Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Compromised Ridges Maxillary Flabby Ridge and Severely Resorbed Mandibular Ridge - A Case Report
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Compromised Ridges Maxillary Flabby Ridge and Severely Resorbed Mandibular Ridge - A Case Report
Copyright:
Available Formats
Volume 7, Issue 10, October – 2022 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Compromised Ridges:
Maxillary Flabby Ridge and Severely Resorbed
Mandibular Ridge – A Case Report
Dr. Riddhi Sharma1, Dr. Naveen Oberoi2, Dr. Ravpreet Singh3
1
Post Graduate Student, Department of Prosthodontics and crown & Bridge, Baba Jaswant Singh Dental College and Hospital,
Ludhiana
2
Professor and Head, Department of Prosthodontics and crown & Bridge, Baba Jaswant Singh Dental College and Hospital,
Ludhiana
3
Associate Professor, Department of Prosthodontics and crown & Bridge, Baba Jaswant Singh Dental College and Hospital,
Ludhiana
Abstract:- Fabrication of any dental prosthesis over a atrophic knife edge mandibular ridge. This condition occurs
compromised residual alveolar ridge is really a challenge due to excessive load on the residual alveolar ridge caused by
for prosthodontists. Fibrous or flabby ridge and highly unstable occlusal forces from an ill-fitting denture or from the
resorbed residual alveolar ridge are two clinical situations remaining natural teeth [2]. Resorption of residual alveolar
that require special considerations during construction of ridge is chronic, progressive, irreversible pathophysiological
any prosthesis. Mobile soft tissue and flattened alveolar process, probably of multifactorial origin [3]. Conventional
ridge significantly compromise denture stability and approach to fabricate a complete denture prosthesis is quite
support. There are different treatment modalities to challenging because denture stability, retention and support
manage these clinical conditions like surgical excision of are significantly jeopardized in these conditions.
soft tissue, ridge augmentation, modification in
impression technique, etc. Prosthodontic management of Management of flabby ridge can be – (1) surgical
a patient with compromised residual alveolar ridges needs excision of fibrous tissue, (2) non-surgical (recording the
special consideration. Selection of treatment modality hypermobile tissue without pressure) (3) injection of
depends on patient’s general health, clinical condition of sclerosing solution. An atrophied mandibular ridge can be
residual alveolar ridges, financial capacity and skill of the surgically corrected by bone grafting and prosthetically
clinician. A modification from conventional impression managed by implant supported overdenture. But surgical
procedure was used to record maxillary flabby anterior treatment is a complex and time consuming procedure and in
ridge and neutral zone concept was applied for teeth severely debilitated patients non-invasive, conservative
arrangement to improve denture stability in atrophied approach is many times preferable.
lower alveolar ridge. This case report is about an old
completely edentulous male patient who reported with a II. CASE REPORT
complaint of difficulty in chewing with his present
denture. A 65 year old male patient reported to the department
of prosthodontics and crown and bridge, Baba Jaswant Singh
Keywords:- Compromised Ridges, Fibrous Tissue, Window Dental College, Hospital and Research Institute, Ludhiana
Technique, Resorbed Ridge, Neutral Zone. and complained of difficulty in chewing with his present
denture. The patient had a history of wearing maxillary and
I. INTRODUCTION mandibular complete dentures for 7 years.
Flabby ridge is a mobile or highly resilient alveolar On examination, flabby tissue in the maxillary anterior
ridge which results from replacement of bone by fibrous region was found. The tissue was blanched on pressure
tissue [1]. Hypermobile ridge tissue is commonly seen in the application. Mandibular ridge was highly resorbed and
anterior portion of the edentulous maxilla or overlying an flattened (Fig. 1).
IJISRT22OCT052 www.ijisrt.com 255
Volume 7, Issue 10, October – 2022 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Fig 1:- Maxillary flabby ridge and resorbed mandibular alveolar ridge
Treatment Planning: flabby tissue area and a single thickness wax spacer was
The patient was 65 years old with a medical history of placed over the remaining non-displaceable areas of the
diabetes and hypertension. He did not agree to undergo any cast. A closely fitting special tray was fabricated using
surgical procedure and refused to take any sclerosing pink coloured autopolymerising resin (DPI RR Cold cure,
solution. So, fabrication of a new complete denture was The Bombay Burmah Trading Corporation, Mumbai,
planned for this patient. Recording of flabby tissue in India). The extension of the tray was checked in the mouth
undisplaced condition using window technique and neutral and necessary adjustment was done. A window was
zone concept for arrangement of mandibular teeth were prepared in special tray corresponding to the area of
decided to construct the complete denture prosthesis. flabby tissue. Border molding was done in conventional
way using green stick impression compound (DPI
Treatment Procedure Pinnacle Tracing Sticks, The Bombay Burmah Trading
Corporation, Mumbai, India). The wax spacer was
Maxillary arch - The preliminary impression (Fig. 2) was removed and impression was made using zinc oxide
made using irreversible hydrocolloid (Algitex ,DPI , eugenol paste (Impression paste, Coltene, Switzerland).
Mumbai, India) to minimize distortion of the displaceable Any excess paste in the flabby area was removed and an
flabby tissue using perforated edentulous stock tray and impression of the displaceable mucosa was recorded by
the primary cast was poured using dental plaster (type -2 light body polyvinyl siloxane material over the fibrous
dental plaster , Neelkanth Healthcare, India). The flabby ridge area. The material was allowed to set and removed
area was marked on the cast with an indelible pencil. A as a single impression (Fig. 3). The master cast was made
double thickness modelling wax spacer (Modelling wax, with type 3 dental stone (Kalstone ,Kalabhai Karson Pvt
MDM Y-Dent, Delhi, India) was adapted over the marked Ltd., Mumbai, India).
Fig 2:- Preliminary Impression of edentulous arches
IJISRT22OCT052 www.ijisrt.com 256
Volume 7, Issue 10, October – 2022 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Fig 3:- Final impression of maxillary arch (Window technique)
Mandibular arch - Primary impression was made in stock One record base for maxillary ridge and two record bases
tray using irreversible hydrocolloid (Algitex ,DPI , for mandibular ridge were made in self cure acrylic resin.
Mumbai, India) and the cast was poured using type 2 The record bases were inserted into the mouth to check
dental plaster. A special tray was fabricated from the stability. The wax occlusal rim was fabricated for upper
working cast and border moulding was done in arch. The maxillary occlusal rim was inserted into the
conventional manner. Tissue conditioner (Visco- gel, mouth and parallelism was checked using fox occlusal
Dentsply De Trey, Germany) was used as final impression plane. Now, four vertical stops (two in molar region and
material to record the highly resorbed mandibular ridge by two in canine region) made of self-cure acrylic resin were
doing functional movements of orofacial musculature fabricated in the lower base plate and a tentative vertical
(functional impression technique). Master cast was made jaw relation (VDO) was then recorded (Fig. 4). These
using type 3 dental stone. resin stops acted as retentive tag of admix material and
maintained the vertical height during neutral zone
recording.
Fig 4:- Tentative jaw relations recorded and wire loops made on lower denture base to maintain vertical dimension
Neutral zone recording was done using a mixture of green Dentsply, India) index was made to preserve the neutral
stick modelling compound and impression compound in zone on the cast. The putty index had two components.
the ratio of 7:3 (w/w). To record neutral zone, the patient One is facial matrix and the other one is lingual matrix.
should be in upright and comfortable position. The Now lower occlusal rim along with recording base was
mixture of green stick and impression compound (admix replaced by the other prefabricated denture base and prtty
material) was placed on the lower recording base and it index was again placed on the cast to confine the neutral
was then inserted into the patient’s mouth. Patient was zone. Melted base plate wax was then poured into the
instructed to perform functional movements such as space limited by the putty index and a duplicate wax
swallowing, licking lips, sucking, puckering, smiling, occlusal rim was thus fabricated.
pronouncing words and these movements were repeated
until the material had set. The displaced excess material Facebow transfer was done to orient the maxillary cast to
was removed and thus the boundary of neutral zone space a semi adjustable articulator similar to the patient’s
was limited by functional movements of orofacial opening axis. The upper and lower occlusal rim were
musculature (Fig. 5). A silicone putty (Aquasil, Soft putty, inserted in the patient’s mouth to verify vertical dimension
IJISRT22OCT052 www.ijisrt.com 257
Volume 7, Issue 10, October – 2022 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
of occlusion and the rims were fused together at centric horizontal component of forces and thus improved
relation. The master casts were then mounted in the semi- stability of the denture on a flat resorbed ridge. Bucco-
adjustable articulator. Proper shade and teeth mould was lingual position and occlusal plane of mandibular teeth
then selected accordingly. Teeth arrangement was done in was verified using putty index.
balanced occlusion using non-anatomic teeth to minimize
Fig 5:- Recording of neutral zone
Try in was done to verify stability and retention of denture material was trimmed and any material that covered the
base, vertical dimension, phonetics, centric relation, denture teeth was removed carefully.
aesthetics and necessary correction was done accordingly.
Now, wax apical to denture teeth was carefully removed After try in procedure the denture was processed with heat
from both facial and lingual aspect of mandibular trial cure acrylic resin (DPI Heat cure, The Bombay Burmah
denture. Zinc oxide eugenol paste was applied on the Trading Corporation, Mumbai, India). Final acrylic
facial aspect of mandibular trial denture and carefully denture was thus fabricated after proper finishing and
inserted into the patient’s mouth. The patient was polishing and inserted into the patient’s mouth. The
instructed to pucker his lips, smile widely and these patient was instructed about the maintenance of complete
functional movements were repeated for several times. denture and advised to come after 24 hours following the
Trial denture was removed from patient’s mouth and the denture insertion. The retention, stability and support were
external impression was checked. External impression of improved significantly and the patient was happy with his
lingual aspect of mandibular trial denture was recorded in newly fabricated denture. There was significant change in
similar way. Evaluation of denture flange extensions and the facial profile after fabrication of complete denture
dimensions was done properly. Excess impression prosthesis (Fig. 6 and Fig. 7).
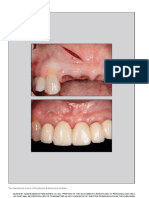
Fig 6:- Final Prosthesis and intra-oral view of the resultant prosthesis
IJISRT22OCT052 www.ijisrt.com 258
Volume 7, Issue 10, October – 2022 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Fig 7:- Pre-operative and Post-operative
III. DISCUSSION the denture foundation area. The concept of neutral zone was
first introduced by Sir Wilfred Fish in 1933.
Prosthodontic management of a patient with
compromised residual alveolar ridges needs special The principle of neutral zone recording in construction
consideration. Displaceable fibrous tissue, resorbed alveolar of complete denture is that to locate an area in the edentulous
ridge significantly compromise denture stability, retention mouth where the teeth should be positioned so that the forces
and support. Selection of treatment modality depends on exerted by muscles will tend to stabilize the denture rather
patients’ general health, clinical condition of residual alveolar unseat it. Tench et al [10] first introduced the use of modelling
ridges, financial capacity and skill of the clinician. Surgical compound to record neutral zone. The materials used for
excision of flabby tissue is considered when adequate bone recording of neutral zone should have sufficient flow and
height is available but in many cases it decreases the sulcus reasonably slow setting so that it can be properly moulded by
depth. Ridge augmentation by grafting is an invasive oral musculatures.
procedure and may cause rejection of graft material.
IV. CONCLUSION
Desjardins and Tollman (1974) [4] popularized the idea
of injecting sclerosing agent to make a hypermobile tissue There is no single technique to rehabilitate
firm. The disadvantages were anaphylactic reactions, patient compromised residual alveolar ridges. A multidisciplinary
discomfort, loss of firmness and technique sensitivity. approach is required to achieve optimal success. Surgical
removal of soft tissue and implant supported prosthesis may
The key to manage flabby ridge conservatively lies in not be possible in all situations. In that case, a conservative
the principle of impression technique. The goal of impression approach using modified impression technique, neutral zone
is to record the non-displaceable tissue in compression to concept provides the basic triad of a successful denture
obtain optimal support and to record the displaceable flabby prosthesis that is retention, stability and support.
ridge without distortion. Liddlelow [5] in 1964 described a
technique where two separate impression materials were used REFERENCES
in a custom tray (plaster of paris over flabby ridge and zinc
oxide eugenol paste over non displaceable tissue). [1]. Crawford RW, Walmsley AD. A review of
prosthodontics management of fibrous ridges. Br Dent
A window technique was proposed by Watson [6] in J 2005; 199:715-9.
1970 where he made a window in the custom tray over the [2]. Kelly E. Changes caused by a mandibular removable
flabby tissue and used impression plaster for flabby ridge and partial denture opposing a maxillary complete denture.
zinc oxide eugenol paste for the healthy denture bearing area. J Prosthet Dent 1972; 27: 140-150.
A similar technique was described by Zafrulla khan et al [7] in [3]. Douglas Allen Atwood. Some clinical factors related to
1981 where they used regular body impression material for rate of resorption of residual ridges. J Prosthet Dent
healthy tissue. Watt and Mcgregor [8] in 1986 used impression 1962; 12(3): 441- 450.
compound to a modified custom tray and a zinc oxide eugenol [4]. Desjardins RP, Tolman DE.Etiology and management
wash impression was taken. of hypermobile mucosa overlying the residual ridge. J
Prosthet Dent 1974; 32: 619- 38.
A highly resorbed and abused residual ridge [5]. Liddelow KP. The prosthetic treatment of the elderly.
significantly compromise denture stability. Chander S et al [9] Br Dent J 1964; 117: 307-315.
in 2007 used tissue conditioners as functional impression [6]. Watson RM. Impression technique for maxillary
material. The advantages to use tissue conditioner are it flows fibrous ridge. Br Dent J 1970; 128: 552.
readily by means of functional stresses and closely adapt to
IJISRT22OCT052 www.ijisrt.com 259
Volume 7, Issue 10, October – 2022 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
[7]. Khan Z, Jaggers J, Shay J. Impressions of unsupported
movable tissues. JADA 1981; 103: 590-92.
[8]. Lynch CD, Allen PF. Management of the flabby ridge:
using contemporary materials to solve an old problem.
Br Dent J 2006; 200:258-261.
[9]. Chander, S., Hill, M., Moore, D. and Morrow, L. (2007)
Tissue Conditioning Materials as Functional
Impression Materials. European Journal of
Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, 15, 67-71.
[10]. Victor E. Beresin. The neutral zone in complete denture.
1973; 5: 53.
IJISRT22OCT052 www.ijisrt.com 260
You might also like
- Liquid-Supported Denture-A Boon To Flabby RidgesDocument4 pagesLiquid-Supported Denture-A Boon To Flabby RidgesTarak ChavadaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Management of Flabby Tissue by Modified Massad S Technique A Case ReportDocument8 pagesProsthetic Management of Flabby Tissue by Modified Massad S Technique A Case ReportMamta SentaNo ratings yet
- A Technique For Impressing The Severely Resorbed MDocument5 pagesA Technique For Impressing The Severely Resorbed MPradeep Prady100% (1)
- Print 6Document5 pagesPrint 6hafidh akbarNo ratings yet
- Windowimpressiontechnique 2018Document5 pagesWindowimpressiontechnique 2018Winda KhosasiNo ratings yet
- Endo Crown: An Approach For Restoring Endodontically Treated Right Mandibular First Molars With Large Coronal Destruction - A Case ReportDocument7 pagesEndo Crown: An Approach For Restoring Endodontically Treated Right Mandibular First Molars With Large Coronal Destruction - A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Method For The Fabrication of Obturator:a Case ReportDocument4 pagesA Simplified Method For The Fabrication of Obturator:a Case ReportinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- 3 (1) 11 14Document4 pages3 (1) 11 14marcelodentNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation On Resorbed Ridge: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation On Resorbed Ridge: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Preprosthetic SurgeryDocument4 pagesPreprosthetic SurgeryVero AngelNo ratings yet
- Supplement The Base To Complement The Crown: Localized Ridge Augmentation Using Connective Tissue GraftDocument5 pagesSupplement The Base To Complement The Crown: Localized Ridge Augmentation Using Connective Tissue GraftBianca DimofteNo ratings yet
- Gingival Mask A Case Report On Enhancing SmilesDocument3 pagesGingival Mask A Case Report On Enhancing SmilesLouis HutahaeanNo ratings yet
- Gingival Mask: A Case Report On Enhancing Smiles: ASE EportDocument3 pagesGingival Mask: A Case Report On Enhancing Smiles: ASE EportLouis HutahaeanNo ratings yet
- Alternative Impression Techniques For Severely Resorbed RidgesDocument8 pagesAlternative Impression Techniques For Severely Resorbed RidgesSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Bridge FlapDocument4 pagesBridge FlapAziz IkbalNo ratings yet
- Case Report - Complete Denture - 2Document4 pagesCase Report - Complete Denture - 2Astri Ggamjong Xiao LuNo ratings yet
- Modified Tray With Mesh Design For The ManagementDocument4 pagesModified Tray With Mesh Design For The ManagementANo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of A Patient With Maxillary Flabby Ridge - A Case ReportDocument4 pagesProsthodontic Rehabilitation of A Patient With Maxillary Flabby Ridge - A Case ReportdedeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Prosthetic Surgery: Mandible: Ental Science - Review ArticleDocument4 pagesPre-Prosthetic Surgery: Mandible: Ental Science - Review ArticleAdrian ERanggaNo ratings yet
- Artigo QDT INGDocument19 pagesArtigo QDT INGJason JNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Flabby Ridge From Modified Impression To DentureDocument14 pagesProsthodontic Management of Flabby Ridge From Modified Impression To DenturePhoebe David100% (1)
- 6038ed9dcef5d IJAR-35170Document5 pages6038ed9dcef5d IJAR-35170Ahmed BadrNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Mandibular Defects With Fixed-Removable Partial Denture Prosthesis Using Precision Attachment - A Twin Case ReportDocument17 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation of Mandibular Defects With Fixed-Removable Partial Denture Prosthesis Using Precision Attachment - A Twin Case ReportIvy MedNo ratings yet
- Telescopic Overdenture: A Case Report: C. S. Shruthi, R. Poojya, Swati Ram, AnupamaDocument5 pagesTelescopic Overdenture: A Case Report: C. S. Shruthi, R. Poojya, Swati Ram, AnupamaRani PutriNo ratings yet
- Management of Hyper-Mobile Tissue With A Modified Combine Technique of Zafrulla and HobkrikDocument5 pagesManagement of Hyper-Mobile Tissue With A Modified Combine Technique of Zafrulla and HobkrikIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Gigi Tiruan GasketDocument5 pagesGigi Tiruan GasketGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- Esthetic Localized Soft Tissue Ridge Augmentation in A Fixed Partial Denture A Case Report PDFDocument3 pagesEsthetic Localized Soft Tissue Ridge Augmentation in A Fixed Partial Denture A Case Report PDFAmar Bhochhibhoya0% (1)
- Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Patient With FlabbDocument4 pagesProsthodontic Rehabilitation of Patient With FlabbLaras Dwi AyuningrumNo ratings yet
- Artículo 2 Técnica para Mandíbula AtróficaDocument4 pagesArtículo 2 Técnica para Mandíbula AtróficaEmmanuel Doroteo NuñezNo ratings yet
- Relining and Rebasing in Pros Tho Don Tics ProsthoDocument21 pagesRelining and Rebasing in Pros Tho Don Tics ProsthoFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Interdisciplinary Approach Using Composite Resin and Ceramic Veneers To Manage An Esthetic ChallengeDocument4 pagesInterdisciplinary Approach Using Composite Resin and Ceramic Veneers To Manage An Esthetic Challengeandres gabrielNo ratings yet
- Clinical: Use of Distal Implants To Support and Increase Retention of A Removable Partial Denture: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesClinical: Use of Distal Implants To Support and Increase Retention of A Removable Partial Denture: A Case ReportDentist HereNo ratings yet
- Resinas Estécticas Inyectables-2216679Document9 pagesResinas Estécticas Inyectables-2216679Roberto PucNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Compromised Ridges and SituationsDocument8 pagesProsthodontic Management of Compromised Ridges and SituationsTiwi SitompulNo ratings yet
- DR RituDocument4 pagesDR RitubhupendraNo ratings yet
- An Innovative Technique For Acrylisation To Fabricate Hollow Bulb Obturator Using Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) PipeDocument8 pagesAn Innovative Technique For Acrylisation To Fabricate Hollow Bulb Obturator Using Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) PipeIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 1233-Article Text-1736-3-10-20200824Document5 pages1233-Article Text-1736-3-10-20200824weiguo guanNo ratings yet
- Caculo Et Al-2013-Journal of Prosthodontics PDFDocument6 pagesCaculo Et Al-2013-Journal of Prosthodontics PDFArchitNo ratings yet
- Hollow Maxillary Denture: A Simplified Approach: Saurabh Chaturvedi, A.K. Verma, Mariyam Ali, Preeti VadhvaniDocument4 pagesHollow Maxillary Denture: A Simplified Approach: Saurabh Chaturvedi, A.K. Verma, Mariyam Ali, Preeti VadhvaniDeasireeNo ratings yet
- Jap 3 43Document4 pagesJap 3 43AmalorNo ratings yet
- Predictable Prosthetic Space Maintenance During Staged Complete-Mouth RehabilitationDocument6 pagesPredictable Prosthetic Space Maintenance During Staged Complete-Mouth Rehabilitationthiên lữNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Restoration of Endodontically Treated Molars Using All Ceramic EndocrownsDocument6 pagesCase Report: Restoration of Endodontically Treated Molars Using All Ceramic EndocrownsTaufiqurrahman Abdul DjabbarNo ratings yet
- PDF 338Document7 pagesPDF 338ali baridiNo ratings yet
- Amcr ParoDocument4 pagesAmcr ParoChokri SahbaniNo ratings yet
- Jpis 42 105Document5 pagesJpis 42 105Jean Pierre Alcántara VigoNo ratings yet
- Crown Lengthening A Comprehensive ReviewDocument11 pagesCrown Lengthening A Comprehensive ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A 5 Year of Evaluation of The MaxillaryDocument4 pagesA 5 Year of Evaluation of The MaxillaryConsultorio dentarioNo ratings yet
- 2 60 1613455536 1ijdrdjun20211Document8 pages2 60 1613455536 1ijdrdjun20211TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- (India) Clinical Management of Highly Resorbed Mandibular Ridge Without Fibrous TissueDocument5 pages(India) Clinical Management of Highly Resorbed Mandibular Ridge Without Fibrous TissueTerran ComanderNo ratings yet
- Equipoise HajjajDocument4 pagesEquipoise HajjajerrelyoNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Bonded Inlays-Onlays: Case SeriesDocument8 pagesCeramic Bonded Inlays-Onlays: Case SeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Lithium Disilicate Posterior Overlays: Clinical and Biomechanical FeaturesDocument8 pagesLithium Disilicate Posterior Overlays: Clinical and Biomechanical FeaturesJose Manuel de la FuenteNo ratings yet
- Surgical and Endodontic Management of Large Cystic Lesion: AbstractDocument5 pagesSurgical and Endodontic Management of Large Cystic Lesion: AbstractanamaghfirohNo ratings yet
- Article-PDF-sheen Juneja Aman Arora Shushant Garg Surbhi-530Document3 pagesArticle-PDF-sheen Juneja Aman Arora Shushant Garg Surbhi-530JASPREETKAUR0410No ratings yet
- Orthodontic Extrusion of Fractured Maxillary Lateral Incisor - A Case ReportDocument4 pagesOrthodontic Extrusion of Fractured Maxillary Lateral Incisor - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Management of Flabby Ridge Case Report.20150524060252Document7 pagesManagement of Flabby Ridge Case Report.20150524060252Rico AnasNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Complete Dentures: Innovative Approach in ProsthodonticsDocument10 pagesUnconventional Complete Dentures: Innovative Approach in ProsthodonticsAastha DuaNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitating Maxillary Defect With Cu-Sil Hollow Bulb Obturator: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesRehabilitating Maxillary Defect With Cu-Sil Hollow Bulb Obturator: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Case Report Gigi Tiruan LengkapDocument3 pagesCase Report Gigi Tiruan LengkapGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDocument6 pagesStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDocument7 pagesBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDocument8 pagesUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDocument33 pagesCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Document8 pagesAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Health Care SystemDocument8 pagesSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesDocument8 pagesInsights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDocument2 pagesParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyDocument19 pagesSmart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Compact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareDocument4 pagesCompact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDocument6 pagesImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Predict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningDocument2 pagesPredict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Air Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMDocument8 pagesAir Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolDocument31 pagesThe Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsDocument5 pagesParkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Investigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatDocument16 pagesInvestigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Implications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewDocument6 pagesImplications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Keywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalDocument7 pagesKeywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsDocument6 pagesAn Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Harnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesDocument7 pagesHarnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterDocument11 pagesThe Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIDocument6 pagesThe Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Advancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisDocument8 pagesAdvancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3Document9 pagesDiabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions On Customer SatisfactionDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions On Customer SatisfactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Terracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonDocument14 pagesTerracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)Document2 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubDocument6 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Gummy SmileDocument13 pagesGummy SmileJuan Carlos MeloNo ratings yet
- The Monoplane Occlusion For Complete Dentures: T H e SP Herical TheoryDocument7 pagesThe Monoplane Occlusion For Complete Dentures: T H e SP Herical TheorySahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- PRD 39 4 Duruel p595 PDFDocument7 pagesPRD 39 4 Duruel p595 PDFBeniya EmilNo ratings yet
- Hollow DenturesDocument31 pagesHollow DenturesAmit BhargavNo ratings yet
- 1-Patient and Operator PositionsDocument33 pages1-Patient and Operator PositionsNs PróteseNo ratings yet
- ImplantDocument37 pagesImplantazizNo ratings yet
- 2001 Seminars BiomecanicaDocument339 pages2001 Seminars BiomecanicaValery V JaureguiNo ratings yet
- Tooth Wear Against Ceramic Crowns in Posterior RegDocument9 pagesTooth Wear Against Ceramic Crowns in Posterior RegPremshith CpNo ratings yet
- Finalmitcharity Event and Gift Givingmariel Joyce ReyesDocument18 pagesFinalmitcharity Event and Gift Givingmariel Joyce ReyesKrystine TuazonNo ratings yet
- Creatingpapilladentalimplantxp PDFDocument9 pagesCreatingpapilladentalimplantxp PDFTuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Versatility of An 810 NM Diode Laser in DentistryDocument10 pagesVersatility of An 810 NM Diode Laser in DentistryGloria SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDocument33 pagesAnchorage in OrthodonticsMini RobertNo ratings yet
- In Search of Improved Skeletal Transverse DiagnosisDocument7 pagesIn Search of Improved Skeletal Transverse DiagnosisAdina SerbanNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion, 1E (2014) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document382 pagesTextbook of Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion, 1E (2014) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Konstantinos Ster90% (20)
- Genny Suwandi - DVIDocument18 pagesGenny Suwandi - DVIgennysuwandiNo ratings yet
- 24 Estetic Facial Owens 1 PDFDocument10 pages24 Estetic Facial Owens 1 PDFValeria Vanessa Membreño AgüeroNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Considerations For Deep-Bite Correction With AlignersDocument5 pagesMechanical Considerations For Deep-Bite Correction With AlignersDavidNo ratings yet
- Ebook: Facial Injectables in DentistryDocument14 pagesEbook: Facial Injectables in DentistryHanan Ansari100% (1)
- Torque in Orthodontics A Review March 2022 7544320615 0608221Document3 pagesTorque in Orthodontics A Review March 2022 7544320615 0608221chaitreeNo ratings yet
- Patient Case PresentationDocument6 pagesPatient Case Presentationapi-613602373No ratings yet
- Layperson 'S Perception of Axial Midline Angulation in Asymmetric FacesDocument7 pagesLayperson 'S Perception of Axial Midline Angulation in Asymmetric FacesPablo BenitezNo ratings yet
- Fixed Appliances: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesFixed Appliances: Patient Information LeafletAANo ratings yet
- Aacd AACD American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry 145 QuestionsDocument39 pagesAacd AACD American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry 145 QuestionsSean DarcyNo ratings yet
- Periapical DiagnosisDocument8 pagesPeriapical Diagnosisazzahra adeliaNo ratings yet
- Dental Hygiene Resume - No ReferencesDocument2 pagesDental Hygiene Resume - No Referencesapi-313829416No ratings yet
- The Periodontal PocketDocument31 pagesThe Periodontal PocketAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKANo ratings yet
- Implant Design and Stress DistributionDocument6 pagesImplant Design and Stress DistributionMahmood E.No ratings yet
- How Voice Exercises Can Assist in Orthodontic TreatmentDocument13 pagesHow Voice Exercises Can Assist in Orthodontic TreatmentPablosky AlfaroskyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Tooth Whitening System Instructions For UseDocument1 pageAdvanced Tooth Whitening System Instructions For Usesoma kiranNo ratings yet
- Communicating Effectively: Some Practical Suggestions: The Psychology of Dental Patient CareDocument5 pagesCommunicating Effectively: Some Practical Suggestions: The Psychology of Dental Patient CareNoNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)