Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Excess Fluid Intake
Uploaded by
jasper pachingel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Excess fluid intake
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views3 pagesExcess Fluid Intake
Uploaded by
jasper pachingelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
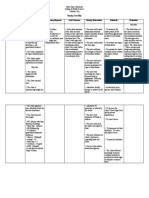
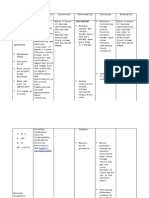
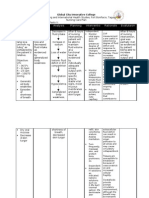
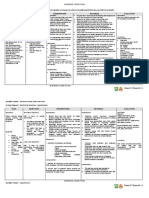
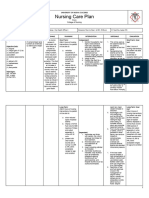
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION Explanation of the
INTERVENTIONS Problem
Fluid Volume Excess
S>”medyo tumabtaba Short Term: > Serve as a baseline data Short Term: Fully met (FVE), or hypervolemia,
dytoy sakak kasla ag > Monitored vital signs and refers to an isotonic
pumtok” After 4-8 hours of nursing record accordingly. After 4-8 hours of nursing expansion of the
interventions, patient will: > To reduce tissue pressure interventions, patient: extracellular fluid (ECF)
O> vital signs taken as >Elevate edematous and of skin breakdown due to an increase in total
follows: 1. Demonstrate extremities, change Demonstrated body sodium content and
-BP=140/80mmHg behaviors to position frequently >To prevent fluid overload behaviors to total body water. This fluid
-RR=20cpm monitor fluid status and monitor intake and monitor fluid status overload usually occurs
-PR=61bpm and reduce >Assessed px appetite output and reduce from compromised
-T=36.5oC recurrence of fluid recurrence of fluid regulatory mechanisms for
➢ conversant and excess excess sodium and water as seen
cooperative >Established rapport. >To assess precipitating commonly in heart failure,
➢ Presence of edema 2. Verbalize and causative factors Verbalized kidney failure, and liver
on foot understanding of >Compare current weight understanding of failure. Other medical
➢ Shortness of breath individual dietary gain with admission or >For presence of crackles individual dietary conditions that could
➢ Jugular vein and fluid previous stated weight or congestion and fluid contribute to FVE are
distention restrictions restrictions hemodialysis, peritoneal
➢ Weight gain >Record occurrence of >To determine full dialysis, and myocardial
Long Term: After 3 days of dyspnea retention infarction. Ultrafiltration or
nursing intervention the Long Term: Fully met dialysis may be required
patient will manifest >Note presence of edema >May indicate increase in for acute cases.
stabilize fluid volume AEB fluid intake After 3 days of nursing
balance I & 0, normal VS, >Record IandO accurately intervention the patient
Nursing diagnosis: stable weight and free from and calculate fluid volume >accurate intake and output manifested to stabilize fluid
Excess fluid volume related signs of edema. balance are necessary for volume AEB balance I & 0,
to excessive fluid intake determining renal function normal VS, stable weight
secondary to kidney failure >Administer diuretics as and fluid replacement and free from signs of
ordered needs and reducing risk of edema.
fluid overload
>Weight patient daily at the
same time each day >To excrete excess fluid
>Daily body weight is best
to monitor fluid status
You might also like
- The Perfect Pancreatitis Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Managing And Healing Pancreatitis With Delectable And Nourishing Recipes;From EverandThe Perfect Pancreatitis Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Managing And Healing Pancreatitis With Delectable And Nourishing Recipes;No ratings yet
- Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesData Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Assessment and ManagementDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Assessment and ManagementKhalid KhanNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- The Ultimate Updated Dialysis Diet Cookbook;The Perfect Nutrition Guide To Managing And Treating Dialysis And Chronic Diseases With Meal Plan And Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Updated Dialysis Diet Cookbook;The Perfect Nutrition Guide To Managing And Treating Dialysis And Chronic Diseases With Meal Plan And Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Chronic Kidney Disease Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Restoring The Health Of Your Kidney With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Chronic Kidney Disease Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Restoring The Health Of Your Kidney With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument3 pagesAssessmentharlequingirl_116No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- NCP HmoleDocument5 pagesNCP HmolemeriiNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention RationaleTrisha DicangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis, Goals, Intervention and Evaluation for HypertensionDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis, Goals, Intervention and Evaluation for HypertensionmarielfmerlanNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Fluid Volume DeficitDocument5 pagesAssessing and Treating Fluid Volume DeficitJennifer B. PascualNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesExcess Fluid VolumeyuddNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNo ratings yet
