Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AC2201 CHAPTER 19 Notes
Uploaded by
Kemuel TantuanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AC2201 CHAPTER 19 Notes
Uploaded by
Kemuel TantuanCopyright:
Available Formats
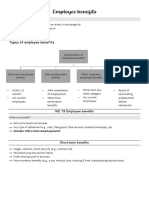
CHAPTER 19: OTHER EMPLOYEE BENEFITS
Short-term Employee Benefits Any short-term benefits paid in advance
o Shall be recognizes as a prepayment
Are employee benefits other than termination
To the extent, that it will lead
benefits
to a reduction in future
o Which are expected to be settled
payments or a cash refund
wholly within 12 months after the end
The cost of short-term benefits
of the annual reporting period
o Shall be recognized as expense
In which the employees
In the period when the
render the related service
economic benefit is given
Includes the following
Except:
o Salaries, wages and social security
o When such
contributions
cost may be
o Short-term compensated or paid
included
absences
within the
Such as
cost of an
Paid annual leave
asset
Paid sick leave
Profit sharing and bonuses payable within 12 Short-term compensated or paid absences
months
An entity may pay employees for absences for
Nonmonetary benefits
various reasons
o Such as
o Such as
Medical care
Vacation
Housing
Sickness
Car
Short-term disability
Free or subsidized goods
Maternity or paternity
Recognition and Measurement Military service
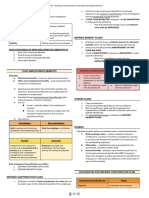
Entitlement to paid absences falls into two
Accounting for short-term employee benefits
categories:
o Fairly straightforward
o Accumulating absences
Because there are no
o Non-accumulating absences
actuarial assumptions
Accumulating paid absences
No requirement to discount future benefits
o Are those that are carried forward
o Because such benefits are all payable
o Can be used in future periods
no later than 12 months
If the current period’s
After the end of the current
entitlement is not used in full
reporting period
o May be either
No possibility of actuarial gain or loss
Vesting
o Because short-term employee
Employees are
benefits are measured on an
entitled to a cash
undiscounted basis
payment for unused
Accounting Procedures entitlement on
(The rules for short-term employee benefits are essentially leaving the entity
an application of basic accounting principles and practice) Nonvesting
Employees are not
Unpaid short-term employee benefits at the
entitled to a cash
end of the accounting period
payment for unused
o Shall be recognized as accrued
entitlement on
expense
leaving the entity
Non-accumulating paid absences
o Those that are not carried forward
o Such benefits lapse if the current Other Long-term Employee Benefits
period’s entitlement is not used
Residual definition
Do not entitle the employees
All employee benefits other than short-term
to a cash payment for unused
employee benefits, postemployment and
entitlement on leaving the
termination benefits
entity
Not expected to be settled wholly within
o This is commonly the case for
twelve months after the end of annual
Sick pay
reporting period
Maternity or paternity leave
o In which the employees render the
Paid absences for military
related service
service
Examples of other long-term employee benefits
Profit-sharing and bonus plans
Long-term paid absences
Under some profit sharing plans
o Such as
o Employees shall receive a share of the
Long service
profit
Sabbatical leave
Only if they remain with the
Jubilee or other long service benefit
entity for a specified period
o Such plans create a constructive Long-term disability benefit
obligation Profit sharing and bonuses
As employees render service Deferred compensation
that increases the amount to Recognition and Measurement
be paid
If they remain in The recognition and measurement for other
service until the end long-term employee benefits
of the specified o Are the same as the recognition and
period measurement of defined benefit
o The measurement of such obligation
constructive obligation Liability recognized for other long-term
Reflects the possibility that employee benefits
some employees may leave o Is equal to the excess of PV of the
without receiving profit- liability over the FV of the plan assets
sharing payments At the end of the reporting
period
Recognition and Measurement Difference
(PAS 19 provides that an entity shall recognize the expected
o Recognition of the components of the
cost of profit-sharing and bonus payment when ALL of the
defined benefit cost
following conditions are present)
For other long-term employee benefits
The entity has a present legal or constructive o All of the following components of
obligation defined benefit cost are recognized in
o To make such payment as a result of profit or loss
past event Included in the computation
A reliable estimate of the obligation can be of employee benefit expense
made Current service cost
Past service cost
A present obligation exists when the entity has no
Any gain or loss on
realistic alternative but to make the payment.
settlement
Any difference between the estimated liability Net interest expense
and actual payment or net interest income
o Accounted for as change in Remeasurements
accounting estimate For defined benefit obligation
Included in profit or loss these are included in the OCI
Termination Benefits Recognition of termination benefits
Are employee benefits provided in exchange An entity shall recognize an expense and a
for the termination of an employee’s liability for termination benefits at the earlier
employment of the following dates:
o As a result of either o When the entity can no longer
An entity’s decision to withdraw the offer of the termination
terminate an employee’s benefits
employment before the When the plan is already
normal retirement date communicated or announced
An employee’s decision to to the affected employee
accept an offer of benefits in o When the entity recognizes the cost
exchange for the termination of restructuring
of employment That involves the payment of
The event that gives rise to the obligation termination benefits
o Termination of Employment Implicit in the recognition criteria
Rather than employee service o There needs to be an offer of
Unrelated for future employee service termination that binds the entity in
Do not include: some way
o Employee benefits resulting from Offer of termination
termination of employment at the o Is the action or activity deemed to
request of the employee give rise to the termination liability
Without an entity offer Termination costs that are part of a
o As a result of mandatory retirement restructuring place
These are postemployment o Are recognized at the same time as
benefits the recognition of other restructuring
Usually lump sum payments but sometimes costs
include Restructuring costs
o Enhancement of postemployment o Expenditures that are necessarily
benefits incurred for the restructuring
Either directly or indirectly Not associated with ongoing
Through an employee activities of the entity
benefit plan o Examples:
o Salary until the end of a specified Salaries and benefits of
period employees to be incurred
If the employee renders no after operation cease
further service
Measurement of termination benefits
That provides
economic benefits to If the termination benefits are expected to be
the entity settled wholly within 12 months after the end of
the reporting period
Fundamental Principles of Termination benefit o In which the termination benefit is
recognized
Not conditional on future service being
The requirements for short-term
provided benefit shall be applied.
Short period between offer of termination and Termination benefits are
actual termination measures at the undiscounted
amount
If the termination benefits are not expected to be
settled wholly within 12 months after the end of
the reporting period
o The requirements for long-term benefit
shall be applied.
o Measured at the discounted amount
You might also like
- AC 2202 CHAPTER 17 NotesDocument8 pagesAC 2202 CHAPTER 17 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- Accounting for Employee BenefitsDocument6 pagesAccounting for Employee BenefitsHannah Jane Arevalo LafuenteNo ratings yet
- PAS 19 Employee BenefitsDocument62 pagesPAS 19 Employee BenefitsBenj FloresNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefit - 181121Document26 pagesEmployee Benefit - 181121KhansaFatinNo ratings yet
- IAS 19 Employee BenefitDocument20 pagesIAS 19 Employee BenefitAklilNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits Part 1.1Document5 pagesEmployee Benefits Part 1.1Shanelle SilmaroNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits Under PAS 19, IAS 19 and RA 7641Document18 pagesEmployee Benefits Under PAS 19, IAS 19 and RA 7641alabwalaNo ratings yet
- IAS 19-Employee BenefitsDocument46 pagesIAS 19-Employee Benefitsmdhuzzal100% (3)
- Ind AS On Employee BenefitDocument81 pagesInd AS On Employee BenefitSanjay GohilNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits: - CA. (DR.) Anand BankaDocument32 pagesEmployee Benefits: - CA. (DR.) Anand BankaNEHA NAYAKNo ratings yet
- IAS 19 Employee Benefits OverviewDocument8 pagesIAS 19 Employee Benefits OverviewAANo ratings yet
- Employees Benefit PalnDocument60 pagesEmployees Benefit PalnHimanshu GaurNo ratings yet
- Accounting-for-Employee-benefitsDocument35 pagesAccounting-for-Employee-benefitsOnwuchekwa Chidi CalebNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefit 2020Document18 pagesEmployee Benefit 2020harman singhNo ratings yet
- 1 IAS 19 EMPLOYEE BENEFITS With Suggested Answers As of 11 10Document13 pages1 IAS 19 EMPLOYEE BENEFITS With Suggested Answers As of 11 10Kimberly IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Handout 3.0 ACC 226 Sample Problems Employee BenefitsDocument12 pagesHandout 3.0 ACC 226 Sample Problems Employee BenefitsLyncee BallescasNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 11: Employee Benefits IAS-19Document3 pagesLecture # 11: Employee Benefits IAS-19ali hassnainNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits P201Document17 pagesEmployee Benefits P201krisha milloNo ratings yet
- Acc 203 FinalsDocument10 pagesAcc 203 Finalspchu4019No ratings yet
- Employee Benefits P201Document18 pagesEmployee Benefits P201krisha milloNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at A Glance IAS 19 Employee BenefitsDocument5 pagesIfrs at A Glance IAS 19 Employee BenefitsnanaNo ratings yet
- Employee BenefitsDocument3 pagesEmployee BenefitsZance JordaanNo ratings yet
- Ias 19 Employee BeneftDocument24 pagesIas 19 Employee Beneftesulawyer2001No ratings yet
- Pas 19Document2 pagesPas 19MMBRIMBAPNo ratings yet
- Salary and Its TaxationDocument12 pagesSalary and Its TaxationBasit BandayNo ratings yet
- IAS 19 Employee BenefitsDocument14 pagesIAS 19 Employee BenefitsShiza ArifNo ratings yet
- Finacc ReviewerDocument4 pagesFinacc Reviewer200617No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - Employee Benefits IFRS (IAS 19) and Then ASPE (Section 3462), Minor Difference Flashcards - QuizletDocument1 pageChapter 21 - Employee Benefits IFRS (IAS 19) and Then ASPE (Section 3462), Minor Difference Flashcards - QuizletcathNo ratings yet
- EmployeebenefitsreportDocument172 pagesEmployeebenefitsreportMikaela LacabaNo ratings yet
- 74702bos60485 Inter p1 cp6 U1Document27 pages74702bos60485 Inter p1 cp6 U1Saroj dasNo ratings yet
- FEU Institute Employee Benefits NotesDocument8 pagesFEU Institute Employee Benefits NotesAj PotXzs ÜNo ratings yet
- Annexure 3 Compensation FeeDocument3 pagesAnnexure 3 Compensation Feewanjariabhi6235No ratings yet
- Employee Benefits: PAS 19, PAS 20, PAS 23, and PAS 24 Philippine Accounting Standards 19 (PAS 19)Document10 pagesEmployee Benefits: PAS 19, PAS 20, PAS 23, and PAS 24 Philippine Accounting Standards 19 (PAS 19)Mica DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Compensation & Reward Management: Dr. Sumita MishraDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Compensation & Reward Management: Dr. Sumita MishraSarthak MohantyNo ratings yet
- IAS 19-EMPLOYEE BENEFITSDocument3 pagesIAS 19-EMPLOYEE BENEFITSfrondagericaNo ratings yet
- For Session DTD 5th Sep by CA Alok Garg PDFDocument46 pagesFor Session DTD 5th Sep by CA Alok Garg PDFLakshmi Narayana Murthy KapavarapuNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits Related Standards: Pas 19 - Employee Benefits Pas 26 - Accounting & Reporting by Retirement Benefit PlansDocument10 pagesEmployee Benefits Related Standards: Pas 19 - Employee Benefits Pas 26 - Accounting & Reporting by Retirement Benefit PlansallyssajabsNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefit (Ias 19) FinalDocument36 pagesEmployee Benefit (Ias 19) FinalKanbiro OrkaidoNo ratings yet
- Forms of Compensation IncomeDocument6 pagesForms of Compensation IncomeMariaHannahKristenRamirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Accounting For Other Liabilities: A. Post Employment BenefitsDocument50 pagesChapter 4 - Accounting For Other Liabilities: A. Post Employment BenefitsLovely AbadianoNo ratings yet
- PDF 15aug23 0724 SplittedDocument1 pagePDF 15aug23 0724 SplittedAshish ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Notes IAS 19Document18 pagesNotes IAS 19Nasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Candidate 1Document2 pagesCandidate 1Fascino WhiteNo ratings yet
- Defined Benefit Plans ExplainedDocument4 pagesDefined Benefit Plans ExplainedJames ScoldNo ratings yet
- Aec64 Audit 2 Notes-19-21Document3 pagesAec64 Audit 2 Notes-19-21Althea RubinNo ratings yet
- FAR23 Employee Benefits - With AnsDocument13 pagesFAR23 Employee Benefits - With AnsAJ Cresmundo100% (1)
- Notes On Employee BenefitsDocument26 pagesNotes On Employee BenefitsSarannyaRajendraNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Employee BenefitsDocument29 pagesAccounting For Employee BenefitsnuggsNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits: PAS 19 Corpuz, Mary Lorie Anne ODocument38 pagesEmployee Benefits: PAS 19 Corpuz, Mary Lorie Anne OMarylorieanne CorpuzNo ratings yet
- IAS-19 at Glance (BDO)Document4 pagesIAS-19 at Glance (BDO)FaraisNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits Guide to Ind-AS 19Document42 pagesEmployee Benefits Guide to Ind-AS 19amarNo ratings yet
- Postemployment BenefitsDocument3 pagesPostemployment BenefitsChristian John PardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary Chapter 5Document10 pagesChapter Summary Chapter 5ellyzamae quiraoNo ratings yet
- Ia 3Document3 pagesIa 3Auguste Anthony SisperezNo ratings yet
- IAS 19 Employee Benefits GuideDocument9 pagesIAS 19 Employee Benefits GuideRichie BoomaNo ratings yet
- CFAS NotesDocument27 pagesCFAS NotesMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Pas 19 - Employee BenefitsDocument25 pagesPas 19 - Employee BenefitsBritnys NimNo ratings yet
- Employee BenefitsDocument18 pagesEmployee BenefitsLavillaNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits: September 21, 2020Document18 pagesEmployee Benefits: September 21, 2020Andrea BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Taxation Laws ExplainedDocument7 pagesTaxation Laws ExplainedKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC 2101 CHAPTER 26 NotesDocument5 pagesAC 2101 CHAPTER 26 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- PPE Chapter 23Document4 pagesPPE Chapter 23Kemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- Consignment Sales AccountingDocument2 pagesConsignment Sales AccountingKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- AC 3101 CHAPTER 10 NotesDocument2 pagesAC 3101 CHAPTER 10 NotesKemuel TantuanNo ratings yet
- Taxsheet 10007162Document2 pagesTaxsheet 10007162Narender KapoorNo ratings yet
- PP Rozdział - 4 - MiniMatura - Grupa - ADocument2 pagesPP Rozdział - 4 - MiniMatura - Grupa - AAleksandra Myślińska50% (2)
- Suggested Answer On Tax Planning and Compliance Nov-Dec, 2023Document18 pagesSuggested Answer On Tax Planning and Compliance Nov-Dec, 2023Erfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Taxation LawDocument67 pagesTaxation LawAdv Sheetal SaylekarNo ratings yet
- Ferma ActDocument21 pagesFerma ActJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Confirmation 1 PDFDocument2 pagesConfirmation 1 PDFENAD TBISHATNo ratings yet
- Taxation NotesDocument33 pagesTaxation NotesNaina AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document2 pagesChapter 8Kate AllanigueNo ratings yet
- Taxation UK ACCA F6Document9 pagesTaxation UK ACCA F6Ankit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Narrative DescriptionDocument2 pagesNarrative DescriptionAnonymous N9dx4ATEghNo ratings yet
- Wealth Management ProjectDocument10 pagesWealth Management ProjectShirsendu DasNo ratings yet
- TESRDocument4 pagesTESRBakhtar FaiziNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Marital Status FormDocument2 pagesDeclaration of Marital Status FormAshrafNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Taxation in IndiaDocument59 pagesA Project Report On Taxation in IndiaYash Bhagat100% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions: Q. What Are The Common Exit Formalities After Resignation?Document12 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: Q. What Are The Common Exit Formalities After Resignation?anshumaan upadhyay100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Employee BenefitsDocument40 pagesChapter 8 Employee BenefitsjammuuuNo ratings yet
- ITR-4 Notified Form AY 2021-22-0Document5 pagesITR-4 Notified Form AY 2021-22-0Kuldeep JatNo ratings yet
- C.M. Hoskins & Co., Inc. vs. Commissioner of Internal RevenueDocument1 pageC.M. Hoskins & Co., Inc. vs. Commissioner of Internal RevenueAlljun SerenadoNo ratings yet
- Incomes Exempt Under Section 10Document10 pagesIncomes Exempt Under Section 10Rahul TiwariNo ratings yet
- Money Saving Strategies: Laura Connerly, PH.D., Assistant Professor - Family and Consumer EconomicsDocument5 pagesMoney Saving Strategies: Laura Connerly, PH.D., Assistant Professor - Family and Consumer EconomicsAhmedinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Tax ExemptionDocument1 pageUnderstanding Tax Exemptionirene ibonNo ratings yet
- Discussion - Accounting ProceduresDocument5 pagesDiscussion - Accounting ProceduresLove KarenNo ratings yet
- Kuenzle V CIRDocument10 pagesKuenzle V CIRRean Raphaelle GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Employee Compensation & How To DeviseDocument9 pagesFactors Influencing Employee Compensation & How To DevisesangeethaNo ratings yet
- Ewac Alloys Limited: Uan No Aadhar NoDocument1 pageEwac Alloys Limited: Uan No Aadhar NoNapoleon DasNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Under Canadian RegulationsDocument10 pagesIncome Tax Under Canadian Regulationshemayal0% (1)
- Income Taxation Chapter on Compensation IncomeDocument17 pagesIncome Taxation Chapter on Compensation IncomeSheilamae Sernadilla GregorioNo ratings yet
- SBF Iocl 19.11.12Document18 pagesSBF Iocl 19.11.12ParameshNo ratings yet
- Regular Income Taxation: Inclusion in Gross Income: Chan, John Mark Juganas, Hazel Madayag, Jovie AnnDocument43 pagesRegular Income Taxation: Inclusion in Gross Income: Chan, John Mark Juganas, Hazel Madayag, Jovie AnnAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- FM's External Factors and Competition in ArboriaDocument3 pagesFM's External Factors and Competition in ArboriaWelldy WldNo ratings yet