Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Biology 12th Term II Ch. 6
Uploaded by
Abhishek GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Biology 12th Term II Ch. 6
Uploaded by
Abhishek GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Term II Biology XII 1
6 Biodiversity and its Conservation
Multiple Choice Questions Short Answer Type Questions
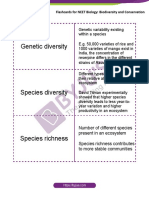
1. (a) The Western ghats have a greater amphibian diversity 1. Ecological diversity refers to the diversity at ecosystem
than the Eastern ghats. Thus, it is an example of species level. Due to the presence of more variety of ecosystems and
diversity which is defined as diversity at species level and is habitats, i.e. rainforest, desert, wetlands, mangroves, coral
indicated by variety and richness of species of a region. reefs and alpine meadows, India has a greater ecological
2. (b) International Union of Conservation of Nature and diversity than Scandinavian countries (e.g. Norway).
Natural Resources (IUCN) maintains a Red data book or 2. Modern agriculture destroys natural vegetation of a site,
Red list which is a catalogue of taxa facing risk of extinction. leading to loss of natural habitat. A cultivated area has less
3. (c) Statements II, III and IV describe natural extinction, but biodiversity and the use of pesticides in modern agriculture,
statement I is not appropriate description of natural can destroy beneficial organisms along with agricultural
extinction. pests.
4. (b) Excessive exploitation of a species, whether a plant or 3. Mass extinction refers to a rapid decline in the biodiversity
animal reduces size of its population such that it becomes of earth. It means a majority of all the species are vanished
vulnerable to extinction. Dodo, passenger pigeon and or not seen in a particular geographical area, e.g. extinction
Steller’s sea cow have become extinct in the last 500 years of dinosaurs that took place due to changing climatic
due to overexploitation by human. conditions. The dinosaurs were unable to survive the
5. (d) Sacred groves are the forest patches around the places of changing climate and got extinct.
worship, which are held in high esteem by tribal 4. Species diversity decreases on moving away from the
communities. They are found in several parts of India. equator towards the poles. It means that biodiversity is more
Assertion-Reasoning MCQs at lower latitudes (equator) than at higher latitude (poles),
e.g. Colombia located near the equator has around 1400
1. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation species of birds and New York located at 41°N has
of A. 105 species of birds whereas Greenland at 71°N has only
Tropical latitudes have greater biological diversity. It is quite 56 species of birds.
true. Ecologists and evolutionary biologists have proposed 5. When a large expanse of habitat is transformed into a
various hypothesis in support of this. Some of them are number of smaller patches of smaller area isolated from each
following speciation is generally a function of time and other, it is called habitat fragmentation. Each piece is then
unlike temperate regions subjected to frequent glaciations in called a fragmented habitat. It is one of the major causes for
the past tropical latitudes remained undisturbed for millions the loss of biodiversity, e.g. 14% of the earth’s land surface
of years, where species continued flourish. Other than this covered by tropical rainforest is now limited upto only 6%
tropical environments are more constant and there is more due to the habitat loss and fragmentation.
solar energy available in tropics which contributes to high 6. (i) Biodiversity can be conserved by protecting its whole
productivity. ecosystem. There are two basic approaches for
2. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation conservation of biodiversity.
of A.
(a) In situ conservation It is conservation and
Species with low genetic variability are generally at protection of the whole ecosystem and its
significantly greater risk of extinction than the species with biodiversity at all levels in order to protect the
more genetic variability, mainly because they have a more threatened species.
limited arienal with which to respond to the varieties of
This strategy includes setting up biodiversity
environmental change. Species with extremely low genetic
hotspots, protected areas like national parks,
variability are particularly vulnerable towards a new disease
wildlife sanctuaries, etc.
predator or other environmental changes.
3. (c) A is true, but R is false because (b) Ex situ conservation It involves placing the
threatened species (both plants and animals) in
The Great Indian bustard is a rare species of birds found in special care units for their protection. It includes
parts of Gujarat and Rajasthan. Due to destruction of natural botanical gardens, zoological parks, seed or gene
habitat and poaching, it has become a rare species. banks, etc.
