Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Writing and Learning Objective
Uploaded by
Pa T EthiopiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Writing and Learning Objective
Uploaded by
Pa T EthiopiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Writing Learning Objectives
Questions to Ask Yourself
What do you want participants to be able to do back at their institutions as a direct result of attending
this session (workshop, course, seminar, etc.)?
What does our audience need to know or be able to do to bridge the gap between where they are today
and where we want them to be tomorrow?
If participants could learn only three things in this session, what would those three things be? What
would be your three take-home messages?
Steps for Writing an Objective
1. Write each objective beginning with the phrase “After participating in this session, attendees should be able
to . . . .”
2. Choose a verb that matches the desired level of knowledge or skill (see information on Bloom’s Taxonomy
below).
Verbs should indicate specific, measurable, and observable behaviors.
3. Review each objective to make sure it is an outcome.
Double check that you have not created a list of learning activity descriptions or agenda items (for
example, “The participants should complete a simulation on how to perform the XYZ procedure”).
Your objectives should describe what participants should be able to know or do as a result of a
learning experience.
4. Examples:
Poorly defined learning objective: After participating in this session, attendees should be able to
explain change management.
Well-defined learning objective: After participating in the session, attendees should be able to
describe the three essential elements of change management.
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy, created by Benjamin Bloom, is a hierarchical classification of the different levels of thinking
© 2016 AAMC. May be reproduced and distributed with attribution.
Writing Learning Objectives
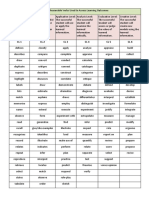
List of Verbs for Formulating Educational Objectives
Remembering
arrange bookmark call out choose define describe
duplicate highlight identify label list locate
match memorize name omit order recite
recognize relate repeat reproduce retrieve search
select state tabulate write
Understanding
annotate arrange attach blog Boolean search categorize
classify comment compare discuss explain express
extend give example illustrate indicate infer interpret
paraphrase report restate review rewrite summarize
subscribe translate tweet
Applying
apply assemble carry out collect compose construct
demonstrate develop dramatize edit execute generalize
hack illustrate implement load network operate
organize play practice prescribe restate run
schedule select share sketch solve
Analyzing
analyze appraise attribute calculate categorize classify
collaborate contrast criticize deliberate differentiate discriminate
distinguish examine experiment infer integrate interpret
manage organize question reverse-engineer structure subdivide
survey tag test validate
Evaluating
coach critique debate defend detect develop
evaluate formulate hypothesize judge manage mentor
moderate plan prepare prioritize propose rate
recommend re-engineer review revise set up support
synthesize test train verify
Creating
argue assess brainstorm budget build compose
conceive conceptualize construct create design direct/produce
engineer envision estimate formulate hypothesize institute
invent justify make up originate predict prototype
publish role play strategize
Words to be avoided:
These words are often used but are open to many interpretations:
appreciate believe know learn understand
Sources:
http://edglossary.org/blooms-taxonomy/
http://edorigami.wikispaces.com/Bloom's+Digital+Taxonomy
© 2016 AAMC. May be reproduced and distributed with attribution.
