Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Church's Principles on Labor and Capital
Uploaded by
jelly beanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Church's Principles on Labor and Capital
Uploaded by
jelly beanCopyright:
Available Formats
REED NOTES “The Church’s principle on the priority of labor over
capital directly concerns the process of production.” (LE
(Chapter 3) 12)
““The conflict originated in the fact that the workers put
their powers at the disposal of the entrepreneurs, and
these, following the principle of maximum profit, tried What are the causes of Production?
to establish the lowest possible wages for the work Material Cause
done by the employees.” (LE 11)
- a thing exists because it is caused by the
materials it was made from
“This conflict, interpreted by some as a socio-economic Efficient Cause
class conflict, found expression in the ideological
conflict between liberalism, understood as the ideology - a thing exists because it is caused by the person
of capitalism, and Marxism, understood as the ideology who desired to make it
of scientific socialism and communism.” (LE 11) Formal Cause
- a thing exists because it is caused by the fact
Marxism that is looks and acts like it’s supposed to
- is conflict theory, it states that society is in Final Cause
conflict with each other. That the conflict is - a thing exists because it is caused by the need
between the rich and the poor. for it, thus it fulfils its purpose as a [thing]
- is a political and economic philosophy
- equal society
- for Marxism, Capitalism is the private
“Labour is always a primary efficient cause while
ownership of the means of production, that our
capital, the whole collection of means of production,
society is run by people who own factories and
remains a mere instrument or instrumental cause.” (LE
business corporations
12)
“The real conflict between labor and capital was
“Capacity for work, that is to say, for sharing efficiently
transformed into a systematic class struggle, conducted
in the modern production process-demands greater and
not only by ideological means but also and chiefly by
greater preparation and, before all else, proper
political means.” (LE 11)
training.” (LE 12)
“The Marxist programme, based on the philosophy of
“Capital cannot be separated from labor; in no way can
Marx and Engels, sees in class struggle the only way to
labor be opposed to capital or capital to labor, and still
eliminate class injustices in society and to eliminate the
less can the actual people behind these concepts be
classes themselves.” (LE 11)
opposed to each other.” (LE 13)
“The structure of the present-day situation is deeply
Working at any workbench, whether a relatively
marked by many conflicts caused by humanity, and the
primitive or an ultramodern one, a human being can
technological means produced by human work play a
easily see through her/his work she/he enters into two
primary role in it.” (LE 12)
inheritances:
1. The inheritance of what is given to the whole What are the kinds of Materialism?
humanity in the resources of nature
Good Materialism
2. The inheritance of what others have already
Bad Materialism
developed on the basis of those resources,
primarily by developing technology, i.e., by
producing a whole collection of increasingly
An example on these errors where labourers are
perfect instruments for work. (LE 13)
exploited:
Hacienda Luisita
“In working, human beings also enter into the labor of
others.”
We have the right to own property because all
“It is a consistent image, one that is humanistic as well
created goods by God is for us.
as theological.”
The right to private property is subordinated to
the right of common use.
In it human being is the master of the creatures placed
Property is acquired through work to serve
at her/his disposal in the visible world. If some
labor.
dependence is discovered in the work process, it is
dependence on the GIVER of all the resources of By serving labour, they should make possible
creation, and also on other human beings, those to the achievement of the first principle of this
whose work and initiative we owe the perfected and order, namely:
increased possibilities of our own work.
a. the universal destination of goods and;
b. the right to common use of them
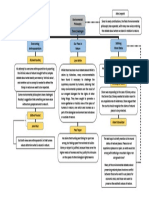
However, this consistent image was broken up in
Capitalism denies the people to own properties.
human thought.
Socialization of certain means of production
The break occurred in such a way that labor was
cannot be excluded.
separated from capital and set in opposition to it, and
capital was set in opposition to labor as though they The Church favors a joint-ownership of means
were two impersonal forces, two production factors of production.
juxtaposed in the same “economistic” perspective.
What is the Personalist argument?
