Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp3 Carino
Uploaded by
cent carinoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp3 Carino
Uploaded by
cent carinoCopyright:
Available Formats
Diode Rectification
Carino, Vincent Paul C.
Group 2
Heartofblood05@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
We decide of how a diode is utilized Half wave
rectifier and a full wave rectifier circuit. We
confirm it by using the oscilloscope and multi-
meter. First we set-up the power supply to the
circuit board at that point associate the oscilloscope.
We came up an AC current in the info and DC
current to the yield. At that point we get the
Voltage, RMS, Peak Voltage, and Average Voltage
in both yield and info.
KEYWORDS
•Anode - the positively charged electrode
by which the electrons leave a device.
•Cathode - the negatively charged electrode On the off chance that there's a bridge rectifier
by which electrons enter an electrical device. where all the diode associated, at that point we
will have a Full-Wave Rectification.
•Rectification - conversion of alternating
current to a pulsating direct current
•Full Wave Rectification - conversion of ac
to dc using both half cycles of the ac voltage.
•Half Wave Rectification - conversion of ac
to dc using only half cycles of the ac voltage.
INTRODUCTION
We analyze how an Alternating Current
proselyte to Direct Current by utilizing a diode.
The appropriate responses is in the diode
circuit. "The way toward getting unidirectional
flows and voltages from substituting flows and
voltages is called amendment." (Bird, 2014). It is important to change over those high
The least complex technique for changing over voltage substituting current into the usable
is the Half-Wave Rectification. direct current.
METHODOLOGY
3-1 / Full-wave diode bridge
rectification
At First, We adjusted the power source to
positive-negative 15Vdc but the circuit board
limits only up to 11Vdc. In this step, we didn’t
turned on the power source. Second, we located
the FULL-WAVE RECTIFICATION WITH
POWER SUPPLY FILTER and connected it to In this step, we determined the alteration of the
the GENERATOR BUFFER as shown below: input voltage that the diode is under test
forward biased
RESULTS
We set up the material needed, oscilloscope,
multi-meter, power supply and circuit block.
We first test the oscilloscope whether it’s
functioning or reading the input terminal. And
then we test the Figure 1 and Figure 2.
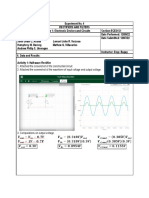
Figure 1. Half-wave diode circuit 1
Third, we setup the oscilloscope channels 1
and 2 for value indicated in the manual using
X10 probes. We connected the channel 1 to the
GENERATOR BUFFER and connected the
channel 2 across the secondary terminals of T1.
We measured the voltage readings displayed in
channel 1 and we determined if it’s a step-down
or step-up voltage relationship. Fourth,
referring to the figure below, we ensured that
the common lead of the test probe is at the
negative terminal of the bridge circuit.
Using the X10 probe on oscilloscope, we
adjusted the output of the external sine wave
generator signal. The position test waveform is Figure 1. Half-wave diode circuit 2
indicated by the figure below:
We are able to see the anticipated yield of the
Figure 1 and Figure 2 and Half-wave of the AC
current. At that point we determined the voltage
CONCLUSION
peak to peak, RMS and so forth. same
methodology to full-wave.
We discovered that a diode is an entirely
Figure 3. Full-wave diode circuit adaptable electronic gadget as it could likewise
be utilized during the time spent amendment.
Knowing the standards of biasing is important
to comprehend the correction procedure. There
are two yield we get, a half-wave rectifier and
full-wave rectifier. The distinctions is that the
full-wave rectifier is utilized as a scaffold
rectifier association where every one of the 4
diode associated one another.
REFERENCES
ECE104L MANUAL
Retrieved from:
https://www.quora.com/What-is-half-wave-
rectifier
The result of our computed and measured https://learning.uonbi.ac.ke/courses/SPH307/sc
experiment are shown below: ormPackages/path_2/43_the_fullwave_rectifier
1.html
Bird, J. (2014). Eletrical and Electronic Principles and Technology. New York: Routledge .
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Modified EXPERIMENT 10 (E) - 8.01.2020Document13 pagesModified EXPERIMENT 10 (E) - 8.01.2020VishalNo ratings yet
- UPM Aerospace Lab Manual on Rectifier CircuitsDocument7 pagesUPM Aerospace Lab Manual on Rectifier CircuitsMohd Fazri SedanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualDocument46 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualManu anand100% (1)
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Document4 pagesDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Half Wave Rectifier SimulationDocument12 pagesSingle Phase Half Wave Rectifier SimulationMuhd HafizzudinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 EST OLIVA PDFDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 EST OLIVA PDFMark joseph BayletNo ratings yet
- School of Electrical Engineering and ComputingDocument8 pagesSchool of Electrical Engineering and Computingsamuel tolossaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Half Wave RectifierDocument15 pagesPhysics Project On Half Wave RectifierMaanu Style100% (4)
- EDASLab Report 1 - CombinedDocument5 pagesEDASLab Report 1 - Combinedbiswaskoushik566No ratings yet
- ECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument4 pagesDocumentationEugene Paul Brian SebiloNo ratings yet
- Full wave rectifier labDocument4 pagesFull wave rectifier labMustafa MhmoodNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectificationDocument4 pagesFull Wave RectificationMohammad alhaboob2030No ratings yet
- N. Bacalso Avenue, Cebu City: Cebu Institute of Technology - UniversityDocument15 pagesN. Bacalso Avenue, Cebu City: Cebu Institute of Technology - UniversityTreyes RobertNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Document5 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Afiq BahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document11 pagesLab Report 2Mike TNo ratings yet
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportDocument11 pages(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- D - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-JkDocument20 pagesD - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-Jktinku990056% (9)
- EXP. 1-Filtered Power SupplyDocument4 pagesEXP. 1-Filtered Power SupplyJustine LentijasNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004No ratings yet
- Lab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherDocument21 pagesLab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherOmer Sheikh100% (1)
- Experiment on clamping circuits adding DC levelDocument11 pagesExperiment on clamping circuits adding DC levelJaypee PascualNo ratings yet
- Electronic Unit 1Document35 pagesElectronic Unit 1Sudheer ManepalliNo ratings yet
- Physics Project MohithaDocument20 pagesPhysics Project MohithaB.LOHITHA BALANo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument6 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierKenneth SanguyoNo ratings yet
- Different Experiment in DiodesDocument16 pagesDifferent Experiment in DiodesDivine Grace GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Report Electronics 1Document13 pagesLab 8 Report Electronics 1Dawn J. OwensNo ratings yet
- Diode Clipping and Clamping CircuitsDocument4 pagesDiode Clipping and Clamping CircuitsBatool FattahNo ratings yet
- Final ActivityDocument8 pagesFinal Activityodrhey hernandezNo ratings yet
- Jasleen Kaur's full wave rectifier projectDocument17 pagesJasleen Kaur's full wave rectifier projectDaily Meme DOSENo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierAdvyth Vaman AkalankamNo ratings yet
- BALUSDAN BasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDocument8 pagesBALUSDAN BasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDANRHEY BALUSDANNo ratings yet
- RC and RL Circuit AnalysisDocument8 pagesRC and RL Circuit AnalysisMagdalena SimicNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationDocument24 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics ReportDocument25 pagesBasic Electronics ReportMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Using Bridge CircuitDocument4 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Using Bridge CircuitZbNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Rectifiers and Filters EXP 4 - ECE005 ME51S1Document9 pagesGroup 6 Rectifiers and Filters EXP 4 - ECE005 ME51S1Jose Enrique Gonzaga100% (1)
- Class +2 SciDocument16 pagesClass +2 SciARYANNo ratings yet
- ECE 201 Electronics Lab: Rectifiers and FiltersDocument4 pagesECE 201 Electronics Lab: Rectifiers and FiltersMathew GidayawanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 01 Name of The Experiment: Experimental Study of A Single Phase Half Wave Uncontrolled RectifierDocument30 pagesExperiment No: 01 Name of The Experiment: Experimental Study of A Single Phase Half Wave Uncontrolled RectifierJahedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers and Voltage Doublers Circuits LabDocument5 pagesRectifiers and Voltage Doublers Circuits Labstar89690% (1)
- Lab Report 2 Phy547: Experiment 2: Zener Diode and Power SupplyDocument8 pagesLab Report 2 Phy547: Experiment 2: Zener Diode and Power SupplyAtikah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- NV6503Document45 pagesNV6503sandeep_226250% (2)
- System Practice 1Document6 pagesSystem Practice 1Angel CiméNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Document8 pagesBasic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Ashutosh GargNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Solayman Ewu - CompressDocument12 pagesLab Report Solayman Ewu - CompressVic100% (1)
- Circuitos Rectificadores: Practica #6Document5 pagesCircuitos Rectificadores: Practica #6Juan Diego MaitaNo ratings yet
- TP Elec PDFDocument3 pagesTP Elec PDFchroeun sokayNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument33 pagesEDC Lab ManualECE dept sietNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectB.LOHITHA BALANo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportMd. Al Amin 201-15-3479No ratings yet
- EEW Lab Manual - FinalDocument51 pagesEEW Lab Manual - FinaljeniferNo ratings yet
- .Design of Smoke Detection Using MicrocontrollerDocument3 pages.Design of Smoke Detection Using Microcontrollerrajesh adhikariNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab Exp3.pdfDocument17 pagesElectronics Lab Exp3.pdfgacc4sitesNo ratings yet
- Measuring Current Using Half-Wave RectifierDocument17 pagesMeasuring Current Using Half-Wave RectifierAryan TengNo ratings yet
- Electronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Document69 pagesElectronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Maithira H0% (1)
- Experiment No.1 Group 3Document25 pagesExperiment No.1 Group 3Janpherson BellecaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument23 pagesBasic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 CarinoDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Carinocent carinoNo ratings yet
- Diode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1Document3 pagesDiode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1cent carinoNo ratings yet
- ECE104 Experiment 4Document4 pagesECE104 Experiment 4cent carinoNo ratings yet
- ECE104 Experiment 4Document4 pagesECE104 Experiment 4cent carinoNo ratings yet
- Ece104 Lab Report 6Document4 pagesEce104 Lab Report 6cent carinoNo ratings yet
- Diode Test and FamiliarizationDocument4 pagesDiode Test and Familiarizationcent carinoNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Individual ReportDocument9 pagesActivity 6 Individual Reportcent carinoNo ratings yet
- Ece104 Experiment 1 Lab ReportDocument2 pagesEce104 Experiment 1 Lab Reportcent carinoNo ratings yet
- ECE Experiment 4Document2 pagesECE Experiment 4cent carinoNo ratings yet
- HP Notebook BIOS Setup GuideDocument8 pagesHP Notebook BIOS Setup GuideBalaRajKumarNo ratings yet
- EPA 2010 SCR System Training Center IntroductionDocument183 pagesEPA 2010 SCR System Training Center Introductionsidhu100% (5)
- Makerspace ProposalDocument4 pagesMakerspace Proposalapi-380257976No ratings yet
- Metode Ugradnje Tunelske FolijeDocument7 pagesMetode Ugradnje Tunelske FolijeIzetNo ratings yet
- GS33J05F10-01EN ExaopcDocument13 pagesGS33J05F10-01EN Exaopctimsar1357No ratings yet
- 601-620 Instruction ManualDocument120 pages601-620 Instruction ManualChinmayMaxNo ratings yet
- 4-Way Reversing ValvesDocument3 pages4-Way Reversing ValvesAbdulSattarNo ratings yet
- Types PF BechmarkingDocument5 pagesTypes PF Bechmarkingshivangi dubeyNo ratings yet
- Electraquip 2015-4Document1 pageElectraquip 2015-4Anonymous M0OEZEKoGiNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Water Current ForcesDocument4 pagesCalculation of Water Current Forcesvasu7900No ratings yet
- User 010613Document60 pagesUser 010613NurZul HealMeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Web CrawlerDocument5 pagesAssignment Web CrawlerAmmarsyedNo ratings yet
- 111 Javascript SyntaxDocument13 pages111 Javascript SyntaxFahim Abdullah Al Wasi -No ratings yet
- Intel Micro ArchitecturesDocument18 pagesIntel Micro ArchitecturesShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Daily Drilling Report: Bha Tally Bit Record Mud Report Mud Pump Drilling InformationDocument25 pagesDaily Drilling Report: Bha Tally Bit Record Mud Report Mud Pump Drilling InformationHamed NazariNo ratings yet
- Estates Projects Design BriefDocument2 pagesEstates Projects Design Briefsachinsaklani23No ratings yet
- UAP Grading Policy Numeric Grade Letter Grade Grade PointDocument2 pagesUAP Grading Policy Numeric Grade Letter Grade Grade Pointshahnewaz.eeeNo ratings yet
- Elster Rotary Gas Meter: I Connected IndustrialDocument6 pagesElster Rotary Gas Meter: I Connected IndustrialAlvaro Joel Quinteros RochaNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision & Image ProcessingDocument34 pagesComputer Vision & Image Processingbasab_ecens100% (2)
- BG Katalog Na BanknotiDocument133 pagesBG Katalog Na BanknotiGoroSoftNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Would Used To GetDocument4 pagesEjercicio Would Used To Getjacs79No ratings yet
- N5ae Ver1-11 21JUN18Document28 pagesN5ae Ver1-11 21JUN18JamesNo ratings yet
- Gain Admin Commands in Roblox with Admin Console ProDocument12 pagesGain Admin Commands in Roblox with Admin Console ProJaveria AliNo ratings yet
- Torsen General Frequently Asked Questions PageDocument4 pagesTorsen General Frequently Asked Questions PagedromakiNo ratings yet
- Full Paper - Case Study FormatDocument4 pagesFull Paper - Case Study Formatdhaval_power123No ratings yet
- Conductivity in Power PlantsDocument4 pagesConductivity in Power PlantsdsoNo ratings yet
- Viewpoint User Manual SEODocument7 pagesViewpoint User Manual SEOkimura takuyaNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUSDocument3 pagesSYLLABUSSyed Sirajul Haq100% (1)
- ZW-5A series wheel loader delivers 10% fuel savings and enhanced controllabilityDocument9 pagesZW-5A series wheel loader delivers 10% fuel savings and enhanced controllabilityallnainggolanNo ratings yet
- SATR-J-6512 - Rev 0 PDFDocument5 pagesSATR-J-6512 - Rev 0 PDFAdel KlkNo ratings yet