Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENGINEERING PHYSICS Problem Set 1 - Midterm
Uploaded by
ShieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING PHYSICS Problem Set 1 - Midterm
Uploaded by
ShieCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING PHYSICS
PROBLEM SET 1 – MIDTERM
Instruction. Write the letters of your answers on the space provided below. Attach a copy of
your solutions for each number. Place all the necessary solutions in a long bond paper. Box
your final answer/s in your solutions.
1. 6. 11. 16.
2. 7. 12. 17.
3. 8. 13. 18.
4. 9. 14. 19.
5. 10. 15. 20.
1. A 20 N horizontal force is applied to a 4.0 kg 8. A student lifts a weight of 10.0 N a distance of
box. The box moves a horizontal distance of 3.0 0.500 meters. The energy needed to do this work
meters. The work done by the 20 N force is: in calories is, (1 cal = 4.186 Joules):
A. 60 J. B. 80 J. C. 10 J. A. 0.570 cal. B. 0.750 cal. C. 1.19 cal.
D. 92 J. E. 65 J. D. 1.75 cal. E. 2.30 cal.
2. A 20.0 N force is applied at an angle of 40.0 9. The graph shows the force on an object as it
degrees above the horizontal to a 4.00 kg box. moves a distance x. What is the work done by
The box moves a horizontal distance of 4.00 the force when the object moves from 2.0 m to
meters. The work done by the 20.0 N force is: 8.0 m?
A. 75.0 J. B. 61.3 J. C. 50.1 J.
D. 46.3 J. E. 40.5 J.
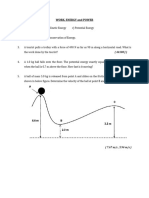
3. A 30.00 kg box slides up a 12.00 meters long
incline at an angle of 30.00 degrees above the
horizontal. The change in gravitational potential
energy is:
A. 35 J B. 48 J C. 50 J
A. 2110 J. B. 1467 J. C. 1080 J.
D. 52 J E. 60 J
D. 1764 J. E. 760.0 J.
.
10 – 12 A 20.0 kg box slides up a 12.0 m long
4. A horizontal force is applied to a 2.0 kg box.
incline at an angle of 30.0 degrees with the
The box starts from rest moves a horizontal
horizontal. A force of 150 N is applied to the box
distance of 12.0 meters and obtains a velocity of
to pull it up the incline. The applied force makes
8.0 m/s. The change in the kinetic energy is:
an angle of 10.0 degrees to the incline.
A. 32 J. B. 48 J. C. 50 J.
10. The change in gravitational potential energy
D. 58 J. E. 64 J.
is, in Joules:
5. A 6.00 kg box slides up a 8.00 m long friction
A. 2,570. B. 2,350. C. 1,450.
incline at an angle of 30.0 degrees by a force
D. 1,180. E. zero.
50.0 N parallel to the incline. The coefficient of
kinetic friction is 0.100. The work done against
11. The work done by the applied force is, in
friction is:
Joules:
A. 22.0 J. B. 26.5 J. C. 30.3 J.
A. 1,870. B. 1,770. C. 1,500.
D. 35.2 J. E. 47.0 J.
D. 1,450. E. zero.
6. As a hiker descends a hill, the work done by
12. The work done by the normal force is, in
gravity on the hiker is:
Joules:
A. 2,352. B. 1,770. C. 1,500.
A. positive and depends on the path taken.
D. 1,450. E. zero.
B. negative and depends on the path taken.
C. positive and independent of the path taken.
13. A car has a mass of 2,000 kg and travels at
D. negative and independent of the path taken.
20.0 m/s. If the drag force is 100 N, then the
power the engine has to provide to keep moving
7. A 2000 kg car accelerates from rest to a
at constant speed is:
velocity of 20 m/s in 10 seconds. The power of
the engine during this acceleration is:
A. 2.0 kW. B. 2.9 kW. C. 3.4 kW.
D. 3.9 kW. E. 4.2 kW.
A. 50 kW. B. 40 kW. C. 30 kW.
D. 20 kW. E. 10 kW
14. A spring is stretched from 0.500 m to 0.800
m. Assume the un-stretched position is 0.00 m.
If the spring constant of the spring is 10.0 N/m,
what is the work done on the spring?
A. 1.95 J B. 2.21 J C. 2.45 J
D. 2.75 J E. 3.01 J
15. A spring-powered dart gun is un-stretched
and has a spring constant 12.0 N/m. The spring
is compressed by 8.00 cm and a 5.00 gram
projectile is placed in the gun. The velocity of the
projectile when it is shot from the gun is:
A. 1.52 m/s. B. 2.54 m/s. C. 3.92 m/s.
D. 4.24 m/s. E. 5.02 m/s.
16. A 90.0 kg person in running up the stairs at
0.500 m/s. The power needed to run up the
stairs is:
A. 441 Watts. B. 395 Watts. C. 302 Watts.
D. 275 Watts. E. 257 Watts.
17. A 75.0 kg skier slides down a 75.0 m high
slope without friction. The velocity of the skier at
the bottom of the slope is:
A. 20.6 m/s. B. 29.7 m/s. C. 38.3 m/s.
D. 40.5 m/s. E. 50.0 m/s
18. An 1800 kg car moving at 20 m/s hits an
initially uncompressed spring with a spring
constant of 2.0 106 N/m. The maximum
compression of the spring is:
A. 0.40 m. B. 0.60 m. C. 0.80 m.
D. 1.0 m. E. 1.2 m.
19. A ski lift carries passengers up a 150 m high
slope at the rate of one chair every 30.0 seconds.
If the chair will hold two passengers with a total
mass of 190 kg, then the power of the engine
that powers the ski lift is:
A. 6.96 kW.
B. 7.83 kW.
C. 8.75 kW.
D. 9.31 kW.
E. 9.90 kW.
20. A 3.00 kg mass slides down a frictionless
incline from a height of 4.00 m. A 6.00 kg mass
also slides down the frictionless incline from the
4.00 m height. The ratio of the velocity of the
3.00 kg mass at the bottom of the incline to the
velocity of the 6.00 kg mass at the bottom of the
incline is:
A. 0.500.
B. 0.710.
C. 1.00.
D. 1.41.
E. 1.50.
You might also like
- Work Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesWork Energy and PowermartinNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions: Energy (Grade 11 Level)Document11 pagesExam Questions: Energy (Grade 11 Level)Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter5Document18 pagesTB Chapter5Jerry HuntNo ratings yet
- Review Notes7 Physics PDFDocument2 pagesReview Notes7 Physics PDFReynee Shaira Lamprea MatulacNo ratings yet
- Physics VIII 1st Term Questions MCQDocument11 pagesPhysics VIII 1st Term Questions MCQShahidul Hassan MontiNo ratings yet
- Pretest Physics For EngineersDocument10 pagesPretest Physics For EngineersIrish NaragNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions-Work, EnergyPowerDocument4 pagesTutorial Questions-Work, EnergyPowerElihle Lihle NyuswaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Work, Energy and PowerDocument5 pagesTutorial Work, Energy and PowerAimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C Web Review Chapter 5 Work and EnergyDocument4 pagesAP Physics C Web Review Chapter 5 Work and EnergyFares HeshamNo ratings yet
- PHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionDocument8 pagesPHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionAli MaarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5, EnergyDocument8 pagesChapter 5, Energynaru_chan1003No ratings yet
- Basic Engineering SciencesDocument5 pagesBasic Engineering SciencesMeet JepsyNo ratings yet
- Statics Solved ProblemsDocument4 pagesStatics Solved ProblemsRomeoNo ratings yet
- Practice-Problems-11_Dynamics-Part-2Document1 pagePractice-Problems-11_Dynamics-Part-2Jayve BasconNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics For Engineers QuizDocument6 pagesPhysics For Engineers QuizIrish NaragNo ratings yet
- UP Physics Exam TitleB. 6.28 rad/sD. 1.57 rad/sDocument12 pagesUP Physics Exam TitleB. 6.28 rad/sD. 1.57 rad/sCharmaine ColetaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium TorquesDocument14 pagesEquilibrium TorquesmartinNo ratings yet
- BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY ECE PRACTICE EXAM <40Document11 pagesBATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY ECE PRACTICE EXAM <40Maria Anndrea MendozaNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument42 pagesEngineering Mechanicsrommel satajoNo ratings yet
- Theme: Force and Motion: Learning Area: 1.0 DynamicsDocument9 pagesTheme: Force and Motion: Learning Area: 1.0 DynamicsChee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium Ex.Document15 pagesStatic Equilibrium Ex.Marc Harold ChuaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2007 EUEEDocument8 pagesPhysics 2007 EUEElikinaw demisieNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Engineering Mechanics Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocument11 pagesMCQ in Engineering Mechanics Part 1 ECE Board ExamJi KanNo ratings yet
- PinoyBix Engineering MechanicsDocument59 pagesPinoyBix Engineering MechanicsChris Balmaceda100% (1)
- Ce2 Sample2Document5 pagesCe2 Sample2ParZiValNo ratings yet
- Physics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsDocument9 pagesPhysics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsNathaly SosaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Quiz - ForcesDocument2 pages3 - Quiz - ForcesMiya GomezNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion Chapter 4 ReviewDocument18 pagesLaws of Motion Chapter 4 ReviewHaw-ChyunNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument17 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Level Work-Energy-MCQDocument4 pagesA Level Work-Energy-MCQKavay KapoorNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument14 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Quỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Physics No KeysDocument4 pagesSample Test Physics No Keysmohanna.esmailzadehNo ratings yet
- F3 Phy 1Document12 pagesF3 Phy 1BUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument2 pagesGeneral PhysicsJonalyn SolivaNo ratings yet
- Gravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeDocument11 pagesGravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeJohnNo ratings yet
- Physics Exit Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesPhysics Exit Exam ReviewJohn Mark Osias100% (1)
- CH 12Document8 pagesCH 12Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Energia Cinética e TrabalhoDocument16 pagesEnergia Cinética e Trabalhosunshine_3No ratings yet
- Modular Test - Chapters 5 To 7 (MCQ)Document7 pagesModular Test - Chapters 5 To 7 (MCQ)Mr Plays shitNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Sample Physics 71Document11 pagesFinal Exam Sample Physics 71Jay VeeNo ratings yet
- Measure Moments with MomentsDocument10 pagesMeasure Moments with MomentsVarshLok100% (2)
- Additional Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesAdditional Sample ProblemsMarifer CavintaNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS EXAM REVIEWDocument8 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS EXAM REVIEWAntonette LimNo ratings yet
- KUE Phys 2033 Home TestDocument3 pagesKUE Phys 2033 Home TestHailemariam WeldegebralNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument22 pagesHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAbdullah ArabiyatNo ratings yet
- Ganda KoDocument99 pagesGanda KoRusvelt Gascon PetroliaNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument2 pagesWork and EnergyMauricioCuellar100% (1)
- Physics Exam ss2 2nd TermDocument14 pagesPhysics Exam ss2 2nd TermchrizyboyziNo ratings yet
- UP College of Science Physics 71 Second Long Exam ReviewDocument11 pagesUP College of Science Physics 71 Second Long Exam ReviewYamiyoNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument52 pagesLaws of Motion ExplainedAmeen ShaikNo ratings yet
- Physics Ix Half Yearly ObjectiveDocument12 pagesPhysics Ix Half Yearly ObjectiveShahidul Hassan MontiNo ratings yet
- 102 Physics Answers-EK EditionDocument15 pages102 Physics Answers-EK Editionadom09No ratings yet
- MCQ in Engineering MechanicsDocument6 pagesMCQ in Engineering MechanicsFrosch EsquierdoNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Midterm Task AnswerDocument1 pageMidterm Task AnswerShieNo ratings yet
- Rosales PoemDocument1 pageRosales PoemShieNo ratings yet
- Finals Assessment 4Document18 pagesFinals Assessment 4ShieNo ratings yet
- Midterm AssessmentDocument3 pagesMidterm AssessmentShieNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assessment 2Document6 pagesMidterm Assessment 2ShieNo ratings yet
- Finals Assessment 3Document3 pagesFinals Assessment 3ShieNo ratings yet
- Finals Assessment 1Document3 pagesFinals Assessment 1ShieNo ratings yet
- Finals Assessment 2Document4 pagesFinals Assessment 2ShieNo ratings yet
- Meet 002Document5 pagesMeet 002ShieNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument5 pagesSample Lab ReportabriowaisNo ratings yet
- RadproDocument21 pagesRadproNikolić MladenNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Answers, Hints & SolutionsDocument10 pagesFiitjee: Answers, Hints & SolutionsZayanmalikNo ratings yet
- Rename Using This Format: First Name of Section - Last Name, Given NameDocument38 pagesRename Using This Format: First Name of Section - Last Name, Given NameChleyde DanguilanNo ratings yet
- CH21Document1 pageCH21Jesha LibreaNo ratings yet
- Angular Displacement, Velocity, AccelerationDocument3 pagesAngular Displacement, Velocity, AccelerationMuhammad JaveedNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Test Physics 11 - SPH3U0 True/False and Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesDynamics Test Physics 11 - SPH3U0 True/False and Multiple Choiceyiyin97No ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsRowena Abdula BaronaNo ratings yet
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation Engineering Physics I. Work and Power V. Impulse and MomentumDocument2 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation Engineering Physics I. Work and Power V. Impulse and MomentumVincent NavaNo ratings yet
- Mech 343 Lab 1 ReportDocument18 pagesMech 343 Lab 1 ReportYousef Meguid0% (1)
- Equation of Motion AccelerationDocument32 pagesEquation of Motion AccelerationAhmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 PDFDocument91 pagesChapter 18 PDF이희인No ratings yet
- Sajc h2 Physics Summary Notes (All Topics)Document43 pagesSajc h2 Physics Summary Notes (All Topics)AjathShatruRajuNo ratings yet
- 03-05-20 SR - Iit N-Super Chaina N-Chaina Jee-Adv 2017 p1 Gta-13 P-I Key SolDocument10 pages03-05-20 SR - Iit N-Super Chaina N-Chaina Jee-Adv 2017 p1 Gta-13 P-I Key SolSubrata KarmakarNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Fuchs (45) July 11, 1972Document4 pagesUnited States Patent: Fuchs (45) July 11, 1972Juan Carlos Peña LugoNo ratings yet
- Physics by Shailendra Sir: Fnyyh OkysDocument4 pagesPhysics by Shailendra Sir: Fnyyh OkysShailendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramsDocument18 pagesFree Body DiagramsManish Shashikant DharekNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICS (Class Xi) : Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesKINEMATICS (Class Xi) : Multiple Choice QuestionsPreetika PargaiNo ratings yet
- DifferencesDocument3 pagesDifferenceschhabra navdeep100% (1)
- Speed VelocityDocument6 pagesSpeed VelocityJudy Grace ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Torque Activity: Name of The Student: DateDocument2 pagesTorque Activity: Name of The Student: DateDomNo ratings yet
- ElectricDocument22 pagesElectricClar TaguinodNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Analysing Linear MotionDocument71 pages2.1 Analysing Linear Motionreaniza100% (2)
- Physics 71 3rd Exam Notes on Static Equilibrium, Elasticity, Gravitation, Fluid Mechanics, Simple Harmonic Motion, and Mechanical WavesDocument5 pagesPhysics 71 3rd Exam Notes on Static Equilibrium, Elasticity, Gravitation, Fluid Mechanics, Simple Harmonic Motion, and Mechanical WavesArthur Conrad DiosanaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity OutlineDocument2 pagesStatic Electricity Outlineapi-293406991No ratings yet
- Sph3u ExamreviewDocument2 pagesSph3u Examreviewapi-237070241No ratings yet
- 6.2 Force Between Differential Current ElementsDocument33 pages6.2 Force Between Differential Current Elementsannambaka satishNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics ME 201 BY Dr. Meyassar N. Al-HaddadDocument29 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics ME 201 BY Dr. Meyassar N. Al-HaddadTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- Energy Work and PowerDocument37 pagesEnergy Work and PowerPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet