Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch.1 Algebraic Expressions
Uploaded by
Antonio Pérez-LabartaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch.1 Algebraic Expressions
Uploaded by
Antonio Pérez-LabartaCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebraic Expressions Cheat Sheet Edexcel Pure Year 1
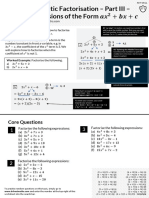
In this chapter you are introduced to simple algebraic concepts that you may have Example 5: Factorise the following expressions
come across before in your previous studies.
Expanding Brackets
When expanding brackets for the product of two expressions, you have to multiply each term a) 𝑥 ! + 5𝑥 + 6
Index Laws in the first expression by each term in the second expression and simplify the final product of
𝑎 = 1, 𝑏 = 5, 𝑐 = 6
There are four key index laws that you need to know for not just this chapter but this by collecting like terms.
for the entirety of your maths course. Two factors of 𝑎 × 𝑐 which also add up to b need to be calculated. Hence
(𝑥 + 2) is the first expression and (𝑥 + 3) is the second agree with the following statements:
• 𝑎# × 𝑎$ = 𝑎#%$ expression. 1. _? _ × _? _ = 𝑎 × 𝑐 = 1 × 6 = 6
• 𝑎# ÷ 𝑎$ = 𝑎#&$ The first term in the first expression is 𝑥 which is 2. _? _ + _? _ = 𝑏 = 5
• (𝑎# )$ = 𝑎#$ (𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 3) multiplied by the terms 𝑥 and 3 in the second
The two numbers which agree with both the statements are 3 and 2.
• (𝑎𝑏)# = 𝑎# 𝑏# expression as indicated by the grey arrows.
Where a & b are the bases and c & d are the powers The ‘b’ term can now be rewritten using the two factors found and hence the
The second term in the first expression is 2 which is also
multiplied by the terms 𝑥 and 3 in the second expression will take the form of:
Example 1: Simplifying expressions using index laws expression as indicated by the green arrows. 𝑥 ! + 2𝑥 + 3𝑥 + 6
a) 𝑥 ' × 𝑥 " = 𝑥 '%" = 𝑥 ( Now factorising the first two terms and the last two terms:
Therefore, (𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 3) = 𝑥(𝑥 + 3) + 2(𝑥 + 3) = 𝑥 ! + 3𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 6
𝑥(𝑥 + 2) + 3(𝑥 + 2)
Collecting the like terms, (𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 3) = 𝑥 ! + 5𝑥 + 6
') ! ' )! = (𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 3)
b) !) "
= ! × ) " = 2𝑦 *&" = 2𝑦 "
Example 4: Expand the following brackets and simplify • Difference of two squares: 𝑥 ! − 𝑦 ! = (𝑥 + 𝑦)(𝑥 − 𝑦)
! ' !×' ,
c) (𝑧 ) = 𝑧 =𝑧
a) 3(𝑝 + 3)(𝑝 + 2) = (3 × 𝑝 + 3 × 3)(𝑝 + 2) = (3𝑝 + 9)(𝑝 + 2)
= 3𝑝(𝑝 + 2) + 9(𝑝 + 2)
Surds and Rationalising Denominators
d) (𝑥 ! " )" 𝑦 =𝑥 !×" "×"
𝑦 =𝑥 𝑦 * -