- NCP - DM - FatigueDocument12 pagesNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToJen BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodKit Alizon BarredoNo ratings yet
- Assessment SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Subjectivejeziel_16No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Document4 pagesFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- In Premature Ventricular Complex, An Impulse That Starts in A Ventricle and Is Conducted Through The Ventricles Before The Next Normal SinusDocument7 pagesIn Premature Ventricular Complex, An Impulse That Starts in A Ventricle and Is Conducted Through The Ventricles Before The Next Normal SinushelloaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureKian Herrera100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPranee diane0% (1)
- NCP - Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancePaolo Belleza78% (9)
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPMaxine RicafortNo ratings yet
- NCP EdemaDocument1 pageNCP EdemaR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Renal Failure PatientDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Renal Failure PatientMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planmust dietNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Study Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Study Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationahz_kerian2No ratings yet
- Nurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonDocument3 pagesNurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Excessaudreyann.acobNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMr. whiteNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Fluid Balance in a Dehydrated PatientDocument9 pagesMaintaining Fluid Balance in a Dehydrated PatientTyn TynNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP AgnMichael Vincent DuroNo ratings yet
- Mendoza, Joana Erica B. JULY 18, 2010 BSN - 127 Maám Castro: Subjective: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument2 pagesMendoza, Joana Erica B. JULY 18, 2010 BSN - 127 Maám Castro: Subjective: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goaljoana_ericaNo ratings yet
- NCP2 (Sultan, J.) - Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP2 (Sultan, J.) - Chronic Kidney DiseaseJohanisa SultanNo ratings yet
- NCP For AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP For Anemiajaira magbanuaNo ratings yet
- DM NCP - Trixia U. Almendral GRP 6Document3 pagesDM NCP - Trixia U. Almendral GRP 6Trixia AlmendralNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument12 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Diagnosis and TreatmentPresciousNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument5 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeCHRISTINE GRACE ELLONo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation Case: Amoebiasis Subjective:" Madalas Po AkongDocument47 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation Case: Amoebiasis Subjective:" Madalas Po AkongNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- DM ncp2Document1 pageDM ncp2Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)Document6 pagesNCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)abcel76% (21)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjovanney100% (10)
- NCP-Acute Gastroenteritis PediatricDocument11 pagesNCP-Acute Gastroenteritis PediatricJhoevina Dulce Capicio0% (1)
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Pachingel - Module 3 - finishedBSN2C - LESSON3Document28 pagesPachingel - Module 3 - finishedBSN2C - LESSON3jasper pachingel100% (1)
- Actaul Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActaul Drug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Gec7 Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesGec7 Case Analysisjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Gec 7Document3 pagesGec 7jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Group 4Document5 pagesNursing Informatics Group 4jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument1 pageJournaljasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Collin Jasper Pachingel - MOD1 Lesson2 FinishedDocument8 pagesCollin Jasper Pachingel - MOD1 Lesson2 Finishedjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2nd DutyDocument2 pagesDrug Study 2nd Dutyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- THE PURSUIT OF HAPPYNESSDocument7 pagesTHE PURSUIT OF HAPPYNESSjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Epoetin Drug Study GuideDocument5 pagesEpoetin Drug Study Guidejasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble Vitamins Deficiency FinalDocument3 pagesWater Soluble Vitamins Deficiency Finaljasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Mod-1-Lesson1 FINISHEDDocument5 pagesMod-1-Lesson1 FINISHEDjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- DETERMINANT OF MORALITY PresentationDocument26 pagesDETERMINANT OF MORALITY Presentationjasper pachingel100% (1)
- Collin Jasper Pachingel - MOD1 Lesson4Document4 pagesCollin Jasper Pachingel - MOD1 Lesson4jasper pachingel0% (1)
- Pathfit AcitivityDocument1 pagePathfit Acitivityjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- CHRISTIAN ETHICS PresentationDocument24 pagesCHRISTIAN ETHICS Presentationjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Top 10 scientists contributionsDocument3 pagesTop 10 scientists contributionsjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Lesson1UNFINISHEDughDocument3 pagesMod 1 Lesson1UNFINISHEDughjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Computers and Nursing Handout SCDocument6 pagesNursing Informatics Computers and Nursing Handout SCjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing ReferencesDocument1 pageReading and Writing Referencesjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Reser CG HHHHDocument4 pagesReser CG HHHHjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document4 pagesExercise 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- EcccccoooDocument2 pagesEcccccooojasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument1 pageConceptual Frameworkjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Reason It OutDocument1 pageReason It Outjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- CE Activity 11Document4 pagesCE Activity 11jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Personal Diet Plan - AssignmentDocument3 pagesPersonal Diet Plan - Assignmentjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms: Literatura/litteratura (Derived Itself From Littera: Letter or Handwriting)Document2 pagesLiterary Terms: Literatura/litteratura (Derived Itself From Littera: Letter or Handwriting)Berr WalidNo ratings yet
- 15 January 2004 1st Lecture Herpetology ECOL 483/583 University of Arizona Spring 2004Document14 pages15 January 2004 1st Lecture Herpetology ECOL 483/583 University of Arizona Spring 2004andreaweiler1No ratings yet
- HEIRS OF BATORI v. REGISTER OF DEEDS OF BENGUETDocument12 pagesHEIRS OF BATORI v. REGISTER OF DEEDS OF BENGUETFaustina del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01Document75 pagesPresentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01yellymarlianapatuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current PDFDocument32 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current PDFAdarshNo ratings yet
- Workshop Francisco (Guardado Automaticamente)Document12 pagesWorkshop Francisco (Guardado Automaticamente)Helena AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Mounting Accessories 2017V03 - EN PDFDocument33 pagesMounting Accessories 2017V03 - EN PDFegalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlansNicholaiCabadduNo ratings yet
- Caglar Araz CVDocument1 pageCaglar Araz CVAnonymous hSKPlVPNo ratings yet
- MisOr Division Template in Action ResearchDocument14 pagesMisOr Division Template in Action ResearchAmorEmbone100% (2)
- Ulep vs. Legal Clinic, Inc., 223 SCRA 378, Bar Matter No. 553 June 17, 1993Document19 pagesUlep vs. Legal Clinic, Inc., 223 SCRA 378, Bar Matter No. 553 June 17, 1993CherNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Vocabulary, Idioms and MetaphorsDocument3 pagesAdvanced - Vocabulary, Idioms and Metaphorsjustttka100% (3)
- Building Machine Learning Systems With Python - Second Edition - Sample ChapterDocument32 pagesBuilding Machine Learning Systems With Python - Second Edition - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Batra, Kanika - Kipps, Belsey, and Jegede - Cosmopolitanism, Transnationalism, and Black Studies in Zadie Smith's On BeautyDocument15 pagesBatra, Kanika - Kipps, Belsey, and Jegede - Cosmopolitanism, Transnationalism, and Black Studies in Zadie Smith's On Beautyjen-leeNo ratings yet
- Study Plan - PharmD Curriculum ReformDocument23 pagesStudy Plan - PharmD Curriculum ReformRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Acc702 - Cost and Management Accounting 1. Assignment 1 - QuestionairesDocument4 pagesAcc702 - Cost and Management Accounting 1. Assignment 1 - QuestionairesLyle BulletzNo ratings yet
- SAT Writing Notes CollegeboardDocument43 pagesSAT Writing Notes CollegeboardEric JoNo ratings yet
- Work Permit ManualDocument20 pagesWork Permit ManualRoni EnjelaniNo ratings yet
- UConn Criminal Information SummaryDocument2 pagesUConn Criminal Information SummaryEllyn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Case Study EntDocument22 pagesCase Study Entnurul syafiqah yahyaNo ratings yet
- ForeverDocument2 pagesForeverLymberth BenallaNo ratings yet
- 450px Huffman2Document23 pages450px Huffman2Nam PhanNo ratings yet
- Teradata Timestamp TricksDocument3 pagesTeradata Timestamp Tricksbhartiya_amit52No ratings yet
- Fractured Root Tips During Dental Extractions and Retained Root Fragments. A Clinical Dilemma?Document7 pagesFractured Root Tips During Dental Extractions and Retained Root Fragments. A Clinical Dilemma?Siti Ulfah NesiaNo ratings yet
- Sept 2013 NewsletterDocument6 pagesSept 2013 NewsletterBKU1965No ratings yet
- Opm MashupDocument1 pageOpm MashupABELLA, HAROLD A.No ratings yet
- Indosat AR10 ENGDocument564 pagesIndosat AR10 ENGHerry Abu DanishNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders Lnu 2018 HandoutDocument58 pagesRespiratory Disorders Lnu 2018 HandoutSamatha SamathaNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers Notes2Document5 pagesRational Numbers Notes2Midhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Advanced Image Stylization With Extended Difference-of-GaussiansDocument10 pagesAdvanced Image Stylization With Extended Difference-of-Gaussianse_gorodinskyNo ratings yet