Professional Documents
Culture Documents
#2electrophysiology of The Heart
Uploaded by
2A - Nicole Marrie Honrado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views8 pagesOriginal Title
#2Electrophysiology of the Heart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views8 pages#2electrophysiology of The Heart
Uploaded by
2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
OF THE HEART
Dr. Alma Sorrera-Banua
Faculty, BUCN
Electrophysiology: Cardiac
electrical activity
• result of movement of (+) and (-)
charged ions such as: Na, Ca & K
across the cell membrane.
• Therefore change in serum Ca & K
concentration may alter heart’s
contraction
• Cardiac action potential- electrical
changes recorded within a single cell
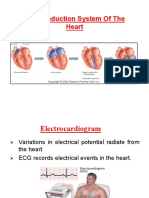
Electrophysiology
Bundle
60-100/ min of his
SA Node
AV Node
40-60/min
Purkinjie Fibers 30-40/min
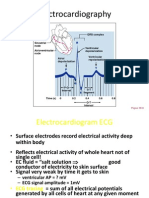
ECG: Record
P wave- Atrial
contraction
QRS
–ventricular
contraction
T wave –
reporalization/
resting
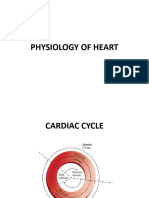
CARDIAC CYCLE
DIASTOLE
üRelaxation,
fills with blood
from coronary
arteries
üS2 (dub)
üAortic &
pulmonary
valves close
CARDIAC CYCLE
§ Ventricular
contraction/ejection
(CO)
§ 1st heart sound-
S1(lub)
§ Mitral & tricuspid
valves close
§ Aortic & Pulmonary
valves open & blood is
ejected to PA into
lungs then to Aorta
then to BODY.
Cardiac Cycle
Diastole/repolarization Systole/depolarization
ü Relaxation, fills with blood • Ventricular
from coronary arteries contraction/ejection (CO)
ü S2 (dub) • 1st heart sound- S1(lub)
ü Aortic & pulmonary • mitral & tricuspid valves
valves close close
• Aortic & Pulmonary valves
open & blood is ejected to
PA into lungs then to Aorta
then to body.
Normal Heart Sounds: S1 S2
Extra heart Sounds: S3 S4
You might also like
- Reviewer 2 Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesReviewer 2 Health AssessmentchristinejeancenabreNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument74 pagesCardiovascular Systemاسامة محمد السيد رمضانNo ratings yet
- ECG ECG Basics PresentationDocument45 pagesECG ECG Basics PresentationLan Anh Pham100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System: DR Charles A Simanjuntak, DR, Spot (K), MPDDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System: DR Charles A Simanjuntak, DR, Spot (K), MPDRobiatulAdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest: April B. Perez, RN, Man, PHD, FpchaDocument50 pagesCardiac Arrest: April B. Perez, RN, Man, PHD, Fpchayuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Module Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesModule Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyPATRICIA KAYE RIONo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument172 pagesCardiovascular Anatomy & PhysiologyYS NateNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument40 pagesCardiovascularÁñèsh Kåøs100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System Study SheetDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System Study SheetTkNo ratings yet
- APEC 611 Scientific and Industrial Instrumentation: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document22 pagesAPEC 611 Scientific and Industrial Instrumentation: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Faisal Bin KashemNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular SystemArtika MayandaNo ratings yet
- Conduction System of Heart-FinalDocument69 pagesConduction System of Heart-FinalAshish ChavanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conduction in The HeartDocument35 pagesElectrical Conduction in The HeartNormasnizam Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgDocument38 pagesGroup 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgTimothy John Bautista100% (2)
- Physiology of HeartDocument74 pagesPhysiology of Heartmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Jantung: Paulus Ola, L, S.KP, RNDocument58 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Jantung: Paulus Ola, L, S.KP, RNmardi supriyansahNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument116 pagesCardioJohnryl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Lawrence A. Olatunji ReaderDocument46 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Lawrence A. Olatunji ReaderMaryam Ogunade0% (1)
- ECG1Document67 pagesECG1Farhan RosliNo ratings yet
- EKG ReviewDocument18 pagesEKG ReviewBalaji BscRTNo ratings yet
- Elektrokardiografi Dasar: Dr. Eka Ginanjar, SPPDDocument81 pagesElektrokardiografi Dasar: Dr. Eka Ginanjar, SPPDNur Rahmat WibowoNo ratings yet
- 1 Heart Anatomy and FunctionDocument38 pages1 Heart Anatomy and Functionsyanita dwi nanda Sulistyani putriNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CyclebhatsindhoorNo ratings yet
- 5a - EKG - 1Document69 pages5a - EKG - 1Sana Ivanovic100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesECG Interpretationsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Notes CardioDocument8 pagesTopic 9 Notes Cardioapi-388956899No ratings yet
- Adi Bestara EKG at A Glance NewestDocument113 pagesAdi Bestara EKG at A Glance Newestkarpax21100% (1)
- MUCLecture 2021 1292271Document34 pagesMUCLecture 2021 1292271Kouka MahfoudiNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : Presented By: Elgeene E. DizonDocument41 pagesElectrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : Presented By: Elgeene E. DizonElgeene DizonNo ratings yet
- HPP Lec Cvs2Document4 pagesHPP Lec Cvs2carlo baculiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument13 pagesCardiovascular AssessmentKathryn Bianca AcanceNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument55 pagesCardiovascular Physiologys8f2dmzdvjNo ratings yet
- How To Read An EcgDocument86 pagesHow To Read An EcgmajdNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The HeartDocument34 pagesPhysiology of The Heartalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument6 pagesCardiac CycleAmit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument21 pagesCardiovascular AssessmentRhitzle AnnNo ratings yet
- 3 EcgDocument34 pages3 EcgAYSHA ANWARNo ratings yet
- Ecg Abdallah - Copy - MergedDocument329 pagesEcg Abdallah - Copy - MergedAya AlntshNo ratings yet
- Medical Test:: ElectrocardiogramDocument26 pagesMedical Test:: ElectrocardiogramMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogra (M) PhyDocument26 pagesElectrocardiogra (M) PhyyansliyaNo ratings yet
- 03 Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyDocument17 pages03 Cardiopulmonary Physiologyice cream1000791100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Physiology 1Document44 pagesCardiovascular Physiology 1maxmus4No ratings yet
- CardioDocument106 pagesCardioPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- Review of The Anatomy of The HeartDocument9 pagesReview of The Anatomy of The HeartJhasseryne Orias SanchezNo ratings yet
- MCB136 SP 22 MT2 Study GuideDocument4 pagesMCB136 SP 22 MT2 Study GuideJeffrey JèwNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared byDocument16 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared bypipoahmed51No ratings yet
- Assessment of The Heart and Neck VesselsDocument10 pagesAssessment of The Heart and Neck VesselsJasmin MolanoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleEdi HidayatNo ratings yet
- 20 2021年1月19日 - IUHW1年生心電図講義1限 - 相澤義泰Document37 pages20 2021年1月19日 - IUHW1年生心電図講義1限 - 相澤義泰Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 5 PDFDocument50 pagesLab Exercise 5 PDFE1- Villapaz, Aiemarie R. (Aie)No ratings yet
- Chapter 020Document4 pagesChapter 020lish9990No ratings yet
- Cardio AssessmentDocument104 pagesCardio Assessmentlowell.cerezo.ihsNo ratings yet
- Santosh DevDocument45 pagesSantosh Devdevdsantosh100% (1)
- ECG Complete LectureDocument33 pagesECG Complete LectureDr. SUVA NATHNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds: Abu Ahmed 2019Document22 pagesHeart Sounds: Abu Ahmed 2019Khalid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (Ecg) : Presented By: Fahad I. HussienDocument102 pagesElectrocardiography (Ecg) : Presented By: Fahad I. HussienMustafa A. DawoodNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physical ExaminationDocument28 pagesCardiovascular Physical ExaminationYusrina AdaniNo ratings yet
- The Conduction System of The HeartDocument25 pagesThe Conduction System of The HeartFarhanNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- Psychobiologic Bases of BehaviorDocument34 pagesPsychobiologic Bases of Behavior2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) & Hiatal Hernia: MedsurgicalDocument2 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) & Hiatal Hernia: Medsurgical2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Awareness and Perception On Contraception Among Women of Reproductive Age Attending Senawang Health ClinicDocument7 pagesKnowledge, Awareness and Perception On Contraception Among Women of Reproductive Age Attending Senawang Health Clinic2A - Nicole Marrie Honrado100% (1)
- #1anaphy HeartDocument19 pages#1anaphy Heart2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- #6risks To CVDDocument27 pages#6risks To CVD2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument15 pagesHiatal Hernia2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- #7assess CV Function Physical ExamDocument27 pages#7assess CV Function Physical Exam2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- CHN ReviewerDocument1 pageCHN Reviewer2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- I. Community OrganizingDocument2 pagesI. Community Organizing2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- CHN ReviewerDocument2 pagesCHN Reviewer2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- CHN Reviewer Topic 1Document1 pageCHN Reviewer Topic 12A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Family and The CommunityDocument3 pagesConcept of Family and The Community2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Promotive and Preventive Health Aspect in CHN & Facts On Healthcare in PHDocument2 pagesPromotive and Preventive Health Aspect in CHN & Facts On Healthcare in PH2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Focus Charting in Pedia WardDocument32 pagesFocus Charting in Pedia Ward2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- (NOTES 1) What Is HistoryDocument2 pages(NOTES 1) What Is History2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- (NOTES 2) Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument2 pages(NOTES 2) Analysis and Interpretation of Data2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Focus Charting in Pediatric Ward: Medsurgical ClinicalDocument2 pagesFocus Charting in Pediatric Ward: Medsurgical Clinical2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- HONRADO-Group 3 - Pedia NCPDocument7 pagesHONRADO-Group 3 - Pedia NCP2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- EINC Handout by Nicole Honrado BSN 2ADocument7 pagesEINC Handout by Nicole Honrado BSN 2A2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- EINC Checklist - DOHDocument2 pagesEINC Checklist - DOH2A - Nicole Marrie Honrado100% (4)
- Program Implementation With The Health Team: Packages of Essential Services For Primary HealthcareDocument1 pageProgram Implementation With The Health Team: Packages of Essential Services For Primary Healthcare2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Checklist SummarizedDocument1 pageChecklist Summarized2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Organization of USAPANDocument3 pagesIntroduction and Organization of USAPAN2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet