0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views30 pagesDesign of Pulley Support Assembly
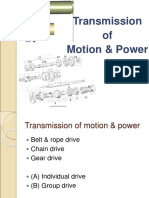
The document describes a report on the design and analysis of a pulley support assembly submitted by four students. It includes a certificate signed by their project guide, Mr. Pritish G. Chitte, acknowledging their work. The abstract indicates that the objective was to reduce time, manpower, and fatigue during the process by improving the design from using a timing belt to a sprocket and chain drive mechanism. The document provides the components and structure of the pulley support assembly designed and analyzed in the project.
Uploaded by
Nani ShaikhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views30 pagesDesign of Pulley Support Assembly
The document describes a report on the design and analysis of a pulley support assembly submitted by four students. It includes a certificate signed by their project guide, Mr. Pritish G. Chitte, acknowledging their work. The abstract indicates that the objective was to reduce time, manpower, and fatigue during the process by improving the design from using a timing belt to a sprocket and chain drive mechanism. The document provides the components and structure of the pulley support assembly designed and analyzed in the project.
Uploaded by
Nani ShaikhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd