Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eut
Uploaded by
asdasdasdasdasdOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eut
Uploaded by
asdasdasdasdasdCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRO
Other membrane-bound organelles present in eukaryotic cells include mitochondria and the
Golgi apparatus, while chloroplasts can be found in plants and algae.
Prokaryotic cells may contain primitive organelles.[14] Eukaryotes can be unicellular or
multicellular, with several cell types creating various types of tissue; prokaryotes are mainly
unicellular.
The most well-known eukaryotes are animals, plants, and fungus; other eukaryotes are
frequently referred to as protists .[15]
Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than prokaryotic cells, with a volume 10,000 times
greater.[17] They have a variety of internal membrane-bound structures called organelles, as
well as a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments,
which play an important role in defining the cell's organization and shape.
During nuclear division, eukaryotic DNA is divided into numerous linear bundles called
chromosomes, which are separated by a microtubular spindle.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Lesson 5: Integrals Leading To Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument7 pagesLesson 5: Integrals Leading To Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Antiderivatives and The Power FormulaDocument13 pagesLesson 1 Antiderivatives and The Power FormulaasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- GED107 Moral TheoriesDocument33 pagesGED107 Moral TheoriesasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Integration by PartsasdasdasdDocument10 pagesLesson 8 Integration by PartsasdasdasdasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16 Arc LengthDocument7 pagesLesson 16 Arc LengthasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World: Applications of EquationsDocument22 pagesMathematics in The Modern World: Applications of EquationsasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 VolumeDocument19 pagesLesson 14 VolumeasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Transformation by Trigonometric FormulasDocument17 pagesLesson 7 Transformation by Trigonometric FormulasasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
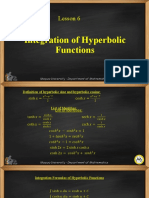
- Lesson 6 Integration of Hyperbolic FuntionsDocument6 pagesLesson 6 Integration of Hyperbolic FuntionsasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
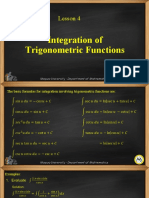
- Lesson 4 Integration of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument8 pagesLesson 4 Integration of Trigonometric FunctionsasdasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)