Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dhruv Practical Halfwave
Uploaded by
Dhruv Gor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesThe document describes an experiment on a halfwave rectifier. It explains that the experiment allows students to generate an input sine wave, observe the input and rectified output waveforms on an oscilloscope, and calculate the ripple factor. A halfwave rectifier only allows the positive half of the AC cycle to pass through, converting it into a pulsating DC signal by using a diode that is forward biased on the positive cycle and reverse biased on the negative cycle.
Original Description:
Original Title
Dhruv practical halfwave
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes an experiment on a halfwave rectifier. It explains that the experiment allows students to generate an input sine wave, observe the input and rectified output waveforms on an oscilloscope, and calculate the ripple factor. A halfwave rectifier only allows the positive half of the AC cycle to pass through, converting it into a pulsating DC signal by using a diode that is forward biased on the positive cycle and reverse biased on the negative cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesDhruv Practical Halfwave
Uploaded by
Dhruv GorThe document describes an experiment on a halfwave rectifier. It explains that the experiment allows students to generate an input sine wave, observe the input and rectified output waveforms on an oscilloscope, and calculate the ripple factor. A halfwave rectifier only allows the positive half of the AC cycle to pass through, converting it into a pulsating DC signal by using a diode that is forward biased on the positive cycle and reverse biased on the negative cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
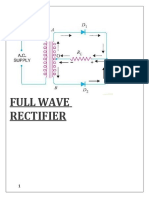
EXPERIMENT-2
Halfwave Rectifier
1. Objectives
2. At the end of the module the student
would be able to
3. Explain Rectification
4. Explain Half Wave Rectification
5. Explain Half Wave Rectification:For
Positive Half Cycle
6. Explain Half Wave Rectification:For
Negative Half Cycle
Procedure
1. Set the resistor RL.
2. Click on 'ON' button to start the
experiment.
3. Click on 'Sine Wave' button to generate
input waveform
4. Click on 'Oscilloscope' button to get the
rectified output.
5. Vary the Amplitude, Frequency, volt/div
using the controllers.
6. Click on "Dual" button to observe both the
waveform.
7. Channel 1 shows the input sine waveform,
Channel 2 shows the output rectified
waveform.
8. Calculate the Ripple Factor. Theoretical
Ripple Factor= 1.21.
Theory
Rectification
A rectifier is a device that converts alternating current (AC) to
direct current (DC), a process known as rectification. Rectifiers are
essentially of two types – a half wave rectifier and a full wave
rectifier.
Half Wave Rectification
On the positive cycle the diode is forward biased and on the
negative cycle the diode is reverse biased. By using a diode we have
converted an AC source into a pulsating DC source. In summary we
have ‘rectified’ the AC signal.
Figure:5
The simplest kind of rectifier circuit is the half-wave rectifier. The
half-wave rectifier is a circuit that allows only part of an input signal
to pass. The circuit is simply the combination of a single diode in
series with a resistor, where the resistor is acting as a load.
Half Wave Rectifiers – Waveforms
You might also like
- Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave Rectifierसूरज कुमारNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Half Wave RectifierDocument15 pagesPhysics Project On Half Wave RectifierMaanu Style100% (4)
- Half Wave Rectifier ProjectDocument8 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Projectritesh singh55% (31)
- Half Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryDocument10 pagesHalf Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryLakshayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 EST OLIVA PDFDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 EST OLIVA PDFMark joseph BayletNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab File: Delhi Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab File: Delhi Technological Universitychetan jangirNo ratings yet
- Aim: Capacitive RectificationDocument9 pagesAim: Capacitive RectificationPriNo ratings yet
- 6 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleDocument5 pages6 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleKenneth SanguyoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document6 pagesExperiment 5VHIMBER GALLUTANNo ratings yet
- Physics Project FileDocument17 pagesPhysics Project FileDhana sekaranNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument17 pagesFull Wave RectifierDhana sekaranNo ratings yet
- BasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDocument8 pagesBasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDANRHEY BALUSDANNo ratings yet
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportDocument11 pages(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Rectifier CircuitsDocument6 pagesLab 2 - Rectifier CircuitsHemil PatelNo ratings yet
- Asmat Ullah (70069423) Experiment:5: Circuit DiagramDocument11 pagesAsmat Ullah (70069423) Experiment:5: Circuit DiagramAsmat NiaziNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 1 - Diode As RectifierDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT 1 - Diode As RectifierSamNo ratings yet
- Report 1 Power eDocument12 pagesReport 1 Power eMuhd HafizzudinNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectB.LOHITHA BALANo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF VinilDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF Vinilteamboys536No ratings yet
- Group 6 Rectifiers and Filters EXP 4 - ECE005 ME51S1Document9 pagesGroup 6 Rectifiers and Filters EXP 4 - ECE005 ME51S1Jose Enrique Gonzaga100% (1)
- Rectifiers and FiltersDocument13 pagesRectifiers and FiltersAko si GianNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier and Full Wave Rectifier-1Document9 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier and Full Wave Rectifier-1xakiti7847No ratings yet
- Lab Session: 4: Demonstrate The Behavior of A Silicon Diode in Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesLab Session: 4: Demonstrate The Behavior of A Silicon Diode in Full Wave RectifierFatima AmjadNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument26 pagesRectifierhemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Experiment No 4: Objective: To Study The Semiconductor Diode As A Half Wave Rectifier. ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No 4: Objective: To Study The Semiconductor Diode As A Half Wave Rectifier. ApparatusUsama SagharNo ratings yet
- Signal GenerationDocument13 pagesSignal GenerationLara Jane ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document4 pagesLab 4Muhammad DawoodNo ratings yet
- 8 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleDocument6 pages8 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleKenneth SanguyoNo ratings yet
- Eee 04Document10 pagesEee 04farah.hoque.cseNo ratings yet
- Class +2 SciDocument16 pagesClass +2 SciARYANNo ratings yet
- EDASLab Report 1 - CombinedDocument5 pagesEDASLab Report 1 - Combinedbiswaskoushik566No ratings yet
- U1 A6a Cruz DominguezDocument11 pagesU1 A6a Cruz DominguezDomms DommsNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Project - Measuring Current Using Halfwave RectifierDocument19 pagesClass 12 Physics Project - Measuring Current Using Halfwave RectifierSarthak GoelNo ratings yet
- SIMULINKDocument5 pagesSIMULINKshresth.gupta.ug22No ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 4Document6 pagesElectronics Lab 4June del MundoNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 4 Diode Application DELGDocument31 pages03 Chapter 4 Diode Application DELGaniq.halmyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Document28 pagesElectronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Kylle SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- نسخة EXPER - 1تقريرDocument9 pagesنسخة EXPER - 1تقريرx98w9p6z9kNo ratings yet
- A Document To Download PDFDocument9 pagesA Document To Download PDFreyansh.keshavaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 4 Rectifiers and FiltersDocument16 pagesLaboratory Experiment 4 Rectifiers and FiltersPajayNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Document14 pagesElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139No ratings yet
- Activity No.6 Ambas, DLDocument8 pagesActivity No.6 Ambas, DLDevee AmbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Diode Circuit ApplicationsDocument31 pagesChapter Five Diode Circuit Applicationsfouad abdNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Document5 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Afiq BahaNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Half-Wave Rectifier: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesUncontrolled Half-Wave Rectifier: ObjectivesKamil Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Power ElectronicDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Power ElectronicfahrizaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document10 pagesExperiment 1Saransh SehgalNo ratings yet
- Postlab Report #5Document11 pagesPostlab Report #5Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Physics Project File 53Document19 pagesPhysics Project File 53Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- TARAY - ACE 14 Laboratory Report FormatDocument16 pagesTARAY - ACE 14 Laboratory Report FormatFeolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Eng NaderDocument8 pagesExperiment 2 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Slemani Polytechnic University Technical College of Engineering Communication Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesSlemani Polytechnic University Technical College of Engineering Communication Engineering DepartmentZahra JabarNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationDocument3 pagesSingle-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationKhushbakht KhushiNo ratings yet
- Exp5 RectifierDocument3 pagesExp5 RectifiertarunkumarcladNo ratings yet
- BEEE Precise NotesDocument56 pagesBEEE Precise Noteskurubamailagani ravaliNo ratings yet
- Exp3 CarinoDocument4 pagesExp3 Carinocent carinoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherDocument21 pagesLab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherOmer Sheikh100% (1)
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualDocument46 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualManu anand100% (1)
- 20el100 - 2el0611 - Exp-2Document14 pages20el100 - 2el0611 - Exp-2Dhruv GorNo ratings yet
- 20el100 Project Report Es102 LabDocument19 pages20el100 Project Report Es102 LabDhruv GorNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ReportDocument20 pagesMini Project ReportDhruv GorNo ratings yet
- 20el100 Ass-2 2el42Document20 pages20el100 Ass-2 2el42Dhruv GorNo ratings yet