Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Edema
Uploaded by
R Hornilla ArcegaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Edema
Uploaded by
R Hornilla ArcegaCopyright:
Available Formats
Arcega, Romar Rico H.
BSN-III
NCP
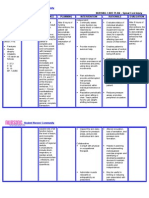
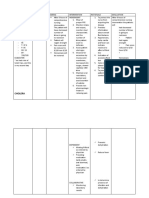
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Namamanas ang paa ko ”as Ineffective Tissue Perfusion After 8 hours of nursing >Explain the need to use >These aids help promote After a series of nursing
verbalized by the patients' interventions, the antiembolic stockings or venous return and minimize intervention, the goal was
(+)irritability patient’s will demonstrate bandages, as ordered. fluid accumulation in the met.
(+)dry lips improved circulation of >Record intake if patient is extremities.
(+)facial grimace connotes affected extremity as on fluid restriction. >Patients should be reminded Client's response to
pain evidenced by palpable and >Assess weight in relation to to include items that are intervention,
(+)pallor equal peripheral pulses, nutritional status. liquid teaching and
(+)anorexia reduced edema. >Note for presence of edema >Poor nutrition and actions performed
(+)hypervolemia by palpating over the tibia, decreased appetite over time Attainment or
(+)peripheral edema on both ankles, feet, and sacrum. result in a decrease in weight, progress toward
feet(bipedal) pitting +2. >Assess for crackles in the which may be accompanied desired outcomes
T-37.4 lungs, changes in respiratory by fluid retention even Client will
RR-16 pattern, shortness of breath, though the net weight demonstrate
PR-70 and orthopnea. remains unchanged. improved
BP-110/80 >Assess for bounding > Edema is graded from trace circulation of
O2sat-97% peripheral pulses (indicating barely affected extremity
(G-2 T-1 P-0 A -0 L-1) >Review serum electrolytes, perceptible) to 4 (severe as evidenced by
urine osmolality, and urine edema). palpable and equal
specific gravity. >These signs are caused by peripheral pulses,
>Elevate edematous an accumulation of fluid in reduced edema.
extremities, and handle with the lungs.
care. >These assessment findings
>Instruct client to avoid are signs of fluid overload.
massaging or rubbing the >All are indicators of fluid
affected extremity. status and guide therapy.
>Elevation increases venous
return to the heart and, in
turn, decreases edema.
Edematous skin is more
susceptible to injury.
>Massaging the extremity
increases the risk of
dislodging the thrombus that
can turn into emboli.
You might also like
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Functional Urinary IncontinenceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Functional Urinary IncontinenceJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementwaadNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentCorinneNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGrace CadawasNo ratings yet
- LortabDocument1 pageLortabSheri490No ratings yet
- Gastrectomy NCP IBPDocument3 pagesGastrectomy NCP IBPKevin T. Katada100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Managing HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Managing Hyperthermiamimingdot33No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJezza RequilmeNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease ManagementDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease ManagementAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Document1 pageTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationDenise Republika100% (1)
- NCP 1Document2 pagesNCP 1Momshie SyNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION Health TeachingDocument3 pagesHYPERTENSION Health TeachingPaulo JavierNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia NCP PDFDocument4 pagesHypokalemia NCP PDFMussaib MushtaqNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- NCP For Bladder CaDocument4 pagesNCP For Bladder CaChris Tine CaccamNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion FdarDocument1 pagePleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Anemia of PrematurityDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Anemia of PrematurityJARIEL L. CATACUTANNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDocument3 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPsimonjosanNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPShubhangi SarwanNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NCP RheumatoidDocument5 pagesNCP RheumatoidJane Elizabeth Gonzales MacahiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Difficulty Breathing Intervention and EvaluationDocument1 pageDifficulty Breathing Intervention and EvaluationJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPChe2x^^100% (2)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseDocument10 pagesDRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseAntonette PereyraNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument6 pagesNCP LeptospirosisJean Marie DavidNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument3 pagesAssessmentharlequingirl_116No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMargaret ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid IntakeDocument3 pagesExcess Fluid Intakejasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesExcess Fluid VolumeyuddNo ratings yet
- Nurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonDocument3 pagesNurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- Managing Anxiety After Heart AttackDocument6 pagesManaging Anxiety After Heart AttackRen VillenaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Nursing Student's Guide to Common Surgical ProceduresDocument2 pagesPhilippines Nursing Student's Guide to Common Surgical ProceduresR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Golden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas CityDocument1 pageGolden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas CityR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Banaag Reflective Journal BlsDocument3 pagesBanaag Reflective Journal BlsR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- El Filibusterimo: Banaag Christine Joy Layag Elaine R. Mindanao John Paul Richard Tablate Vivien Rosebelle BDocument13 pagesEl Filibusterimo: Banaag Christine Joy Layag Elaine R. Mindanao John Paul Richard Tablate Vivien Rosebelle BR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Of The Bpo IndustryDocument4 pagesOf The Bpo IndustryR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Golden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas City: College of NursingDocument7 pagesGolden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas City: College of NursingR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Sip - CD Post - TestDocument2 pagesSip - CD Post - TestR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Nursing Student's Guide to Common Surgical ProceduresDocument2 pagesPhilippines Nursing Student's Guide to Common Surgical ProceduresR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- The greatest impact on the development of Filipino national consciousness, his publication of two novels- Noli Me Tangere, in 1886 and el Filibusterismo in 1891, Rizal drew on his personal experiences and depicted tDocument3 pagesThe greatest impact on the development of Filipino national consciousness, his publication of two novels- Noli Me Tangere, in 1886 and el Filibusterismo in 1891, Rizal drew on his personal experiences and depicted tR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Golden Gate Colleges College of Nursing, Caregiving and MidwiferyDocument1 pageGolden Gate Colleges College of Nursing, Caregiving and MidwiferyR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Golden Gate Colleges College of Nursing, Caregiving and MidwiferyDocument1 pageGolden Gate Colleges College of Nursing, Caregiving and MidwiferyR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Sip - CD Post - TestDocument2 pagesSip - CD Post - TestR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Patient 01Document1 pagePatient 01R Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Golden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas City: College of NursingDocument7 pagesGolden Gate Colleges P. Prieto ST., Batangas City: College of NursingR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer-: Figure 28. Metro Manila and Rizal Province Age-Standardized IncidenceDocument2 pagesProstate Cancer-: Figure 28. Metro Manila and Rizal Province Age-Standardized IncidenceR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer-: Figure 28. Metro Manila and Rizal Province Age-Standardized IncidenceDocument2 pagesProstate Cancer-: Figure 28. Metro Manila and Rizal Province Age-Standardized IncidenceR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Lived Experiences of Nurses in a COVID Ward: From Selflessness to FlexibilityDocument9 pagesLived Experiences of Nurses in a COVID Ward: From Selflessness to FlexibilityR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Document2 pagesNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Patient 01Document1 pagePatient 01R Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Document2 pagesNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition FocusDocument2 pagesNutrition FocusR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- ARCEGA PertussisDocument10 pagesARCEGA PertussisR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- NCP EdemaDocument1 pageNCP EdemaR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Lived Experiences of Nurses in a COVID Ward: From Selflessness to FlexibilityDocument9 pagesLived Experiences of Nurses in a COVID Ward: From Selflessness to FlexibilityR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Nutrition During PregnancyDocument2 pagesMaintaining Nutrition During PregnancyR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Arcega, Romar Rico H. Bsn-Iii NCP IndividualDocument2 pagesArcega, Romar Rico H. Bsn-Iii NCP IndividualR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition FocusDocument2 pagesNutrition FocusR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Arcega Self ReflectionDocument1 pageArcega Self ReflectionR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Clinical Instructor: Ms. Ruby Ann B. Dimayuga, RN, MANDocument19 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: Clinical Instructor: Ms. Ruby Ann B. Dimayuga, RN, MANR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Masai School Code of Conduct - Prefinal 11.10.2019Document3 pagesMasai School Code of Conduct - Prefinal 11.10.2019xavigatorNo ratings yet
- Agility Logistics SolutionsDocument5 pagesAgility Logistics SolutionsWagner MontielNo ratings yet
- CLASS 7B Result Software 2023-24Document266 pagesCLASS 7B Result Software 2023-24JNVG XIB BOYSNo ratings yet
- Skills Test Unit 1 Test A EmailDocument4 pagesSkills Test Unit 1 Test A EmailЛиза ОмельченкоNo ratings yet
- SDM - Session 6Document21 pagesSDM - Session 6Rohith NairNo ratings yet
- IFCRecruitment Manual 2009Document52 pagesIFCRecruitment Manual 2009Oklahoma100% (3)
- Calculating Calories for Weight Training SuccessDocument12 pagesCalculating Calories for Weight Training SuccessFadil Arif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Policy - SIM Cards Point of Sale Registration EngDocument6 pagesPolicy - SIM Cards Point of Sale Registration EngSHALOM SHUMBANo ratings yet
- Se Lab Da-2Document12 pagesSe Lab Da-2Anvesh PenkeNo ratings yet
- Jumpin' Beans Cafe Near SchoolDocument4 pagesJumpin' Beans Cafe Near SchoolJhon Axl Heart RaferNo ratings yet
- What Is ReligionDocument15 pagesWhat Is ReligionMary Glou Melo PadilloNo ratings yet
- Italy, Through A Gothic GlassDocument26 pagesItaly, Through A Gothic GlassPino Blasone100% (1)
- Ap Finance Go PDFDocument3 pagesAp Finance Go PDFSuresh Babu ChinthalaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Capital Market Report Week Ending 22.07.2022 2022-07-22Document2 pagesWeekly Capital Market Report Week Ending 22.07.2022 2022-07-22Fuaad DodooNo ratings yet
- ResMed Case Study AnalysisDocument12 pagesResMed Case Study Analysis徐芊芊No ratings yet
- Obessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)Document10 pagesObessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)marketingmoneyindiaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Unit IDocument14 pagesAbnormal Psychology Unit IMahadevan K V100% (1)
- Lesson 5 Classifications of CommunicationDocument48 pagesLesson 5 Classifications of CommunicationRovenick SinggaNo ratings yet
- Royal Scythians and the Slave Trade in HerodotusDocument19 pagesRoyal Scythians and the Slave Trade in HerodotusSinan SakicNo ratings yet
- A Text-Book of Colloquial Japanese, Based On The Lehrbuch Der Japanischen Umgangssprache by Dr. Rudolf Lange (1907)Document634 pagesA Text-Book of Colloquial Japanese, Based On The Lehrbuch Der Japanischen Umgangssprache by Dr. Rudolf Lange (1907)asdf123123100% (1)
- Postpaid Bill AugDocument2 pagesPostpaid Bill Augsiva vNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument9 pagesBipolar Disorderapi-306929216No ratings yet
- L.G.B.T. Fiction: Book ReviewDocument4 pagesL.G.B.T. Fiction: Book ReviewDejana KosticNo ratings yet
- EasyGreen ManualDocument33 pagesEasyGreen ManualpitoupitouNo ratings yet
- PH.D Scholars UGCDocument25 pagesPH.D Scholars UGCUsha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Warren BuffetDocument11 pagesWarren BuffetSopakirite Kuruye-AleleNo ratings yet
- 100-Word Replacement PDFDocument14 pages100-Word Replacement PDFTheodore Vijay100% (1)
- The Tale of Sweet-Friend and Ali-NurDocument2 pagesThe Tale of Sweet-Friend and Ali-NurJomarie Siason Sumagpao100% (1)
- Lab Manual 06 CSE 314 Sequence and Communication DiagramDocument6 pagesLab Manual 06 CSE 314 Sequence and Communication DiagramMufizul islam NirobNo ratings yet
- Business Decision Making Assignment (July 2015)Document23 pagesBusiness Decision Making Assignment (July 2015)Michael Oppong100% (1)