2 CBSE Term II Biology XII
(ii) Out of the two basic approaches, in situ or on-site many plants, thus ensuring cross-pollination which is
conservation is preferred as it consists of methods to required to ensure genetic diversity for other species.
maintain the species of wildlife in their natural habitat. Since, plants are the primary food source for animals,
Methods include establishing biodiversity hotspots, possible disappearance of pollinators will affect animals
national parks, sacred groves, wildlife sanctuaries, etc. (including humans) and thus, affect ecosystem.
All of these methods aim at providing protection to the 2. (i) Biodiversity hotspots are the regions of accelerated
wildlife related to that area. habitat loss. These can reduce the ongoing mass
Long Answer Type Question extinctions by almost 30%.
1. (i) Seeds of different genetic strains are kept for long Sacred groves are important in biodiversity
periods in seed banks. They involve ex situ conservation conservation, as these are naturally protected by the
of biodiversity. native population without much effort. In Meghalaya,
The strategy approaches toward conserving samples of the sacred groves are the last refuges for large number
crop seeds of commercially important crops under of rare and threatened plants.
frozen storage conditions, where they remain viable for (ii) Commensalism because Ophrys employs sexual deceit
longer periods of time. to get pollinated by species of bumble bee as petal of its
Sometimes, cryopreservation method also takes in use. flower bears resemblance to female of the bee in size,
colour and marking and so, male bee is attracted to
Sealed samples of individual accessions are placed in what it perceives as female, pseudocopulates with the
frozen conditions and are regenerated from time to flower and thus, pollinates it. If the female bee’s colour
time in order to get better results. patterns change even slightly due to any reason during
(ii) Yes, extinction of an insect pollinator will affect the evolution, pollination success will be reduced unless
whole ecosystem directly or indirectly. Insect the orchid flowers coevolves to maintain the
pollinators participate in the sexual reproduction of resemblance of its petal to the female bee.
You might also like
- Ecological-Profile LegCity 2023Document178 pagesEcological-Profile LegCity 2023Maricel Listana JulocNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Plants and AnimalsDocument9 pagesConservation of Plants and Animalsdhivya sankarNo ratings yet
- CL8 - UNIT IV WorksheetDocument11 pagesCL8 - UNIT IV WorksheetSahej100% (3)
- Biodiversity 1Document22 pagesBiodiversity 1Krish BagNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Threats and Conservation: StructureDocument21 pagesBiodiversity: Threats and Conservation: StructureramanNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument9 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationChinnam rama krishnaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument32 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationRani KumariNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyDocument41 pagesBiodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument2 pagesBiodiversity and Conservationsrk.abhinandhanNo ratings yet
- 36 ch15Document7 pages36 ch15shodhan shettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Class 12 BioDocument4 pagesChapter 12 Class 12 Biotanyaverma2729No ratings yet
- Biodiversity NotesDocument6 pagesBiodiversity Notesraushankumar05072No ratings yet
- SR4758Document9 pagesSR4758smrutishree25No ratings yet
- 1 BiodiversityDocument10 pages1 Biodiversityxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Biodiverity and Conservation PDF SummarizedDocument15 pagesBiodiverity and Conservation PDF SummarizedmohtashimahmNo ratings yet
- Biodiversityconservation 140413102641 Phpapp02Document37 pagesBiodiversityconservation 140413102641 Phpapp02Anita Arora100% (1)
- BiodiversityDocument10 pagesBiodiversityMaanas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Conservation PDFDocument7 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation PDFDeepikaNo ratings yet
- Biodivesity and Its Conservation PyqDocument10 pagesBiodivesity and Its Conservation PyqSoumya Ranjan NaikNo ratings yet
- BiodivesrityDocument47 pagesBiodivesrityBenzDave AgsoyNo ratings yet
- Conservation MCQ and LA QuestionsDocument7 pagesConservation MCQ and LA QuestionsSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- Biological Conservation: Cameron D. Siler, Andrés Lira-Noriega, Rafe M. BrownDocument9 pagesBiological Conservation: Cameron D. Siler, Andrés Lira-Noriega, Rafe M. Brownmarie parfanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-15 Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument6 pagesChapter-15 Biodiversity and Its ConservationbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation QuestionsDocument7 pagesClass 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation Questionstechy techyNo ratings yet
- Revision 1 BiodiversityDocument7 pagesRevision 1 BiodiversitySilent WarriorNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument5 pagesBiodiversityArgha senguptaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Chapter 7 - Conservation of Plants and Animals Notes - HakimDocument19 pagesClass 8 Chapter 7 - Conservation of Plants and Animals Notes - HakimHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Theacher GuideDocument4 pagesTheacher GuideAlejandro Lavid SaizNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document14 pagesCH 7sujaljaiswal759No ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY: Understanding Species, Ecosystems & Genetic DiversityDocument27 pagesBIODIVERSITY: Understanding Species, Ecosystems & Genetic DiversityJemimah Anne Santos FerrerNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity-and-its-Conservation Project PDFDocument21 pagesBiodiversity-and-its-Conservation Project PDFprincepatnaik.bbsrNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION NewDocument6 pagesBIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION Newkanishk17295No ratings yet
- Biodiversity Scenario, Threats and Its Conservation in IndiaDocument27 pagesBiodiversity Scenario, Threats and Its Conservation in IndiaESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNo ratings yet
- Science - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Document18 pagesScience - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Gan Wei ShengNo ratings yet
- 1.biodiversity 20 20conservation-1Document55 pages1.biodiversity 20 20conservation-1Faiqa AfzalNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument18 pagesBiology Projectrexol67424No ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument3 pagesBiodiversityshodhan shettyNo ratings yet
- Presentation Group 3 Animal EcologyDocument24 pagesPresentation Group 3 Animal EcologyCindi SinambelaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument5 pagesBiodiversity and Conservationnaveen kumarNo ratings yet
- ES UNIT - 3: BiodiversityDocument7 pagesES UNIT - 3: Biodiversityxijiwo8667No ratings yet
- Biologial DiversityDocument22 pagesBiologial Diversityvikas21014005No ratings yet
- Biodiversity Conservation ChapterDocument4 pagesBiodiversity Conservation ChapterMeenakshi VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- "Inventory of Terrestrial Arthropods in The Vicinity of Dila Falls, Brgy. Impalutao, Impasug-Ong Bukidnon" - Medura, MMMDocument14 pages"Inventory of Terrestrial Arthropods in The Vicinity of Dila Falls, Brgy. Impalutao, Impasug-Ong Bukidnon" - Medura, MMMs.medura.mamarielleNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Conservationmundesandeep45No ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity Exploration and ConservationDocument6 pagesMicrobial Diversity Exploration and ConservationRedd ZhuangNo ratings yet
- In Situ Conservation: ES - Biodiversity and Wildlife ConservationDocument38 pagesIn Situ Conservation: ES - Biodiversity and Wildlife ConservationJaffy BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Habitat Conservation Through Butterfly Zone: A New Approach To In-Situ Conservation of Butterfly DiversityDocument5 pagesHabitat Conservation Through Butterfly Zone: A New Approach To In-Situ Conservation of Butterfly DiversityIra PradhiftaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity and ConservationDocument31 pagesChapter 15 Biodiversity and ConservationGillu SinghNo ratings yet
- Journal For Nature Conservation: Gabriel J. Casta No-Villa, Jaime V. Estevez, Francisco E. FontúrbelDocument5 pagesJournal For Nature Conservation: Gabriel J. Casta No-Villa, Jaime V. Estevez, Francisco E. FontúrbelKarla AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Biodiversity ConservationDocument3 pagesWildlife Biodiversity ConservationPegNo ratings yet
- Biology DiversityDocument13 pagesBiology Diversityshalini haninah madhuNo ratings yet
- Butterfly diversity across agricultural ecotonesDocument12 pagesButterfly diversity across agricultural ecotonesAlessio VovlasNo ratings yet
- TMP 7 B88Document7 pagesTMP 7 B88FrontiersNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument4 pagesBiodiversityPagwadan FonacierNo ratings yet