“Error of Economism” – considering human labor solely
The person who works desires not only due
according to its economic purpose.
remuneration for her/his work; she/he also wishes that,
within the production process, provision be made for
her/him to be able to know that in her/his work, even
“Error of Materialism” – when Economism directly or
something that is owned in common, she/he is working
indirectly includes a conviction of the primacy and
“for herself/himself.”
superiority of the material, and directly or indirectly
places the spiritual and the personal (man’s activity,
moral values and such matters) in a position of
The Church’s teaching has always expressed the strong
subordination to material reality.
and deep conviction that humanity’s work concerns not
only the economy but also, and especially, personal
values. 12. What is acquired first of all through work in
order that it may serve work?
Guide Questions for Chapter Three of
Laborem Exercens 13. What is Joint Ownership?
- A situation in which two or more persons co-
own a property.
1. Who is Karl Marx 14. What are the two inheritances where Human
beings can easily see through their work?
2. What is Marxism?
15. What are the principles achieved when property
3. What is Liberalism? is acquired through work that it may serve
- is a political and moral philosophy based on work?
liberty and equality
16. What are the two ideologies which express the
4. What is Communism? conflict between labor and capital?
- all property is publicly owned and each person
works and is paid according to their abilities and 17. What are the consistent images in the sphere
needs. and process of labor?
5. What is Class Struggle? 18. What is the meaning of the phrase “man enters
into the labor of others”?
6. What is Conflict Theory?
19. What is the relevance of the consistent images
7. What is the difference between the Proletariat of human beings in the sphere and process of
and the Bourgeoisie? humanity’s labor?
- the proletariat is the working class, including
farmers and low-skilled factory workers. They 20. What is the “Personalist” Argument?
do not own any means of production. The
bourgeoisie are the capitalist class, the
wealthy, who own most of the means of
production.
8. What are the different alienation of laborers?
- Alienation of the worker from their product
- Alienation of the worker from the act of
production
- Alienation of the worker from their
Gattungswesen (species-essence)
- Alienation of the worker from other workers
9. What is the difference between the error of
Economism and the error of Materialism?
10. What is the difference between Good
Materialism and Bad Materialism?
11. What are the causes of production according to
Aristotle?
You might also like
- Allergen Sensitization: Primary MediatorsDocument14 pagesAllergen Sensitization: Primary Mediatorsjelly bean100% (1)
- Case Study - Nike: NIKE, Inc. - Beaverton, OregonDocument16 pagesCase Study - Nike: NIKE, Inc. - Beaverton, OregonAlejandro Martinez100% (1)
- Re Envisioning SocialismDocument8 pagesRe Envisioning Socialismapi-3740264No ratings yet
- Trading Options Income: Strangle vs Double Ratio SpreadDocument1 pageTrading Options Income: Strangle vs Double Ratio Spreadsergiob63No ratings yet
- SAP Analytics Cloud for Planning Use Cases ExplainedDocument23 pagesSAP Analytics Cloud for Planning Use Cases ExplainedGasserNo ratings yet
- Resolution of The Board of Directors ofDocument2 pagesResolution of The Board of Directors ofEdy GunawanNo ratings yet
- Paolo Virno-General IntellectDocument4 pagesPaolo Virno-General Intellectmario22h0% (1)
- Historical MaterialismDocument23 pagesHistorical MaterialismJade Connoly67% (3)
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument41 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsSheilaMarieAnnMagcalasNo ratings yet
- SBLC DOA - ANGCC - SignedDocument9 pagesSBLC DOA - ANGCC - SignedfranviNo ratings yet
- Financial Crisis Prevention MeasuresDocument3 pagesFinancial Crisis Prevention MeasuresFergus Gerodias100% (4)
- Property in General - CasesDocument18 pagesProperty in General - CasesEm AlayzaNo ratings yet
- Pier Vittorio Aureli. Labor and Architecture. Log 23 2011Document23 pagesPier Vittorio Aureli. Labor and Architecture. Log 23 2011yo_iso100% (1)
- Branded Jewellery Consumer SurveyDocument3 pagesBranded Jewellery Consumer SurveyPratima Nair70% (10)
- How labor has shaped architecture and urbanismDocument27 pagesHow labor has shaped architecture and urbanismSabin-Andrei ŢeneaNo ratings yet
- Week 8-9 LectureDocument26 pagesWeek 8-9 LectureJERRY YuanNo ratings yet
- Art, Activism and RecuperationDocument57 pagesArt, Activism and RecuperationPatricia ColleyNo ratings yet
- 2 Priority of Labor Over CapitalDocument37 pages2 Priority of Labor Over CapitalKhaela MercaderNo ratings yet
- A Sharing On Karl Marx's Social Theory and The Theory of AlienationDocument2 pagesA Sharing On Karl Marx's Social Theory and The Theory of AlienationRenante AvergonzadoNo ratings yet
- CH 13 HakimDocument13 pagesCH 13 Hakimapi-26547187No ratings yet
- On The "Creative Commons": A Critique of The Commons Without CommonaltyDocument4 pagesOn The "Creative Commons": A Critique of The Commons Without CommonaltydavidmemeNo ratings yet
- Immaterial Civil WarDocument9 pagesImmaterial Civil WarcotofomiNo ratings yet
- NussHeller IPR IPL Linux 1998Document8 pagesNussHeller IPR IPL Linux 1998Kopija KopijaNo ratings yet
- Human Development and Socialist AccountingDocument9 pagesHuman Development and Socialist AccountingmlebowitNo ratings yet
- Ghosh Ba Honours Economics Delhi University / by Naresh Sehdev 85270 18189 9971548875Document6 pagesGhosh Ba Honours Economics Delhi University / by Naresh Sehdev 85270 18189 9971548875Naresh SehdevNo ratings yet
- 143-Article Text-390-1-10-20220521Document7 pages143-Article Text-390-1-10-20220521kimtinh18012005No ratings yet
- Tor EngelsDocument8 pagesTor EngelsAvneesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Reification (Marxism)Document6 pagesReification (Marxism)Paul Miers100% (1)
- Critique of Hegel'S Philosophy of Right, IntroductionDocument18 pagesCritique of Hegel'S Philosophy of Right, IntroductionVamsi VirajNo ratings yet
- Oxford Handbook AlienationDocument18 pagesOxford Handbook AlienationRoberto della SantaNo ratings yet
- Distributive JusticeDocument26 pagesDistributive JusticeVenlyn GassilNo ratings yet
- 2002 Schwarzen BachDocument13 pages2002 Schwarzen BachlecaracalNo ratings yet
- Capitalism: Nicolò BellancaDocument10 pagesCapitalism: Nicolò BellancaAdftNo ratings yet
- Globalization and Race for Resources ReviewedDocument3 pagesGlobalization and Race for Resources ReviewedResistBookNo ratings yet
- Human dignity and labor: An analysis of philosophical principlesDocument30 pagesHuman dignity and labor: An analysis of philosophical principlesShena Fernandez BeruelaNo ratings yet
- Justifying Ipr Module 2Document62 pagesJustifying Ipr Module 2vishwas125No ratings yet
- Labor Theory of PropertyDocument5 pagesLabor Theory of PropertyThomas CrosNo ratings yet
- Theory of AlienationDocument8 pagesTheory of AlienationZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Marx - Structure and Contradiction in CapitalDocument35 pagesMarx - Structure and Contradiction in Capitalktlau127100% (1)
- A Tabular Presentaion On Economic HistoryDocument6 pagesA Tabular Presentaion On Economic Historyancaye1962No ratings yet
- Major Social Theories in 40 CharactersDocument32 pagesMajor Social Theories in 40 CharactersFrancis Kate SaguiguitNo ratings yet
- entrep unit 1 reviewerDocument4 pagesentrep unit 1 reviewerermitaalexagwynethNo ratings yet
- The Revolt of The Salaried BourgeoisieDocument4 pagesThe Revolt of The Salaried BourgeoisieKostasBaliotisNo ratings yet
- Marcuse Conference 2011 Rev10Document36 pagesMarcuse Conference 2011 Rev10Charles ReitzNo ratings yet
- A4 Art2-Miller by Alex-Material Culture and Mass ConsumptionDocument12 pagesA4 Art2-Miller by Alex-Material Culture and Mass ConsumptionAnne Carolina dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentTannNo ratings yet
- CRIM 108 Lesson 1Document3 pagesCRIM 108 Lesson 1PRINCES ALLEN MATULACNo ratings yet
- Marxist Theory in Community DevelopmentDocument7 pagesMarxist Theory in Community DevelopmentCloud Lucis Knox100% (1)
- Capitalism: February 2013Document11 pagesCapitalism: February 2013Supriya KhajuriaNo ratings yet
- Laborem ExercensDocument4 pagesLaborem ExercensAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Man, Property, and TechnologyDocument7 pagesMan, Property, and TechnologyEgrolf YsNo ratings yet
- Modernity and the Challenge of Neo-TechnicsDocument7 pagesModernity and the Challenge of Neo-TechnicsJose RafaelNo ratings yet
- Joseph Dietzgen, Review of Marx's Capital, Vol. 1 (1868)Document2 pagesJoseph Dietzgen, Review of Marx's Capital, Vol. 1 (1868)danielgaidNo ratings yet
- Paper RTnNE2aDDocument12 pagesPaper RTnNE2aDRaul MercauNo ratings yet
- Pasquinelli Immaterial Civil WarDocument13 pagesPasquinelli Immaterial Civil WarΑλέξανδρος ΓεωργίουNo ratings yet
- To Bit or Not To BitDocument16 pagesTo Bit or Not To BitJenny WallaceNo ratings yet
- Buso MidtermDocument4 pagesBuso MidtermVi NguyenNo ratings yet
- IdeologyDocument19 pagesIdeologychankarunaNo ratings yet
- The Human Person Flourishing in Terms of Science & TechnologyDocument2 pagesThe Human Person Flourishing in Terms of Science & TechnologyEunjina MoNo ratings yet
- Labour vs Capital ConflictDocument8 pagesLabour vs Capital ConflictNneka LaurenteNo ratings yet
- BusnEthics Mandatory Readings1Document10 pagesBusnEthics Mandatory Readings1Brian GinesNo ratings yet
- Diss Week 5Document30 pagesDiss Week 5j70048116No ratings yet
- Exploitation, Labor, and Basic Income: Michael W. HowardDocument12 pagesExploitation, Labor, and Basic Income: Michael W. HowardtobaramosNo ratings yet
- MarxDocument20 pagesMarxiwizszsNo ratings yet
- Labor Philosophy PDFDocument9 pagesLabor Philosophy PDFArjan JoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Intellectual Property: Is It Worth The Effort?: Guest EditorialDocument1 pageTheories of Intellectual Property: Is It Worth The Effort?: Guest EditorialKirtivaan mishraNo ratings yet
- 23 Reviewer DissDocument2 pages23 Reviewer DissTine DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- AlienationDocument4 pagesAlienationNaren TigoteNo ratings yet
- Entrep Lesson 6Document1 pageEntrep Lesson 6jelly beanNo ratings yet
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Reviewerjelly beanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Product Innovation Why Newness Raises Prices and Makes Your Product ViralDocument14 pagesLesson 7 - Product Innovation Why Newness Raises Prices and Makes Your Product Viraljelly beanNo ratings yet
- EnPhi MAP NarrativeDocument1 pageEnPhi MAP Narrativejelly beanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Developing A 7 Figure BrandDocument16 pagesLesson 1 - Developing A 7 Figure Brandjelly beanNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C InfographicDocument1 pageHepatitis C Infographicjelly beanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gerontology Why Should You Be Interested in Gerontology?Document5 pagesIntroduction To Gerontology Why Should You Be Interested in Gerontology?jelly beanNo ratings yet
- Gerontology Study GuideDocument4 pagesGerontology Study Guidejelly beanNo ratings yet
- Nonstochastic& NursingTheoriesofAgingDocument44 pagesNonstochastic& NursingTheoriesofAgingjelly beanNo ratings yet
- Test Your Knowledge. True or FalseDocument11 pagesTest Your Knowledge. True or Falsejelly beanNo ratings yet
- Module 9 10 Suctioning Tracheostomy CareDocument13 pagesModule 9 10 Suctioning Tracheostomy Carejelly beanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance and BurnsDocument9 pagesAcid-Base Balance and Burnsjelly beanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Clients with STDs/STIs/HIV/AIDSDocument16 pagesNursing Care for Clients with STDs/STIs/HIV/AIDSjelly beanNo ratings yet
- DMS-IIT Delhi Compendium 2019-21Document55 pagesDMS-IIT Delhi Compendium 2019-21Sounak Chatterjee100% (1)
- Forex Money ManagementDocument2 pagesForex Money ManagementДаваасамбуу ЧадраабалNo ratings yet
- Cfas Chapter 10Document16 pagesCfas Chapter 10Str PNo ratings yet
- AGK Buddhism EssayDocument7 pagesAGK Buddhism EssayAaron KingNo ratings yet
- Importance of Microeconomics - Microeconomics - Microeconomics PDFDocument6 pagesImportance of Microeconomics - Microeconomics - Microeconomics PDFShikhar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tell Me Why Co. Is Expected To Maintain A Constant...Document2 pagesTell Me Why Co. Is Expected To Maintain A Constant...awaisNo ratings yet
- Handouts 04.04 - Part 3Document3 pagesHandouts 04.04 - Part 3John Ray RonaNo ratings yet
- From Seers to Sen: The Evolution of Economic DevelopmentDocument22 pagesFrom Seers to Sen: The Evolution of Economic DevelopmentBusola Esther DunmadeNo ratings yet
- PepsodentDocument106 pagesPepsodentBoopathi KalaiNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Use and Management of Natural Resources: EEA Report No 9/2005Document72 pagesSustainable Use and Management of Natural Resources: EEA Report No 9/2005Vethavarnaa SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- FM & Eco Marathon 2019: Ca Rahul Garg'SDocument50 pagesFM & Eco Marathon 2019: Ca Rahul Garg'Sajay palkarNo ratings yet
- Berger Paints Bangladesh Limited Statement of Financial PositionDocument8 pagesBerger Paints Bangladesh Limited Statement of Financial PositionrrashadattNo ratings yet
- General Provident Fund RulesDocument65 pagesGeneral Provident Fund RulesAhmed FawadNo ratings yet
- Apllied Econ Wk1 - 2 Summative TestDocument2 pagesApllied Econ Wk1 - 2 Summative TestJay SyNo ratings yet
- AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION PROPERTY TAX BILLDocument1 pageAHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION PROPERTY TAX BILLEng SvshahNo ratings yet
- Mankiw Chapter 4 (19) : The Monetary System, What It Is and How It WorksDocument39 pagesMankiw Chapter 4 (19) : The Monetary System, What It Is and How It WorksGuzmán Gil IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Industrialized Building System (IBS)Document17 pagesCase Study in Industrialized Building System (IBS)Mohamed A. SattiNo ratings yet
- Pitch Deck: Mirjam NilssonDocument21 pagesPitch Deck: Mirjam NilssonHIRAWATI BINTI ABDUL RAHMAN (IPGM-SARAWAK)No ratings yet
- Singapore City Skyline at Night PowerPoint Template #54219Document20 pagesSingapore City Skyline at Night PowerPoint Template #54219Faaz ZubairNo ratings yet
- Major Challages of Organization CompleteDocument11 pagesMajor Challages of Organization Completekhawar hafeezNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Human Resource Planning: Prepared By:-Akanksha Kumari 117503Document17 pagesStrategies and Human Resource Planning: Prepared By:-Akanksha Kumari 117503geetukumariNo ratings yet
- Merger Timing and Performance AnalysisDocument43 pagesMerger Timing and Performance AnalysisAileenJessicaNo ratings yet