Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map Module 5
Concept Map Module 5
Uploaded by
JASMINE CEDE�OOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map Module 5
Concept Map Module 5
Uploaded by
JASMINE CEDE�OCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Puerperium If with postpartum complications:
The period known as the puerperium includes the days leading up to and immediately
following the delivery of the placenta. Typically, this time frame is thought to last for six
weeks. Most pregnancy-related alterations, labor-related changes, and postpartum changes MASTITIS
have passed by six weeks after delivery, and the body has returned to its pre-pregnancy Mammary gland irritation is referred to as mastitis. Typical signs
form. include a warm, erythematous, and sensitive region of the breast.
Uterus Breast abscesses should be taken into consideration when the
exam reveals a painful, firm, perhaps fluctuant mass with
- weighs approximately 1000 g. In the 6 weeks following delivery, the uterus recedes to a overlaying erythema.
weight of 50-100 g.
The underlying causes of mastitis include milk stasis and
Most of the reduction in size and weight occurs in the first 2 weeks, at which time the uterus damaged nipples, which facilitate the entrance of skin flora.
has shrunk enough to return to the true pelvis. Additionally, primiparity, insufficient breast emptiness, and poor
nursing technique are linked to mastitis. It may take up to three
The endometrial lining rapidly regenerates, so that by the seventh day endometrial glands
weeks for the infection to go away, but it should do so in 10 days.
are already evident.
Sometimes mastitis resolves without the need for medical
The size of the placental bed decreases by half, and the changes in the placental bed result intervention.
in the quantity and quality of the lochia that is experienced. PUERPERAL INFECTION
The red discharge (lochia) progressively changes to brownish red, with a watery consistency A puerperal infection, also called a postpartum infection, affects
(lochia serosa). the uterus and the tissues around it. This typically occurs following
Cervix the trauma of a vaginal or cesarean delivery.
The cervix also begins to rapidly revert to a non-pregnant state, but it never returns to the The majority of postpartum patients are typically identified within
nulliparous state. 10 days of giving birth. The full development of certain cases,
nevertheless, can take up to 6 weeks.
Vagina
The vagina also regresses but it does not completely return to its pre-pregnant size. POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE
Perineum - massive blood loss during or after the third stage of labor.
Average blood loss during normal vaginal delivery is 500 ml, and
The perineum has been stretched and traumatized, and sometimes torn or cut, during the 1000 ml during cesarean delivery.
process of labor and delivery. The swollen and engorged vulva rapidly resolves within 1-2
weeks. Most of the muscle tone is regained by 6 weeks, with more improvement over the - Early postpartum hemorrhage is described as that occurring
following few months. within the first 24 hours after delivery. Late postpartum
hemorrhage most frequently occurs 1-2 weeks after delivery but
Abdominal wall may occur up to 6 weeks postpartum.
The abdominal wall remains soft and poorly toned for many weeks. Early postpartum may result from:
Ovaries - Uterine atony
The resumption of normal function by the ovaries is highly variable and is greatly influenced - Retained products from conception
by breastfeeding the infant.
- Uterine rupture
Breasts
- Uterine inversion
The changes to the breasts that prepare the body for breastfeeding occur throughout
pregnancy. - Placenta accreta
- Lower genital tract lacerations
- Coagulopathy
Signs and Symptoms: - hematoma
Physiological: Uterine involution or uterine atony, lochia Causes of late postpartum hemorrhage
rubra, hemorrhage
- retained products of conception
Physiological: Postpartum Blues
- infection
Progressive- Filling or engorgement
- sub involution of placental site
Management: - coagulapathy
Medical Management:
Uterine atony: Pharmacological methods, surgical treatment
Hemorrhage: Uterine massage, uterotonic agents’ administration (oxytocin, ergot
alkaloids, and prostaglandins), and blood transfusion
Engorgement: Pharmacological methods (taking pain relievers)
Nursing Management:
Uterine involution or uterine atony: Assess the fundal height
Lochia: Monitor perineal pad and evaluate lochia character
Hemorrhage:
Perform assessment to determine amount of bleeding, condition of the uterus,
maternal vital signs.
Place the patient in a side lying position to avoid pooling of blood underneath her.
Assess lochia frequently to determine the amount discharged is still within the normal
limits.
Postpartum blues:
Offer supportive care.
Encourage patient to express her feelings and thoughts
Involve the mother to all decisions and have control on taking care of the baby.
Filling or engorgement:
Teach the patient non-pharmacological methods such as warm compress, breastfeed
every three hours, massage breast during breastfeeding or pumping, and avoid tight
bras.
Assess mother’s milk production.
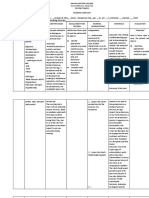
POSTPARTAL MATERNAL CHANGES
Name: Narda The important physiological events that occur
during the puerperium include, among others, the
Age: 29 yrs old return of the reproduction organs and the levels
of the female hormones to approximately their
pre-pregnant state
System Physiological Psychological VS Changes Progressive Retro
Changes Changes Changes Changes Progressive
May have difficulty Reproductive System: Maternal Concerns & Temperature - Patient Lactation: - Shrinkage and descent
voiding because of Feelings: may show a slight of the uterus into its
decreased abdominal After birth, the fundus increase in temperature The secretion from the prepregnancy position in
pressure or trauma of contracts downward into Taking- In Phase - 1-3 during the first 24 hours breast called colostrum the pelvis.
the bladder. Glomerular the pelvis one days after delivery, after birth it caused by increases after
filtration rate decreases centimeter each day. passive and dependent, dehydration or childbirth. The high - Sloughing of the uterine
to normal by 6 weeks, After two weeks the difficult making decision. excessive intrapartum levels of estrogen and lining and development of
women can have uterus will have blood loss. It is not sign progesterone make the lochia
contracted and return Taking- Hold Phase- 4- breast tissue
difficulty sensing when 7 days, after delivery, of infection. - Contraction of the cervix
they have to void after into the pelvis. unresponsive to
has more energy, prolactin. However, it and vagina
receiving an epidural or Uterus – returns to its demonstrate
spinal block. Difficulty Pulse – Normal post- still begins to secrete - Recovery of vaginal and
normal size through the independence, receptive partum physiologic milk through the
voiding can be gradual process of to infant care. pelvic floor muscle tone.
increased by perineal bradycardia (50-70) activation in the
involution because of cardiac mammary glands. It
trauma. Urinary Letting Go Phase- 8
retention is a major Involution involves 3 days after delivery, strain. starts on the third or
cause of uterine atony. processes: assumption of mother fourth day postpartum
- It may be elevated for wherein it is activated by
role, acceptance of a few hours after
1. Contraction of muscle neonate’s real image. suckling or stimulation of
fibres childbirth due to the nipples. Breasts are
Delayed of bowel excitement or pain. By typically soft and non-
evacuation post partly 2. Catabolism or the end of the first week,
Development Parental tender first 2 days
may be due to muscle breaking down of the pulse rate will return
Attachment& Bonding postpartum. If a woman
tone, lack of food plus myometrial cells doesn’t breastfeed,
enema during labor,
3. Regeneration of the Skin-to-skin contact Respiratory- it changes breast engorgement and
dehydration and fear of
uterine epithelium soon after birth immediately after milk production start to
pain from perineal
facilitates the early delivery due to decrease subside within 2-3 days
tendered due to
Typically descends from attachment and binding postpartum.
episiotomy or laceration. in pressure on the
umbilicus by 1 cm per phase. This should diaphragm and Engorgement can occur
day ideally occur within the reduction in pulmonary from 2-4 days
After birth, the estrogen first hour of any birth, blood volume.
Afterpains – Involution postpartum, breasts are
and progesterone levels even cesarean
involves Contractions, hard and tender to
stop dramatically which deliveries, as soon as - The respiratory rate
multiparous women may
can contibute to the the mother and baby are also begins to fall back
be more aware of them Return of Menstrual
“baby blue” (mood stable and last until to the pre-pregnancy
completion of the first within 2 to 3 days. Period:
swings, anxiety, Cervix – Returns to pre-
sadness or irritability pregnancy state by 6 breastfeeding (Moore, It is common for
which resolve within a weeks Bergman, Anderson, et
Blood Pressure- patient’s period changed
week or so of birth) or al., 2016).
Elevated BP may after giving birth. Some
Vagina – Following birth
postpartum depression. Looking directly at the experiences heavier or
is edematous and thin indicate pregnancy
newborn’s face, with induced hypertension. painful periods while
with few rugae, rugae
direct eye contact others become easier.
The diuresis that is return in 3-4 weeks &
(termed an en face - Total blood volume About a month after
evident between the mucosa thickens with
position), is a sign a doubles during giving birth, periods may
second and fifth days return of ovarian and
woman is beginning pregnancy, putting be irregular but may
after birth, as well as the estrogen production
effective attachment. additional strain on the return to normal over
blood loss at birth, acts Lochia – the vaginal blood vessels. Usually, time. For non-lactating
to reduce the added discharge that occurs the patient’s blood women, menstruation
blood volume a woman after birth. Larger pressure levels off after usually returns within 7-
accumalated during amount with vaginal delivery, but this can 9 weeks postpartum.
pregnancy. This delivery than c-section take time. The return of
reduction occurs so menstruation is much
rapidly, In fact, that the Types more unpredictable with
blood volume return to women who breastfeed.
its normal pre- Lochia Rubra – deep-
red, occurs during first With the lactating
pregnancy level by the woman menstruation
first or second week 3-4 days
usually returns between
after birth. Lochia Serosa – pink / 2-18 months.
brown, 3-10 days
After birth, the stretch
postpartum
marks on a woman’s
abdomen (striae Lochia Alba – white,
gravidarum) still appear occurs days 10-14, but
reddened and maybe can last for 3-6 weeks
even more prominent for some women
than during pregnancy.
During first 2 weeks, Perineum – often
abdominal wall remains edematous and bruised
relaxed. Woman has for the first days
still-pregnant following birth Pelvic
appearance. Return to floor muscles are
prepregnancy state stretched, restoring tone
takes 6 weeks. Depends can take 6 months –
on previous tone, proper kegel exercises should
exercise, and amount of be encouraged
adipose tissue Diastasis
recti abdominus.
You might also like
- M5 Module 12G-26203Document33 pagesM5 Module 12G-26203Ruthangela Garcia100% (1)
- Physiology PF PuerperiumDocument34 pagesPhysiology PF PuerperiumKholoud Kholoud100% (4)
- New NORMAL PUERPERIUMDocument21 pagesNew NORMAL PUERPERIUMvarshaNo ratings yet
- Postpartal and Newborn Care MCN LECTURE MidtermsDocument19 pagesPostpartal and Newborn Care MCN LECTURE MidtermsKaela ChoiNo ratings yet
- XaxaxDocument3 pagesXaxaxDarren BalbasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Normal Puerperium and Nursing Management: 5.0 ObjectivesDocument14 pagesUnit 5 Normal Puerperium and Nursing Management: 5.0 ObjectivesJissa Daison100% (1)
- Care of Postpartum Woman: Reproductive ChangesDocument9 pagesCare of Postpartum Woman: Reproductive ChangesLovey DoveNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 10Document7 pagesNcma217 Week 10Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 MidtermDocument34 pagesNCM 107 MidtermChiaraNo ratings yet
- Puerperium (Trans)Document7 pagesPuerperium (Trans)Charlie65129No ratings yet
- Pathway NhsDocument30 pagesPathway NhsEvi AmrianiNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Management of Normal PuerperiumDocument132 pagesPhysiology and Management of Normal PuerperiumAmuNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal PeriodDocument82 pagesAssessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal Periodsweta0% (1)
- Physiology of Normal Pueperium and Its ManagementDocument13 pagesPhysiology of Normal Pueperium and Its ManagementSandhya s100% (3)
- PuerperiumDocument12 pagesPuerperiumWesam Al-TawilNo ratings yet
- Detty Nurdiati Dept of Obstetric & Gynecology Fac of Medicine, Gadjah Mada University YogyakartaDocument34 pagesDetty Nurdiati Dept of Obstetric & Gynecology Fac of Medicine, Gadjah Mada University Yogyakartaanon_55864979No ratings yet
- Finals Post Partum Week 13Document7 pagesFinals Post Partum Week 13loui catuNo ratings yet
- Involution of The UterusDocument13 pagesInvolution of The Uteruslandegre KNo ratings yet
- Normal PuerperiumDocument64 pagesNormal PuerperiumBilisummaa OromooNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument85 pagesPuerperiumHema MaliniNo ratings yet
- Management of Postnatal CareDocument31 pagesManagement of Postnatal Caresinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Lec Week10 ModuleDocument10 pagesNcma217 Lec Week10 ModuleABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- Phy PuerperiumDocument27 pagesPhy PuerperiumDevuchandana RNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument43 pagesUntitledDakshayini MbNo ratings yet
- 4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559Document54 pages4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559annu panchalNo ratings yet
- Postpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumDocument17 pagesPostpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Psychotic DisordesDocument71 pagesPostpartum Psychotic DisordesramandeepNo ratings yet
- Puerperum Notes 1Document7 pagesPuerperum Notes 1Google SecurityNo ratings yet
- Post Partal Care 7Document36 pagesPost Partal Care 7Christian OpinaldoNo ratings yet
- OB NotesDocument9 pagesOB NotesDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Post Partum HemorrhageDocument9 pagesPost Partum HemorrhageghsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Module Postnatal Care 1Document12 pagesUnit 5 Module Postnatal Care 1Kyla CapituloNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument58 pagesPuerperiumYazeed AsrawiNo ratings yet
- Normal PuerperiumDocument19 pagesNormal Puerperiumsubashik100% (1)
- Module 6 - MCN MaternalDocument5 pagesModule 6 - MCN MaternalChristine DuqueNo ratings yet
- Normal PuerperiumDocument23 pagesNormal Puerperiumnaga maniNo ratings yet
- 1 HoDocument1 page1 HoGelsam DerramasNo ratings yet
- 8.. PuerperiumDocument83 pages8.. PuerperiumDegefaw BikoyNo ratings yet
- Puerperium and AnalgesiaDocument12 pagesPuerperium and AnalgesiaKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Puerperium SeminarDocument79 pagesPuerperium SeminarMariam Abdul Rashid100% (3)
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDocument63 pagesPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- Puerperium and Its Management 1Document35 pagesPuerperium and Its Management 1Elvis100% (2)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing - Postpartum PeriodDocument3 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing - Postpartum PeriodkimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- Postpartum: Vanneza Trixzy V. TamparongDocument37 pagesPostpartum: Vanneza Trixzy V. TamparongVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document14 pagesUnit 12KumareshNo ratings yet
- BrerastDocument6 pagesBrerastlunamoonvaleria00No ratings yet
- NORMALPOSTPARTUMDocument178 pagesNORMALPOSTPARTUMannyeong_123No ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum CareDocument37 pagesPost-Partum Careャチ100% (1)
- CH. 12 Study GuideDocument10 pagesCH. 12 Study GuidePaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Physiologic and Psychologic Changes During PregnancyDocument12 pagesPhysiologic and Psychologic Changes During Pregnancyyannie100% (1)
- (OBa) 1.6 Matrnal Adaptations To Pregnncy (Marinas) - PacisDocument10 pages(OBa) 1.6 Matrnal Adaptations To Pregnncy (Marinas) - PacisClyde Yuchengco Cu-unjiengNo ratings yet
- Puerperium ManagementDocument19 pagesPuerperium ManagementDavina DakapNo ratings yet
- Postpartum - Physiology and NSG Care 15Document33 pagesPostpartum - Physiology and NSG Care 15yuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- MCN Chapter 17Document2 pagesMCN Chapter 17Mary Joy Teylan CalongoNo ratings yet
- Case 01 - Maternal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCase 01 - Maternal PhysiologyRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- PPDS Prep - Nifas Dan KontrasepsiDocument49 pagesPPDS Prep - Nifas Dan KontrasepsiArum HastutiNo ratings yet
- Normalpuerperium 200523093433Document99 pagesNormalpuerperium 200523093433STANN KAZIPETNo ratings yet
- NCM-107 4Document10 pagesNCM-107 4FERNANDEZ, RELLY ANDREWNo ratings yet
- OB1 3.3A Normal Puerperium and Puerperal FeverDocument7 pagesOB1 3.3A Normal Puerperium and Puerperal FeverManjulaNo ratings yet
- Hernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Learners WorksheetDocument5 pagesLearners WorksheetRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia NcaDocument123 pagesFibromyalgia NcaRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - NCA-To The Bone (Anorexia)Document109 pagesGroup 2 - NCA-To The Bone (Anorexia)Ruthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument61 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsRuthangela Garcia100% (1)
- The Iliad by Homer-LucasDocument22 pagesThe Iliad by Homer-LucasRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- 12G Lab3 GARCIADocument3 pages12G Lab3 GARCIARuthangela Garcia100% (1)
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- M2 Module - 12G 26203Document49 pagesM2 Module - 12G 26203Ruthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Newborn RevDocument14 pagesNewborn RevRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaDocument1 pageFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- COMPILATION TFN-THEORISTS-Garcia FinalDocument6 pagesCOMPILATION TFN-THEORISTS-Garcia FinalRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and ExaminationsDocument9 pagesLaboratory and ExaminationsRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain RUTH FinalDocument7 pagesAcute Pain RUTH FinalRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum RevDocument11 pagesPostpartum RevRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Manuscriptm1 203 Grp26 12gDocument61 pagesManuscriptm1 203 Grp26 12gRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MEFENAMIC - GARCIADocument3 pagesDrug Study - MEFENAMIC - GARCIARuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage: ReviewDocument6 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage: ReviewBodat BodatsNo ratings yet
- 1577-Article Text-3940-1-10-20170710Document12 pages1577-Article Text-3940-1-10-20170710aghniajolandaNo ratings yet
- 9 of West: Following Register For Kolkata Municipal Corporation of BengalDocument2 pages9 of West: Following Register For Kolkata Municipal Corporation of BengalShuvajoyyyNo ratings yet
- Cotton-Top Tamarin - Husbandry - ManualDocument98 pagesCotton-Top Tamarin - Husbandry - Manualjoaquin chan100% (1)
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument2 pagesNeonatal JaundiceChamCham AquinoNo ratings yet
- Interview SheetDocument3 pagesInterview SheetSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Case Study MCDDocument16 pagesCase Study MCDJohn kananamanNo ratings yet
- Biodata Blank SheetDocument3 pagesBiodata Blank SheetMelvin Cabanda EbalNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox in Pregnancy - A Challenge To The Obstetrician: Hem Kanta SarmaDocument2 pagesChicken Pox in Pregnancy - A Challenge To The Obstetrician: Hem Kanta SarmaDrDevdatt Laxman PitaleNo ratings yet
- 1 X 1 ID Picture: Barangay Official'S Information SheetDocument1 page1 X 1 ID Picture: Barangay Official'S Information SheetJordan Paul DangelanNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and HeartDocument53 pagesPregnancy and HeartgibreilNo ratings yet
- Case Management NICU July 2020 Sam WibowoDocument6 pagesCase Management NICU July 2020 Sam WibowoSamuel WibowoNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaDocument13 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaesakkiammalNo ratings yet
- Santana 2019Document12 pagesSantana 2019gcereiraaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument313 pagesPDFOki NurpatriaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health MindmapDocument11 pagesReproductive Health MindmapSuyagya PundirNo ratings yet
- Doppler in ObstetricsDocument13 pagesDoppler in ObstetricsPrajakta TumbareNo ratings yet
- Lesson (5) Neonatal ResuscitationDocument14 pagesLesson (5) Neonatal ResuscitationDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Pre Ec and Policy in The Philippines FIXDocument26 pagesPrevention of Pre Ec and Policy in The Philippines FIXummaNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument7 pagesBirth InjuriesWendy NyamweyaNo ratings yet
- Why Methotrexate Is An Immoral Response To Ectopic PregnancyDocument21 pagesWhy Methotrexate Is An Immoral Response To Ectopic PregnancyelainemenezNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestone (Week 8) ReviewerDocument8 pagesDevelopmental Milestone (Week 8) ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- RD Rosalinda C. Apura, D.MDocument4 pagesRD Rosalinda C. Apura, D.MMaria AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Child Nursing Care in Canada 1st Edition Perry Test BankDocument14 pagesMaternal Child Nursing Care in Canada 1st Edition Perry Test Bankalicenhan5bzm2z100% (30)
- Psychiatric Disorders in PregnancyDocument93 pagesPsychiatric Disorders in Pregnancyjinijinu100% (4)
- Stages of Fetal Development in EmbryoDocument6 pagesStages of Fetal Development in EmbryobilvaroyNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument2 pagesPregnancy ComplicationsAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Polyhydramnios: SymptomsDocument4 pagesPolyhydramnios: Symptomsbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- NAME: Sonwalkar Pratik Rohidas Class: 12 R1 Subject: Biology TOPIC: Detailed Study On Infertility Its Causes and TreatmentDocument27 pagesNAME: Sonwalkar Pratik Rohidas Class: 12 R1 Subject: Biology TOPIC: Detailed Study On Infertility Its Causes and TreatmentPratik Sonwalkar0% (1)
- Complete Mother KindDocument12 pagesComplete Mother KindThe Productive Muslim CompanyNo ratings yet