Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy
Uploaded by
KooksOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy
Uploaded by
KooksCopyright:
Available Formats
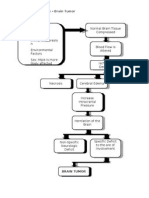
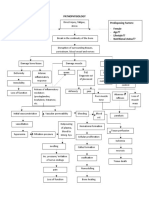
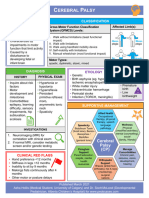
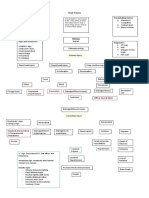
CEREBRAL PALSY
preterm births
multiple gestation
one -time brain injury, abnormal development oxygen
intrauterine growth restriction
deprivation
male sex before birth, during birth, or immediately after
trauma
low APGAR score birth infection
intrauterine infections
Maternal thyroid abnormalities
prenatal strokes
birth asphyxia
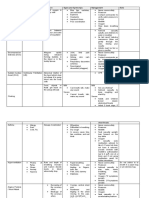
Oral muscle relaxants: botox onabotulinumtoxinA
maternal iodine deficiency damage to the white
baclofen, tizanidine,
matter of the brain diazepam, dantrolene
Contracture
Orthopedic surgery Malnutrition
Cutting nerve fibers mental health
joint pain, Redness
(selective dorsal rhizotomy) conditions bruising Redness
abnormal back pain,
heart & lung disease infection and pain bruising
brain muscle pain,
osteoarthritis at the injection site dizziness
development respiratory infection,
osteoporosis may occur nausea
or and injection-site
brain damage pain. headache
muscle weakness
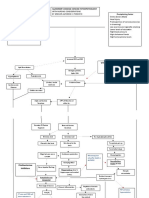
bleeding in
the brain
lack of
oxygen in the
brain
nutrition
deplexion to
sustain the
functionof the
brain
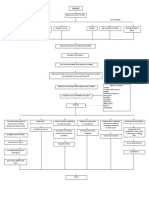
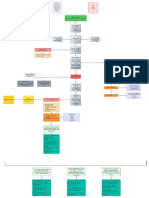
affects
affects the affects the
cerebral
cerebellum basal ganglia
cortex
spastic CP athetoid atomic
dystonia
Physical therapy hyperreflexia chorea Shaky when doing precise
Other occupational therapy hypertonic movements Neuroimaging- MRI and CT Scan
athetosis
Speech and language therapy clonus reflex Balance and coordination problems Metabolic, Genetic, EEG
choreoathetoid
Recreational therapy positive Babinski reflex ataxia Wide-based gait
dyskinesia
mixed CP
nursing dx: risk for nursing dx: risk
nursing dx: nursing dx: Risk for
delayed infant for impaired nursing dx:
Impaired decreased activity
motor development verbal Risk for injury
Physical Mobility tolerance
communication
-Determine patient ability to -Identify cognitive or physical deficits of
participate in specific -Initiate genetic counselling -Determine the patient?s learning -Dress patient in nonrestrictive the patient that may increase potential
activities intervention based upon risk needs clothing of falling in a particular environment
-Assist patient to focus on identification, as appropriate -Enhance the patient?s readiness -Provide low-height bed, as -Identify behaviors and factors that
abilities, rather than on -Plan for long-term monitoring to learn, as appropriate appropriate affect risk of falls
deficits of health risksidentify typical -Set mutual, realistic learning -Assist patient to sit on side of bed -Ask patient for perception of balance,
-Coordinate patient coping strategies goals with the patient to facilitate postural adjustments as appropriate
selection of age appropriate -Identify biological, -Select appropriate teaching -Consult physical therapist about -Monitor gait, balance, and fatigue level
activities environmental, and methods and strategies ambulation plan, as needed with ambulation
-Provide motor activity to behavioural risks and their -Provide an environment -Instruct in availability of assistive -Provide assistive devices (e.g., cane
relieve muscle tension interrelationships conducive to learning devices, if appropriate and walker) to steady gait
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT DISEASE PROCESS SIGNS & SYMPTOMS NURSING INTERVENTION NURSING DIAGNOSIS MEDICAL MANAGEMENT SURGICAL MANAGEMENT DIAGNOSTIC TEST ETIOLOGY PREDISPOSING
You might also like
- TNCC Study GuideDocument6 pagesTNCC Study Guidekristinekat96% (24)
- Field Trip ReportDocument1 pageField Trip ReportWee Soon Chai100% (1)
- CASE PRESENTATION ON UTI Case 3Document14 pagesCASE PRESENTATION ON UTI Case 3Safoora RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Brain TumorDocument1 pagePathophysiology - Brain Tumornories_150% (2)
- REVISED Head InjuryDocument4 pagesREVISED Head InjuryJanselle H Arma50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Brain Injury: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Brain Injury: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsHoney Lorie D. Simbajon100% (2)
- Headache Barja Edited 1Document8 pagesHeadache Barja Edited 1Eduardo Marco Villarama DayritNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis (Neuro, Peads)Document1 pageDifferential Diagnosis (Neuro, Peads)manar180406No ratings yet
