Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summarize The Basic Differences (In Tabular Form) Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Summarize The Basic Differences (In Tabular Form) Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Uploaded by
Vanclaver Sanchez BangalonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summarize The Basic Differences (In Tabular Form) Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Summarize The Basic Differences (In Tabular Form) Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Uploaded by
Vanclaver Sanchez BangalonCopyright:
Available Formats
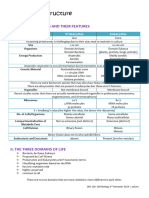
Prokaryote Eukaryote
Nucleus Absent Present
Membrane-bound organelles Absent Present
Cell structure Unicellular Mostly multicellular; some
unicellular
Cell size Smaller (0.1-5 μm) Larger (10-100 μm)
Complexity Simpler More complex
DNA Form Circular Linear
Examples Bacteria, archaea Animals, plants, fungi,
protists
1. Summarize the basic differences (in tabukar form) between prokaryotic and eukaryotic
cells.
2. Cite the applications of prokaryotes in biotechnology.
One of the significant application of prokaryotes in biotechnology is Microbial
bioremediation. It uses prokaryotes to remove pollutants. Agricultural chemicals (pesticides,
fertilizers) that leach into groundwater and the subsurface are removed using bioremediation.
To remove selenium ions from water, reduce SeO4-2 to SeO3-2 and Se0 (metallic selenium).
Mercury is a toxic metal that can be bioremediated. As a pesticide ingredient and byproduct of
battery production, mercury is used in industry. Methyl mercury is present in low
concentrations in natural environments but accumulates in living tissues, making it highly toxic.
Various bacteria can biotransform toxic mercury into nontoxic forms. These bacteria, like
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can convert Hg+2 into Hg0, which is nontoxic.
The importance of prokaryotes in petroleum bioremediation has been shown in recent
oil spills, such as the Exxon Valdez spill in Alaska (1989), the Prestige oil spill in Spain (2002), the
spill into the Mediterranean from a Lebanon power plant (2006), and the BP oil spill in the Gulf
of Mexico (2010). Add inorganic nutrients that help bacteria grow to promote bioremediation.
Bacteria that degrade hydrocarbons feed on oil droplets to break them down. Alcanivorax
borkumensis produces surfactants that solubilize oil, while other species degrade oil into
carbon dioxide. In the case of oil spills in the ocean, natural bioremediation occurs because oil-
consuming bacteria were already in the ocean. In addition to naturally occurring oil-degrading
bacteria, humans select and engineer bacteria with increased efficacy and hydrocarbon
processing range. Under ideal conditions, up to 80% of nonvolatile oil components can degrade
in a year after a spill. Other oil fractions with aromatic and highly branched hydrocarbon chains
are harder to remove and last longer in the environment.
3. Predict an advantage and disadvantage on the presence of a capsule in some prokaryotes.
Give at most three (3) examples.
Advantage:
1. It may prevent dehydration by absorbing water and swelling up of a bacterial cell
2. It may interfere with viruses (bacteriophages) which attack bacterial cells and can also cover
cell-surface antigens which mean that phagocytosis is impaired, so that the body's defence
mechanisms are defeated.
Disadvantage:
1. It may be considered a factor of virulence. For instance, Pneumococcus exists in rough (R)
and smooth (S) forms (S). The capsule is produced by the more virulent S form. This distinction
formed the basis for Frederick Griffith's experiment demonstrating bacterial transformation - an
important step in the history of DNA, as demonstrated by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and
Maclyn McCarter.
