Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 Answers
Uploaded by
John LebizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 Answers
Uploaded by
John LebizCopyright:
Available Formats
Student book answers
Chapter 2
B2 2.1 Photosynthesis
In-text questions A An organism that makes its own food.
B carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
C chloroplasts
Activity Hypothesis
Credit hypotheses along the lines of: If a plant is placed in the dark for a week,
photosynthesis will decrease/glucose and oxygen will not be produced. Students
should include a suitable plan for testing this hypothesis.
Definitions
Producer – organism that makes its own food. Consumer – organism that has to eat
other organisms to gain energy. Photosynthesis – process where plants make their
own food.
Summary 1 algae, producers, photosynthesis, carbon dioxide, glucose, light (6 marks)
questions 2 Photosynthesis provides energy for plants to grow. Animals cannot make their own food.
Animals have to eat plants to gain energy. (3 marks)
3a Yes because sunlight is available. (1 mark)
b No because no sunlight is available. (1 mark)
c No because there is no sunlight. There are no chloroplasts in the root hair cells. (2
marks)
4 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Carbon dioxide and water are the reactants. Carbon dioxide enters through the stomata in
the leaves. Water enters through root/root hair cells by diffusion/osmosis. Water travels
up the xylem to leaves (transpiration).
Light is also required for photosynthesis to occur. Light is trapped in
chlorophyll/chloroplasts in leaf cells.
Oxygen and glucose are the products. Oxygen comes out through stomata. Glucose is
taken to all cells in the plant (via the phloem). The plant cells use glucose to provide
energy.
B2 2.2 Leaves
In-text questions A They contain chlorophyll.
B top of the leaf
C To reduce evaporation of water.
D They allow gases to diffuse into and out of the leaf. They close to prevent water
loss.
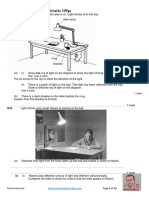
Activity Observing stomata
For the labelled diagram of the underside of a leaf, labels should include: stomata,
guard cells, veins, and, possibly, the waxy cuticle.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
Summary 1 stomata – allow gases to diffuse into and out of the leaf
questions waxy layer – reduces amount of water evaporating
guard cells – open and close stomata
veins – bring water to cells in leaf
cells in palisade layer – main site of photosynthesis (5 marks)
2 To prevent water evaporating. (1 mark)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Leaves contain chlorophyll, which traps light. Leaves are thin, which allows gases to
diffuse in and out of the leaf easily. Leaves have a large surface area to absorb as
much light as possible. Leaves have veins/xylem to transport water to cells. Leaves
have a palisade layer/cells with more chloroplasts near the top of the leaf, to
maximise the absorption of sunlight. Leaves have stomata to allow carbon dioxide
into (and oxygen out of) the leaf.
B2 2.3 Plant minerals
In-text questions A nitrates, phosphates, potassium, and magnesium
B Dissolved in soil water, absorbed through root hair cells.
C A plant is not receiving enough of a particular mineral.
D Chemical product containing plant minerals.
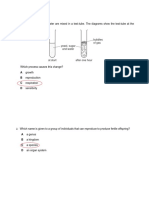
Activity Mineral deficiency
Leaflet should include prompts for farmers in their diagnosis of plants using a labelled
diagram of a healthy plant. Prompts include nitrate deficiency (plant will have poor
growth and older leaves are yellowed), magnesium deficiency (plant leaves will turn
yellow), phosphorus deficiency (plant will have poor root growth, and younger leaves
look purple), and potassium deficiency (plant has yellow leaves with dead patches).
Summary 1 minerals, hair, xylem, magnesium, nitrates (5 marks)
questions 2 Nitrates make amino acids, amino acids join together to make proteins, proteins
needed for growth. (3 marks)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Plants take minerals from the soil. Minerals are absorbed into the plant through root
hairs. Plants use minerals for growth. Plants normally return minerals back to the soil
when they die/leaves are shed. If crops are removed, the minerals are not returned to
the soil. Fertilisers contain minerals. Examples are nitrates, phosphates, and
potassium. A supply of minerals is needed for healthy plant growth. Nitrates are used
to make amino acids, and subsequently proteins. Magnesium is needed to make
chlorophyll.
