of AM350Document15 pagesAnalyisis of en of AM350Jesús JáquezNo ratings yet
- Tds CA 1000 Mastinox PPGDocument2 pagesTds CA 1000 Mastinox PPGAstari Putri NuarisaNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steels and Their PropertiesDocument45 pagesStainless Steels and Their PropertiesSH1961No ratings yet
- Wellter Catalog 2023 Version - ThailandDocument41 pagesWellter Catalog 2023 Version - ThailandgaurangNo ratings yet
- Duplex 2205 AlloyDocument2 pagesDuplex 2205 AlloyJose DonaireNo ratings yet