You might also like
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesMicrobiology MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (2)
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- DMLT Microbiology BookDocument598 pagesDMLT Microbiology BookTeamGGxKick Esports100% (10)
- Safe Food Handling QUIZ FINALDocument4 pagesSafe Food Handling QUIZ FINALmtlpcguys100% (1)
- Marlene L. Durand, Joan W. Miller, Lucy H. Young (Eds.) - Endophthalmitis-Springer International Publishing (2016) PDFDocument293 pagesMarlene L. Durand, Joan W. Miller, Lucy H. Young (Eds.) - Endophthalmitis-Springer International Publishing (2016) PDFeunike lahagu100% (2)
- Microbiology 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMicrobiology 1 PDFRaven CocjinNo ratings yet
- Phle Reviewer Module 6 Qa QCDocument66 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 6 Qa QCMARIA FREDIJEAN CARIÑONo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Microbiology: Dr. Thaigar Parumasivam Email: Thaigarp@usm - MyDocument26 pagesAn Overview of Microbiology: Dr. Thaigar Parumasivam Email: Thaigarp@usm - MyHuii Jiing WongNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Classification of BacteriaDocument20 pagesMorphology and Classification of Bacteriavineetvishal73100% (1)
- USP General Chapter (1115) Bioburdin Control For Non Sterile Drug SubstanceDocument8 pagesUSP General Chapter (1115) Bioburdin Control For Non Sterile Drug SubstanceDr usama El Shafey100% (7)
- Micro OrganismsDocument12 pagesMicro OrganismsDony GregorNo ratings yet
- 5 CelluleDocument34 pages5 Cellulejaya1129No ratings yet
- Lecutre 1 & 10Document34 pagesLecutre 1 & 10SELVI ANo ratings yet
- 3- Kingdom of Bacteriaمحاضرة -Document34 pages3- Kingdom of Bacteriaمحاضرة -OlaNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Pdfbio El2 PDFDocument20 pagesPdfbio El2 PDFAnonymous X4QS89Um8wNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Guy SebNo ratings yet
- 2 MicrobiologyDocument26 pages2 MicrobiologyBhoni KumariNo ratings yet
- Study Guide MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesStudy Guide MicrobiologyChristian Jewel GambolNo ratings yet
- in Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Document21 pagesin Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Mica-Ella CasasolaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TextDocument54 pagesBiochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TexttNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes: Justin Abasula & Sofia Isabelle AbayDocument17 pagesProkaryotes & Eukaryotes: Justin Abasula & Sofia Isabelle AbayjasminedevesaNo ratings yet
- Layssa - Biochem Chapter 12Document8 pagesLayssa - Biochem Chapter 12Gayle BocalaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology PDFDocument19 pagesBacteriology PDFDarshana Juvekar0% (1)
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document67 pagesChapter 1Serra ÖzışıkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 BIO201Document31 pagesLecture 2 BIO201Madiha Abu Saied Tazul Islam 1721217No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- Chem113lec Week 3.2Document5 pagesChem113lec Week 3.2Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFwilliam.collins296100% (24)
- Chem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Document21 pagesChem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Elif Deniz YeşilyaprakNo ratings yet
- MICRO211 LecDocument3 pagesMICRO211 LecKathy HgNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeSK BuntunNo ratings yet
- Introduction On Biodiversity: Kingdom ArcheabacteriaDocument3 pagesIntroduction On Biodiversity: Kingdom ArcheabacteriaRyzaRosalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson II: The Living Cells: Jonald P. Regio, RN, RMTDocument30 pagesLesson II: The Living Cells: Jonald P. Regio, RN, RMTDana TabingNo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 2Document34 pagesMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethNo ratings yet
- PDF Reference1-Lesson3-ProkaryotesvseukaryotesDocument3 pagesPDF Reference1-Lesson3-Prokaryotesvseukaryotesjg teNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Classification of Bacteria: October 2016Document20 pagesMorphology and Classification of Bacteria: October 2016Jœ œNo ratings yet
- CEEDG010 Microbiology Rev 01Document16 pagesCEEDG010 Microbiology Rev 01cluelessteen43No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument26 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsKirito HatakuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- What Is Microbiology: Study of Micro-Organisms: Organisms That EXIST As Single Aid of A MicroscopeDocument19 pagesWhat Is Microbiology: Study of Micro-Organisms: Organisms That EXIST As Single Aid of A MicroscopePREMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Origins of LifeDocument8 pagesLecture 4 - Origins of Lifesmart.beach1431No ratings yet
- Parker 2001Document6 pagesParker 2001Chinasa EkejiubaNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2-LecDocument10 pagesChapter 1 and 2-LecPam ArienzaNo ratings yet
- 3-Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic MicroorganismsDocument16 pages3-Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic Microorganismsguestiam29No ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Pratik PawarNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Classification of Bacteria: October 2016Document20 pagesMorphology and Classification of Bacteria: October 2016starskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- Cell Organization and Structure (Option C)Document4 pagesCell Organization and Structure (Option C)-Sabiraaa -No ratings yet
- CH 01 Lecture Presentation PCDocument58 pagesCH 01 Lecture Presentation PCInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument65 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Micro 1st ProkaryotesDocument16 pagesMicro 1st ProkaryotesMatahari SempurnaNo ratings yet
- 1-Basics of MicrobiologyDocument53 pages1-Basics of MicrobiologyKiran ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Lec MergedDocument28 pagesBiochem-Lec MergedNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- 978 1 4471 5304 7 - Chapter - 8Document30 pages978 1 4471 5304 7 - Chapter - 8Lu OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesisDocument12 pagesAntibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesismidoNo ratings yet
- 10 IM Food MicroDocument23 pages10 IM Food MicroNader SedighiNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Lysis and Disruption of Microbial CellsDocument5 pagesEnzymatic Lysis and Disruption of Microbial CellsSeptian JauhariansyahNo ratings yet
- Rendueles. 2012. Environmental MicrobiolDocument13 pagesRendueles. 2012. Environmental MicrobiolAfra FitrianitaNo ratings yet
- CLED AgarDocument2 pagesCLED AgarDuayt StiflerNo ratings yet
- The Red Weaver Ant, Oecophylla Smaragdina As VectorsDocument5 pagesThe Red Weaver Ant, Oecophylla Smaragdina As VectorsmadhanNo ratings yet
- MC 3 (LAB) (LEC) - Prelim NotesDocument11 pagesMC 3 (LAB) (LEC) - Prelim NotesJustineNo ratings yet
- ბაქტერიული მენინგიტიDocument42 pagesბაქტერიული მენინგიტიGiorgi PopiashviliNo ratings yet
- 5090 w16 QP 12 PDFDocument24 pages5090 w16 QP 12 PDFStop spamming on weverseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 An Introduction To BiologyDocument29 pagesChapter 1 An Introduction To BiologyMario and Krinon MocciaNo ratings yet
- Bchet-149 eDocument382 pagesBchet-149 eAakash JhaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination in EalsDocument2 pages2nd Quarter Examination in EalsMarlou M. De ChavezNo ratings yet
- BiopesticideDocument14 pagesBiopesticideSurendra KarkiNo ratings yet
- AQA - Biology - Cell Biology - GraspIT - GCSE - Re-Usable WorksheetDocument6 pagesAQA - Biology - Cell Biology - GraspIT - GCSE - Re-Usable Worksheetmaaa7No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 MicroparaDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 16 MicroparaKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch02 Biological ClassificationDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch02 Biological ClassificationArnavNo ratings yet
- Sundqvist, G. (1976) Bacteriological Studies of Necrotic Dental Pulps. Umea University, Umea.Document101 pagesSundqvist, G. (1976) Bacteriological Studies of Necrotic Dental Pulps. Umea University, Umea.Jaime BarraganNo ratings yet
- Review On Thymus Vulgaris Traditional Uses and Pharmacological PDFDocument3 pagesReview On Thymus Vulgaris Traditional Uses and Pharmacological PDFPsicólogo Clinico clinicoNo ratings yet
- Final Manuscript Banaba (Lagerstroemia Speciosa) Leaf Extract As Anti-Bacterial SoapDocument30 pagesFinal Manuscript Banaba (Lagerstroemia Speciosa) Leaf Extract As Anti-Bacterial SoapbelmarinaNo ratings yet
- Alginate Bachelor ThesisDocument50 pagesAlginate Bachelor ThesisTereza100% (5)
- Vision Holoarquica de La Vida y Del CosmoDocument29 pagesVision Holoarquica de La Vida y Del CosmoLuis AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Factory FarmingDocument6 pagesFactory Farmingapi-529718174No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 HomeworkDocument5 pagesChapter 11 HomeworkKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Smart MaterialsDocument27 pagesSmart Materialssri priyanka kathirvelNo ratings yet
- FAQMicrobes and Oil SpillsDocument16 pagesFAQMicrobes and Oil SpillsDaniel SánchezNo ratings yet