B2 2.4 Chemosynthesis
In-text questions A Using a chemical reaction to produce glucose.
B carbon dioxide
C sulfur bacteria and nitrogen bacteria
Activity Interesting organisms
Credit research on a different chemosynthetic organism, to be presented to a
partner, for example, iron bacteria or methanobacteria.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
Summary 1 bacteria, reactions, glucose, chemosynthesis (4 marks)
questions 2a sulfur bacteria or nitrogen bacteria (1 mark)
b Light is not available on the sea floor/underground, so they do not possess chloroplasts,
therefore photosynthesis cannot take place. (1 mark)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Seaweed are producers.
They use photosynthesis to create glucose.
Photosynthesis is powered by light energy from the Sun.
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Tubeworms are consumers.
This means they must eat other organisms to survive.
Bacteria within tubeworms produce glucose by chemosynthesis.
Light is not required for chemosynthesis.
Energy for chemosynthesis comes from chemical reactions.
carbon dioxide + water + hydrogen sulfide → glucose + sulfur compounds
B2 2.5 Aerobic respiration
In-text questions A (aerobic) respiration
B glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)
C in the mitochondria
D red blood cells or haemoglobin
E plasma
Activity Defining respiration
Answers should include a definition and a description of aerobic respiration. Students
could include the word equation for aerobic respiration.
Students should swap answers with a partner, and discuss ways to improve their
answers.
Summary 1 mitochondria, respiration, glucose, energy, water (5 marks)
questions 2 Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria. Mitochondria are found in cells.
Oxygen reacts with glucose. It releases carbon dioxide and water, together with
energy. (4 marks)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Inhaling fills alveoli in the lungs with oxygen. Oxygen diffuses into the
bloodstream. Oxygen is carried to the cells in the red blood cells/haemoglobin.
Glucose is taken in through food. Food is digested and glucose is absorbed through
the wall of the small intestine. Glucose is carried to the cells in the blood (plasma).
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria of cells, releasing carbon dioxide and water.
Waste carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs in the blood plasma. Carbon dioxide is
exhaled. Excess water is lost as water vapour in exhaled breath, or in urine.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
B2 2.6 Anaerobic respiration
In-text questions A glucose → lactic acid (+ energy)
B Aerobic respiration releases more energy and doesn’t cause muscle cramps (from lactic
acid).
C glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide (+ energy)
D bread, beer, wine
Activity Useful microorganisms
Credit correct description of how anaerobic respiration is used to make bread, beer,
or wine.
Summary 1 anaerobic, oxygen, energy, lactic acid, cramp, fermentation, ethanol (7 marks)
questions 2 Anaerobic respiration is without oxygen, produces lactic acid, does not produce
water, produces less energy per glucose molecule. Aerobic respiration is with
oxygen, does not produce lactic acid, does produce water, has more energy per
glucose molecule. (3 marks)
3 Example answers (6 marks):
A marathon runner requires energy over a long period of time. A sprinter requires
a lot of energy in a short period of time. A person can only respire anaerobically
for a short period of time but can respire aerobically for a long period of time. A
sprinter requires extra energy for a short period of time. A sprinter cannot take
in enough oxygen to respire aerobically to produce the required amount of energy.
If a runner respires anaerobically for a longer period of time, lactic acid would
build up in their muscles. This would cause cramp.
B2 2.7 Food chains and webs
In-text questions A It is a diagram that shows what an organism eats. It shows the flow of energy between
organisms.
B A herbivore only eats plants, a carnivore only eats other animals.
C A predator eats other animals, whereas prey are eaten by other animals.
D A set of linked food chains.
Activity How much energy?
First level = 1000 kJ
Second level = 0.1 × 1000 kJ = 100 kJ
Third level = 0.1 × 100 kJ = 10 kJ
10 kJ would be passed to the top predator.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
Summary 1 food chain – diagram showing the flow of energy through organisms
questions food web – diagram showing linked food chains
predator – animal that eats another animal
prey – animal that is eaten (4 marks)
2a giraffe/impala/zebra (1 mark)
b acacia tree/grass (1 mark)
c acacia tree (1 mark)
d Credit any suitable answer. For example, grass impala leopard lion
(1 mark for correct order of organisms, 1 mark for arrows in correct direction)
3 Example answers (6 marks):
Grasshopper eats grass, field mouse eats grasshopper, owl eats field mouse.
The producer is the grass.
The herbivore is the grasshopper.
The carnivores are the field mice and the owls.
The predators are the field mice an the owls.
The prey are the grasshoppers and the field mice.
The top predator is the owl.
500 kJ of energy are transferred to the grasshopper.
50 kJ are transferred to the field mouse.
5 kJ are transferred to the owl.
B2 2.8 Disruptions to food chains and webs
In-text questions A Organisms depending on each other to survive, grow, and reproduce.
B Number of animals or plants of the same type that live in the same area.
C Population of consumers will decrease.
D The build-up of (toxic) chemicals through a food chain.
Activity Interpreting food webs
Credit sensible suggestions for what would happen to other organisms in the food
web if disease reduced the population of frogs. For example:
Fox will consume more rabbits and voles, due to lack of frogs. The population of
rabbits and voles would decrease.
Hawks will consume more voles and thrushes, due to lack of frogs. The population of
voles and thrushes would decrease.
Few predators for insects and slugs. The population of insects and slugs may
increase.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
Summary 1 interdependence, decrease, bioaccumulation (3 marks)
questions 2a Rabbit population would increase as it has no predators/it will not get eaten. (2
marks)
b The hawk and fox population may decrease as they have reduced food supplies.
The insect population may increase as they have fewer predators. (4 marks)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
plankton → fish → fish-eating birds
Insecticide runs into river.
Taken up by plankton.
DDT accumulates in fish when they eat the plankton.
One fish eats lots of plankton, but not enough to cause death.
DDT accumulates in birds when they eat the fish.
One bird eats many fish.
DDT level is now so high/concentrated that it causes death in the bird.
B2 2.9 Ecosystems
In-text questions A Name given to plants and animals found in a particular location, and the area/habitat in
which they live.
B The area in which an organism lives.
C A particular place or role occupied by an organism within an ecosystem.
Activity Scientific glossary
Credit key words from this chapter given with definitions. Each key word should be
accompanied by an example or a diagram where possible.
Summary 1 ecosystem – living organisms in a particular area, and the habitat they live in
questions community – plants and animals found in a particular habitat
habitat – place where a plant or animal lives
niche – particular place or role that an organism has in an ecosystem (4 marks)
2 Bees and birds have different niches. They eat different things. Bees require
nectar from flowers, whereas
birds live off insects living on the leaves. (2 marks)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
A niche is the place or role that an organism has in a habitat. For example, many
organisms live in an oak tree (or suitable example). Not every organism lives in
the same part of the tree. Microorganisms at the base of the tree break down old
leaves. This gives the tree further nutrients to absorb for growth. Insects live in
the tree trunk. The insect larvae are food for birds that may live in the canopy.
Squirrels and bees also live in the canopy. Bees gather pollen and nectar when the
tree is in blossom. Squirrels gather acorns as food. The activities of each organism
do not conflict each other, and so different organisms can co-exist.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
B2 Chapter 2 summary
End-of-chapter 1a (aerobic) respiration (1 mark)
questions b mitochondria (1 mark)
c oxygen, carbon dioxide (2 marks)
2a corn mouse owl (1 mark)
b corn (1 mark)
c Producers have energy transferred from glucose.
Consumers have energy transferred from the organisms they eat. (2 marks)
d The spider population would increase as less organisms eat them. (2 marks)
(Alternatively, spider population stays the same/decreases as shrew and mice population
increase due to no predators, so eat the excess spiders.)
3a oxygen (1 mark)
b carbon dioxide and water (2 marks)
c Bubbles would stop/decrease, photosynthesis would stop, as there is no light. (3
marks)
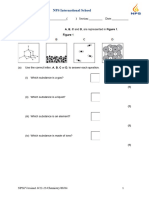
d Stomata allow carbon dioxide in to the leaf and allow oxygen out of the leaf. (2 marks)
4a The mice population would increase as there are no predators/nothing would eat
them. (2 marks)
b The grasshopper population would decrease as shrews and spiders would need to eat
more of them to survive. (2 marks)
c Mice and shrews occupy different niches because they eat different foods. (2 marks)
d Any three from: toxic chemical builds up in the food chain. Owls eat many other
organisms so owls receive a higher dose of the toxic chemical. High levels can cause
death to an organism. Correct use of term bioaccumulation. (4 marks)
5a Minerals are absorbed into root (hair) cells by diffusion. They travel through the
xylem/water vessels to different parts of the plant. (3 marks)
b Magnesium deficiency means less chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs light for
photosynthesis. (2 marks)
c large surface area, contains lots of chloroplasts/chlorophyll, chloroplasts concentrated
in top of leaf/palisade layer. (3 marks)
6 This is a QWC question. Students should be marked on the use of good English,
organisation of information, spelling and grammar, and correct use of specialist scientific
terms. The best answers will provide a full explanation of fermentation, with the process
explained in a logical order (maximum 6 marks).
Examples of correct scientific points:
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration. It occurs in some microorganisms/yeast.
These microorganisms respire in the absence of oxygen.
Energy is transferred from glucose.
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide (+ energy)
The ethanol product can be used in alcoholic drink production.
The carbon dioxide product is used in bread production/to make dough rise.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 2
Answer guide for Big Write
Developing Secure Extending
1–2 marks 3–4 marks 5–6 marks
● The essay has little structure ● The essay contains some ● The essay is well structured,
However, the student has structure, with an attempt to with key ideas clearly presented
correctly used at least two use paragraphing. in separate paragraphs.
scientific terms or one word ● The student has correctly used ● The student has correctly used
equation at least two scientific terms and more than two scientific terms
one word equation. and two word equations.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
You might also like
- Ib Chemistry Revision PDFDocument27 pagesIb Chemistry Revision PDFSrushti71% (7)
- 3.electricity and Magnetism EOT 2021 TestDocument9 pages3.electricity and Magnetism EOT 2021 TestvaraprasadNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry: 5 Kinetics Exam-Style QuestionsDocument9 pagesAQA Chemistry: 5 Kinetics Exam-Style QuestionsKarandip CheemaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Single Replacement Reaction WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemistry Single Replacement Reaction WorksheetNurmuhamed Masirdinov100% (1)
- WCH15 01 2024 Jan QPDocument36 pagesWCH15 01 2024 Jan QPbmaniafuNo ratings yet
- KS3 Chemistry Baseline TestDocument14 pagesKS3 Chemistry Baseline Testfadua barakatNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Sport Lexis Terms Explanatory Dictionary in EnglishDocument788 pagesSport Lexis Terms Explanatory Dictionary in EnglishjovenlouNo ratings yet
