100% found this document useful (2 votes)
501 views6 pagesConnective Tissue Notes
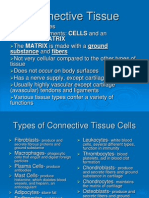
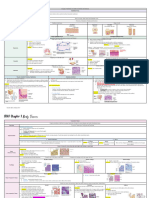
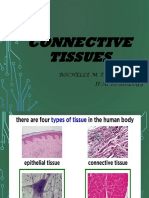
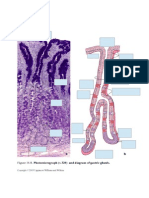
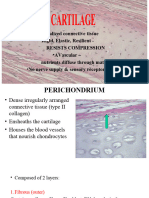
Connective tissue is the most diverse and abundant tissue in the body. It connects and supports other tissues. Connective tissue is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix of protein fibers and ground substance. The main cell types are fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, mast cells, and stem cells. Connective tissue is divided into connective tissue proper, blood, cartilage, and bone. Connective tissue proper includes loose connective tissue such as areolar and adipose tissue, as well as dense irregular connective tissue.
Uploaded by
ferdinand padillaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
501 views6 pagesConnective Tissue Notes
Connective tissue is the most diverse and abundant tissue in the body. It connects and supports other tissues. Connective tissue is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix of protein fibers and ground substance. The main cell types are fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, mast cells, and stem cells. Connective tissue is divided into connective tissue proper, blood, cartilage, and bone. Connective tissue proper includes loose connective tissue such as areolar and adipose tissue, as well as dense irregular connective tissue.
Uploaded by
ferdinand padillaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd