Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2022 First Quarter Test Grade 10 Science
Uploaded by
Mary Ann MercadoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2022 First Quarter Test Grade 10 Science
Uploaded by
Mary Ann MercadoCopyright:
Available Formats
FIRST QUARTER EXAMINATION IN GRADE 10 SCIENCE
Part I consists of 30 multiple-choice questions. Read each number carefully then write only the letter of the best
answer on the separate answer sheet.
1. You were provided with data showing the arrival time
of the P and S-waves recorded from three seismic
stations. Which of these can you possibly determine?
A. the damage at the focus
B. the distance to the earthquake
C. the intensity of the earthquake
D. the location of the epicenter
2. From the seismogram, the distance to the epicenter A. volcanoes
can be determined by measuring B. volcanic island arcs
A. the arrival time of surface wave C. mountain ranges
B. the difference in the arrival times of the P D. rift valleys
and S-waves 11. You were asked to locate the epicenter of a recent
C. the ratio of the amplitude of the largest P earthquake. Which correct sequence of events should
and S-waves you follow?
D. the speed of the surface wave I. Determine the difference in the arrival time of S and
3. Which of the following plate boundaries can produce P waves recorded from each of the seismological
rift valleys? stations.
II. Use the triangulation method to locate the center.
III. Obtain data from three different seismological
stations.
IV. Determine the distance of the epicenter from the
A. station.
A. I, III, II, IV C. IV, II, I, III
B. III, IV, I, II D. III, I, IV, II
12. If you visit a place in the Pacific known to be along
converging plates, which of these should you NOT
B. expect to see?
A. active volcanoes C. rift valleys
B. mountain ranges D. volcanic islands
13. Which of the following can we expect to find at a
mid-ocean ridge?
C. A. relatively young rocks C. very ancient rocks.
4. When two tectonic plates collide, the oceanic crust B. reverse fault D. thick accumulation of sediments
usually subducts beneath the continental crust because 14. The lithospheric plates are believed to be moving
it is slowly. What is the driving force that facilitates this
A. denser than continental crust movement?
B. less dense than continental crust A. gravitational force of the moon
C. thicker than continental crust B. magnetic force at the poles
D. thinner than continental crust C. convection current in the mantle
5. Why does the oceanic crust sink beneath the D. the force of the atmosphere
continental crust at the subduction zone? 15. What kind of plate boundary occurs where two plates
A. The oceanic crust has a greater density. grind past each other without destroying or producing
B. The oceanic crust is pulled downward by Earth’s lithosphere?
magnetic field. A. divergent boundary
C. The oceanic crust is pushed from the ridge. B. convergent boundary
D. The continental crust has a denser composition. C. transitional boundary
6. What do you expect to find parallel to a trench? D. transform fault boundary
A. hot spot C. rift valley 16. This area is both a major earthquake zone and
B. ocean ridge D. volcanic arc volcano zone.
7. An oceanographer noticed that there is a portion in A. Pacific Ring of Volcanoes
the ocean floor which is relatively much deeper than the B. Pacific Ring of Fire
rest. What most likely is that deeper part? C. Oceanic Ring of Fire
A. linear sea C. rift valley D. Pacific Island Arc
B. oceanic ridge D. trench 17. What is the epicenter of an earthquake?
8. Which plate boundary is formed between the A. the location along a fault where the first
Philippine plate and the Eurasian plate? motion of an earthquake occurs
A. convergent C. reverse fault B. a seismic wave that travels along the
B. divergent D. transform fault surface of Earth
9. Which of these is false about lithospheric plates: C. the point on Earth’s surface directly above
A. have the same thickness everywhere the earthquake’s focus
B. include the crust and upper mantle D. the last place that motion in an earthquake
C. thickest in the mountain regions is detected
D. vary in thickness 18. What is produced in the convergence of two
10. What geologic feature can be formed in this type of continental plates?
plate boundary? A. mountain range C. rift valleys
B. island arcs D. trenches
19. The movement of the lithospheric plates is facilitated
by a soft, weak and plastic-like layer. Which of the
following layers is described in the statement?
A. Asthenosphere C. Lithosphere
B. Atmosphere D. Mantle
20. Scientists disagreed with Wegener's idea because
he could not explain:
A. similar fossils' in different continents
B. forces necessary to move continents.
C. identical rock formations.
D. climate changes
21. If you are a cartographer, what will give you an idea
that the continents were once joined?
A. Ocean depth
B. Position of the south pole A. A; temperature C. C; temperature
C. Shape of the continents B. B; pressure D. D; pressure
D. Size of the Atlantic Ocean 25. Which of the following can you infer from the
22. During the 1960’s, scientists were already equipped continuous movement of the lithospheric plates over the
with gadgets needed to explore the deep ocean. What asthenosphere?
discovery about the ocean floor is associated with the A. All the continents will cease to exist.
sea floor spreading? B. All the volcanoes in the Philippines will
A. Mountains are denser than the mantle. become inactive.
B. The rotational poles of the Earth have C. The continents will not be located in the
migrated. same place as they are now.
C. The crust of the continents is denser than D. The islands of the Philippines will become
the crust of the ocean. scattered all over the world.
D. The crust of the ocean is very young
relative to the age of the crust of the continents. For numbers 26-27, what features of a plate determine
23. Which observation was NOT instrumental in whether a plate will subduct under another plate? Pick
formulating the hypothesis of seafloor spreading? the two correct features:
A. Depth of the ocean A. How much ocean water is on top of the
B. Identifying the location of glacial deposits plate
C. Magnetization of the oceanic crust B. The age of the plate
D. Thickness of seafloor sediments C. Whether the plate is made of basalt or
24. Use the diagram of the Earth’s layers to select the granite
best answer. D. How fast the plate is traveling
Layer ____ is solid because of the extreme ____. E. Whether the plate is in the northern or
southern hemisphere
F. Whether the plate is traveling east or west
For numbers 28-30, choose the letter that will describe the processes in each number.
A. Mid-ocean ridge forms whenever diverging plates continue to separate, creating a new ocean
basin. As the rising magma cools, it forms new ocean crust.
B. When an oceanic plate converges with a less dense continental plate, the denser oceanic plate sinks
under the continental plate.
C. When two oceanic plates converge, the denser plate is forced beneath the other plate and volcanic
islands form above the sinking plate.
28. _________ 30. _________
29. _________
Part II. Study the following illustrations and answer the following questions. Write your answers in your answer
sheet.
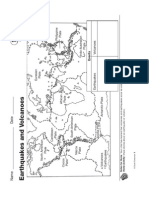
Answer the following questions based on the map.
31. Give an example of convergent plate boundary.
32. Give an example of divergent plate boundary.
33. Give an example of transform fault plate boundary.
34-35. Where do most earthquakes and volcanoes are
located?
36-39. Study the following diagram of the seafloor.
Then match the letters to the statements
below.
_____36. Molten rock flows onto the seafloor and hardens as it cools.
_____37. Hot, molten rock is forced upward toward the seafloor at a mid-ocean ridge.
_____38. New sea floor moves away from the ridge, cools denser, and sinks.
_____39. Molten rock pushes sideways in both directions as it rises, moving the mantle with it.
40. The heat process caused by the uneven distribution of thermal energy in Earth’s interior is called
A. Ridge push B. slab pull C. Seafloor spreading D. mantle convection
41-45. Identify the words that will best describe the letters in the diagram. Use the words in the word bank.
41.convection current 42.moving toward 43.moving apart
44.expands and rises 45.cools and sinks
B C
A
D
E
46-50. Match the pictures and text below to arrange the movement of the continents into chronological order (oldest to
newest).Write the letter of your answer.
46. 47. 48.
49. 50.
A. About 225 million years ago, all of the world’s landmass were joined together in the supercontinent Pangaea. Pangaea
was surrounded by a vast sea called Panthalassa.
B. Approximately 200 million years ago, the Tethys Sea formed as Pangaea began to split. The two continents that
formed were called Laurasia and Gondwana. Laurasia included the landmasses that are now North America, Europe,
Greenland and Asia. Gondwana included South America, Africa, Antarctica, India, Madagascar and Australia.
C. Gondwana began to break up about 135 million years ago. The South Atlantic Ocean formed between Africa and
South America.
D. About 65 million years ago, Australia separated from Antarctica.
E. The continents today
You might also like
- First Periodical Test in Science 10Document7 pagesFirst Periodical Test in Science 10Ron Adrian Sarte SebastianNo ratings yet
- Science 10: Department of Education Division of Oriental Mindoro Puerto Galera Nhs Dulangan ExtensionDocument3 pagesScience 10: Department of Education Division of Oriental Mindoro Puerto Galera Nhs Dulangan ExtensionJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Name: - Section: - ScoreDocument2 pagesName: - Section: - ScoreJoenald Kent Ordoña100% (1)
- First Quarter Science 10 Summative TestDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter Science 10 Summative Testjimbo09No ratings yet
- Science 10 FDocument8 pagesScience 10 FQuianie Lee Lingating Arnoza-Revelo100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test Science 10Document8 pagesDiagnostic Test Science 10Pilar Angelie Palmares VillarinNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Science 10 2222Document5 pages1st Periodical Science 10 2222Mark Kelvin Dinong100% (2)
- 1ST Quarter Exam - in Science 10Document5 pages1ST Quarter Exam - in Science 10Allen Marohombsar100% (2)
- First Quarter Examination in Science 10Document5 pagesFirst Quarter Examination in Science 10melanie magbooNo ratings yet
- Earth Science True or False and Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesEarth Science True or False and Multiple Choice QuestionsJolo MercadoNo ratings yet
- Grade10 Quarterly Examination Q1 EditedDocument5 pagesGrade10 Quarterly Examination Q1 EditedShanrey Mirones100% (1)
- First Periodical Test Science Grade 10Document7 pagesFirst Periodical Test Science Grade 10janice alquizar89% (38)
- Commonwealth High School Grade 10 Diagnostic Test focuses on plate tectonicsDocument3 pagesCommonwealth High School Grade 10 Diagnostic Test focuses on plate tectonicsAngela Elaine UrquiaNo ratings yet
- Science Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesScience Exam ReviewRonald Valenzuela0% (1)
- Earth's Layers TestDocument5 pagesEarth's Layers TestJenelyn SarbodaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - First Periodical ExamDocument5 pagesScience 10 - First Periodical ExamJademar Sebonga TadiqueNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Science 10 Quarter 1Document2 pagesLong Test in Science 10 Quarter 1MARIA THEA CALAGUASNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science 1st Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science 1st Quarter ExamCharizza Cabrera100% (1)
- Q1 Periodic Test in Science 10Document4 pagesQ1 Periodic Test in Science 10Jezha Mae Nelmida50% (2)
- Summative Test Science10 1stDocument3 pagesSummative Test Science10 1stDominga SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-Summative Assessment 1.2 ScienceDocument2 pagesGrade 10-Summative Assessment 1.2 ScienceSylvs Enong100% (3)
- 2nd QUARTER EXAM SCIENCE 10Document13 pages2nd QUARTER EXAM SCIENCE 10Manuela Kassandra Soriao Tribiana0% (1)
- Science Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesScience Exam ReviewRonald ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science Exam Covers Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPhilippine Science Exam Covers Plate TectonicsJaenicaPaulineCristobal0% (1)
- First Periodical Exam in Science-10Document3 pagesFirst Periodical Exam in Science-10cristito inovalNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Exam Science Grade 10Document2 pages1st Grading Exam Science Grade 10Ann Necdote100% (2)
- Tectonic Plates and Earthquakes Test ReviewDocument4 pagesTectonic Plates and Earthquakes Test ReviewLey F. Fajutagana100% (2)
- Banban National High School Science ExamDocument4 pagesBanban National High School Science Examrobert valdezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Periodic TestDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Periodic TestJennifer O. Catubig100% (1)
- Mother Teresa Academy of Marilao, Bulacan IncDocument32 pagesMother Teresa Academy of Marilao, Bulacan IncNikko CarilloNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method: The Foundation of ScienceDocument1 pageScientific Method: The Foundation of ScienceTeacherbhing Mitrc80% (15)
- Korondal National HS Science 10 Summative Test 1Document2 pagesKorondal National HS Science 10 Summative Test 1Maera Angela Dajay50% (2)
- 2nd Grading Science 10Document3 pages2nd Grading Science 10Russel Ocho100% (1)
- Science10 Summative TestDocument4 pagesScience10 Summative TestESTHER MAE ANN TRUGILLO100% (1)
- g10-2nd Quarter Exam Science 10Document4 pagesg10-2nd Quarter Exam Science 10Kier Black100% (1)
- Pre Test Science g10Document3 pagesPre Test Science g10Ading Sam100% (1)
- Reviewer in Science: LithosphereDocument3 pagesReviewer in Science: LithosphereNatasha Loujille Collado100% (1)
- TOS For G10 First Quarter ExamDocument1 pageTOS For G10 First Quarter ExamBoyeth Rulida100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test in Science 10Document2 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 10Pepito Rosario Baniqued, Jr100% (6)
- Plate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesArgie Mabag100% (2)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum QuizDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Quizprince adilan planas100% (5)
