Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FMA Topic 9, 10
Uploaded by
YuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FMA Topic 9, 10
Uploaded by
YuCopyright:
Available Formats
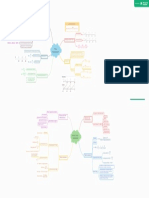
The r isk iness of t he fir m’s asset s if no debt is used
The m or e st able t he dem and for a fir m’s pr oduct s, ot h
er t hings held const ant, t he low er it s business r isk.
Sales
Fir m s w hose pr oduct s ar e sold in volat ile m
ar ket s ar e ex posed t o m or e business r isk t h
Capit al st r uct ur e (m ix of debt, pr efer r ed, and com m on e Bu sin ess r isk an fir m s w hose out put pr ices ar e st able.
quit y) at w hich P0 is m ax im ized+W ACC is m inim ized. Sales pr ice
opt im al capit al st r uct ur es consider o Fir m s w hose input cost s ar e uncer t ai
nly t he financial aspect s of a fir m. n have higher business r isk.
Opt im al capit al st ruct ure I nput cost
higher business r isk < = > pr obabilit y of financial dist r ess w oul
The fast er pr oduct s becom e out dat ed, t
d be gr eat er < = > opt im al capit al st r uct ur e has less debt.
he gr eat er a fir m’s business r isk.
Pr oduct
Operat ing leverage
The ex t ent t o w hich fixed cost s ar e used in a fir m’s operat ions.
a high operat ing leverage im plies t hat a sm all chang
Op t im a l ca p it a l st r u ct u r e Ca p i t a l St r u ct u r e Operat ing leverage e in sales r esult s in a lar ge change in ROI C.
an d t ar g et st r u ct u r e a n d Le v e r a g e Fir m has higher operat ing leverage < = > higher business r isk.
WACC
The addit ional r isk placed on t he com m on
Div idend Discount Model
st ock holder s as a r esult of using debt.
The m ix of debt, pr efer r ed st ock, and com m on equi
Com pany has m or e debt < = > m or e financial r isk.
t y w it h w hich t he fir m int ends t o raise capit al.
Tar get capit al st r uct ur e cont ain considerat ion Financial Risk
s of t he fir m, t he cust om er s, t he societ y, and Target capit al st ruct ure
t he gover nm ent r egulat ion
The ex t ent t o w hich fixed incom e secur it ies (d
ebt and pr efer r ed st ock) ar e used in a fir m’s c
Fi n a n c i a l Ri s k
apit al st r uct ur e.
Financial Leverage
I f t he level of debt incr ease, t he r isk iness of fir m i
ncr eases, r esult ing in a higher rat e of r et ur n.
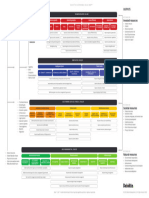
The decision t o pay out ear nings ver sus r et aining and r einvest ing t hem.
Devidend Policy
For ecast capit al needs over a planning hor izon, oft en 5 year s.
Pay out any left over ear nings as div idends if m or Set a t ar get capit al st r uct ur e.
e ear nings ar e available t han ar e needed suppor t
t he opt im al capit al budget. Est im at e annual equit y needs.
Set t ing Dividend Policy
Set t ar get payout based on t he r esidual m odel.
Maint ain t ar get gr ow t h rat e if possible, var y ing
capit al st r uct ur e som ew hat if necessar y.
Re s i d u a l D i v i d e n d M o d e l Div id en d p o licy I nvest or s do n’t car e about payout.
t h eor ies w ant cash = > sell st ock
I f Div idends < 0 = > Payout = 0% I nvest or s can cr eat e t heir ow n div idend policy
Dividend irrelevance t heory do n’t w ant cash = > use div idends t o buy st ock
Mor e good invest m ent s = > need m or e m oney t o r ein
vest = > a low er div idend payout. Unr ealist ic assum pt ions (n o t axes or br okerage cost s)
I nvest or s pr efer a high payout
Shar eholder s can aut om at ically r einvest t heir div iden I nvest or s t hink div idends ar e less r isk y t h
ds in shar es of t he com pan y’s com m on st ock. Bir d- in- t he- hand
an pot ent ial fut ur e capit al gains
Dollar s t o be r einvest ed ar e t ur ned over t o t r us High payout w ould r esult in a high P0
t ee, w ho buy s shar es on t he open m ar ket.
Open Mar ket Pur chase Plan Div iden d Dividend relevance t heory I nvest or s pr efer a low payout.
Fir m issues new st ock t o DRI P enr ollees (u sually Re i n v e s t m e n t Pl a n Tax pr efer ence Capit al gains ar e t axed at low er rat es t han div idends
at a discount fr om t he m ar ket pr ice), hence, t he
se plans raise new capit al for t he fir m.
New St ock Plan
D i v i d e n d Po l i cy High payout w ould r esult in a low P0
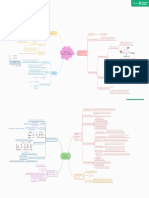
I nvest or s r egar d div idend changes as signals of m anagem en t’s ear nings for ecast s.
Buy ing ow n st ock back fr om st ock holder s
Manager s do not raise div idends unless t hey believe fut ur e ear ning
As an alt er nat ive t o dist r ibut ing cash as div idends s w ill be sust ain t he higher level div idends
St ock Repur chases
To dispose of one- t im e cash fr om an asset sale. Reasons for r epur chases Si g n a l i n g h y p o t h e s i s A div idend r educt ion is a signal t hat m anagem ent for ecast
s poor fut ur e ear nings.
To m ake a lar ge capit al st r uct ur e change
Manager s should consider signaling effect s w hen t hey set div idend policy.
Fir m issues new shar es inst ead of pay ing a cash div idend
I ncr ease t he num ber of out st anding shar es, P0 decr ease
St ock div idends Differ ent gr oups of invest or s, or client eles, pr efer differ ent div idend policies.
I f 10%, get 10 shar es for each 100 shar es ow ned
Fir m’s past div idend policy det er m ines it s cur r ent client ele of invest or s.
t he sam e as a st ock div idend except for rat io ex pr ess
Alt er n at iv e div iden ds Cl i e n t e l e e f f e c t
A change in div idend policy m ight upset t he m aj or it y clie
a 2 for 1 st ock split = 100% st ock div idend nt ele and have a negat ive effect on t he st oc k’s pr ice.
Ther e’s a w idespr ead belief t hat t he opt im al pr ice r St ock split s
ange for st ock s is $2 0 t o $8 0. St ock split s can be u
sed t o keep t he pr ice in t his opt im al range.
Fact or s Affect ing Div idend policy
You might also like
- General Supply Company Profile Sample PDFDocument3 pagesGeneral Supply Company Profile Sample PDFMohzin Km72% (25)
- Format Draft LC Cif 100% (Dec'12)Document3 pagesFormat Draft LC Cif 100% (Dec'12)rudiawan80% (5)
- Sushma Industries: The Gordian Knot of Compensation DesignDocument9 pagesSushma Industries: The Gordian Knot of Compensation DesignAVNo ratings yet
- 980F Loader (5XJ588 Up)Document2 pages980F Loader (5XJ588 Up)NovakurniawanNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Principles of Managerial Finance 6th Australia by Gitman PDFDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Principles of Managerial Finance 6th Australia by Gitman PDFrosalie.ashworth789100% (40)
- SCOTT M Carney PDFDocument288 pagesSCOTT M Carney PDFfosezzle92% (25)
- SAP New GL #9 Customise Cross Company Code Postings For Document SplittingDocument11 pagesSAP New GL #9 Customise Cross Company Code Postings For Document SplittingAlan Cheng100% (2)
- Case Study 2 Part 1: The StoryDocument5 pagesCase Study 2 Part 1: The StoryMary Jane InsigneNo ratings yet
- Starting Dut Mobile: His Business Quickly Made ADocument2 pagesStarting Dut Mobile: His Business Quickly Made AEmrehan GökçayNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Part 1: The StoryDocument5 pagesCase Study 1 Part 1: The StoryMary Jane InsigneNo ratings yet
- Jthomas 2010Document408 pagesJthomas 2010Frankie MurdockNo ratings yet
- Mts PamphletDocument4 pagesMts Pamphletilhamina.athirahNo ratings yet
- Osmo JD International BusinessDocument1 pageOsmo JD International BusinessSaviNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument7 pagesMarketing ManagementNaturallyNo ratings yet
- 2-3 December 2009, LondonDocument4 pages2-3 December 2009, LondonArk GroupNo ratings yet
- C BDM ME Week 1 Tutor PresentationDocument11 pagesC BDM ME Week 1 Tutor PresentationAnoofa AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1) Build-A-BearDocument1 page1) Build-A-BearVlad SteliutaNo ratings yet
- Fisher Light Load - Catalogue - en - 01Document24 pagesFisher Light Load - Catalogue - en - 01Gibson leeNo ratings yet
- Regulated Commodity Market in India 1Document7 pagesRegulated Commodity Market in India 1Tanisha DoshiNo ratings yet
- Simple Resume For JobsDocument1 pageSimple Resume For JobsDionNo ratings yet
- d14 1 HistDocument2 pagesd14 1 Histwilliamlord8No ratings yet
- Behavior Life CycleDocument1 pageBehavior Life CycleSubash VenkataNo ratings yet
- Salesforce Sales Playbook - Adam GilberdDocument24 pagesSalesforce Sales Playbook - Adam GilberdRafa EgeaNo ratings yet
- International Busiess Unit 2-3Document3 pagesInternational Busiess Unit 2-3DaisylaziieeNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument4 pagesResearch ProposalSandesh SawaleNo ratings yet
- ArchiMate 3.1 PosterDocument1 pageArchiMate 3.1 PosterTom KakanowskiNo ratings yet
- LawsoftheStateofMaineVolumes1and2 10967060Document509 pagesLawsoftheStateofMaineVolumes1and2 10967060jurebieNo ratings yet
- A Nine-Digit Number That Is Assigned by The IRS and Used To Identify Taxpayers in A Business EntityDocument2 pagesA Nine-Digit Number That Is Assigned by The IRS and Used To Identify Taxpayers in A Business Entitynadjibbou25No ratings yet
- d03 Chicoenterpriserecord PDFDocument1 paged03 Chicoenterpriserecord PDFDavid LittleNo ratings yet
- FMA Topic 5,6Document2 pagesFMA Topic 5,6YuNo ratings yet
- Offshore Procurement ModelsDocument12 pagesOffshore Procurement ModelsSuhail KhanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Tasneem Akhter Lecture # 2 Market Forces Demand & SupplyDocument16 pagesDr. Tasneem Akhter Lecture # 2 Market Forces Demand & SupplyprofNo ratings yet
- Capital Output Ratioits Uses and AbusesDocument4 pagesCapital Output Ratioits Uses and AbusesTeresa LagundayaoNo ratings yet
- TFB Enterprise Chapter20Document8 pagesTFB Enterprise Chapter20NoreenNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning: MODULE 14: Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Product Data Management (PDM)Document4 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning: MODULE 14: Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Product Data Management (PDM)PradeeP VNo ratings yet
- ZAP BI For AXDocument4 pagesZAP BI For AXShivshankar IyerNo ratings yet
- Us Sustainable Value MapDocument1 pageUs Sustainable Value Mapfethi aslanNo ratings yet
- Img 20220103 0005Document1 pageImg 20220103 0005SciencemanNo ratings yet
- Simple Blue Resume-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageSimple Blue Resume-WPS Officeahmed nabilNo ratings yet
- Hotelogix PmsDocument2 pagesHotelogix PmsSandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- # (Article) How To Improve The Global S&OP Process - Hollister's Journey (2012)Document8 pages# (Article) How To Improve The Global S&OP Process - Hollister's Journey (2012)AbusamraMousaNo ratings yet
- Douglass High-Resume and Portfolio-SMLDocument9 pagesDouglass High-Resume and Portfolio-SMLDouglass HighNo ratings yet
- Douglass High-Resume and PortfolioDocument9 pagesDouglass High-Resume and PortfolioDouglass HighNo ratings yet
- Pmitr Mart 2018 Web 1Document72 pagesPmitr Mart 2018 Web 1Gokhan CaliNo ratings yet
- In Notte Placida: F.CouperinDocument1 pageIn Notte Placida: F.CouperinAntonio OrganNo ratings yet
- Iqra Iqbal My Fashion BrandDocument1 pageIqra Iqbal My Fashion BrandiqraNo ratings yet
- 18aabfd8 10Document138 pages18aabfd8 10Jon Mckenzie GoNo ratings yet
- Logistics-Discussion-Questions (1) - 1Document1 pageLogistics-Discussion-Questions (1) - 1Lidia GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Goldman Profit Slides 43% As Bank Details Big Shake-Up: For Personal, Non-Commercial Use OnlyDocument32 pagesGoldman Profit Slides 43% As Bank Details Big Shake-Up: For Personal, Non-Commercial Use OnlyRazvan Catalin CostinNo ratings yet
- SCM Cha17Document30 pagesSCM Cha17WEYKANo ratings yet
- Demmans Product Catalogue 2017Document16 pagesDemmans Product Catalogue 2017Muhammed MekkiNo ratings yet
- Express 021908Document8 pagesExpress 021908aptureincNo ratings yet
- 44040.raheel 20tariq - LiteraturereviewDocument3 pages44040.raheel 20tariq - LiteraturereviewDaim AliNo ratings yet
- Canara Robeco Multi Cap Fund NFO LeafletDocument8 pagesCanara Robeco Multi Cap Fund NFO LeafletMohan AsokanNo ratings yet
- Gartner - We Shape AI, AI Shapes UsDocument19 pagesGartner - We Shape AI, AI Shapes UstamlqNo ratings yet
- Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesMotivation LettermuhammadTz0% (1)
- E-Mai L:: Daspr I Yar Anj An111@gmai L - ComDocument5 pagesE-Mai L:: Daspr I Yar Anj An111@gmai L - Compraveen nairNo ratings yet
