Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nyxv Nyxwv Nyxg ENA ELI ENU LRS LCB LGS: Science & Justice 62 (2022) 327-335 S. Skobeeva Et Al
Uploaded by
THE IMAN'S YOUTUBEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nyxv Nyxwv Nyxg ENA ELI ENU LRS LCB LGS: Science & Justice 62 (2022) 327-335 S. Skobeeva Et Al
Uploaded by
THE IMAN'S YOUTUBECopyright:
Available Formats
S. Skobeeva et al.
Science & Justice 62 (2022) 327–335
0
-5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30
NYXV
NYXWV
PC2 (1%)
-1
NYXG
ENA
-2 ELI
ENU
LRS
-3
LCB
LGS
-4
-5
PC1 (99%)
1.5
NYXV
NYXWV
1
NYXG
LRS
0.5 LCB
LGS
0
PC2 (1%)
-8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8
-0.5
-1
-1.5
-2
PC1 (99%)
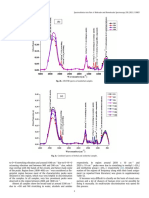
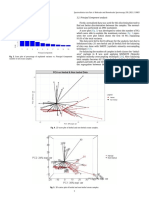
Fig. 2. 2D PCA scores plot of lighter foundation shades (Table 1, samples 1–3, 7–9, 13–15) all together (2.1) and zoomed in part of the scores plot (2.2). The first two
Principal Components were used, both of which contributed to sample separation. Foundation sample clustering appears to be based on colour, for example, lighter
shades NYX V and NYX WV group together.
classes or none [27]. While hard analysis may lead to misclassification of were very similar to each other in colour, were more likely to be mis
a sample, such risk could be reduced by expanding the cosmetics classified [39], similar to what was observed with NYX V, NYX WV and
database. LES, LEB samples. In addition, there seemed to be a variation among
Sharma and colleagues [20] constructed PCA-LDA classification different batches produced by the same manufacturer [40], which led to
model which could classify all samples with 100% accuracy, however, lower classification accuracy (81.48%). Kaur and coworkers [41] ach
only fair, light, and medium shades were used, which could have ieved 100% classification accuracy with LDA when samples were ana
contributed to high classification accuracy. As observed in section 3.2 lysed in three individual groups separated by colour (brown, pink, red).
and 3.3, lighter foundation shades tended to be classified more accu LDA classification accuracy and sensitivity could potentially be
rately and had lower FPR (median 0.0% and average 0.3%) compared to improved by separating the foundation database in groups by colour,
darker shades (median 0.5% and average 0.5%). Studies done on other similar to studies done on lipsticks [39,41].
types of cosmetics, such as lipsticks [39–41] and vermilion (sindoor) Type of material used as a matrix for smears did not appear to affect
[42], similar level of accuracy was achieved. With lipsticks, samples that classification results in a meaningful way, which was likely because the
332
You might also like
- Schematic - Automatic Water Level Controller - 2022-02-06Document1 pageSchematic - Automatic Water Level Controller - 2022-02-06StudyNo ratings yet
- D75 Man Part2Document34 pagesD75 Man Part2Francarlo FogaçaNo ratings yet
- KP701 FL200 Ismob: Not To ScaleDocument1 pageKP701 FL200 Ismob: Not To ScaleJorge JorgeNo ratings yet
- Supply: Mesin G Mesin G Mesin G Mesin GDocument1 pageSupply: Mesin G Mesin G Mesin G Mesin GFerdi BayuNo ratings yet
- Sbae - Rnav Lutvi 1a - Nevku 1a - Oprak 1a Rwy 35 - Sid - 20180524Document1 pageSbae - Rnav Lutvi 1a - Nevku 1a - Oprak 1a Rwy 35 - Sid - 20180524Edoardo MarkezNo ratings yet
- IGT Trimline Motherboard I960 (759-093-11) PDFDocument5 pagesIGT Trimline Motherboard I960 (759-093-11) PDFdgb2227100% (1)
- Key Pad LCD Controller: KHZ HZ WF Esc Mode 3 6 9 DPDocument1 pageKey Pad LCD Controller: KHZ HZ WF Esc Mode 3 6 9 DPaless2056No ratings yet