- 3RD Grading TestDocument3 pages3RD Grading TestAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in Science 10 Test I Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pages1st Quarter Exam in Science 10 Test I Multiple Choice Questionsvon88% (25)
- Science Reviewer Q1Document4 pagesScience Reviewer Q1Alexie AlmohallasNo ratings yet
- Second Monthly Test Science 10Document4 pagesSecond Monthly Test Science 10Sher Sherwin100% (3)
- Earth and Space Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument6 pagesEarth and Space Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Best AnswerJesmar Quirino TutingNo ratings yet
- Science 10 PretestDocument3 pagesScience 10 PretestMario Uy86% (7)
- Grade-10-Science-Q1 SUMMATIVE TESTDocument2 pagesGrade-10-Science-Q1 SUMMATIVE TESTNhet Ytienza100% (8)
- Science 10 First Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 10 First Quarter ReviewerPlayer 456No ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Science 10Document5 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 10MarioSabitNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Science Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages1st Term Science Exam ReviewerAndie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Panabo City National High School Science 10 AssessmentDocument2 pagesPanabo City National High School Science 10 AssessmentJoshua Robert Gaviola100% (3)
- 2nd Quarter Exam Final Na ToDocument5 pages2nd Quarter Exam Final Na ToMerlyn Mendoza100% (1)
- Earth's MechanismDocument22 pagesEarth's MechanismJohn Van Dave Taturo100% (2)
- Earths Interior (2nd Summative Test)Document11 pagesEarths Interior (2nd Summative Test)ndramonedaNo ratings yet
- Pre Assessment Grade 10 60 ItemsDocument6 pagesPre Assessment Grade 10 60 ItemsRachael Chavez100% (1)
- SCIENCE GRADE 10 QUIZ BEEDocument4 pagesSCIENCE GRADE 10 QUIZ BEEjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Examination ReviewerDocument40 pagesFirst Periodical Examination ReviewerDeodat Boi LawsonNo ratings yet
- First Quarter SCI 9Document4 pagesFirst Quarter SCI 9bryan100% (1)
- Q1ST1Document3 pagesQ1ST1Des Carbonilla100% (1)
- EarthreadingcompDocument2 pagesEarthreadingcompapi-254428474No ratings yet
- PJK T2 PPT 19Document8 pagesPJK T2 PPT 19noorNo ratings yet
- Earth Moon Sun Vocab AnswersDocument3 pagesEarth Moon Sun Vocab AnswersMariel Efren100% (1)
- Pengertian Dan Ruang Lingkup VektorDocument10 pagesPengertian Dan Ruang Lingkup VektorArlin KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes VolcanoesDocument5 pagesEarthquakes VolcanoesHusna Hafiza RazamiNo ratings yet
- Lastpkt RegDocument200 pagesLastpkt RegaruvindhuNo ratings yet
- Scope and Sequence Grade 7 Science Earth ScienceDocument13 pagesScope and Sequence Grade 7 Science Earth Sciencemarjorie abreganaNo ratings yet
- 7L Solar System and BeyondDocument62 pages7L Solar System and BeyondRamesh IyerNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson by SlidesGoDocument35 pagesBiology Lesson by SlidesGoaconk rizkyNo ratings yet
- Planting Calendar India 2021Document28 pagesPlanting Calendar India 2021Bharat ShahiNo ratings yet
- Simple Pastel Company Profile by SlidesgoDocument40 pagesSimple Pastel Company Profile by Slidesgoadityabubna23No ratings yet
- Researc H Project: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsDocument44 pagesResearc H Project: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsYovi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Mysterious MarsDocument30 pagesMysterious Marsjohn_crawford_1100% (1)
- ES Q2 Week-4bDocument10 pagesES Q2 Week-4bIrish KriselleNo ratings yet
- World Laughter Day by SlidesgoDocument50 pagesWorld Laughter Day by SlidesgoADMINISNo ratings yet
- Project On Eclipse and Its TypesDocument21 pagesProject On Eclipse and Its Typesapi-3731257100% (2)
- Script Solar SytemDocument3 pagesScript Solar SytemmasyaliNo ratings yet
- Physics and Natural SciencesDocument8 pagesPhysics and Natural SciencesJames BangNo ratings yet
- Tam Sam SOM InfographicsDocument33 pagesTam Sam SOM Infographicsruth lopezNo ratings yet
- Orb of InfluenceDocument2 pagesOrb of Influencevikram.devathaNo ratings yet
- IPLAN Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesIPLAN Lesson PlanKarlzNo ratings yet
- Geological Time With Major Evolutionary Events in The Fossil RecordDocument1 pageGeological Time With Major Evolutionary Events in The Fossil RecordPsg FunNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis ReportDocument24 pagesGap Analysis ReportDzana MuzurovicNo ratings yet
- What Causes Convection Currents?Document2 pagesWhat Causes Convection Currents?Mary Rose DomingoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 presentation on planetsDocument6 pagesGroup 3 presentation on planetsNikko MagsilangNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarter 4 Week 8Document46 pagesScience 7 Quarter 4 Week 8Kayle PoblacionNo ratings yet
- XXVCDocument2 pagesXXVCgreatsworddesigns0% (1)
- Sample 4As Lesson Plan English (1)Document153 pagesSample 4As Lesson Plan English (1)Ukay FindsNo ratings yet
- Year End Pupils Progress Report Sy 2022 2023Document14 pagesYear End Pupils Progress Report Sy 2022 2023GENESIS MANIACOPNo ratings yet
- Earth InteriorDocument13 pagesEarth InteriorEjaz Ul Haq KakarNo ratings yet