Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AC 3101 CHAPTER 9 Notes
Uploaded by
Kemuel Tantuan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesUnder a consignment arrangement, an entity known as the consignor delivers goods to another party called the consignee to sell on the consignor's behalf. The consignor only recognizes revenue when the consignee sells the goods to end customers. Until then, the consigned goods remain in the consignor's inventory. Typically the consignee is entitled to a commission based on the consignor's sales price. Repair costs for damaged goods are the consignor's expense.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUnder a consignment arrangement, an entity known as the consignor delivers goods to another party called the consignee to sell on the consignor's behalf. The consignor only recognizes revenue when the consignee sells the goods to end customers. Until then, the consigned goods remain in the consignor's inventory. Typically the consignee is entitled to a commission based on the consignor's sales price. Repair costs for damaged goods are the consignor's expense.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesAC 3101 CHAPTER 9 Notes
Uploaded by
Kemuel TantuanUnder a consignment arrangement, an entity known as the consignor delivers goods to another party called the consignee to sell on the consignor's behalf. The consignor only recognizes revenue when the consignee sells the goods to end customers. Until then, the consigned goods remain in the consignor's inventory. Typically the consignee is entitled to a commission based on the consignor's sales price. Repair costs for damaged goods are the consignor's expense.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
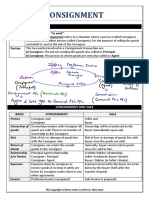
CHAPTER 9: CONSIGNMENT SALES
Introduction Through mark-up on the final
selling price
An entity applies
In some arrangements
o PFRS 15
o Consignee receives both
Revenue from contracts with
Markup
customers
Commission
Supersedes PAS 18
Commission
Revenue
o Consignor
Consignment Arrangements Expense
o Consignee
Under a consignment arrangement
Income
o An entity (consignor) delivers to
Normally, consignee
another party (consignee)
o Deducts commission from the amount
Who undertakes to sell the
remitted to the consignor
goods to end customers in
In cases where commission is given in advance
behalf of the consignor
o Consignor records the advance
Consignor recognizes revenue
commission
o ONLY when the consignee sells the
As receivable
consigned goods to end customers
Not cost of inventory
Because this is the only time
o When sold to end customer
that the consignor
Derecognize receivable
relinquishes control over the
Recognize commission
goods
expense
Consigned goods
When goods are sold to end customers
o Remain in the consignor’s inventory
o Consignor
Until they are sold to end
Recognizes revenue at gross
customers
amount of consideration
Consignee records the consigned goods
Sales price agreed
o Only through memo entries
with the consignee
Freight and Other Incidental costs
o Consignee
o That the consignor incurs
Recognizes revenue
Are capitalized as cost of the
At commission or fee
consigned goods
to which it is entitled
Repair costs for damages
It is uncommon
o Expenses
o For a consignor to be notified for
If the consignor shoulders the freight and
every sale
other incidental costs
o There are scheduled dates instead
o When reimbursable
Depending on the
Consignee records it as a
arrangement
receivable from the consignor
o If not reimbursable Principal vs Agent Considerations
Considered as expense (additional guidelines according to PFRS 15)
In a typical consignment When another party is involved in providing
o Consignee is entitled to a commission goods or services to a customer
Based on the consignor’s o The entity shall determine whether it
sales price is acting as
In other arrangements Principal
o As the it is sold to the end customer Agent
the consignee as if purchases it Principal
o Consignee earns income o If it controls the good or service