- DiagramsDocument14 pagesDiagramssuman saeedNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Bacterial Meningitis 2Document2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY Bacterial Meningitis 2Luis Leh100% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYJeroham CoNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysioDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysioKrystele CangaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho PhysiologykhaeydiancoNo ratings yet
- 2 2CDPDHeadacheVISIONDocument7 pages2 2CDPDHeadacheVISIONEduardo Marco Villarama DayritNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyZyra HernandoNo ratings yet
- 05 Potassium Phosphate - Kali PhosDocument5 pages05 Potassium Phosphate - Kali PhosKarthikNo ratings yet
- Gambar. Gambaran Karakteristik CephalgiaDocument4 pagesGambar. Gambaran Karakteristik Cephalgiadella rafika sariNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injuries Study GuideDocument18 pagesTraumatic Brain Injuries Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Case 6Document41 pagesCase 6Christian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Tetanus Schematic DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Tetanus Schematic DiagramEnzo DyNo ratings yet
- Pathway Stroke Non Hemoragik EngDocument1 pagePathway Stroke Non Hemoragik EngFitria NorkhalidaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Causes Signs and Symtomps Management NoteDocument5 pagesEmergency Causes Signs and Symtomps Management NoteAna Victoria JiménezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Drug Study DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study DiazepamjolibeecaldonaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Patho Physiology: Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele and HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesPatho Physiology: Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele and Hydrocephalusjettski_10No ratings yet
- Drug Study DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study DiazepamAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- Pain Dr. HenryDocument36 pagesPain Dr. Henryreagan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CabreraDocument2 pagesDrug Study CabreraJOSIAH JEFFERSON CABRERANo ratings yet
- MM SK 1 Kelompok - InggrisDocument1 pageMM SK 1 Kelompok - InggrisFirda JinanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Final 1)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Final 1)Clarence BravioNo ratings yet
- Jan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy AtaxiaDocument2 pagesJan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy Ataxia박우진No ratings yet
- Patho FractDocument1 pagePatho FractJordan Garcia AguilarNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nsg. ConsiderationDocument6 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nsg. ConsiderationjeremyescaraNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP)Document11 pagesDiabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP)gjgibson2784No ratings yet
- Neurology (Peads)Document1 pageNeurology (Peads)manar180406No ratings yet
- Teratogen For Pregancy W2 ObgynDocument15 pagesTeratogen For Pregancy W2 Obgyndevita nadilaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Meniere FinalDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Meniere Final1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan Pada Pasien Space Occupying Lesion (Sol) SerebriDocument20 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Pada Pasien Space Occupying Lesion (Sol) SerebriNovi WinriNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Note (SP Edit)Document1 pageCerebral Palsy Note (SP Edit)medical chroniclesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MafDocument3 pagesDrug Study MafSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Neuro Study NotesDocument6 pagesNeuro Study Notescj.ljndrn624No ratings yet
- Epidural Flow ChartDocument1 pageEpidural Flow ChartAmira Paguyo QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Anes Drugs TableDocument20 pagesAnes Drugs TableKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragik Main MapDocument1 pageStroke Hemoragik Main MapdinarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsCleobebs AgustinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Update Management Pain (Dokter & Medical)Document30 pages2021 Update Management Pain (Dokter & Medical)Andri MuliaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Nf1.Nms OrthoDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Nf1.Nms OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- PATHWAY HNP EnglishDocument1 pagePATHWAY HNP EnglishMuhammad Vicky SuhartantoNo ratings yet
- Stereo TacticDocument61 pagesStereo TacticPowool LalaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Med WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study Med WardJoshNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument1 pageBuscopanmichpaduaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Head TraumaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Head TraumaGrace Jane Dionaldo100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentMean ElepañoNo ratings yet
- Woc Abses SerebriDocument2 pagesWoc Abses SerebriMarinaLestari100% (2)
- Fentanyl (Sublimaze)Document2 pagesFentanyl (Sublimaze)yeshaellatapucayNo ratings yet
- Modul 10 - Pengelolaan NyeriDocument96 pagesModul 10 - Pengelolaan NyeriAyu PermataNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan Nyeri DLL 2018Document14 pagesPenatalaksanaan Nyeri DLL 2018Silvia HandikaNo ratings yet
- Children's Emergency Relief and Protection ActDocument2 pagesChildren's Emergency Relief and Protection ActKooksNo ratings yet
- Child and Welfare CodeDocument4 pagesChild and Welfare CodeKooksNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta For HealthworkersDocument15 pagesMagna Carta For HealthworkersKooksNo ratings yet
- Responsible Parenthood & Reproductive Health Law of 2012Document3 pagesResponsible Parenthood & Reproductive Health Law of 2012KooksNo ratings yet
- OB Abortion PROMDocument8 pagesOB Abortion PROMKooksNo ratings yet
- Violence Against Women InfographDocument5 pagesViolence Against Women InfographKooksNo ratings yet
- Gouty Arthritis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageGouty Arthritis PathophysiologyKooksNo ratings yet
- Republic Act. 7610-MergedDocument28 pagesRepublic Act. 7610-MergedKooksNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Atmosphere InfographicDocument2 pagesLayers of The Atmosphere InfographicKooksNo ratings yet
- Transcultural Nursing: Madeleine LeiningerDocument28 pagesTranscultural Nursing: Madeleine LeiningerJoyce EricaNo ratings yet
- Organizing Community Dance Program 2Document3 pagesOrganizing Community Dance Program 2Sassy BlaireNo ratings yet
- Synonyms: Sreedhar's CCEDocument5 pagesSynonyms: Sreedhar's CCEOmaisNo ratings yet
- Psychological Resiliency and Job-Related Burnout of Female EmployeesDocument5 pagesPsychological Resiliency and Job-Related Burnout of Female EmployeesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Long Subjects Revision BTR (PSM - SURGERY - OBGY) AnnotatedDocument39 pagesLong Subjects Revision BTR (PSM - SURGERY - OBGY) AnnotatedAshok DaukiyaNo ratings yet
- Food and Eating Habits in UkraineDocument2 pagesFood and Eating Habits in UkraineДаніелла АдаменкоNo ratings yet
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan MaharashtraDocument18 pagesSwachh Bharat Abhiyan Maharashtra01 - Shweta BaraveNo ratings yet
- 2022 Abdullah AL Harbi - Prevalence of Insomnia Among Patients With BronchiDocument6 pages2022 Abdullah AL Harbi - Prevalence of Insomnia Among Patients With BronchiSteve aokiNo ratings yet
- Cdi8 Lesson 1Document8 pagesCdi8 Lesson 1juje jaulaNo ratings yet
- Mau 14Document2 pagesMau 14bped.balagtasmaureen03No ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Perspective of Pediatric NursingDocument110 pagesCh1 Perspective of Pediatric Nursing9cptb4x7sxNo ratings yet
- October 2019 October 2019Document40 pagesOctober 2019 October 2019Vaibhav DafaleNo ratings yet
- Botulinum Toxin in Facial ReanimationDocument13 pagesBotulinum Toxin in Facial ReanimationAna Caroline Ramirez de AndradeNo ratings yet
- Perio ProjectDocument26 pagesPerio Projectkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Англійська моваDocument41 pagesАнглійська моваLê TùngNo ratings yet
- Group DR - Script - Allergic Rhinitis (Peanut Allergy) Health EducationDocument10 pagesGroup DR - Script - Allergic Rhinitis (Peanut Allergy) Health EducationKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Anuraag Kumar 2k20-Se-24, Piyush Maurya 2k20-Se-95 MTE ReportDocument11 pagesAnuraag Kumar 2k20-Se-24, Piyush Maurya 2k20-Se-95 MTE Reportanuraagkumar 24No ratings yet
- Margaret Wangari Waithaka CVDocument4 pagesMargaret Wangari Waithaka CVNerea SemoNo ratings yet
- 2024 Winter Retreat AnnouncementDocument2 pages2024 Winter Retreat AnnouncementDineshM78No ratings yet
- Mental DisabilitiesDocument11 pagesMental DisabilitiesKaren IrasemaNo ratings yet
- AIS and YogaDocument3 pagesAIS and Yogasale18No ratings yet
- NCP 1 Na-SnapDocument1 pageNCP 1 Na-SnapAlvia ArvenaNo ratings yet
- Key Article Air Pollution - PGIDocument8 pagesKey Article Air Pollution - PGIopyadav544No ratings yet
- Thermal Effect of Food A Myth or A TruthDocument4 pagesThermal Effect of Food A Myth or A TruthTafhim Ahmad Awan100% (1)
- Precis Writing Class ActivityDocument2 pagesPrecis Writing Class ActivityABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- The NCLEX-RN Exam Study Guide Premium Edition - Proven Methods To Pass The NCLEX-RN Examination With Confidence (Belinelli, Rachel Media Group, Scientia) PDFDocument509 pagesThe NCLEX-RN Exam Study Guide Premium Edition - Proven Methods To Pass The NCLEX-RN Examination With Confidence (Belinelli, Rachel Media Group, Scientia) PDFColeen Yraola80% (5)
- 31 - Past Perfect Tense (İleri) - Okuma ParçasıDocument10 pages31 - Past Perfect Tense (İleri) - Okuma Parçası28 eylülNo ratings yet