Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio2 91156 Satovolume
Bio2 91156 Satovolume
Uploaded by
Victoria RadchenkoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio2 91156 Satovolume
Bio2 91156 Satovolume
Uploaded by
Victoria RadchenkoCopyright:
Available Formats
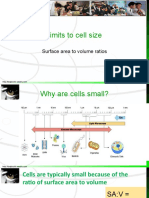
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY AS 91156
unicellular organism multicellular efficiency
Surface area to volume ratio.
Surface area refers to the outside area of an object, e.g. it is the area around the Why is SA:V ratio important:
outside of a cell. Unit = cm2. Cells need to be small because they rely on diffusion for getting substances into
Volume refers to the amount of space inside of the object, e.g. it is the space and out of their cells. When a cell grows, there is comparatively less membrane
inside the cell. Unit = cm3. for the substances to diffuse through resulting in the centre of the cell not
receiving the substances that it needs. Diffusion is less efficient, cell processes
slow down and the cell stops growing. The cell then needs to divide into two
smaller cells, which each have a larger SA: V ratio and can diffuse materials more
efficiently again.
Small cells are more efficient at diffusion as
they have a HIGH SA:V ratio.
Cube size Surface area Volume SA:V ratio
2 cm cube 2 x 2 x 6 = 24cm2 2 x 2 x 2 = 8cm3 24 to 8 = 3:1 In class you may have done an experiment where you placed special agar into a
4 cm cube 4 x 4 x 6 = 96cm2 4 x 4 x 4 = 64cm3 96 to 64 = 1.5:1 solution of NaOH. All three cubes soaked in the solution for the same amount of
6 cm cube 6 x 6 x 6 = 216cm2 6 x 6 x 6 = 216cm3 216 to 216 = 1:1 time but the bigger cubes did not change colour on the inside as the NaOH hadn’t
diffused in yet. This shows that large cell takes long/is less efficient at diffusing
diffusion
8 cm cube 8 x 8 x 6 = 384cm2 8 x 8 x 8 = 512cm3 384 to 512 = 0.75:1
materials into the centre of the cell.
As the cube size increases or the cell gets bigger , then the surface area to volume Cubes cut in
ratio - SA:V ratio decreases. half to
measure how
far the NaOH
SA:V ratio
When an object/cell is very small, it has a large surface area to volume ratio, while
has diffused.
a large object/ cell has a small surface area to volume ratio.
When a cell grows, its volume increases at a greater rate than its surface area,
therefore it’s SA: V ratio decreases.
SA:V ratio in unicellular organisms. Their small size means that they have a large
surface area volume
Cells may increase their SA:V ratio by having: SA:V ratio and it is adequate for the many materials to move into and out of the
• Long thin shape / elongated shape. e.g. nerve cells cell by diffusion and active transport. But it does limit the organism’s size. Once
• Folding the surface of the object/ cell they get too big, they must divide.
membrane. e.g. villi of the lining in the small
SA:V ratio in multicellular organisms. By being multicellular, plants and animals
intestines
have overcome the problems of small cell sizes. Each cell has a large SA:V ratio
• Plant cells are much larger than animal cells and
but they have evolved features such as gas exchange organs (lungs) and
they have a large vacuole which pushes the
circulatory system (blood) to speed up and aid the movement of materials into
organelles to the edge of the cell where they get
and out of the organism.
regular access to resources.
You might also like
- Cell Shape and Size 1Document3 pagesCell Shape and Size 1Patience Pena100% (2)
- POGIL Cell Size-KEYDocument5 pagesPOGIL Cell Size-KEYKali WarnkeNo ratings yet
- 11.1 To 11.2 YellowDocument7 pages11.1 To 11.2 YellowKay0% (1)
- 9 Cell Size-SDocument4 pages9 Cell Size-StomglockNo ratings yet
- SAP MRO Business Process SSDocument16 pagesSAP MRO Business Process SSjanto gmf80% (5)
- GR Answers To End of Chapter Textbook QuestionspdfDocument65 pagesGR Answers To End of Chapter Textbook Questionspdfalicia80% (5)
- SB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsDocument4 pagesSB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsSiaNo ratings yet
- Asco Series 300 Ats Operators ManualDocument20 pagesAsco Series 300 Ats Operators ManualGera Ortiz Martinez100% (1)
- Surface Area To Volume RatioDocument1 pageSurface Area To Volume Ratioapi-292439032No ratings yet
- 1.1.U3 Cell Surface To Volume Is An Important Limitation To Cell SizeDocument13 pages1.1.U3 Cell Surface To Volume Is An Important Limitation To Cell SizeJosepNo ratings yet
- STA. ANA - LAB - 00 Diffusion of A Spherical Cell - SA-VDocument2 pagesSTA. ANA - LAB - 00 Diffusion of A Spherical Cell - SA-VCassandra Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet SAtoVratioworksheetwithkeyDocument2 pagesWorksheet SAtoVratioworksheetwithkeynim35No ratings yet
- CH 11 Cell Growth Divison and Reproduction (3) rYsR2Document14 pagesCH 11 Cell Growth Divison and Reproduction (3) rYsR2emancairoNo ratings yet
- Limits To Cell Size: Surface Area To Volume RatiosDocument8 pagesLimits To Cell Size: Surface Area To Volume RatiosSurya NairNo ratings yet
- Cell Magnification and Surface AreaDocument21 pagesCell Magnification and Surface Areajohnosborne100% (1)
- Ritika Gogna - Cell Size PogilDocument5 pagesRitika Gogna - Cell Size PogilRitika GognaNo ratings yet
- F 08082021105910 F 1-Chapter-3Document14 pagesF 08082021105910 F 1-Chapter-3Ayaan ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Cell Size-KEYDocument7 pagesCell Size-KEYMichael IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Bio InvestigationDocument2 pagesBio InvestigationMary26297No ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Cell Theory and Size - StudentDocument33 pagesCell Theory and Size - Studenttackevin000No ratings yet
- B1.10 Exchanging Materials - Surface Area ACL TeacherDocument19 pagesB1.10 Exchanging Materials - Surface Area ACL TeacherssjundiNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument15 pagesCell PhysiologyTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 - The Cell in ActionDocument22 pagesChapter - 04 - The Cell in ActionBily roriguesNo ratings yet
- Ans End of Chapter Biologi KimiaDocument23 pagesAns End of Chapter Biologi KimiaDouble Diamond Art ChannelNo ratings yet
- Diffusion in Agar CubesDocument4 pagesDiffusion in Agar Cubeshannah kommel100% (1)
- Cell Size Shape and SAV Surface-Area VolumeDocument8 pagesCell Size Shape and SAV Surface-Area VolumeAylin Gutiérrez JuárezNo ratings yet
- Sa Vol Ratio ActivityDocument3 pagesSa Vol Ratio ActivitySamuel CNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Q3-Week-1-2Document11 pagesSCIENCE Q3-Week-1-2April KylaNo ratings yet
- Sa To Volume Ratio ApDocument14 pagesSa To Volume Ratio Apapi-280807408No ratings yet
- Cambridge Science Year 7 LB Lyp Removed CompressedDocument268 pagesCambridge Science Year 7 LB Lyp Removed CompresseddivyamohandasNo ratings yet
- (Lab) Investigation Why Are Cells So SmallDocument3 pages(Lab) Investigation Why Are Cells So SmallMay TreeNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: + Factors Affecting The Rate of MovementDocument44 pagesOsmosis: + Factors Affecting The Rate of MovementCharlotte BurkeNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Bubble LabDocument7 pagesCell Membrane Bubble LabRic Anthony LayasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Diffusion & OsmosisDocument26 pagesChapter 3 - Diffusion & Osmosisapi-3728508100% (6)
- Agar Cube Lab PhenolpthaleinDocument4 pagesAgar Cube Lab PhenolpthaleinnichelleNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Surface Area To Volume Ratio LabDocument5 pagesSurface Area To Volume Ratio LabElizaNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 T3 Holiday Homework. Teachers' AnswersDocument18 pagesSec 1 T3 Holiday Homework. Teachers' Answerslogy of bioNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings (N)Document5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings (N)MGMT1 armNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell TransportDocument19 pagesPlant Cell TransportJenniferNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells 1Document10 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells 1saadNo ratings yet
- 03 Movement of Substances NotesDocument7 pages03 Movement of Substances Notestarankaur401No ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter Particle Model PowerpointDocument23 pages1 States of Matter Particle Model Powerpointloupoo80No ratings yet
- Reminder B3Document9 pagesReminder B3Daniel thanh ducNo ratings yet
- Cell Size Lab AgarDocument4 pagesCell Size Lab AgarUkjun JungNo ratings yet
- Cell Size StudentDocument6 pagesCell Size StudentAmanda NorrisNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Particle Characterization and Their DistributionDocument20 pagesUnit-1 Particle Characterization and Their Distributionyouga SriNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Division and MitosisDocument35 pages1.3 Cell Division and MitosisJay XieNo ratings yet
- Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties PropertiesDocument3 pagesKey Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties PropertiesShimaa ElsharnobyNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryDocument16 pagesYear 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryOlivia YinNo ratings yet
- The Aga Khan Academy, Hyderabad Agar Cube Diffusion (Lab Report)Document7 pagesThe Aga Khan Academy, Hyderabad Agar Cube Diffusion (Lab Report)Soumil KuraniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Investigating Cell TransportDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Investigating Cell Transportaileen kristel bernardoNo ratings yet
- Osmosis&diffusion 3NDocument8 pagesOsmosis&diffusion 3Nms_m_tan100% (7)
- Phy Ex. 1.1 SolutionDocument3 pagesPhy Ex. 1.1 SolutionDilip deotaleNo ratings yet
- Acosta, Niel Biochemistry Task 4Document5 pagesAcosta, Niel Biochemistry Task 4Algrin Acosta0% (1)
- Samian AQA Biology GCSE Combined B1 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesSamian AQA Biology GCSE Combined B1 Practice AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- 01 - Structure and Bonding CornellDocument19 pages01 - Structure and Bonding CornellMogusNo ratings yet
- Volume/Surface Area: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesVolume/Surface Area: Name: - DateatikaNo ratings yet
- The Memory of Places: Clearing Energy Fields from Apartements, Buildings, and Spaces using Systemic ConstellationsFrom EverandThe Memory of Places: Clearing Energy Fields from Apartements, Buildings, and Spaces using Systemic ConstellationsNo ratings yet
- MCA Syallabus PDFDocument136 pagesMCA Syallabus PDFjoby georgeNo ratings yet
- CSS Report 51Document30 pagesCSS Report 51Rohit GadekarNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter LESSON 7: Probabilities of Simple Events I. InstructionDocument5 pagesFourth Quarter LESSON 7: Probabilities of Simple Events I. InstructionainahNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of ChiliDocument6 pagesThe Feasibility of ChiliMark Paul100% (1)
- Structural Analysis and Design Report of Residential BuildingDocument44 pagesStructural Analysis and Design Report of Residential BuildingSandip BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- BoB Assistant User ManualDocument46 pagesBoB Assistant User ManualAlen KuharićNo ratings yet
- A Review of Regrinding and Fine GrindingDocument27 pagesA Review of Regrinding and Fine GrindingabrahanNo ratings yet
- E463 PDFDocument13 pagesE463 PDFJuan Alex CayyahuaNo ratings yet
- 7 Stylistic Syntax of The English Languag Expressive Means of TheDocument50 pages7 Stylistic Syntax of The English Languag Expressive Means of TheKaterina AndreevaNo ratings yet
- RISH Master 3450: Digital Multifunction InstrumentDocument4 pagesRISH Master 3450: Digital Multifunction InstrumentCareer Focus ClassesNo ratings yet
- Jenkins Job Builder PDFDocument315 pagesJenkins Job Builder PDFJaganmohanarao SiddelaNo ratings yet
- AON7403 P-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor: Features General DescriptionDocument4 pagesAON7403 P-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor: Features General DescriptionAry Riyadi AnasNo ratings yet
- CBNHS Salinas G7 Q1 W4Document8 pagesCBNHS Salinas G7 Q1 W4Ella LlamasNo ratings yet
- Problems On TrainDocument3 pagesProblems On TrainNitin DangiNo ratings yet
- ChE Objective Type Questions Compilation-Dean MedinaDocument165 pagesChE Objective Type Questions Compilation-Dean MedinaSasi Kumar100% (10)
- Lec 11Document37 pagesLec 11chandrasekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Bipolar Junction Transistor Transistor Principle of OperationDocument45 pagesChapter - 1 Bipolar Junction Transistor Transistor Principle of OperationDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- bufferDocument51 pagesbufferdiah ayu romadhaniNo ratings yet
- Custom UoDocument20 pagesCustom UoSanjiv ChNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Intelligent Techniques For Pattern Analysis and Understanding PDFDocument393 pagesHybrid Intelligent Techniques For Pattern Analysis and Understanding PDFfghjkltyuioNo ratings yet
- Aperture Shutter Speed ISO Explanations PDFDocument63 pagesAperture Shutter Speed ISO Explanations PDFaakhyar_2No ratings yet
- 30 LTE ERAN7.0 PCI Conflict Detection Self-OptimizationDocument22 pages30 LTE ERAN7.0 PCI Conflict Detection Self-OptimizationPhan AnNo ratings yet
- 1.10 DistanceDocument10 pages1.10 DistanceMadhur GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2125 General Studies MCQ For UPSC /SSC and All Competitive ExamsDocument177 pages2125 General Studies MCQ For UPSC /SSC and All Competitive ExamsAnilkumar RockNo ratings yet
- WeekDocument82 pagesWeekMaaz ChowdhryNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Physics 0625/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Physics 0625/42Susan GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 - Q2 - W2 DLLDocument5 pagesMathematics 4 - Q2 - W2 DLLDivine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DHS Module1Document27 pagesDHS Module1Sajed AbdulrahmanZaiNo ratings yet