Before it is transferred to a exchange for the other party’s goods or
customer services
However, entity is not a principal if it obtains
legal time (only momentarily)
o Before transferred to a customer
Principal
o May personally satisfy a performance
obligation
o Or it may engage another party or a
subcontractor
To satisfy some or all of a
performance obligation, on its
behalf
o When the performance obligation is
satisfied
The principal
Recognizes revenue
at the gross amount
of consideration
Agent
o Is its performance obligation is to
arrange the provision of goods or
services
By another party
o When performance obligation is
satisfied
The agent
Recognizes revenue
at the commission or
fee to which it is
entitled to
Indicators that an entity is an agent
o Another party is primarily responsible
for fulfilling the contract
o The entity does not have inventory
risk
Before or after the goods
have been ordered by a
customer
During shipping
On return
o The entity does not have discretion in
establishing prices for the other
party’s goods or services
The benefit that the entity
receives from those goods or
services
LIMITED
The entity’s consideration
o In the form of commission
The entity is not exposed to credit risk for the
amount receivable from the customer in
You might also like
- Consignment PDFDocument31 pagesConsignment PDFBijay Aryan DhakalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Consignment: Learning OutcomesDocument35 pagesUnit 3: Consignment: Learning OutcomesDurga Prasad HNo ratings yet
- Summary PADocument6 pagesSummary PAKhansa RasyaNo ratings yet
- MEDYOFINALPPTDocument9 pagesMEDYOFINALPPTKen Keiro CayananNo ratings yet
- CH 06 Unit 03Document31 pagesCH 06 Unit 03ASIFNo ratings yet
- AC 3101 CHAPTER 10 NotesDocument2 pagesAC 3101 CHAPTER 10 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- MEDYOFINALPPTDocument9 pagesMEDYOFINALPPTKen Keiro CayananNo ratings yet
- PAS 2 - InventoriesDocument3 pagesPAS 2 - InventoriesCzar RabayaNo ratings yet
- ISC Accounts ConsignmentDocument4 pagesISC Accounts Consignmentbcom100% (3)
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource WasTrixie HicaldeNo ratings yet
- Consignment SalesDocument10 pagesConsignment SalesMhelka TiodiancoNo ratings yet
- Inoterms 2000 GridDocument8 pagesInoterms 2000 GridPankil R ShahNo ratings yet
- ConsignmentDocument5 pagesConsignmentMANKARAN SINGH BHATIA 21-22No ratings yet
- Consignment Accounting Notes and CPAR QuizzerDocument5 pagesConsignment Accounting Notes and CPAR QuizzerAman SinayaNo ratings yet
- HO Inventories IntroDocument2 pagesHO Inventories IntroAl Francis GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Consignment AccountDocument9 pagesConsignment AccountGamers 4 lyfNo ratings yet
- Presentation Incoterms - CompressedDocument12 pagesPresentation Incoterms - CompressedAlma DwiyNo ratings yet
- Incoterms 2020 Rules Chart of Responsibility: Any Transport Mode Sea/Inland Waterway Transport Any Transport ModeDocument2 pagesIncoterms 2020 Rules Chart of Responsibility: Any Transport Mode Sea/Inland Waterway Transport Any Transport ModeRicardo PirelaNo ratings yet
- Class Notes of Consignor & ConsigneeDocument13 pagesClass Notes of Consignor & ConsigneeDb100% (1)
- ConsignmentDocument22 pagesConsignmentAkshat jainNo ratings yet
- Consignment Accounts Proforma EntriesDocument4 pagesConsignment Accounts Proforma EntriesM SHILPANo ratings yet
- LNG Trader: Take-Or-Pay Transaction Contractual RelationshipsDocument1 pageLNG Trader: Take-Or-Pay Transaction Contractual RelationshipsMohd Sufian SahranNo ratings yet
- Purchases With Cash DiscountsDocument3 pagesPurchases With Cash Discountsgnzg.belaNo ratings yet
- Chartered Accountants: Hospitality - Conract SynopsisDocument7 pagesChartered Accountants: Hospitality - Conract Synopsisabdullahsaleem91No ratings yet
- INCOTERM - HillebrandDocument18 pagesINCOTERM - HillebrandjosecastillejocamposNo ratings yet
- Combined Transport Bill of Lading: NegotiableDocument2 pagesCombined Transport Bill of Lading: NegotiableFahrieMan ManNo ratings yet
