0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views10 pagesDigestive System Overview and Functions
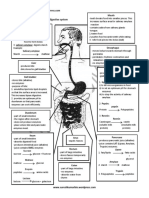
The document provides information about the digestive system and its organs. It begins with an overview of the functions of food and sources of nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals. It then describes the anatomy and roles of key digestive organs like the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. The document also discusses disorders of the digestive system and provides diagrams of teeth anatomy and the pathway of food through the digestive tract.
Uploaded by
Mikhael Devalino 1537036Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views10 pagesDigestive System Overview and Functions
The document provides information about the digestive system and its organs. It begins with an overview of the functions of food and sources of nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals. It then describes the anatomy and roles of key digestive organs like the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. The document also discusses disorders of the digestive system and provides diagrams of teeth anatomy and the pathway of food through the digestive tract.
Uploaded by
Mikhael Devalino 1537036Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd