Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lect 1.4 If Else
Uploaded by
Qazia Aiman HafeezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lect 1.4 If Else
Uploaded by
Qazia Aiman HafeezCopyright:
Available Formats
Python - Decision Making
Decision making is the most important aspect of almost all the programming languages. As the name
implies, decision making allows us to run a particular block of code for a particular decision. Here, the decisions are
made on the validity of the particular conditions. Condition checking is the backbone of decision making.
In python, decision making is performed by the following statements.
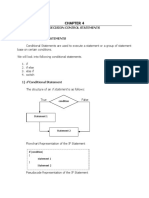
The if statement
The if statement is used to test a particular condition and if the condition is true, it executes a block of code known
as if-block. The condition of if statement can be any valid logical expression which can be either evaluated to true or
false.
The syntax of the if-statement is given below.
if expression:
statement
Program:
num = int(input("enter the number?"))
if num%2 == 0:
print("Number is even")
Example 2 : Program to print the largest of the three numbers.
a = int(input("Enter a? "));
b = int(input("Enter b? "));
c = int(input("Enter c? "));
if a>b and a>c:
print("a is largest");
if b>a and b>c:
print("b is largest");
if c>a and c>b:
print("c is largest");
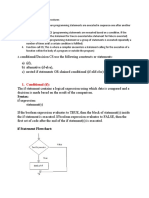
The if-else statement
The if-else statement provides an else block combined with the if statement which is executed in the false case of the
condition.
If the condition is true, then the if-block is executed. Otherwise, the else-block is executed.
The syntax of the if-else statement is given below.
if condition:
#block of statements
else:
#another block of statements (else-block)
Example 1 : Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not.
age = int (input("Enter your age? "))
if age>=18:
print("You are eligible to vote !!");
else:
print("Sorry! you have to wait !!");
Example 2: Program to check whether a number is even or not.
num = int(input("enter the number?"))
if num%2 == 0:
print("Number is even...")
else:
print("Number is odd...")
The elif statement
The elif statement enables us to check multiple conditions and execute the specific block of statements
depending upon the true condition among them. We can have any number of elif statements in our program
depending upon our need. However, using elif is optional.
The elif statement works like an if-else-if ladder statement in C. It must be succeeded by an if statement.
The syntax of the elif statement is given below.
if expression 1:
# block of statements
elif expression 2:
# block of statements
elif expression 3:
# block of statements
else:
# block of statements
Program:
number = int(input("Enter the number?"))
if number==10:
print("number is equals to 10")
elif number==50:
print("number is equal to 50");
elif number==100:
print("number is equal to 100");
else:
print("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
Program:
marks = int(input("Enter the marks? "))
if marks > 85 and marks <= 100:
print("Congrats ! you scored grade A ...")
elif marks > 60 and marks <= 85:
print("You scored grade B + ...")
elif marks > 40 and marks <= 60:
print("You scored grade B ...")
elif (marks > 30 and marks <= 40):
print("You scored grade C ...")
else:
print("Sorry you are fail ?")
Python indentation
Python indentation uses to define the block of the code. The other programming languages such as C, C++, and Java
use curly braces {}, whereas Python uses an indentation. Whitespaces are used as indentation in Python.
Indentation uses at the beginning of the code and ends with the unintended line. That same line indentation defines
the block of the code (body of a function, loop, etc.)
Generally, four whitespaces are used as the indentation. The amount of indentation depends on user, but it must be
consistent throughout that block.
n = int(input("Enter the number:"))
if(n%2 == 0):
print("Even Number")
else:
print("Odd Number")
print("Task Complete")
The above code, if and else are two separate code blocks. Both code blocks are indented four spaces. The
print("Task Complete") statement is not indented four whitespaces and it is out of the if-else block.
If the indentation is not used properly, then that will result in IndentationError.
You might also like
- Decision Making StatementsDocument3 pagesDecision Making StatementsISR EducationsNo ratings yet
- 11 Computer Science-Python Conditional Statements-NotesDocument16 pages11 Computer Science-Python Conditional Statements-NotesSaravana Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Python If ConditionsDocument11 pagesPython If ConditionsKamalakumar VNo ratings yet
- Control StructuresDocument26 pagesControl StructuresNarendra ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PythonDocument164 pagesUnit 2 Pythonviveksharma50011No ratings yet
- Module 3 MergedDocument80 pagesModule 3 MergedSARANSH PRAJAPATI 22BCE10795No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document7 pagesUnit 2Pranjul KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Control Structures: Structure, and The Repetition Structure. The Sequence Structure Is Built Into C#. UnlessDocument21 pagesControl Structures: Structure, and The Repetition Structure. The Sequence Structure Is Built Into C#. Unlessبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Avengers TeamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Python Programming - UNIT IVDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Python Programming - UNIT IVDhruv SojitraNo ratings yet
- Conditional Statement Lab GiudeDocument5 pagesConditional Statement Lab GiudeNelajala NelajalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PythonDocument15 pagesUnit 2 PythonVikas PareekNo ratings yet
- PythonProgramming Unit2Document27 pagesPythonProgramming Unit2abhijeetkumar7985No ratings yet
- LESSON2 C ProgrammingDocument75 pagesLESSON2 C ProgrammingFerdinand Guiquing Jr.No ratings yet
- LESSON2 C ProgrammingDocument67 pagesLESSON2 C ProgrammingJanine CallanganNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii, PPS PDFDocument23 pagesUnit Ii, PPS PDFVARUN KUMAR V SNo ratings yet
- Py Section B Part 1Document103 pagesPy Section B Part 1Avinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Swe-102 Lab 04!Document6 pagesSwe-102 Lab 04!Hammad QamarNo ratings yet
- Handout 04Document17 pagesHandout 04abibual desalegnNo ratings yet
- Python LAB 04998Document9 pagesPython LAB 04998farazsiddiqui2003No ratings yet
- Unit2 Python StudentsDocument17 pagesUnit2 Python StudentsSumit RajputNo ratings yet
- Python Module IIDocument21 pagesPython Module IIaswinNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Python Module II FinalDocument19 pagesSem 3 Python Module II Finalasnaph9No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers Laboratory Manual: Experiment #4 SelectionsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Computers Laboratory Manual: Experiment #4 SelectionsanumNo ratings yet
- 002.1 Python - Revision TourDocument38 pages002.1 Python - Revision TourArushi VermaNo ratings yet
- Control Structures: Structure, and The Repetition Structure. The Sequence Structure Is Built Into C#. UnlessDocument16 pagesControl Structures: Structure, and The Repetition Structure. The Sequence Structure Is Built Into C#. Unlessبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- If Statement in CDocument30 pagesIf Statement in CJashwanth Reddy EarlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Jimwell Enriquez AbiertasNo ratings yet
- Decisions (Ifelse)Document20 pagesDecisions (Ifelse)Alina RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Python Control Statments PDFDocument19 pagesPython Control Statments PDFAnirudhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes AutonomousDocument31 pagesUnit 2 Notes AutonomoussirishaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Selection Part IDocument32 pagesLecture 3 - Selection Part IaliNo ratings yet
- Python FundamentalsDocument100 pagesPython Fundamentalsmyanmar lover tamuNo ratings yet
- PF Lab 04Document7 pagesPF Lab 04sufyankhankhattak33No ratings yet
- CFP Lab 9Document22 pagesCFP Lab 9Talha xDNo ratings yet
- Flow of Control: Type of Statements in PythonDocument4 pagesFlow of Control: Type of Statements in PythonPriyanshi ShahNo ratings yet
- Flow of Control 10Document28 pagesFlow of Control 10MADHUSUDAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Loop PythonDocument11 pagesLoop PythonMuthumeenatchi UNo ratings yet
- Unit2L1 2 3Document15 pagesUnit2L1 2 3Niraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Session 03: Control Structures, Decision Making Using Simple If, If-Else StatementDocument7 pagesLab Session 03: Control Structures, Decision Making Using Simple If, If-Else StatementRamshaNo ratings yet
- Instructions in C Programming LanguageDocument17 pagesInstructions in C Programming LanguagepankajusbNo ratings yet
- If StatementsDocument3 pagesIf Statementslillia142000No ratings yet
- CSE 4235c Python Assignment 01Document14 pagesCSE 4235c Python Assignment 01Anonymous mw8QhbhfhONo ratings yet
- C Programming Decision MakingDocument27 pagesC Programming Decision MakingKartheeban KamatchiNo ratings yet
- NOTES There Are 4 Types of Control StructuresDocument5 pagesNOTES There Are 4 Types of Control StructuresBlessedNo ratings yet
- Control StatementsDocument20 pagesControl StatementsDhillonmannat466 DhillonNo ratings yet
- Python 2 While and For Loops and FunctionsDocument11 pagesPython 2 While and For Loops and Functionslsimm2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document34 pagesLecture 5jai singhalNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Flow of ControlDocument15 pagesCh-5 Flow of ControlnithinNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 03 (Conditional Statement)Document11 pagesExperiment No 03 (Conditional Statement)MG Master GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Pythons Control StatementsDocument37 pagesChapter - 4 Pythons Control StatementspsukeshwarNo ratings yet
- Control Structures in PythonDocument50 pagesControl Structures in PythonDURAIMURUGAN MNo ratings yet
- Control Day2Document25 pagesControl Day2Samanwita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Conditional Statements: If True: Print ("First Conditional Statement") If False: Print ("Second Conditional Statement")Document6 pagesConditional Statements: If True: Print ("First Conditional Statement") If False: Print ("Second Conditional Statement")DebbieNo ratings yet
- Types of If StatementDocument15 pagesTypes of If StatementvipularunpatilNo ratings yet
- Control StatementsDocument17 pagesControl Statementsyatendra kashyapNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Question Bank With Answers (Introduction To Python) VTUDocument22 pagesModule 1 Question Bank With Answers (Introduction To Python) VTURavish br100% (6)
- PWP Ch2 by Syed AteeqDocument28 pagesPWP Ch2 by Syed AteeqkrantiNo ratings yet
- Lab Session 07 - PagenumberDocument17 pagesLab Session 07 - Pagenumbermiqbal66126612No ratings yet
- Lect 1.5 LoopDocument6 pagesLect 1.5 LoopQazia Aiman HafeezNo ratings yet
- Lect 1.1 Basic SyntaxDocument4 pagesLect 1.1 Basic SyntaxQazia Aiman HafeezNo ratings yet
- Lect 1.1 Basic SyntaxDocument4 pagesLect 1.1 Basic SyntaxQazia Aiman HafeezNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesLect 1 IntroductionQazia Aiman HafeezNo ratings yet
- GBP Statement: Beatriz Manchado FloresDocument2 pagesGBP Statement: Beatriz Manchado Floresmr.laravelNo ratings yet
- Filipino ThinkingDocument2 pagesFilipino ThinkingRheyven JuanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Book ThePalgraveHandbookOfGlobalSocDocument1,039 pages2020 Book ThePalgraveHandbookOfGlobalSocYoussef AmzilNo ratings yet
- Sensair Manual 1.0 en PDFDocument104 pagesSensair Manual 1.0 en PDFPaul KinsellaNo ratings yet
- MindmapDocument2 pagesMindmapapi-545246569No ratings yet
- Egcuwa - Butterworth Profile PDFDocument84 pagesEgcuwa - Butterworth Profile PDFsbuja7No ratings yet
- GGFHJDocument1 pageGGFHJanon_791172439No ratings yet
- Tata Teleservices LTDDocument19 pagesTata Teleservices LTDrajvarshaNo ratings yet
- Basics On Piping LayoutDocument11 pagesBasics On Piping Layoutpuru55980No ratings yet
- Program - 1:: Lab - Data Structure Using CDocument50 pagesProgram - 1:: Lab - Data Structure Using Ceshmnash9298No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process AssignmentDocument5 pagesManufacturing Process AssignmentPalani SuntharajanNo ratings yet
- Pallet Truck wp3000 Spec1 GBDocument6 pagesPallet Truck wp3000 Spec1 GBEjaz EjazNo ratings yet
- Book v. Movie Rubric Eng 11 - Rev. 12 - 19Document2 pagesBook v. Movie Rubric Eng 11 - Rev. 12 - 19Lucia Perez ValenciaNo ratings yet
- ADSA Assignment-1 Group - 3Document16 pagesADSA Assignment-1 Group - 3Animesh KumarNo ratings yet
- All The Words I Should Have Said - Rania NaimDocument167 pagesAll The Words I Should Have Said - Rania NaimNan Nan100% (2)
- 1000-211-V8-0000-01003 Concrete Works (Trial Mix)Document38 pages1000-211-V8-0000-01003 Concrete Works (Trial Mix)hodigojiggfjlgkdgiohghfdiohghjfNo ratings yet
- Joshi - Quant Job InterviewDocument329 pagesJoshi - Quant Job InterviewPiciBivNo ratings yet
- Expressive Vocabulary Test - Record Form & ManualDocument7 pagesExpressive Vocabulary Test - Record Form & ManualKHALIDOO6No ratings yet
- BLUE COLLAR JOBS Vs WHITE COLLAR JOBS.Document2 pagesBLUE COLLAR JOBS Vs WHITE COLLAR JOBS.Nelson VersozaNo ratings yet
- Constructionandmaintenanceof Riverembankments (Levees) - GuidelinesDocument7 pagesConstructionandmaintenanceof Riverembankments (Levees) - GuidelinesSushil DhunganaNo ratings yet
- Temporary Housing Kobe EarthquakeDocument18 pagesTemporary Housing Kobe EarthquakeMeenu100% (1)
- Image PlacementDocument4 pagesImage PlacementJanix MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- MKTED208071EN CatalogueDocument618 pagesMKTED208071EN Cataloguecarlos augustoNo ratings yet
- Micro SplatDocument17 pagesMicro SplatCarlosAndresGarnicaSalazarNo ratings yet
- KL-710 Conventional Temprature Detector PDFDocument1 pageKL-710 Conventional Temprature Detector PDFghenriquezNo ratings yet
- Highlands FM: Jacqueline LawrenceeDocument14 pagesHighlands FM: Jacqueline LawrenceeLydia LaizaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 1 Math Algebra and Trigonometry SET ADocument2 pagesEvaluation Exam 1 Math Algebra and Trigonometry SET AEngr. HLDCNo ratings yet
- Inv - 2469306Document2 pagesInv - 2469306rajeshNo ratings yet
- Lesson - TrendsDocument26 pagesLesson - TrendsLloydNo ratings yet
- F639 1479757-1Document3 pagesF639 1479757-1Thaweekarn ChangthongNo ratings yet