- Consignment ConceptsDocument34 pagesConsignment ConceptsRanne BalanaNo ratings yet
- OS ContractsDocument4 pagesOS Contractspablo.castiella.esqNo ratings yet
- Consignment SalesDocument1 pageConsignment SalesSantiago BuladacoNo ratings yet
- RFBT Law On Sale NotesDocument7 pagesRFBT Law On Sale NotesSAMANTHA GEL SABELA PANLILEONo ratings yet
- 101rev TradingDocument3 pages101rev TradingJerah Marie PepitoNo ratings yet
- USJ-R College of Commerce - Acctg 101 RM 403 MWF 8:30 AM - 10:30 AM - NEF, CPADocument3 pagesUSJ-R College of Commerce - Acctg 101 RM 403 MWF 8:30 AM - 10:30 AM - NEF, CPAJerah Marie PepitoNo ratings yet
- Documentos TareaDocument5 pagesDocumentos TareaInes Toral CusmeNo ratings yet
- Financing of Foreign TradeDocument18 pagesFinancing of Foreign Tradepriya nNo ratings yet
- 9 Consignment SalesDocument11 pages9 Consignment SalesNil Justeen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Law On SalesDocument20 pagesLaw On SalesbimsantosNo ratings yet
- Incoterms 2010Document1 pageIncoterms 2010Ahmed SaudNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ConsignmentDocument7 pagesAccounting For ConsignmentsmlingwaNo ratings yet
- Contracting Carrier 1F Fu Ho BLDG 5 Kao Hong Kong 91 Hong Kong HK Datateck Ind E Com de Comp Eletro Est Costa Gama 110 Guaiba Rs 92500-000Document12 pagesContracting Carrier 1F Fu Ho BLDG 5 Kao Hong Kong 91 Hong Kong HK Datateck Ind E Com de Comp Eletro Est Costa Gama 110 Guaiba Rs 92500-000David Solorzano GuerraNo ratings yet
- Accounting 511 - ConsignmentDocument6 pagesAccounting 511 - ConsignmentLorenz BaguioNo ratings yet
- 3 Joint VentureDocument9 pages3 Joint VentureRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- International LawDocument6 pagesInternational LawShin JieNo ratings yet
- Guide To Due Dilligence Bills of Lading Ver2.2Document5 pagesGuide To Due Dilligence Bills of Lading Ver2.2Xue Feng DuNo ratings yet
- Consignment Account With Del Credere Clause: by Nikhil BabuDocument8 pagesConsignment Account With Del Credere Clause: by Nikhil BabuVarsha ThimmaiahNo ratings yet
- The Incoterms: Port of Destination)Document4 pagesThe Incoterms: Port of Destination)KlaudiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Intermediate Accounting Part 3Document6 pagesReviewer - Intermediate Accounting Part 3Derek Dale Vizconde NuñezNo ratings yet
- Merch 1Document3 pagesMerch 1Angelica EcliseNo ratings yet
- Incoterms Chart of Responsibility 2020 1Document1 pageIncoterms Chart of Responsibility 2020 1Hiro Katsumoto100% (1)
- Afar.2905 Business Combination Mergers PDFDocument5 pagesAfar.2905 Business Combination Mergers PDFCyrille Keith FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Cansingnment Account)Document24 pagesChapter 1 (Cansingnment Account)Bravish GowardhanNo ratings yet
- Tariff and Customs CodeDocument7 pagesTariff and Customs CodeJaylin DizonNo ratings yet
- CONSIGNMENT ACCOUNT - Docx2Document8 pagesCONSIGNMENT ACCOUNT - Docx2Gamer nestNo ratings yet
- Afar 2814 Consignment Sales PDFDocument4 pagesAfar 2814 Consignment Sales PDFMay Grethel Joy Perante100% (1)
- Incoterms 2020 Eng 04 2020Document3 pagesIncoterms 2020 Eng 04 2020Indra Budi PerwiraNo ratings yet
- AC 2101 CHAPTER 2 NotesDocument2 pagesAC 2101 CHAPTER 2 NotesChriz VillasNo ratings yet
- Consignment Account PDFDocument13 pagesConsignment Account PDFAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- CONSIGNMENT - Focus NotesDocument5 pagesCONSIGNMENT - Focus NotesbrunxNo ratings yet
- Textbook+Examples+9.2-9.10+ Copy+From+Old+TextbookDocument13 pagesTextbook+Examples+9.2-9.10+ Copy+From+Old+Textbookotlotleng.sebelebeleNo ratings yet
- AC 2202 CHAPTER 17 NotesDocument8 pagesAC 2202 CHAPTER 17 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC 2202 CHAPTER 2 NotesDocument7 pagesAC 2202 CHAPTER 2 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC 2101 CHAPTER 26 NotesDocument5 pagesAC 2101 CHAPTER 26 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC 2101 Chapter 23 NotesDocument4 pagesAC 2101 Chapter 23 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC 3101 CHAPTER 10 NotesDocument2 pagesAC 3101 CHAPTER 10 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC2201 CHAPTER 19 NotesDocument3 pagesAC2201 CHAPTER 19 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- "A Study On Working Capital Management of Apollo Tyres LTD": Project Report Submitted ToDocument59 pages"A Study On Working Capital Management of Apollo Tyres LTD": Project Report Submitted ToNITISH CHANDRA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Operating Costing HotelDocument1 pageOperating Costing Hotelmonish147852No ratings yet
- Extra DatosDocument33 pagesExtra DatosPatricia MariaNo ratings yet
- Summary - A Short Course On Swing TradingDocument2 pagesSummary - A Short Course On Swing TradingsumonNo ratings yet
- FM PFDocument12 pagesFM PFJenelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- T1 Capstone Project Submission TemplateDocument16 pagesT1 Capstone Project Submission TemplateSurbhi SoodNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument52 pagesStrategic ManagementDesmondNo ratings yet
- Sundram Fasteners Annual Report 2023Document247 pagesSundram Fasteners Annual Report 2023vijayNo ratings yet
- Business Law Assignment by Savreen KaurDocument9 pagesBusiness Law Assignment by Savreen KaurShambhavi NarangNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionRasy DuddinNo ratings yet
- CGC HACCP ChecklistDocument9 pagesCGC HACCP ChecklistmahmoodabdellatifNo ratings yet
- AntiCor RevisitedDocument79 pagesAntiCor RevisitedAbba MakNo ratings yet
- GG METALKRAFTS, Moradabad: Missing Documents in BUSY Data (GSTR2)Document1 pageGG METALKRAFTS, Moradabad: Missing Documents in BUSY Data (GSTR2)HeliumByBGC AccountsNo ratings yet
- Sales Coaching A Practical Guide For Sales ManagersDocument18 pagesSales Coaching A Practical Guide For Sales ManagersAgnes Yu100% (1)
- Hazard Mitigation and Preparedness An Introductory Text For Emergency Management and Planning Professionals 2nd Schwab Test BankDocument23 pagesHazard Mitigation and Preparedness An Introductory Text For Emergency Management and Planning Professionals 2nd Schwab Test Bankpeelefisc7vnzww100% (35)
- Technopreneurship Course OutlineDocument9 pagesTechnopreneurship Course OutlineDino Dizon100% (1)
- Business Plan Jute BagDocument5 pagesBusiness Plan Jute BagToshika Monika75% (8)
- Industry Report - Wael AlhathalDocument8 pagesIndustry Report - Wael AlhathalWael Talal AlhathalNo ratings yet
- Handling Guidelines: Part 4: Handling Fibcs With Fork-Lift TrucksDocument4 pagesHandling Guidelines: Part 4: Handling Fibcs With Fork-Lift TrucksZahir KhiraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Civil Engineering Construction - Abebe Dinku, Alfred Ngowi and Ninatubu Lema Final Version 20.1.2015Document500 pagesFundamentals of Civil Engineering Construction - Abebe Dinku, Alfred Ngowi and Ninatubu Lema Final Version 20.1.2015Nyakikaye MatesigwaNo ratings yet
- Design Dissertation: Vibhav A. Chavan 2018017Document8 pagesDesign Dissertation: Vibhav A. Chavan 201801717 Vibhav ChavanNo ratings yet
- Termpaper-Mgt211.3 NameDocument7 pagesTermpaper-Mgt211.3 NameMD. SAZID HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- Verification of InsuranceDocument1 pageVerification of InsuranceJeremy Ware100% (2)
- E02754802 PESA 2022 ElayDocument256 pagesE02754802 PESA 2022 ElayAziel MeloNo ratings yet
- North American Journal of Economics and Finance: Meiyu Tian, Wanyang Li, Fenghua WenDocument21 pagesNorth American Journal of Economics and Finance: Meiyu Tian, Wanyang Li, Fenghua Wenmaria ianNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Skillsof Womeninthe Rural CommunitiesDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurial Skillsof Womeninthe Rural Communities娜奎No ratings yet
- CT NZ Solutions 2010Document16 pagesCT NZ Solutions 2010Dave MudfordNo ratings yet
- The Economic Impacts of The 4IR On BangladeshDocument5 pagesThe Economic Impacts of The 4IR On BangladeshManjur AlamNo ratings yet
- Money LaunderingDocument56 pagesMoney Launderingstudent-mbaNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0 RealDocument8 pagesIndustry 4.0 Realmohan sarasNo ratings yet
- Learn the Essentials of Business Law in 15 DaysFrom EverandLearn the Essentials of Business Law in 15 DaysRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)
- Buffettology: The Previously Unexplained Techniques That Have Made Warren Buffett American's Most Famous InvestorFrom EverandBuffettology: The Previously Unexplained Techniques That Have Made Warren Buffett American's Most Famous InvestorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- Law of Leverage: The Key to Exponential WealthFrom EverandLaw of Leverage: The Key to Exponential WealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Introduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsFrom EverandIntroduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Getting Through: Cold Calling Techniques To Get Your Foot In The DoorFrom EverandGetting Through: Cold Calling Techniques To Get Your Foot In The DoorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (63)
- AI For Lawyers: How Artificial Intelligence is Adding Value, Amplifying Expertise, and Transforming CareersFrom EverandAI For Lawyers: How Artificial Intelligence is Adding Value, Amplifying Expertise, and Transforming CareersNo ratings yet
- Disloyal: A Memoir: The True Story of the Former Personal Attorney to President Donald J. TrumpFrom EverandDisloyal: A Memoir: The True Story of the Former Personal Attorney to President Donald J. TrumpRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- Secrecy World: Inside the Panama Papers Investigation of Illicit Money Networks and the Global EliteFrom EverandSecrecy World: Inside the Panama Papers Investigation of Illicit Money Networks and the Global EliteRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Wall Street Money Machine: New and Incredible Strategies for Cash Flow and Wealth EnhancementFrom EverandWall Street Money Machine: New and Incredible Strategies for Cash Flow and Wealth EnhancementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Startup Visa: U.S. Immigration Visa Guide for Startups and FoundersFrom EverandThe Startup Visa: U.S. Immigration Visa Guide for Startups and FoundersNo ratings yet
- California Employment Law: An Employer's Guide: Revised and Updated for 2024From EverandCalifornia Employment Law: An Employer's Guide: Revised and Updated for 2024No ratings yet
- The Motley Fool's Rule Makers, Rule Breakers: The Foolish Guide to Picking StocksFrom EverandThe Motley Fool's Rule Makers, Rule Breakers: The Foolish Guide to Picking StocksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The SHRM Essential Guide to Employment Law, Second Edition: A Handbook for HR Professionals, Managers, Businesses, and OrganizationsFrom EverandThe SHRM Essential Guide to Employment Law, Second Edition: A Handbook for HR Professionals, Managers, Businesses, and OrganizationsNo ratings yet
- Nolo's Quick LLC: All You Need to Know About Limited Liability CompaniesFrom EverandNolo's Quick LLC: All You Need to Know About Limited Liability CompaniesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- International Business Law: Cases and MaterialsFrom EverandInternational Business Law: Cases and MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Eagle on the Street: The SEC and Wall Street during the Reagan YearsFrom EverandEagle on the Street: The SEC and Wall Street during the Reagan YearsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Chickenshit Club: Why the Justice Department Fails to Prosecute ExecutivesWhite Collar CriminalsFrom EverandThe Chickenshit Club: Why the Justice Department Fails to Prosecute ExecutivesWhite Collar CriminalsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (24)
- Contract Law in America: A Social and Economic Case StudyFrom EverandContract Law in America: A Social and Economic Case StudyNo ratings yet
- New York Management Law: The Practical Guide to Employment Law for Business Owners and ManagersFrom EverandNew York Management Law: The Practical Guide to Employment Law for Business Owners and ManagersNo ratings yet