You might also like
- UG I Sem 2021 Batch QP Pattern For End Sem ExamDocument2 pagesUG I Sem 2021 Batch QP Pattern For End Sem ExamMaxila Sabu VNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonamy ListDocument1 pageBlooms Taxonamy ListksatyamNo ratings yet
- AAMEC Blooms TaxonomyDocument1 pageAAMEC Blooms Taxonomythiruvengadam cNo ratings yet
- Writing Measurable Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesWriting Measurable Learning Objectivesrabe.acctngfirmNo ratings yet
- Tips For Developing Learning Objectives: KnowledgeDocument2 pagesTips For Developing Learning Objectives: Knowledgemeriam tad-oNo ratings yet
- Cognitive, Psychomotor, AffectiveDocument3 pagesCognitive, Psychomotor, AffectiveJovelyn CadatalNo ratings yet
- CL1 CL2 CL3 CL4 CL5 CL6Document2 pagesCL1 CL2 CL3 CL4 CL5 CL6San DNo ratings yet
- Measurable VerbDocument2 pagesMeasurable VerbSan DNo ratings yet
- EDU 505 - Blooms TaxonomyDocument1 pageEDU 505 - Blooms Taxonomybonie1677No ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesDanjo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainLyn Gel AnNo ratings yet
- Verbs Checklist (Cognitive, Affective, Psychomotor) 3 DomainsDocument3 pagesVerbs Checklist (Cognitive, Affective, Psychomotor) 3 DomainsGypsie Ann PaconNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainElaine MandiaNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive Domainangelilou regaspiNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesApple Janine Orillaneda-Campos AndoyNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesKuloumiNo ratings yet
- WTF No 7777 PDFDocument3 pagesWTF No 7777 PDFfame charity porioNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainRutchelNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesHanna Trinidad TagoctocNo ratings yet
- Study No. 246 PDFDocument3 pagesStudy No. 246 PDFfame charity porioNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesJonwille Mark CastroNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainKuloumiNo ratings yet
- Verbs ChecklistDocument3 pagesVerbs ChecklistMercy AbaretaNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive Domainᜃᜒᜋ᜔ ᜎᜓᜐNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesArcelina LumasNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesMar Zuo Flores AvrilleNo ratings yet
- Verbs Checklist PDFDocument3 pagesVerbs Checklist PDFCyra MandigmaNo ratings yet
- Verbs - Checklist For Writing Educational Objectives PDFDocument3 pagesVerbs - Checklist For Writing Educational Objectives PDFMycz DoñaNo ratings yet
- Verbs - Checklist Domain PDFDocument3 pagesVerbs - Checklist Domain PDFRaquelNo ratings yet
- Verbs Writing Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesVerbs Writing Educational ObjectivesEdna BalingitNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Cognitive, Affective and Pyschomotor DomainsDocument3 pagesVerb List For Cognitive, Affective and Pyschomotor DomainsJames Flores100% (1)
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainElla Cagadas PuzonNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainCÿ Rïl ĆyNo ratings yet
- Verbs Checklist FileDocument3 pagesVerbs Checklist FileJohnriel Cueva LeponNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesArnold DonadilloNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainMercy AbaretaNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainJonwille Mark CastroNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainLyn Gel AnNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesAprilyn G. PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainMelanie Jane DaanNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainKim Angela BulaongNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainAlmira Francia AbadNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainMuhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesLyn Gel AnNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesLigsanan John PatrickNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainCHARLIE TORRESNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainFrancisco Dacuya AlajasNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainCrystal Ramos-FloriaNo ratings yet
- Verb List Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesVerb List Educational ObjectivesNathaniel DalisayNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesDea Marie PauloNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainTakeshi YukataNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainMuhammad Waseem100% (1)
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainjulstensNo ratings yet
- Write Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesWrite Educational ObjectivesDea Marie PauloNo ratings yet
- Verbs To Be Use in Lesson Plan - S ObjectivesDocument3 pagesVerbs To Be Use in Lesson Plan - S ObjectivesAlexis Roy GajilomoNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainJonwille Mark CastroNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainJean LeysonNo ratings yet
- Verb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesVerb List For Writing Educational Objectives: Cognitive DomainChristianne VenturaNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet
- Auditor's primary responsibility and assurance servicesDocument14 pagesAuditor's primary responsibility and assurance servicesTricia Mae FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Brand Experience On Customer Satisfaction in Courier Services of Sindh, PakistanDocument13 pagesThe Impact of Brand Experience On Customer Satisfaction in Courier Services of Sindh, PakistanSURESH NIL (RA1931201020184)No ratings yet
- GE2022 TQM Notes 3Document20 pagesGE2022 TQM Notes 3Rexmar Christian BernardoNo ratings yet
- QAQC GuidelinesDocument19 pagesQAQC GuidelinesBonaventure Nzeyimana100% (1)
- PDFDocument30 pagesPDFDeepak RathoreNo ratings yet
- Regression: Descriptive StatisticsDocument5 pagesRegression: Descriptive StatisticsNedy SwiftNo ratings yet
- Liberal Arts Program: Myanmar Institute of TheologyDocument6 pagesLiberal Arts Program: Myanmar Institute of TheologyNang Bu LamaNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument9 pagesNarrative ReportPearl AudeNo ratings yet
- Is Rizal Truly the Philippines' National HeroDocument8 pagesIs Rizal Truly the Philippines' National HeroCamille Flores0% (1)
- Structural Geology Laboratory Manual: Third EditionDocument166 pagesStructural Geology Laboratory Manual: Third Editionforscribd1981100% (1)
- 101 MUET Hacks - A Cheat Sheet For MUET Report WritingDocument14 pages101 MUET Hacks - A Cheat Sheet For MUET Report Writingdesiree heavensNo ratings yet
- 18MAB303T - F-Test 2023Document24 pages18MAB303T - F-Test 2023JEMINA J (RA2011037010010)No ratings yet
- Bibliography, Qualitative Methods Social SciencesDocument20 pagesBibliography, Qualitative Methods Social SciencesMelonie A. FullickNo ratings yet
- Artigo Publicado Revista Estudos de Psicologia Campinas 2022Document13 pagesArtigo Publicado Revista Estudos de Psicologia Campinas 2022Antonio Augusto Pinto JuniorNo ratings yet
- F. Thesis 1Document21 pagesF. Thesis 1rashelann dalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii Group 6 11 Humss 2Document5 pagesChapter Iii Group 6 11 Humss 2Edcel BaragaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Design ThinkingDocument12 pagesThe Use of Design ThinkingJane Claire Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Theory Hub BookDocument199 pagesTheory Hub Bookmohamed elkubtiNo ratings yet
- Archaeology Dissertation ExamplesDocument5 pagesArchaeology Dissertation ExamplesBuyALiteratureReviewPaperCanada100% (1)
- Advances in Accounting, Incorporating Advances in International AccountingDocument9 pagesAdvances in Accounting, Incorporating Advances in International AccountingSouheil LahmerNo ratings yet
- English 10 Q4 Module 1Document22 pagesEnglish 10 Q4 Module 1Mary Jane Silva100% (1)
- A Geographical Study of Jewellery Shops in Chandigarh SectorsDocument11 pagesA Geographical Study of Jewellery Shops in Chandigarh SectorsLAKHVEER SINGHNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Single-Laboratory Validation of Methods of Analysis - IUPAC PDFDocument21 pagesGuidelines For Single-Laboratory Validation of Methods of Analysis - IUPAC PDFmraleman717No ratings yet
- Dark Triad and Emotional Intelligence Correlation StudyDocument35 pagesDark Triad and Emotional Intelligence Correlation StudyAlexander Spivey100% (2)
- Hotel Feasibility StudyDocument32 pagesHotel Feasibility StudyKamlesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Gtu Dissertation Report FormatDocument4 pagesGtu Dissertation Report FormatWhereToBuyPapersSingapore100% (1)
- Entire All: C. Probability of Success in Any Given TrialDocument10 pagesEntire All: C. Probability of Success in Any Given Triallana del reyNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence and Transformational Leadership in RetailingDocument9 pagesEmotional Intelligence and Transformational Leadership in RetailingDavid DickensNo ratings yet
- Organizing India's Unorganized Construction SectorDocument3 pagesOrganizing India's Unorganized Construction SectorHasan ArmoghanNo ratings yet
- Primary vs Secondary SourcesDocument19 pagesPrimary vs Secondary SourcesJovy ArellanoNo ratings yet