- December Remtt.Document1 pageDecember Remtt.KIMBERLY BALISACANNo ratings yet
- Yardi Commercial SuiteDocument52 pagesYardi Commercial SuiteSpicyNo ratings yet
- Solución Capitulo 3Document75 pagesSolución Capitulo 3ArnoldoGonzalezNo ratings yet
- 2017 - T1 HaierDocument45 pages2017 - T1 HaierONYNo ratings yet
- Ebrochure MICA DM B9Document8 pagesEbrochure MICA DM B9Inevitable CowboyNo ratings yet
- FMA Topic 7,8Document2 pagesFMA Topic 7,8YuNo ratings yet
- FMA Topic 5,6Document2 pagesFMA Topic 5,6YuNo ratings yet
- FMA Topic 1,2Document2 pagesFMA Topic 1,2YuNo ratings yet
- FMA Topic 3,4Document2 pagesFMA Topic 3,4YuNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates - List of Foreign Currency Rates TodayDocument2 pagesExchange Rates - List of Foreign Currency Rates TodayHasan Bin AliNo ratings yet
- Operation Managemen T Assignment-II: Submitted By: Sakshi Sachdeva ROLL NO. - BM-019143 Sec-C, PGDM 1 YearDocument6 pagesOperation Managemen T Assignment-II: Submitted By: Sakshi Sachdeva ROLL NO. - BM-019143 Sec-C, PGDM 1 YearrohanNo ratings yet
- Poa T - 3Document2 pagesPoa T - 3SHEVENA A/P VIJIANNo ratings yet
- SQ00001544 SICIM RFQ SA010-MR-005 REV.A MANUAL BALL VALVES - UnpricedDocument4 pagesSQ00001544 SICIM RFQ SA010-MR-005 REV.A MANUAL BALL VALVES - UnpricedMohamed Wasim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Management AssignmentDocument3 pagesManagement Assignmentgolu tripathiNo ratings yet
- MAC (Misdirected Directive Case Analysis)Document3 pagesMAC (Misdirected Directive Case Analysis)Prasad GowdNo ratings yet
- Balcanica: Institute For Balkan StudiesDocument17 pagesBalcanica: Institute For Balkan StudiesGajevic SlavenNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces Model AnalysisDocument2 pagesPorter's Five Forces Model AnalysisLika OragvelidzeNo ratings yet
- DOCSDocument10 pagesDOCSSWATINo ratings yet
- Review ch.6Document15 pagesReview ch.6LâmViên100% (9)
- Repayment Schedule 12-21-23Document1 pageRepayment Schedule 12-21-23Akash MajhiNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Macroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Solutions Manual PDFDocument13 pagesDwnload Full Macroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Solutions Manual PDFprunellamarsingillus100% (10)
- Unilever in India: Hindustan Lever S Project Shakti - Marketing FMCG To The Ruralconsumer Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnilever in India: Hindustan Lever S Project Shakti - Marketing FMCG To The Ruralconsumer Case Analysismahtaabk100% (4)
- BMGT 26 International Trade and AgreementsDocument10 pagesBMGT 26 International Trade and AgreementsJULIUS CAESAR MANABATNo ratings yet
- Samsung The Frame Bezel 2021 TV (50 Inch) : Grand Total 8974.00Document1 pageSamsung The Frame Bezel 2021 TV (50 Inch) : Grand Total 8974.00Anil ChanduriNo ratings yet
- Methodology StatementDocument3 pagesMethodology StatementMichael Tauna KekeiNo ratings yet
- LH - 05 - CAC - Process CostingDocument27 pagesLH - 05 - CAC - Process CostingRaven Claire ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Ground FloorDocument1 pageGround FloorAyad GamalNo ratings yet
- TresGo Ratecard 2021 - D (New)Document7 pagesTresGo Ratecard 2021 - D (New)zseyo1No ratings yet
- Packaging Market in Poland: Economic Information Department Polish Information and Foreign Investment AgencyDocument6 pagesPackaging Market in Poland: Economic Information Department Polish Information and Foreign Investment AgencyMera SamirNo ratings yet
- Understanding Canadian Business Canadian 8th Edition Nickels Test BankDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Canadian Business Canadian 8th Edition Nickels Test BankIsabellaNealaiys100% (40)
- Credit PolicyDocument9 pagesCredit PolicyVikash Jain100% (1)
- Budget Operation Agm-Mje 1 Fleet 2 BargeDocument6 pagesBudget Operation Agm-Mje 1 Fleet 2 BargeAchmad DjunaidiNo ratings yet
- DK Automation ComplaintDocument48 pagesDK Automation ComplaintDhruv PandeyNo ratings yet
- Rexa Uni CatalogDocument18 pagesRexa Uni CatalogLupu AlinNo ratings yet
- IELTS 6 - 06 - 08 - Đã CH ADocument7 pagesIELTS 6 - 06 - 08 - Đã CH ANguyên Phạm ThuNo ratings yet