Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Chemistry - 5359493 (1644335237664)
Uploaded by
Kingro SimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Chemistry - 5359493 (1644335237664)
Uploaded by
Kingro SimCopyright:
Available Formats
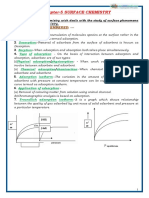
SURFACE CHEMISTRY
1) Write any three differences between Physisorption and 6) Write steps involved in enzyme catalysed 10) What is Tyndal effect?
chemisorptions. reactions. Ans: Scattering of light by colloidal particles in colloidal sol
Ans: Step-1: Enzyme combines with substrate to form is called as Tyndal effect.
Physical adsorption Chemical adsorption enzyme-substrate complex.
1) It involves van der 1. It involves chemical
Waals’ forces. bond formation. E + S ⎯⎯ → ES* 11) What is Brownian movement? What is the cause for it?
Step-2: Decomposition of the enzyme-substrate Ans: Zig-Zag motion of colloidal particles in colloidal sol is
2. It is not specific 2. It is highly specific
complex to form product. called as Brownian movement.
3. It is reversible 3. It is irreversible
Reason or cause; Due to collision of colloidal particles with
4. Enthalpy of 4. Enthalpy of adsorption is ES* ⎯⎯
→ E+P dispersion medium
adsorption is low high
5. Adsorption favoured 5. Adsorption is favoured 7) Write any three differences between lyophilic and 12) What is Electrophoresis? Write one application of it.
at low temperature at high temperature. lyophobic sols. Ans: The movement of colloidal particles towards
6. Multilayer adsorption 6. Monolayer adsorption
oppositely charged electrodes under an applied electric
Lyophilic (Hydrophilic) Lyophobic (Hydrophobic)
field is called electrophoresis.
2) Write mathematical form Freundlich adsorption 1) More stable 1) Less stable
Electrophoresis is used for the determination of charge on
isotherm. 2) Hydration take place 2) Hydration does not take
place the colloidal particles.
x 1
Ans: Mathematical form; 3) Cannot be easily
= K p n (where, n > 1) 3) Easily coagulated
m coagulated 13) What is coagulation? Write any two methods of
4) Reversible in nature 4) Irreversible in nature coagulation.
3) What is homogeneous catalysis? Give an example. 5) Stabilising agents not 5) Stabilising agents Ans: The process of settling of colloidal particles is
Ans: The catalysis in which the reactants and the needed needed called coagulation or precipitation of the sol.
catalyst are in the same phase is called as Methods: (i) Electrophoresis (ii) Boiling (iii) Addition of an
8) Explain electrical disintegration or Brdig’s electric electrolyte (iv) adding oppositely charged sols
homogeneous catalysis. arc method of preparation of metal sols.
Ex: 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ⎯⎯⎯ → 2SO3(g)
NO(g)
Ans; Au sol or Ag sol or Pt sol can be prepared in this 14) State Hardy-Schulze rule
Or acid catalysed hydrolysis of methyl acetate or method. Ans: The greater the charge on the coagulating ion, the
acid catalysed hydrolysis of sugar In this method, electric arc is struck between greater is its coagulating power
electrodes of the metal like gold or platinum
4) What is heterogeneous catalysis? Give an example. immersed in the dispersion medium. The intense heat NOTE: In the coagulation of a negative sol, the flocculating
produced vaporises the metal, which then condenses power is in the order: Al3+>Ba2+>Na+
Ans: The catalytic process in which the reactants and
to form particles of colloidal size. Similarly, in the coagulation of a positive sol, the
the catalyst are in different phases is known as
heterogeneous catalysis. flocculating power is in the order: PO43– > SO42– > Cl–
Ex: Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide in
15) What is an emulsion? Give an example.
the presence of Pt. or
Ans: Colloidal system in which both dispersed phase and
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⎯⎯⎯
FeO(s)
→ 2NH3(g) or dispersion medium are liquids is called as an emulsion.
Hydrogenation of vegetable oils in the presence (i) Oil dispersed in water (O/W type) ex; milk and vanishing
of nickel as catalyst. cream
9) What is peptization? Give an example (ii) Water dispersed in oil (W/O type) ex; Butter and cream
5) What is shape selective catalysis? Give an Ans: Peptization may be defined as the process of
example. converting a freshly prepared precipitate into 16) What is the sign of enthalpy and entropy change for
Ans: The catalytic reaction that depends upon the colloidal sol in the presence of suitable electrolyte. adsorption?
pore structure of the catalyst and the size of the Ex: Conversion of Fe(OH)3 ppt into colloid by FeCl3 as Ans: Enthalpy change is negative or H = −ve
reactant and product molecules is called shape- electrolyte. Or Entropy change is negative or S = −ve
selective catalysis. Conversion of AgI ppt into colloid by KI as
Ex; Zeolites or ZSM-5 electrolyte
You might also like
- Unit 5 - Chemistry-CMPDocument5 pagesUnit 5 - Chemistry-CMPsmitakamath6686No ratings yet
- Progress in the Science and Technology of the Rare Earths: Volume 2From EverandProgress in the Science and Technology of the Rare Earths: Volume 2No ratings yet
- Scheme of Evaluation: Ii Year Puc Annual Examination April/ May - 2022 Subject Code: 34 Subject: ChemistryDocument13 pagesScheme of Evaluation: Ii Year Puc Annual Examination April/ May - 2022 Subject Code: 34 Subject: ChemistryYashwanth HMNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 5Document10 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 5Ûdây RäjpütNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Adsorption and Absorption Sr. No. Adsorption Absorption 1Document10 pagesDifference Between Adsorption and Absorption Sr. No. Adsorption Absorption 1Naym MiaNo ratings yet
- Concerted Reactions.: Reaction ProgressDocument38 pagesConcerted Reactions.: Reaction ProgressSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Qn. No. Part - A MarksDocument13 pagesQn. No. Part - A MarkslingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Solid state reaction fundamentalsDocument11 pagesSolid state reaction fundamentalsakibNo ratings yet
- COLLOIDSDocument15 pagesCOLLOIDSKADAMBARINo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Important 3 Marks Questions With Answers PDFDocument25 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Important 3 Marks Questions With Answers PDFDipti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry 1Document12 pagesSurface Chemistry 1Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- C 5 - Notes - Surface ChemistryDocument14 pagesC 5 - Notes - Surface ChemistryAtharva BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument17 pagesSurface ChemistryFourte GuNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII - Chemistry: Board Paper Solution - 2012Document12 pagesCBSE XII - Chemistry: Board Paper Solution - 2012rahulNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemistry Questions and Answers on Surface ChemistryDocument6 pagesClass XII Chemistry Questions and Answers on Surface ChemistryAbhay BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem NotesDocument12 pagesInorganic Chem NotesHadia RehmanNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry Chapter SummaryDocument7 pagesSurface Chemistry Chapter SummaryANANT MISHRANo ratings yet
- Chemical bonding essentialsDocument17 pagesChemical bonding essentialsHamad FarooqueNo ratings yet
- Merit Science Academy Chemistry 1st Year Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesMerit Science Academy Chemistry 1st Year Exam QuestionsShakaibNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Colloid ChemistryDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Colloid ChemistrySrynnENo ratings yet
- 8 - Chem - TB Sol - CH 6 Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pages8 - Chem - TB Sol - CH 6 Chemical ReactionsNetra VasoyaNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Chemical BondingDocument145 pagesSheet - 01 - Chemical BondingMankirat SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFDocument16 pages5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFArinjayNo ratings yet
- Creative Learning Classes, Karkala: Second Pu Annual Examination April - 2022 Chemistry Detailed SolutionDocument14 pagesCreative Learning Classes, Karkala: Second Pu Annual Examination April - 2022 Chemistry Detailed SolutionBazil 9393No ratings yet
- First Year Higher Secondary Examination June 2022 CHEMISTRY - ANSWER KEY (Unofficial)Document7 pagesFirst Year Higher Secondary Examination June 2022 CHEMISTRY - ANSWER KEY (Unofficial)Ashkar AshrafNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Solution Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Solution Set 1Sidharth SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Basics PDFDocument19 pagesCorrosion Basics PDFAdityaRamaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class XII Chemistry Board Paper - 2015 SolutionDocument16 pagesCbse Class XII Chemistry Board Paper - 2015 SolutionrahulNo ratings yet
- 08 Pericyclic ReactionsDocument27 pages08 Pericyclic ReactionsEmmanuel YakubuNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry: 17 Thermodynamics Exam-Style Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesAQA Chemistry: 17 Thermodynamics Exam-Style Mark SchemeSarai AliNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry: Physical Adsorption Chemical AdsorptionDocument6 pagesSurface Chemistry: Physical Adsorption Chemical Adsorptioniipud072.giridhar.k MESKKPUCNo ratings yet
- Water Coagulation and Flocculation 1663749610Document53 pagesWater Coagulation and Flocculation 1663749610salehNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and Flocculation Water Treatment ProcessDocument53 pagesCoagulation and Flocculation Water Treatment ProcessConstantinTudoseNo ratings yet
- 1.lattice EnergyDocument18 pages1.lattice EnergyaqidahNo ratings yet
- 5. Surface Chemistry_watermarkDocument29 pages5. Surface Chemistry_watermarkendlesshacker123No ratings yet
- Annual Exam Chemistry Answer KeyDocument8 pagesAnnual Exam Chemistry Answer KeyKala LandNo ratings yet
- Slow Learners Copy 2019-20NEW-2 PDFDocument16 pagesSlow Learners Copy 2019-20NEW-2 PDFVishwajith ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemistry Marks:40Document4 pagesClass XII Chemistry Marks:40kannan2030No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 3Document104 pagesIlovepdf Merged 3api-533764142No ratings yet
- Cbse Class XII Chemistry Board Paper - 2015 SolutionDocument14 pagesCbse Class XII Chemistry Board Paper - 2015 SolutionSaugata HalderNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and BatteriesDocument1 pageElectrochemistry and BatteriesPRUTHVINo ratings yet
- Karnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper 2019Document12 pagesKarnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper 2019sparkysanthosh69No ratings yet
- Model Paper 6 SchemeDocument11 pagesModel Paper 6 SchemeKalyan ReddyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Solution Set 5Document13 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Solution Set 5Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Lattice Enthalpies and Born Haber CyclesDocument8 pagesLattice Enthalpies and Born Haber CyclesAlexander HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry - MCQsDocument11 pagesSurface Chemistry - MCQsHumaira RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Lattice Energy ExplainedDocument22 pagesLattice Energy Explainednotabc gamer100% (1)
- Surface Chemistry: Short Answer QuestionsDocument7 pagesSurface Chemistry: Short Answer QuestionsReddi Venkata SridharNo ratings yet
- Nature of Chemical Bond S IDocument13 pagesNature of Chemical Bond S I4 bagwe OmNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument6 pagesSurface ChemistryMstr SanatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Lattice EnergyDocument10 pagesChapter 20 Lattice EnergyWhyte MayTooNo ratings yet
- Specification Points Covered: Ionic SubstancesDocument11 pagesSpecification Points Covered: Ionic SubstancesIsabella ThomasNo ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument9 pagesSample PaperPc xoixaNo ratings yet
- 620oswaal CBSE Class-10, Term-1 Science - Revision NotesDocument22 pages620oswaal CBSE Class-10, Term-1 Science - Revision NotesDivyam RohillaNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemstry Question BankDocument4 pagesSurface Chemstry Question Bankeeshwar saagarNo ratings yet
- Unit-5-Surface ChemistryDocument3 pagesUnit-5-Surface ChemistryRSNo ratings yet
- CATALYSTS AND COLLOIDS EXPLAINED UNDER 40 CHARACTERSDocument16 pagesCATALYSTS AND COLLOIDS EXPLAINED UNDER 40 CHARACTERSmehak aulakhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Physical Chemistry: Recommended Prior Knowledge: ContextDocument4 pagesUnit 2: Physical Chemistry: Recommended Prior Knowledge: ContextHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Class XII Chemistry SolutionsDocument17 pagesMaharashtra Board Class XII Chemistry SolutionsSaniya MujawarNo ratings yet
- Grade 5. Unit 15Document6 pagesGrade 5. Unit 15Đình ThuậnNo ratings yet
- Subway 2009Document12 pagesSubway 2009sparklers_mNo ratings yet
- Bab 06 PindahPanasDocument41 pagesBab 06 PindahPanasPurna Satria NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Choosing the Right Handbag or Food Product (38 charactersDocument24 pagesChoosing the Right Handbag or Food Product (38 charactersNiceman NatiqiNo ratings yet
- Sarah Fahy CV College PDFDocument4 pagesSarah Fahy CV College PDFapi-487352339No ratings yet
- ECSS Q ST 70 02C (15november2008)Document45 pagesECSS Q ST 70 02C (15november2008)jsadachiNo ratings yet
- Inr Si47 1038g e PDFDocument107 pagesInr Si47 1038g e PDFsd23No ratings yet
- Caffeine Natural Coffee BeanDocument1 pageCaffeine Natural Coffee BeanMayang TariNo ratings yet
- Exxonmobil High Density Polyethylene Product Guide: Extrusion MoldingDocument6 pagesExxonmobil High Density Polyethylene Product Guide: Extrusion MoldingDaikinllcNo ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla Would Have Celebrated Christmas On January 7thDocument3 pagesNikola Tesla Would Have Celebrated Christmas On January 7thAnonymous DfeajF100% (1)
- Maximize muscle gains with reverse pyramid trainingDocument8 pagesMaximize muscle gains with reverse pyramid trainingMusadiq Ahmed100% (1)
- With Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western MountainsDocument3 pagesWith Reference To Relief, Drainage and Economic Importance, Explain The Differences Between The Northern Mountains and Western Mountainshajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- 4140DE Data SheetDocument1 page4140DE Data SheetNabeel AmeerNo ratings yet
- DBXLH 8585B VTMDocument4 pagesDBXLH 8585B VTMmau_mmx5738No ratings yet
- Minutes of The MeetingDocument2 pagesMinutes of The MeetingJeremy Gaddi100% (1)
- Continuous Renal Replacement TherapyDocument9 pagesContinuous Renal Replacement Therapydoc_next_doorNo ratings yet
- Wörterbuch Der Humanbiologie - Dictionary of Human Biology - Deutsch - Englisch - Englisch - Deutsch. English - German - German - English (PDFDrive)Document1,002 pagesWörterbuch Der Humanbiologie - Dictionary of Human Biology - Deutsch - Englisch - Englisch - Deutsch. English - German - German - English (PDFDrive)MilaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Components and InteractionsDocument31 pagesEcosystem Components and InteractionsBirraa TajuNo ratings yet
- Examination of Power Electronics (Pel) : AnswerDocument10 pagesExamination of Power Electronics (Pel) : Answerves vegasNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods for Terrestrial Amphibians and ReptilesDocument39 pagesSampling Methods for Terrestrial Amphibians and ReptilesBenzu Shawn100% (1)
- NASA Water Filtration System GuideDocument54 pagesNASA Water Filtration System GuideBoey Soo Yin100% (1)
- NFPA 97 - 2003 Standard Glossary of Terms Relating To Chimneys, Vents, and Heat-Producing AppliancesDocument34 pagesNFPA 97 - 2003 Standard Glossary of Terms Relating To Chimneys, Vents, and Heat-Producing Appliancesonepunchman yaoNo ratings yet
- DC-FAST 1.000, 2.000, 3.000, 5.000, 6.000 e 7.000 - New Project - 2021 - PT - BRDocument65 pagesDC-FAST 1.000, 2.000, 3.000, 5.000, 6.000 e 7.000 - New Project - 2021 - PT - BRCentrifugal SeparatorNo ratings yet
- Lodging EstablishmentsDocument2 pagesLodging EstablishmentsMich A. Gonzales0% (1)
- Topic - 2015 Quality MethotdDocument12 pagesTopic - 2015 Quality MethotdclaudiaNo ratings yet
- TS68Document52 pagesTS68finandariefNo ratings yet
- SKF Frecuently Questions With AnswersDocument16 pagesSKF Frecuently Questions With AnswersCarlos AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Post-Emulsified Fluorescent (Hydrophilic & Lipophilic)Document13 pagesChapter 11 Post-Emulsified Fluorescent (Hydrophilic & Lipophilic)maxpan maxNo ratings yet
- Form Ibpr Haul Road PDFDocument2 pagesForm Ibpr Haul Road PDFelvandi100% (1)
- Online Medicine Industry Competitor AnalysisDocument14 pagesOnline Medicine Industry Competitor Analysispawangadiya1210No ratings yet