- P3 Chapter 1 End-Of-Chapter Test (Foundation)Document6 pagesP3 Chapter 1 End-Of-Chapter Test (Foundation)Paul LloydNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument194 pagesUntitledJack HaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Transport in PlantsDocument45 pagesTopic 8 Transport in PlantsCOXMIC FNNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Conduction and ConvectionDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Conduction and ConvectionJaKyi Whitehead50% (2)
- Solubility InvestigationDocument3 pagesSolubility InvestigationNoaNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Interdependence and Food WebsDocument3 pagesInterdependence and Food WebsArchieNo ratings yet
- 9f Word SheetsDocument2 pages9f Word SheetsbanaliaNo ratings yet
- Particles, Atomic Structure, Ionic Bonding, The Periodic Table CIE iGCSE 0620 PPQDocument12 pagesParticles, Atomic Structure, Ionic Bonding, The Periodic Table CIE iGCSE 0620 PPQsanaahNo ratings yet
- SWH AQA Revision Guide Biology 1Document42 pagesSWH AQA Revision Guide Biology 1afshinNo ratings yet
- English6 Ans WBDocument26 pagesEnglish6 Ans WBSonal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Essential Science Primary 4 Teachers GuideDocument91 pagesEssential Science Primary 4 Teachers GuideCarolyne AchiengNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 8 - 2018 - tcm143-353967Document90 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 8 - 2018 - tcm143-353967Seema ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Biology Binder Final For PrintingDocument196 pagesGrade 8 Biology Binder Final For PrintingSai YeddanapudiNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Geograpy ADocument264 pagesGrade7 Geograpy AJannet YangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Mysteries Summarising and RespondingDocument83 pagesUnit 1 Mysteries Summarising and RespondingAfnan Zarok100% (1)
- KS3 LightDocument19 pagesKS3 LightCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Science Challenge 7 - Part 01Document9 pagesCheckpoint Science Challenge 7 - Part 01KhNo ratings yet
- Challenge Workbook 9 Answers: Unit 1 PlantsDocument29 pagesChallenge Workbook 9 Answers: Unit 1 PlantsLizaaNo ratings yet
- My Photosynthesis Summary Poster March 2016Document1 pageMy Photosynthesis Summary Poster March 2016amr ahmedNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Exam Qs and Ms HomeworkDocument5 pagesStem Cells Exam Qs and Ms HomeworkPauline ZwanikkenNo ratings yet
- G8 Preparation of Salts Lab ExperimentDocument4 pagesG8 Preparation of Salts Lab Experimentaswin100% (1)
- KS3 Science 2005 Paper 1 Level 3-6Document36 pagesKS3 Science 2005 Paper 1 Level 3-6Qiana Hayward100% (2)
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument17 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- 4CH1 1C 2023 Jan MSDocument17 pages4CH1 1C 2023 Jan MSTimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Science Year 7 WB 2nd Edition PDF Chemical Compounds Chlorine 5Document1 pageCambridge Primary Science Year 7 WB 2nd Edition PDF Chemical Compounds Chlorine 5Rafih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Practical Workbook Answers: Exam-Style Questions Practical Investigation 1.1Document27 pagesPractical Workbook Answers: Exam-Style Questions Practical Investigation 1.1Adah JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ks3 Chem 9e Eq Q1to10 54marks 4students Metals and Corrosion 11pgsDocument11 pagesKs3 Chem 9e Eq Q1to10 54marks 4students Metals and Corrosion 11pgsmatthewansell6977No ratings yet
- Year 8 - Food and Digestion and RespirationDocument11 pagesYear 8 - Food and Digestion and RespirationyomnahelmyNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Revision Pack SCIENCEDocument35 pagesYear 7 Revision Pack SCIENCEM KordyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics-and-classification-of-living-organisms-Paper 2 Classified Solved Question CIE IGCSE GCSE OLevel BiologyDocument32 pagesCharacteristics-and-classification-of-living-organisms-Paper 2 Classified Solved Question CIE IGCSE GCSE OLevel BiologyIGCSE Physics & ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Coordinated SciencesDocument166 pagesCoordinated SciencesRaghadNo ratings yet
- Focus Smart Science M2 - AK (WB)Document9 pagesFocus Smart Science M2 - AK (WB)2422 ทัศน์พล เพ็ญสังข์No ratings yet
- Contentdamone Dot Comone Dot Cominternational Schoolspdfsilower Secondaryinspire English InternatDocument24 pagesContentdamone Dot Comone Dot Cominternational Schoolspdfsilower Secondaryinspire English InternatErny MasiloNo ratings yet
- G9 Metals and Reactivity TESTDocument4 pagesG9 Metals and Reactivity TESTMiral AlasbahiNo ratings yet
- Free Cambridge Checkpoint Science Workbook 8 PDFDocument5 pagesFree Cambridge Checkpoint Science Workbook 8 PDFWin Myat ThuzarNo ratings yet
- Physics: Revising For Your Physics ExamsDocument10 pagesPhysics: Revising For Your Physics ExamsKamrul Hasan SagarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Science Scheme of Work Learning Objectives Stage 2Document4 pagesCambridge Primary Science Scheme of Work Learning Objectives Stage 2Carolyne AchiengNo ratings yet
- Density Worksheet HADocument2 pagesDensity Worksheet HALê Phạm Ngọc KhánhNo ratings yet
- Pri Eng 2ed Tr5 Language Skills and Vocab Dev AnswersDocument7 pagesPri Eng 2ed Tr5 Language Skills and Vocab Dev AnswersMrs Nneoma Ndoma egbaNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science Scheme of WorkDocument90 pagesYear 8 Science Scheme of WorkMimiNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE GuideDocument20 pagesBiology IGCSE GuideJeremiah SinggihNo ratings yet
- Mce Igcse Chemistry PPT c02Document27 pagesMce Igcse Chemistry PPT c02Lim Khee HanNo ratings yet
- Compiled Reviewer For Midterm ExamDocument12 pagesCompiled Reviewer For Midterm ExamMelony Dela fuenteNo ratings yet
- Human respiratory system model explainedDocument7 pagesHuman respiratory system model explainedPRIYA100% (1)
- The Diagram Shows A Mother Fox and Her CubsDocument11 pagesThe Diagram Shows A Mother Fox and Her CubsTansra KaurNo ratings yet
- Earth in Space - Level 6 - QuestionsDocument3 pagesEarth in Space - Level 6 - Questionsmanoj0% (1)
- Unit of Study PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesUnit of Study PhotosynthesisNaurah Khairiyah RumakatNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Physics Chapter1 AnswersDocument5 pagesActivate 1 Physics Chapter1 AnswersPapi ParikhNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Biology Revision GuideDocument13 pagesYear 8 Biology Revision GuideKHAUSALYA A/P VERAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Revision of Specialised Cells: Name of Organelles FunctionDocument2 pagesRevision of Specialised Cells: Name of Organelles Functioncheezypeezy100% (1)
- The HodgehegDocument15 pagesThe HodgehegVenugopalan ManaladikalamNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Answers: RememberingDocument13 pages3.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowJunriel Arig BonachitaNo ratings yet
- 7_SolubilityDocument4 pages7_SolubilityJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W10Document1 pageT1W10John LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W4(Revision)Document4 pagesT1W4(Revision)John LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W9Document1 pageT1W9John LebizNo ratings yet
- Booking Confirmation - 28342216136Document2 pagesBooking Confirmation - 28342216136John LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 3 Physics Chapter1 AnswersDocument7 pagesActivate 3 Physics Chapter1 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 AnswersDocument4 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter1 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz0% (1)
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Answers To Lesson 5 Mark SchemeDocument2 pagesAnswers To Lesson 5 Mark SchemeJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument4 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- NPS International SchoolDocument2 pagesNPS International SchoolJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Physics Worksheet 1Document3 pagesGrade 7 Physics Worksheet 1John LebizNo ratings yet
- Nobody's Home - Integrity - EditDocument15 pagesNobody's Home - Integrity - EditJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- CME - LP 3 Honesty in The Family - Integrity - Edit2015Document2 pagesCME - LP 3 Honesty in The Family - Integrity - Edit2015John LebizNo ratings yet
- 1a (I) (1) (A) (Ii) (1) (A) (Iii) (1) (Iv) (1) B (1) (1) (1) Number Mark 2 (A)Document2 pages1a (I) (1) (A) (Ii) (1) (A) (Iii) (1) (Iv) (1) B (1) (1) (1) Number Mark 2 (A)John LebizNo ratings yet
- ADDITION REACTIONSDocument21 pagesADDITION REACTIONSJaqen H'gharNo ratings yet
- Section 2.3 Chemical Properties: Reading StrategyDocument2 pagesSection 2.3 Chemical Properties: Reading StrategyBobNo ratings yet
- CCW SystemDocument2 pagesCCW SystemAbdulyunus AmirNo ratings yet
- Mitigation of Internal Corrosion in Carbon Steel Gas Pipeline SystemsDocument24 pagesMitigation of Internal Corrosion in Carbon Steel Gas Pipeline Systemsakshat agrawalNo ratings yet
- Acumer5000 PDFDocument13 pagesAcumer5000 PDFdalton2003No ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 8 Fuels and Earth Science - Edexcel Chemistry GCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 8 Fuels and Earth Science - Edexcel Chemistry GCSEsamNo ratings yet
- Water Quality ParametersDocument5 pagesWater Quality ParametersAsyraf Malik100% (2)
- 7T Respiration in Plants and AnimalsDocument22 pages7T Respiration in Plants and AnimalsPOONAM SHARMANo ratings yet
- Puritan-Bennett Companion Liquid Oxygen - Technical ManualDocument82 pagesPuritan-Bennett Companion Liquid Oxygen - Technical ManualNasro JuvNo ratings yet
- 2004 TOEFL Reading Comprehension and Structure QuestionsDocument19 pages2004 TOEFL Reading Comprehension and Structure QuestionsJuli CrudoNo ratings yet
- Process Design and Energy Requirements For The Capture of CO2 From AirDocument12 pagesProcess Design and Energy Requirements For The Capture of CO2 From AirKeena RahimNo ratings yet
- PTFE Release Agent Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesPTFE Release Agent Safety Data SheetNICKYNo ratings yet
- CO2 Storage Tank Product Manual WsDocument34 pagesCO2 Storage Tank Product Manual WsGalang Hanif AbdulahNo ratings yet
- Thermal CuttingDocument18 pagesThermal CuttingSarah100% (1)
- 9.8 Endothermic and ExothermicDocument24 pages9.8 Endothermic and ExothermicHema LataNo ratings yet
- Philippines Animal ExtinctionDocument45 pagesPhilippines Animal ExtinctionRoa CabanelaNo ratings yet
- FireDocument35 pagesFireAdmin Bataraza Fire Station PalawanNo ratings yet
- Minimax BrochureDocument20 pagesMinimax BrochureDevieAgungNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Notes + Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 4Document9 pagesForm 2 Science Notes + Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 4Kelvin100% (4)
- Science 2&3 SymbolsDocument11 pagesScience 2&3 SymbolsThadicherlaHrishithNo ratings yet
- Understanding Elements and CompoundsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Elements and CompoundsDeborah Mae MondoyNo ratings yet
- 6.7 Pipeline Material Selection Corrosion Protection and Monitoring PhilosophyDocument13 pages6.7 Pipeline Material Selection Corrosion Protection and Monitoring Philosophyadenlan100% (3)
- Newlife FamilyDocument420 pagesNewlife FamilyRobel MTNo ratings yet
- Earth Math Classroom ActivitiesDocument106 pagesEarth Math Classroom ActivitiesAviation/Space History Library100% (1)
- HSC June 2009 Paper and Marking Scheme On Same Paper Word DocumentDocument26 pagesHSC June 2009 Paper and Marking Scheme On Same Paper Word DocumentreekoyeNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Ozone LayerDocument33 pagesCase Study On Ozone LayerVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4325 Mark Scheme November 05 P1F FINALDocument12 pagesIGCSE Biology 4325 Mark Scheme November 05 P1F FINALVarun PanickerNo ratings yet