- 60765B, 04Document2 pages60765B, 04Oscar beltranNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno: Loadcell - 1 IN HX711 A+ Tombol1 E-SCK Loadcell - 2 GND GND A - Echo Ultrasonic Trig GND 12VDC IC1 12VDC 5V GNDDocument1 pageArduino Uno: Loadcell - 1 IN HX711 A+ Tombol1 E-SCK Loadcell - 2 GND GND A - Echo Ultrasonic Trig GND 12VDC IC1 12VDC 5V GNDAndri AstinoNo ratings yet
- Schematic 2.4G Telecontrol Board 2021-07-15Document1 pageSchematic 2.4G Telecontrol Board 2021-07-15Ash VigilNo ratings yet
- SolderingStation2 Schematic v2.4Document1 pageSolderingStation2 Schematic v2.4bela.gondaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Blue Print I Puc 2023-24Document2 pagesComputer Science Blue Print I Puc 2023-24riscomputersirNo ratings yet
- All Use SMD Component If Possible: Snap Off BoardDocument6 pagesAll Use SMD Component If Possible: Snap Off Board王军No ratings yet
- Exploded Views and Parts List: Digital Laser MFP The Keynote of ProductDocument25 pagesExploded Views and Parts List: Digital Laser MFP The Keynote of Productlee sin yong xiuNo ratings yet
- FRC NI RoboRIO User Manual PDFDocument31 pagesFRC NI RoboRIO User Manual PDFJuan de Dios Alardín HernándezNo ratings yet
- RoboRIO ManualDocument31 pagesRoboRIO ManualHectorNo ratings yet
- X5 GT Wiring DiagramDocument2 pagesX5 GT Wiring DiagramBrian Thompson0% (1)
- Power In: Samyung Enc Co.,LtdDocument1 pagePower In: Samyung Enc Co.,LtdjasonelectronicsphilNo ratings yet
- DFR0063 v1.2 Schematic PDFDocument1 pageDFR0063 v1.2 Schematic PDFljubimirNo ratings yet
- SolderingStation2 Schematic v2.7Document1 pageSolderingStation2 Schematic v2.7bela.gondaNo ratings yet
- SolderingStation2 Schematic v2.6Document1 pageSolderingStation2 Schematic v2.6bela.gondaNo ratings yet
- PICKit2 Clone - SchematicDocument1 pagePICKit2 Clone - SchematicArmando HernandezNo ratings yet
- Connection Dengan BeumerDocument1 pageConnection Dengan BeumerAshona Maulana FahmiNo ratings yet
- Stany Alpha V 1.0.0.1 COMPLETODocument1 pageStany Alpha V 1.0.0.1 COMPLETOLeonardo QuinteroNo ratings yet
- OpticalpickupDocument2 pagesOpticalpickupVipin VcNo ratings yet
- Bias Oscillator With Single TransistorDocument1 pageBias Oscillator With Single TransistorFederico PunteriNo ratings yet
- Road Proposal MAP-ModelDocument1 pageRoad Proposal MAP-Modelyenebeb tarikuNo ratings yet
- Appendix 6 TemplateDocument30 pagesAppendix 6 TemplateCakasana AlifNo ratings yet
- RTD 10 20 W RaDocument59 pagesRTD 10 20 W RaRicardo Molina SánchezNo ratings yet
- Corrolla 2014Document11 pagesCorrolla 2014Rum Zin ApellidosNo ratings yet
- Schematic - AVR Colour LCD Tester - LCR TC1 - 20180912214500 PDFDocument1 pageSchematic - AVR Colour LCD Tester - LCR TC1 - 20180912214500 PDFanshumantech anshumantech0% (1)
- JVC RX-9010VBK Service ManualDocument21 pagesJVC RX-9010VBK Service ManualklynsdadNo ratings yet
- Schematic For The STK551U3A2AGEVB Evaluation BoardDocument1 pageSchematic For The STK551U3A2AGEVB Evaluation BoardDouglas FurlanNo ratings yet
- DVDD DVDD Exp3V 5vin Fpga5V MSCK MCSN: Userout6 Userout5 Userout4 Userout3 Userout2 Userout1 Userout0Document1 pageDVDD DVDD Exp3V 5vin Fpga5V MSCK MCSN: Userout6 Userout5 Userout4 Userout3 Userout2 Userout1 Userout0Gopakumar KNo ratings yet
- Pijp201 Pijp202 Pijp203 Pijp204: Pisp102Document1 pagePijp201 Pijp202 Pijp203 Pijp204: Pisp102luigigerula100% (1)
- Typical 6 Units Steel Cabinet EnclosureDocument1 pageTypical 6 Units Steel Cabinet EnclosureMark John DrilonNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document2 pagesSheet 2Jesus Crispin100% (1)
- AK-AT42QT1010 - Capacitive Touch Button: BoardDocument1 pageAK-AT42QT1010 - Capacitive Touch Button: BoardMiquel BallesterNo ratings yet
- Electronically Controlled TransmissionDocument8 pagesElectronically Controlled TransmissionEsteban LefontNo ratings yet
- DRV To stm32f4xxDocument1 pageDRV To stm32f4xxFriendy PrasetiawanNo ratings yet
- JOHNEL Model - PDF 1Document1 pageJOHNEL Model - PDF 1john02 deanNo ratings yet
- Schematic 150mainDocument1 pageSchematic 150mainjijil1100% (2)
- SolderingStation2 Schematic v2.5Document1 pageSolderingStation2 Schematic v2.5Steven ChanNo ratings yet
- ATMEGA64M1 - CanBoard V1Document1 pageATMEGA64M1 - CanBoard V1Fabian Alfonso100% (1)
- Izlazni Prekidaki Moduli Mikrokomtroler I Logika: TitleDocument1 pageIzlazni Prekidaki Moduli Mikrokomtroler I Logika: TitleDanijel MacakanjaNo ratings yet
- Thomson 32lb220b4 Chassis Ifc228-LcdDocument19 pagesThomson 32lb220b4 Chassis Ifc228-LcdwgononNo ratings yet
- Use The Designated Fuse & Relay Only: SD100-1 Fuse & Relay Information (1) I/P Junction BoxDocument4 pagesUse The Designated Fuse & Relay Only: SD100-1 Fuse & Relay Information (1) I/P Junction BoxAndrésNo ratings yet
- Schematic PrintsDocument1 pageSchematic Printsgeo automNo ratings yet
- IC5301 C1BA00000407 Q5154 2SB0709AHL:: Main Signal LineDocument1 pageIC5301 C1BA00000407 Q5154 2SB0709AHL:: Main Signal LinewilfreddelgadoNo ratings yet
- 12Vdc Power Supply: Lcd1 Buz1Document1 page12Vdc Power Supply: Lcd1 Buz1kalsiumbikarbon4493No ratings yet
- 4x4 DriveDocument1 page4x4 DriveJoil LeandroNo ratings yet
- Pipower01 Pipower02 Pipower02 Pipower01: NL9 NlresetDocument1 pagePipower01 Pipower02 Pipower02 Pipower01: NL9 NlresetMario Felix MartinezNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram FH (4) : Volvo Trucks. Driving ProgressDocument404 pagesWiring Diagram FH (4) : Volvo Trucks. Driving ProgressXair367% (3)
- Digital Torque Indicator For IndofabDocument1 pageDigital Torque Indicator For IndofabGulzar KkNo ratings yet
- LKS NAS 2020 16 ESP ProjectOutputDocument3 pagesLKS NAS 2020 16 ESP ProjectOutputdwiaguspurwantoNo ratings yet
- Schematic - Full Protocol Power Bank IP5358 - 2021!02!22Document1 pageSchematic - Full Protocol Power Bank IP5358 - 2021!02!22risirarocksNo ratings yet
- Jura XJ9 Wiring DiagramDocument3 pagesJura XJ9 Wiring DiagramGrom Neposeda50% (2)
- 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - X24VDC - X24VDC - S01: 1551429 4tpe1551429n0007Document2 pages10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - X24VDC - X24VDC - S01: 1551429 4tpe1551429n0007Ngọc Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Assessment of Fingermark Detection TechniquesDocument1 pageGuidelines For The Assessment of Fingermark Detection TechniquesTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Phase 1 (Pilot Studies Section 3) Involves Initial PilotDocument1 pagePhase 1 (Pilot Studies Section 3) Involves Initial PilotTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Phase 4 (Operational Evaluation & Casework: Trials Section 6) Focuses On Eventual CaseworkDocument1 pagePhase 4 (Operational Evaluation & Casework: Trials Section 6) Focuses On Eventual CaseworkTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- T. Casey, Et Al. Vibrational Spectroscopy 109 (2020) 103065Document1 pageT. Casey, Et Al. Vibrational Spectroscopy 109 (2020) 103065THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- 2.1 General: 2 Key VariablesDocument1 page2.1 General: 2 Key VariablesTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Table 5: Science & Justice 62 (2022) 327-335 S. Skobeeva Et AlDocument1 pageTable 5: Science & Justice 62 (2022) 327-335 S. Skobeeva Et AlTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- A. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803Document1 pageA. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- 6Document1 page6THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Det ÐWÞ Det ÐTÞ: R. Kumar, V. Sharma / Trends in Analytical Chemistry 105 (2018) 191 E201 192Document1 pageDet ÐWÞ Det ÐTÞ: R. Kumar, V. Sharma / Trends in Analytical Chemistry 105 (2018) 191 E201 192THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Science & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlDocument1 pageScience & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Science & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlDocument1 pageScience & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Chemometric Methods in FS 2Document11 pagesChemometric Methods in FS 2THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- A. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803Document1 pageA. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- 3.2. Construction of A Binary PCA Model: Science & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlDocument1 page3.2. Construction of A Binary PCA Model: Science & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Science & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlDocument1 pageScience & Justice 62 (2022) 349-357 C. Prakash Sharma Et AlTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- A. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803Document1 pageA. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- 2.1. Sample Preparation 2.3. Spectral Analysis: 2. Materials and MethodsDocument1 page2.1. Sample Preparation 2.3. Spectral Analysis: 2. Materials and MethodsTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Procida HoneychurchDocument1 pageProcida HoneychurchTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Fig. 3 Fig. 3Document1 pageFig. 3 Fig. 3THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Microchemical Journal 180 (2022) 107620 G. Wang Et Al.: Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3Document1 pageMicrochemical Journal 180 (2022) 107620 G. Wang Et Al.: Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3 Fig. 3THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- X. Wei, K. Yu, H. Wu Et Al. Forensic Science International 333 (2022) 111205Document1 pageX. Wei, K. Yu, H. Wu Et Al. Forensic Science International 333 (2022) 111205THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- A. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803Document1 pageA. Sharma, R. Chauhan, R. Kumar Et Al. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 258 (2021) 119803THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction: Procida HoneychurchDocument1 page1 - Introduction: Procida HoneychurchTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Microchemical Journal 180 (2022) 107620 G. Wang Et AlDocument1 pageMicrochemical Journal 180 (2022) 107620 G. Wang Et AlTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Fig. 2 Fig. 2: 3.1. Classification Model of Human and Non-Human Bloodstains On Cotton CarriersDocument1 pageFig. 2 Fig. 2: 3.1. Classification Model of Human and Non-Human Bloodstains On Cotton CarriersTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Chemometric Methods in FS 1Document18 pagesChemometric Methods in FS 1THE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Chemometric Methods in FS VERY GOOD TutorialDocument35 pagesChemometric Methods in FS VERY GOOD TutorialTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- 2.3. Multivariable Statistical Analysis: 2. Materials and MethodsDocument1 page2.3. Multivariable Statistical Analysis: 2. Materials and MethodsTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- Forensic Science InternationalDocument9 pagesForensic Science InternationalTHE IMAN'S YOUTUBENo ratings yet