- Causes and Solutions for Degradation of Natural ResourcesDocument11 pagesCauses and Solutions for Degradation of Natural ResourcesKristianFelixNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY & CONSERVATIONDocument73 pagesBIODIVERSITY & CONSERVATIONNandini ChughNo ratings yet
- Shankar IAS Environment-Part-II.Document26 pagesShankar IAS Environment-Part-II.rajatNo ratings yet
- Notes On BiodiversityDocument4 pagesNotes On BiodiversityNidal SajeerNo ratings yet
- RRL 5kDocument18 pagesRRL 5kfilesjatcabuangNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7Document9 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7JollyNo ratings yet
- Biology and Subject Code PDFDocument12 pagesBiology and Subject Code PDFpuranjan kaphleNo ratings yet
- Kulim SR 2018 2019Document64 pagesKulim SR 2018 2019Carissa May Maloloy-onNo ratings yet
- Conservation VS Development 1Document47 pagesConservation VS Development 1Andrea HonradaNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India and EnvironmentDocument7 pagesConstitution of India and EnvironmentSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- EcoProduction Katarzyna Grzybowska, Anjali Awasthi, Rapinder SawhneyDocument298 pagesEcoProduction Katarzyna Grzybowska, Anjali Awasthi, Rapinder SawhneyYimer Meshesha100% (1)
- DENR Questions Tourism Operations on Leyte's Kalanggaman IslandDocument2 pagesDENR Questions Tourism Operations on Leyte's Kalanggaman IslandAngel BroczNo ratings yet
- Bonaire National Marine Park Management Plan (2006)Document108 pagesBonaire National Marine Park Management Plan (2006)TaisyNo ratings yet
- CSSOC03 - 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesCSSOC03 - 3rd Quarter ReviewerDRIFT KMGNo ratings yet
- Proximity Manufacturing For Enhancing Clothing Supply Chain SustainabilityDocument33 pagesProximity Manufacturing For Enhancing Clothing Supply Chain Sustainabilityarafat saleheenNo ratings yet
- Shinthia Ghosh - Roll No-20js031003 - Law & Justice in A Globalizing World - Paper Code-Plo4003 - ProjectDocument11 pagesShinthia Ghosh - Roll No-20js031003 - Law & Justice in A Globalizing World - Paper Code-Plo4003 - ProjectShinthia GhoshNo ratings yet
- Hobbs Et Al. 2017-Movers and Stayers - Novel Assemblages in Changing EnvironmentsDocument13 pagesHobbs Et Al. 2017-Movers and Stayers - Novel Assemblages in Changing EnvironmentsMiguel AlexiadesNo ratings yet
- Environmental Movements (Aecc-2, Unit 7) Bishnoi MovementDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Movements (Aecc-2, Unit 7) Bishnoi MovementSPN CDYNo ratings yet
- WWF Tanzania Vacancies AugustDocument24 pagesWWF Tanzania Vacancies AugustSaumu MbanoNo ratings yet
- Social Internshipp Final ReportDocument41 pagesSocial Internshipp Final ReportVansh NamdevNo ratings yet
- Philippine Mangrove Related PoliciesDocument1 pagePhilippine Mangrove Related PoliciesAndrea Anne TulabutNo ratings yet
- Buss1000 Full Notes High HD StudentDocument31 pagesBuss1000 Full Notes High HD Studentkarthik sNo ratings yet
- DRRR Quarter 1 - Module 2Document3 pagesDRRR Quarter 1 - Module 2Shelly Ryn Saligumba75% (4)
- English For Fisheries and Marine Science - Unit 2 MUHAMMAD NANDA FIRDAUS - 205070307111019Document7 pagesEnglish For Fisheries and Marine Science - Unit 2 MUHAMMAD NANDA FIRDAUS - 205070307111019Nanda FirdaNo ratings yet
- NSTP CWTS - CHAPTER 5 and 6Document33 pagesNSTP CWTS - CHAPTER 5 and 6Rezia Lustria0% (1)
- Keep Asia Green: Volume III "South Asia"Document221 pagesKeep Asia Green: Volume III "South Asia"Md Arshadul IslamNo ratings yet
- THE Sonoran Desert: InteractionsDocument1 pageTHE Sonoran Desert: InteractionsDreammyNo ratings yet
- NSTP-Environmental Awareness-CarreonDocument3 pagesNSTP-Environmental Awareness-CarreonShaine Michael CarreonNo ratings yet
- Walkathon-Concept, Routes EtcDocument12 pagesWalkathon-Concept, Routes EtcaaronNo ratings yet
- Land Use CompetitionDocument370 pagesLand Use CompetitionLINA FERNANDA SANCHEZ TAQUIBANo ratings yet
- Environmental Law CourseDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Law CourseMr BerreoNo ratings yet
- English Wingspan of BirdsDocument13 pagesEnglish Wingspan of BirdsAkanksha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Philippine Agenda 21Document7 pagesPhilippine Agenda 21Joel EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Trail Assessment - Lake MahagnaoDocument4 pagesRapid Trail Assessment - Lake MahagnaoJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Essay Comparing Two PeopleDocument5 pagesEssay Comparing Two Peoplehupkakaeg100% (2)