Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WEEK 6-Speech Context
Uploaded by
Wayne Dolorico Millamena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageWEEK 6-Speech Context
Uploaded by
Wayne Dolorico MillamenaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
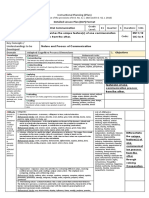
ORAL COMMUNICATION – TYPES OF SPEECH
TYPES OF SPEECHES
1. Types of Speech According to Purpose
a. informative or expository speech
• is mainly performed for the purpose of educating the audience on new or relevant piece of information on a particular topic.
example: lecture of a teacher
b. persuasive speech
• is given solely for the purpose of convincing the audience to agree with the speaker’s opinion on a particular topic.
example: speech of a lawyer
c. entertainment speech
• aims to share laughter and enjoyment to the audience through witty and humorous lines.
example: speech of a comedian
2. Types of Speech According to Delivery
a. manuscript speech
• is the word-for-word iteration of a written message using visual aids.
example: news anchor with a teleprompter
b. memorized speech
• is the rote recitation of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory.
example: actor’s dialogue
c. extemporaneous speech
• is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. example:
a campaign speech before a voting public
d. impromptu speech
• is the presentation of a short message without advance preparation and is for people knowledgeable about the subject.
example: a doctor’s response to the question of a patient
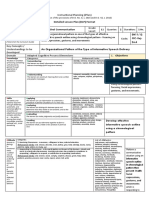
3. Types of Speech Style
1.Intimate – This style is private. It occurs between or among close family members or individuals
-is used for very close relationships.
example: couple, lovers, mother and daughter
note: Language used in this style may not be shared in public
2.Casual – This style is common among peers and friends is an in communication between groups and peers who have
something to share and have shared background information but do not have close relations.
example: classmates
note: Jargon, slang, and vernacular language are used
3.Consultative - is used in semi- and standard communication.
example: teacher and student, doctor and patient, judge and lawyer ,
note: Professional or mutually acceptable language is a must in this style.
4.Formal- is a one-way straightforward speech.
example: State of the Nation Address, pronouncement by judges
note: What the speaker says is something that has been prepared beforehand.
5.Frozen – it is frozen in time and remains unchanged. It mostly occurs in ceremonies and is usually used during solemn
ceremonies and events.
example: pledges , the Lord’s Prayer, Panunumpa sa Watawat,
note: It does not require any feedback from the audience.
You might also like
- CNF Melc3 Final Field-ValidatedDocument32 pagesCNF Melc3 Final Field-ValidatedWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNF Melc2 Final Field-Validated-V2Document22 pagesCNF Melc2 Final Field-Validated-V2Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Shift in Speech ElementsDocument18 pagesShift in Speech ElementsWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- 4 Distinguishes The Unique Feature(s) of One Communication Process From The OtherDocument4 pages4 Distinguishes The Unique Feature(s) of One Communication Process From The OtherWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNF Melc1 Final Field-Validated v3Document24 pagesCNF Melc1 Final Field-Validated v3Kare CaspeNo ratings yet
- 3 Differentiates The Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pages3 Differentiates The Various Models of CommunicationWayne Dolorico Millamena100% (1)
- 5 Explains Why There Is A Breakdown of CommunicationDocument4 pages5 Explains Why There Is A Breakdown of CommunicationWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- 30 Explains That A Shift in Speech Context, Speech Style, Speech Act and Communicative Strategy Affects The MessageDocument4 pages30 Explains That A Shift in Speech Context, Speech Style, Speech Act and Communicative Strategy Affects The MessageWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- 34.4 Uses Principles of Effective Speech Writing Focusing On Word ChoiceDocument4 pages34.4 Uses Principles of Effective Speech Writing Focusing On Word ChoiceWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- 2 Explains The Nature and Process of CommunicationDocument4 pages2 Explains The Nature and Process of CommunicationWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- 35.4 Uses Principles of Effective Speech Writing Focusing On Facial Expressions, Gestures and MovementsDocument4 pages35.4 Uses Principles of Effective Speech Writing Focusing On Facial Expressions, Gestures and MovementsWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- 29 Explains That A Shift in Speech Context, Speech Style, Speech Act and Communicative Strategy Affects The Role and Responsibilities of The SpeakerDocument4 pages29 Explains That A Shift in Speech Context, Speech Style, Speech Act and Communicative Strategy Affects The Role and Responsibilities of The SpeakerWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNFW Lesson 5Document7 pagesCNFW Lesson 5Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNFW Lesson 6Document7 pagesCNFW Lesson 6Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 V.2Document2 pagesWeek 5 V.2Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 QuizDocument4 pagesWeek 1 QuizWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 QuizDocument2 pagesWeek 2 QuizWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 QuizDocument6 pagesWeek 5 QuizWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNFW Lesson 4Document5 pagesCNFW Lesson 4Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNFW Lesson 2Document3 pagesCNFW Lesson 2Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNFW Lesson 3Document3 pagesCNFW Lesson 3Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- CNFW Lesson 1Document4 pagesCNFW Lesson 1Wayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Group DiscussionDocument4 pagesGroup DiscussionZahida MariyamNo ratings yet
- (Phonetics and Phonology) Session 6: I. Weak Forms II. Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument24 pages(Phonetics and Phonology) Session 6: I. Weak Forms II. Aspects of Connected SpeechĐặng Lê Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Scholes, R. - Structuralism in LiteratureDocument230 pagesScholes, R. - Structuralism in LiteratureGermán GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Global Stage 4 Literacy U1-3Document55 pagesGlobal Stage 4 Literacy U1-3Lưu Thanh TâmNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Lesson Plan TS25Document20 pagesForm 2 Lesson Plan TS25Ct NurNo ratings yet
- 1 Innovative Methods of Teaching English Language PDFDocument4 pages1 Innovative Methods of Teaching English Language PDFトラ グエンNo ratings yet
- Lockdown Class 1 Planning Sheet 2021-22Document53 pagesLockdown Class 1 Planning Sheet 2021-22Special Excise Commissioner EnforcementNo ratings yet
- Jurnals and BooksDocument7 pagesJurnals and BooksTESL10620 Aida Nur Athilah Binti Mat SohNo ratings yet
- RPT Bi Tahun 6Document4 pagesRPT Bi Tahun 6Saroja NathanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Computation - Question BankDocument19 pagesTheory of Computation - Question BanksuperaladNo ratings yet
- 3140 02 6RP AFP tcm143-700710Document8 pages3140 02 6RP AFP tcm143-700710james100% (1)
- Simple Past Presentand Future Tense Activity FreebieDocument9 pagesSimple Past Presentand Future Tense Activity FreebieMusab AbdulrazzakNo ratings yet
- JWS HiraganaDocument11 pagesJWS HiraganaFervi BongcoNo ratings yet
- Lost in TranslationDocument6 pagesLost in TranslationAli Al-HalawaniNo ratings yet
- Bury 03 Phrase StructureDocument208 pagesBury 03 Phrase StructureseadahmetovicNo ratings yet
- Benchmark Unit 7 Week 1Document6 pagesBenchmark Unit 7 Week 1api-448690566No ratings yet
- The Revelation Explained by Smith, F. G. (Frederick George), 1880-1947Document198 pagesThe Revelation Explained by Smith, F. G. (Frederick George), 1880-1947Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- English Progress Test 1 Tests 87294Document3 pagesEnglish Progress Test 1 Tests 87294Anca CiupercăNo ratings yet
- Estrategias AuditivasDocument63 pagesEstrategias Auditivasdayan244No ratings yet
- AH2 Exam Units 7 and 8Document2 pagesAH2 Exam Units 7 and 8English Plus ChileNo ratings yet
- Training For EVS Trainers From EECA Region: 15-23 September 2007, Simeiz - Crimea, UkraineDocument79 pagesTraining For EVS Trainers From EECA Region: 15-23 September 2007, Simeiz - Crimea, UkraineLukaszCudnyNo ratings yet
- Task - Unit Iv - Present ContinuousDocument5 pagesTask - Unit Iv - Present ContinuousYosuni RamosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 7 (Fourth Quarter) Week 4 - Day 1 I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in English 7 (Fourth Quarter) Week 4 - Day 1 I. ObjectivesJay Ann Canillo-ArceoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesConditional Sentencesabdellah dandoumNo ratings yet
- Consciouness & SuperconsciosnessDocument20 pagesConsciouness & SuperconsciosnessNarayan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Critique by Gemma B. PagaddutDocument30 pagesCritique by Gemma B. PagaddutGem BahingawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Maidir MaidirNo ratings yet
- Past and Past PerfectDocument3 pagesPast and Past PerfectNurul FadilahNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Internet Languages - World Internet StatisticsDocument4 pagesTop Ten Internet Languages - World Internet Statisticsfred_cassieNo ratings yet