- QC Tools ProblemsDocument5 pagesQC Tools ProblemsernestoNo ratings yet
- Become A Sap PP Consultant & Job Profile: Learn More About Highly Paid Jobs in ITDocument9 pagesBecome A Sap PP Consultant & Job Profile: Learn More About Highly Paid Jobs in ITHaythem NoukazNo ratings yet
- Toyota SCMDocument10 pagesToyota SCMsampathfriendNo ratings yet
- ReviewerrrrrDocument8 pagesReviewerrrrrDEVALISMNo ratings yet
- 121 OPM Product Development User GuideDocument440 pages121 OPM Product Development User Guidesand_reddyNo ratings yet
- Gaiger - Aesthetics and PaintingDocument205 pagesGaiger - Aesthetics and PaintingEmil Sennewald100% (1)
- 2-Way Slab Design To Aci Trial Version)Document8 pages2-Way Slab Design To Aci Trial Version)Abdul KabasyNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometry Theory - eDocument20 pagesInverse Trigonometry Theory - ethinkiitNo ratings yet
- On Minimal Number of Terms in Representation of Natural Numbers As A Sum of Fibonacci NumbersDocument2 pagesOn Minimal Number of Terms in Representation of Natural Numbers As A Sum of Fibonacci NumbersCharlie PinedoNo ratings yet
- Shovel Truck SystemDocument7 pagesShovel Truck Systemفردوس سليمان100% (1)
- Tekla Quick RefrenceDocument2 pagesTekla Quick RefrenceAtul Kumar Engineer100% (1)
- Tourism MGT DefinitionDocument4 pagesTourism MGT DefinitionAvery Jan Magabanua SilosNo ratings yet
- PuzzlesDocument9 pagesPuzzlespraveen_1288No ratings yet
- Vision: University of The AssumptionDocument10 pagesVision: University of The AssumptionJC Parilla Garcia100% (1)
- Time ManagementDocument157 pagesTime Managementpar8528100% (1)
- RWBY - AlternateDocument59 pagesRWBY - AlternateManuela BuzovNo ratings yet
- Earth Work and Channel InstallationDocument7 pagesEarth Work and Channel Installationrefaalana4No ratings yet
- Tess' Fateful LifeDocument19 pagesTess' Fateful LifeSufi Ikrima Sa'adahNo ratings yet
- Leadership Case PDFDocument2 pagesLeadership Case PDFJawahirul MahbubiNo ratings yet
- Earth Moving Machinery BS en 474-8Document14 pagesEarth Moving Machinery BS en 474-8Augusto RiveraNo ratings yet
- For November 16 Asynchronous SessionDocument2 pagesFor November 16 Asynchronous Sessiongabriel sansebastianNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For PodcastDocument75 pagesOptics and Refraction For Podcastapi-213285088No ratings yet
- Online College Registration System Sample DocumentationDocument5 pagesOnline College Registration System Sample DocumentationHamza Wiz-Ziboi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Samsung Secrete Codes PDFDocument4 pagesSamsung Secrete Codes PDFRupesh911No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Rubric-BiomesDocument1 pagePowerpoint Rubric-Biomesapi-578922660No ratings yet
- HS 1 Ecology Practice ReviewerDocument5 pagesHS 1 Ecology Practice ReviewerRamon GasgasNo ratings yet
- ADA Programming LanguageDocument2 pagesADA Programming LanguageLakshmi N SureshNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 DLL English 6 q4 Week 1Document3 pagesGrade 6 DLL English 6 q4 Week 1Evan Mae Lutcha100% (1)
- Share Point Customization TricksDocument49 pagesShare Point Customization Trickssemalaiappan100% (5)
- Nivel IvDocument4 pagesNivel IvMaria MezaNo ratings yet