Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1 Question
Uploaded by
Ievana InsyirahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1 Question
Uploaded by
Ievana InsyirahCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY 098
SERWAY VUILLE, COLLEGE PHYSICS, 11TH EDITION
2021/2022
Tutorial 1
Chapter 15.1 – 15.2
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. Conductors are materials in which charges move _______ in response to an electric field while
__________ are materials in which electric charges do not move freely.
A. do not move freely, insulators.
B. freely, semiconductors.
C. freely, insulators.
D. do not move freely, semiconductors.
2. ________________ state that the magnitude of the electric force F between charges q1 and q2
separated by a distance r is given by
𝑘𝑒 |𝑞 1||𝑞 2 |
𝐹=
𝑟2
where 𝑘𝑒 is a constant called the Coulomb constant.
A. Coulomb’s Law
B. Franklin’s Law
C. Millikan’s Law
D. Newton’s Law
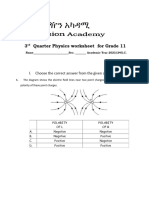
3. Choose the CORRECT properties of electric charge.
i) Like charges attract one another and unlike charges repel one another.
ii) Electric charge is always conserved in which, charge is not created nor can be destroyed and
object becomes charged because negative charge is transferred from one object to the other.
iii) Charge is quantized; it occurs in discreet with magnitude of 1.60x10 -19 C.
A. i and iii
B. i and ii
C. i, ii and iii
D. ii and iii.
4. A suspended object A is attracted to a neutral wall. It’s also attracted to a positively charged object B.
Which of the following is true about object A?
A. It is uncharged.
B. It has a negative charge.
C. It has a positive charge.
D. It may be either charged or uncharged.
5. Object A has a charge of +2𝜇𝐶, and object B has a charge of +6𝜇𝐶. Which statement is true?
A. 𝐹⃑𝐴𝐵 = −3𝐹⃑𝐵𝐴
B. 𝐹⃑𝐴𝐵 = −𝐹⃑𝐵𝐴
C. 3𝐹⃑𝐴𝐵 = −𝐹⃑𝐵𝐴
D. 𝐹⃑𝐵𝐴 = −2𝐹
⃑⃑⃑⃑⃑⃑𝐴𝐵
6. Some electrons leave the grounded sphere metal through the ground wire. This is one of the steps
charging an object by _____________.
A. conduction
B. polarization
C. induction
D. production
PHY098 Sem II 2021/2022
1 Prepared by Nor Faridah Hanim Mat Junit, Noor Arda Adrina Daud, Norjuliyati Hamzah, Mas Fiza Mustafa,
PHY 098
SERWAY VUILLE, COLLEGE PHYSICS, 11TH EDITION
2021/2022
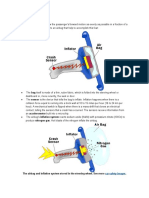
7. Figure 1 shows an effect known as polarization. Choose a reason of why the charges on the wall are
just realigning their position instead of transferring to the balloon.
A. This is charging by conduction in insulators where charges do not move freely.
B. This is charging by induction in insulators where charges do not move freely.
C. This is charging by conduction in insulators where charges move freely.
D. This is charging by induction in insulators where charges move freely.
Figure 1
Structured Questions
1. A small sphere of mass m = 7.50 g and charge q1 = 32.0 nC is attached to the end of a string and
hangs vertically as in Figure 2. A second charge of equal mass and charge q2 = -58.0 nC is located
below the first charge a distance d = 2.00 cm below the first charge as in Figure 2.
Figure 2
(a) Find the tension in the string.
Answer: 0.115 N
(b) If the string can withstand a maximum tension of 0.180 N, what is the smallest value d can have
before the string breaks?
Answer: 1.25 cm
2. A charged particle A exerts a force of 2.62 N to the right on charged particle B when the particles are
13.7 mm apart. Particle B moves straight away from A to make the distance between them 17.7 mm.
What vector force does particle B then exert on A?
Answer: 1.57 N directed to the left
3. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the Coulomb force on each of the three charges shown in
Figure 3.
Figure 3
Answer: F 6µC =46.7N to the left, F 1.5µC =157N to the right, F -2µC=111N to the left
PHY098 Sem II 2021/2022
2 Prepared by Nor Faridah Hanim Mat Junit, Noor Arda Adrina Daud, Norjuliyati Hamzah, Mas Fiza Mustafa,
PHY 098
SERWAY VUILLE, COLLEGE PHYSICS, 11TH EDITION
2021/2022
4. Three charges are arranged as shown in Figure 4. Find the magnitude and direction of the
electrostatic force on the charge at the origin.
Answer: 1.38 x 10 -5N at 77.5o below the –x-axis
Figure 4
5. Three point charges are located at the corners of an equilate ral triangle as in Figure 5. Find the
magnitude and direction of the net electric force on the 2.00 µC charge.
Answer: 0.438N, 85.2 o below the +x-axis
Figure 5
6. Particle A of charge 3.00 x 10 -4 C is at the origin, particle B of charge -6.00 x 10-4 C is at (4.00 m, 0)
and particle C of charge 1.00 x 10 -4 C is at (0, 3.00 m). Find the magnitude and direction of the
resultant electric force acting on C.
Answer: 24.3N, 44.5 o above +x-axis
7. A positive charge q1 = 2.70 µC on a frictionless horizontal surface is attached to a spring of force
constant k as in Figure 6. When a charge of q2 = -8.60 µC is placed 9.50 cm away from the positive
charge, the spring stretches by 5.00 mm, reducing the distance between charg es to d = 9.00 cm. Find
the value of k.
Answer: 5.15 x 10 3 N/m
Figure 6
PHY098 Sem II 2021/2022
3 Prepared by Nor Faridah Hanim Mat Junit, Noor Arda Adrina Daud, Norjuliyati Hamzah, Mas Fiza Mustafa,
You might also like
- PHY098 Electric Fields MCQs and ProblemsDocument4 pagesPHY098 Electric Fields MCQs and ProblemsIevana InsyirahNo ratings yet
- GP2 - Q3 - Melc 17 - Mod 8Document27 pagesGP2 - Q3 - Melc 17 - Mod 8Aguila Ronz EnguerraNo ratings yet
- Physics TutorialDocument4 pagesPhysics Tutorial2023844318No ratings yet
- PHYS 102 - Exam 1 - Spring 2015: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 pagesPHYS 102 - Exam 1 - Spring 2015: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 3Document2 pagesSummative Test 3Nathalie Garmeles MiñosaNo ratings yet
- Direction: Choose The Best Answer. Write The Letter Only.: General Physics 2 Long Quiz 1 DATEDocument11 pagesDirection: Choose The Best Answer. Write The Letter Only.: General Physics 2 Long Quiz 1 DATEJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Coulomb's LawDocument20 pagesModule 2 - Coulomb's LawPatrick CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument17 pagesChapter15 Electric Forces and Electric FieldsSky SailingNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 Answer Key PartialDocument8 pagesQUIZ 1 Answer Key Partialmikelandrew30No ratings yet
- Topic 5.1 Worksheet (1) - Electric Force & FieldDocument11 pagesTopic 5.1 Worksheet (1) - Electric Force & FieldananNo ratings yet
- Chaptest BDocument6 pagesChaptest Bdeezm579No ratings yet
- Electric FieldsDocument8 pagesElectric FieldsrealNo ratings yet
- Exercise 21.4: G G/molDocument9 pagesExercise 21.4: G G/molMahmoud HamdyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 ElectricityDocument1 pageExercise 1 ElectricityFredrick Felicio SusiloNo ratings yet
- Long Test and Midterm ReviewerDocument7 pagesLong Test and Midterm ReviewerMiko PenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For 3rd Grading ExamDocument5 pagesReviewer For 3rd Grading ExamJordano CadeliñaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and FieldDocument19 pagesElectric Potential and FieldhakitNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument113 pagesPhysicsShivam SainiNo ratings yet
- Test 2 AP Physics C - Quarter 2 2021Document9 pagesTest 2 AP Physics C - Quarter 2 2021Joshua CooperNo ratings yet
- Infinite Learning Electrical ForcesDocument7 pagesInfinite Learning Electrical ForcesAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Physics 72 Sample 1st LE PDFDocument14 pagesPhysics 72 Sample 1st LE PDFGwenShepherdNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesElectricity and Magnetismnaethan.harshaliNo ratings yet
- G11 PHYSICS worksheetDocument5 pagesG11 PHYSICS worksheetKanAlNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Dec ExamDocument3 pagesReviewer Dec ExamCamille Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 (Electric Charge and Coulomb's Law)Document5 pagesAssignment - 1 (Electric Charge and Coulomb's Law)IshanNo ratings yet
- GP 2 Diagnostic Test Answer KeyDocument11 pagesGP 2 Diagnostic Test Answer KeyPatricia TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSDocument21 pagesELECTROSTATICSHemanthNo ratings yet
- Select One of The FollowingDocument6 pagesSelect One of The FollowingHoang PhuonghaNo ratings yet
- 3rd QE QDocument4 pages3rd QE QJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument28 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsYash Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- 14 TestrDocument5 pages14 TestrΧρίστος ΠαπαναστασίουNo ratings yet
- 04 Electric Field Part 2Document6 pages04 Electric Field Part 2kayla888No ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Term 1 - Electric Charges and Fields - 01Document5 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Term 1 - Electric Charges and Fields - 01Utsav ShawNo ratings yet
- 2012 Chapter 1617 Multiple Choice AnswersDocument7 pages2012 Chapter 1617 Multiple Choice AnswersZaid Razali0% (1)
- Electrostatics Practice Test MCQs and FRQsDocument4 pagesElectrostatics Practice Test MCQs and FRQsSpring BballNo ratings yet
- Cblephpu 02Document8 pagesCblephpu 02sakthibala4545No ratings yet
- Phy PB Sample PaperDocument7 pagesPhy PB Sample Paperkomalkapri156No ratings yet
- Physics Class 12Document6 pagesPhysics Class 12EVAN GERSHONNo ratings yet
- MÃ 311 Nam DinhDocument4 pagesMÃ 311 Nam DinhHa HoangNo ratings yet
- Bản Sao Bank of Questions - Physics 2Document63 pagesBản Sao Bank of Questions - Physics 2Nguyễn UyênNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 1 XIIDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 1 XIIDr SaabNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields Learning GuideDocument15 pagesElectric Fields Learning GuideRana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- FOUNDATION PREPARATORY ACADEMY GENERAL PHYSICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMDocument5 pagesFOUNDATION PREPARATORY ACADEMY GENERAL PHYSICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMKazuya Sensei67% (3)
- 12 Physics Revision Questions Chapter 2Document4 pages12 Physics Revision Questions Chapter 2abhiNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Em-I (Bs-Ii)Document2 pagesMid Term Em-I (Bs-Ii)bozdarghalibNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 2 (1)Document62 pagesElectrostatics 2 (1)Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- CLASS_XII_PHYSICS_NCERT_TEXTBOOK_SOLUTION_Chapter_1_Electric_ChargesDocument33 pagesCLASS_XII_PHYSICS_NCERT_TEXTBOOK_SOLUTION_Chapter_1_Electric_Chargesrajvanshiaditya549No ratings yet
- BEST Mult Choice ReviewDocument5 pagesBEST Mult Choice ReviewTariq ZaitounNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Document14 pagesElectrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Sameera ShanakaNo ratings yet
- 1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticeDocument12 pages1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticerbgrossNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics ConceptsDocument32 pagesElectrostatics ConceptsRichmond NyamadiNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument63 pagesPhysicsprisha4No ratings yet
- Notes on Common Exam 1 Electric Charge and FieldsDocument7 pagesNotes on Common Exam 1 Electric Charge and Fieldssergey500No ratings yet
- Lesson2 Electric Force FieldDocument22 pagesLesson2 Electric Force FieldAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Electric Charge, Force, Field and Materials (39Document28 pagesElectrostatics: Electric Charge, Force, Field and Materials (39wonuNo ratings yet
- Le2 Ay14-15 2SDocument12 pagesLe2 Ay14-15 2STonicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6+7 - Electric Field (With Answers)Document58 pagesChapter 6+7 - Electric Field (With Answers)ngu lonNo ratings yet
- GP2 Q3 Melc-6 Mod-2Document29 pagesGP2 Q3 Melc-6 Mod-2Diana AfableNo ratings yet
- B PH 1 S EnglishDocument19 pagesB PH 1 S Englishnifty.vedNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pediatric Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Kathryn Rudd Diane KociskoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Pediatric Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Kathryn Rudd Diane Kociskolaurencelittlehdcj100% (26)
- TársalkodóDocument7 pagesTársalkodóOrsolya Loószné BernáthNo ratings yet
- Kafka Netdb 06 2011 PDFDocument15 pagesKafka Netdb 06 2011 PDFaarishgNo ratings yet
- Airbag Inflation: The Airbag and Inflation System Stored in The Steering Wheel. See MoreDocument5 pagesAirbag Inflation: The Airbag and Inflation System Stored in The Steering Wheel. See MoreShivankur HingeNo ratings yet
- Gen - Biology 2 Module 2Document12 pagesGen - Biology 2 Module 2Camille Castrence CaranayNo ratings yet
- Compass 5000.1.12 157605HDocument360 pagesCompass 5000.1.12 157605HApurbajyoti Bora100% (2)
- M HNDTL SCKT Imp BP RocDocument2 pagesM HNDTL SCKT Imp BP RocAhmed Abd El RahmanNo ratings yet
- Consumer PerceptionDocument61 pagesConsumer PerceptionPrakhar DwivediNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying Factors Behind Patient Safety IncidentsDocument5 pagesRoot Cause Analysis: Identifying Factors Behind Patient Safety IncidentsPrabhas_Das7No ratings yet
- Invoice Request for Digitize Global InovasiDocument1 pageInvoice Request for Digitize Global InovasiAsa Arya SudarmanNo ratings yet
- The History of Coins and Banknotes in Mexico: September 2012Document35 pagesThe History of Coins and Banknotes in Mexico: September 2012Mladen VidovicNo ratings yet
- FSA&V Case StudyDocument10 pagesFSA&V Case StudyAl Qur'anNo ratings yet
- Readings On The History and System of The Common Law - Roscoe PoundDocument646 pagesReadings On The History and System of The Common Law - Roscoe PoundpajorocNo ratings yet
- Book Notes - The Life Changing Magic of Tidying Up PDFDocument6 pagesBook Notes - The Life Changing Magic of Tidying Up PDFAilyn Bagares AñanoNo ratings yet
- Marine Ecotourism BenefitsDocument10 pagesMarine Ecotourism Benefitsimanuel wabangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Research and DesignDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Research and Designalvin salesNo ratings yet
- The 10 Most Inspiring Quotes of Charles F HaanelDocument21 pagesThe 10 Most Inspiring Quotes of Charles F HaanelKallisti Publishing Inc - "The Books You Need to Succeed"100% (2)
- HE HOUSEKEEPING GR11 Q1 MODULE-6-for-teacherDocument25 pagesHE HOUSEKEEPING GR11 Q1 MODULE-6-for-teacherMikaela YtacNo ratings yet
- Architecture After Modernism - Diane GhirardoDocument10 pagesArchitecture After Modernism - Diane GhirardoCebo DharuNo ratings yet
- SAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008Document6 pagesSAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008cjherrera2No ratings yet
- NAFTA CertificateDocument2 pagesNAFTA Certificateapi-522706100% (4)
- Aptamers in HIV Research Diagnosis and TherapyDocument11 pagesAptamers in HIV Research Diagnosis and TherapymikiNo ratings yet
- PowerHA SystemMirror Session 2 OverviewDocument80 pagesPowerHA SystemMirror Session 2 OverviewFabrice PLATELNo ratings yet
- Tem 2final PDFDocument9 pagesTem 2final PDFSkuukzky baeNo ratings yet
- 41-How To Calculate Air Temp in Unconditioned SpacesDocument3 pages41-How To Calculate Air Temp in Unconditioned Spacesalmig200No ratings yet
- Detailed Pacing Guide HMH Science Dimensions Grades K-5Document70 pagesDetailed Pacing Guide HMH Science Dimensions Grades K-5Milica PejcicNo ratings yet
- Water Booster Pump Calculations - Plumbing Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument3 pagesWater Booster Pump Calculations - Plumbing Engineering - Eng-TipsNeal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Qy130v633 Operation ManualDocument414 pagesQy130v633 Operation ManualumamNo ratings yet
- Kak MhamadDocument1 pageKak MhamadAyub Anwar M-SalihNo ratings yet
- 5e3 Like ApproachDocument1 page5e3 Like Approachdisse_detiNo ratings yet