Surds are irrational numbers which come in the exact form of √𝒂 and where 𝒂 is not a
= 3𝑝! + 6𝑝 + 9𝑝 + 18
= 3𝑝! + 15𝑝 + 18 square number. The following rules can be applied to surds:
Negative and Fractional Indices • √𝑎𝑏 = √𝑎 × √𝑏
Indices (powers) can come in the form of fractions or negative numbers. The
b) (𝑞 + 1)(𝑞 + 2)(𝑞 + 3) 0 √0
index laws can still be applied contingent on the powers being rational. • N7 =
√7
Ø 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑡 𝑏𝑦 𝑒𝑥𝑝𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 𝑡𝑤𝑜 𝑏𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑘𝑒𝑡𝑠 You may come across fractions with the denominator being a surd. To get rid of this
• 𝑎. = 1 (𝑞 + 1)(𝑞 + 2) = 𝑞! + 2𝑞 + 𝑞 + 2 = (𝑞! + 3𝑞 + 2) irrational number in the denominator we can rationalise it by using the following
/
• 𝑎&# = 0# rules/methods which apply to different forms of fractions:
•
$
𝑎 # = √𝑎
# Ø Rewrite the initial expression as (𝑞! + 3𝑞 + 2)(𝑞 + 3) and expand
1 𝑎 For this form we multiply the numerator and
#
% (𝑞! + 3𝑞 + 2)(𝑞 + 3)
• 𝑎 % = √𝑎 # = 𝑞! (𝑞 + 3) + 3𝑞(𝑞 + 3) + 2(𝑞 + 3) 𝑎 𝑎 denominator by √𝑎
= 𝑞" + 3𝑞! + 3𝑞! + 9𝑞 + 2𝑞 + 6
Example 2: Simplify the following expressions = 𝑞" + 6𝑞! + 11𝑞 + 6 1 𝑎 + √𝑏 For this form we multiply the numerator and
&
"
𝑎 − √𝑏 𝑎 + √𝑏 denominator by 𝑎 + √𝑏
a) 𝑥 " = √𝑥 ! Factorising
Factorising is the reverse of expanding brackets. When expanding brackets, you find the For this form we multiply the numerator and
1 𝑎 − √𝑏
b) 36𝑥 ! ÷ 6𝑥 &/ = 6𝑥 !&(&/) = 6𝑥 " product of two or more expressions, however when you find the factors of a given expression
𝑎 + √𝑏 𝑎 − √𝑏 denominator by 𝑎 − √𝑏
it is called factorising.
$
/ / /
c) (81𝑦 ! )&& = $ = = -) Example 6: Expand and simply the following expression.
(,/) & )& √,/×4) & 4 The common factor of both
terms in the expression is 4 1 1 1
Example 3: Given that 𝑠 = 𝑡 ! , express each of the following in terms of t. = =
(4𝑥 + 24) = 4(𝑥 + 6) O5 + √44Q 5 + √4 × 11 5 + O√4 × √11Q
& &
!×
& ' 1 × (5 − 2√11)
a) 𝑠 = (𝑡 ! ) = 𝑡
" " " =𝑡 " To factorise quadratic expressions with the form 𝑎𝑥 ! + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 where a, b and c are areal =
numbers and 𝑎 ≠ 0. 5 + 2 √11 × (5 − 2√11)
$
b) 𝑠 &
' =
/
=
/
=
/
=
/
𝑜𝑟
/ • Calculate the product of 𝑎 × 𝑐 and find two factors of this product which add up to (5 − 2√11)
$ $ $ $
√6 =
5' (6 & )' 6
&×
' 6& 𝑏. 25 − 10√11 + 10√11 − 4(11)
• Rewrite the initial expression and substitute the 𝑏𝑥 term with the two factors found
(5 − 2√11) −(−5 + 2√11)
before. = =
• Factorise the first two terms and the last two terms of the rewritten expression. 25 − 44 −19
−5 + 2√11
• Simplify by taking out the common factor. =
19
.
https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
https://bit.ly/pmt-edu https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
You might also like
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument1 pageAlgebraic ExpressionsF JNo ratings yet
- Section 4 - ALGEBRA Part-1Document8 pagesSection 4 - ALGEBRA Part-1MunaNo ratings yet
- DFM AllInOne QuadraticFactorisation3 Ax2Document1 pageDFM AllInOne QuadraticFactorisation3 Ax2saipkNo ratings yet
- Performing Operations On Rational Algebraic Expressions: Grade 8 - Mathematics Week 4, Quarter 1Document34 pagesPerforming Operations On Rational Algebraic Expressions: Grade 8 - Mathematics Week 4, Quarter 1RHEALINDA RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Monthly Class Test 01: Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Document1 pageMonthly Class Test 01: Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- FNDMATH Problem Set 1Document2 pagesFNDMATH Problem Set 1寂XaviNo ratings yet
- SMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 QDocument2 pagesSMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 QZurainiNo ratings yet
- MAAHL12 Mockp1Document14 pagesMAAHL12 Mockp1Nadia VellaNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionsDocument46 pagesRational Functionscristha estropeNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions IDocument4 pagesRelations and Functions IOm TipsetwarNo ratings yet
- SE1 - AddMath - Final Exam 2021 - QDocument13 pagesSE1 - AddMath - Final Exam 2021 - QDerron LimNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q2 M7Document8 pagesMath7 Q2 M7Jie GodinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 ExponentialFunctionsDocument7 pagesLesson 4 ExponentialFunctionsMarybel CarantoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Natural Sciences Math 1011 Worksheet On Chapters 3 and 4Document2 pagesMathematics For Natural Sciences Math 1011 Worksheet On Chapters 3 and 4Eyob LakewNo ratings yet
- Creating A ModuleDocument12 pagesCreating A ModuleJhun Rey MoralesNo ratings yet
- Muar (Q)Document3 pagesMuar (Q)Ys DingNo ratings yet
- Quadratics Cheat Sheet Edexcel Pure Year 1: Function 3 + 2 11Document1 pageQuadratics Cheat Sheet Edexcel Pure Year 1: Function 3 + 2 11online classNo ratings yet
- Follow Us:: Related VideosDocument1 pageFollow Us:: Related VideosVig LalNo ratings yet
- Sample Test 1-2 For Calculus 1Document2 pagesSample Test 1-2 For Calculus 1Teodora MihaiNo ratings yet
- P4 MAY BATCH (Upto CH 4)Document2 pagesP4 MAY BATCH (Upto CH 4)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument2 pagesAlgebrampatt846No ratings yet
- p4 May Batch (Upto CH 4)Document2 pagesp4 May Batch (Upto CH 4)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - NAZDocument61 pagesChapter 1 - NAZAisha QasimNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Gen MathDocument14 pagesModule 7 Gen MathAndreah DavidNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions (Autosaved)Document27 pagesPartial Fractions (Autosaved)Imaya SenuriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Exponential Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Exponential Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesUgsang, LiannaNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2019 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument24 pagesJames Ruse 2019 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsHazard Messi100% (1)
- Solving Quadratics by FactoringDocument4 pagesSolving Quadratics by FactoringShraddha NayakNo ratings yet
- Rearranging FormulaeDocument15 pagesRearranging FormulaeNagmudiin AhmethNo ratings yet
- Sir Tino Polynomials Binomial Expansion and Polynomials TestDocument2 pagesSir Tino Polynomials Binomial Expansion and Polynomials TestLaban KainsNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Document2 pagesPure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- P3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersDocument3 pagesP3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersSheikh HassanNo ratings yet
- AlgebraBasicsCheatSheets 1Document4 pagesAlgebraBasicsCheatSheets 1Jeraldine RamisoNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Has A Maximum Point at (2, )Document8 pagesInstructions:: Has A Maximum Point at (2, )WAH XIN YEE MoeNo ratings yet
- Sample Test 1-1 For Calculus 1Document2 pagesSample Test 1-1 For Calculus 1Teodora MihaiNo ratings yet
- Rational ExpressionsDocument6 pagesRational ExpressionsAlrian Jay SampalayNo ratings yet
- ChE Partial-Fraction-Decomposition PDFDocument17 pagesChE Partial-Fraction-Decomposition PDFFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- MfE T1 Midterm - Mock + Formula SheetDocument4 pagesMfE T1 Midterm - Mock + Formula SheetVindra WikanandaNo ratings yet
- GenMath Module 3 Week 3Document16 pagesGenMath Module 3 Week 3Immanuel CañecaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Integration of Rational FunctionsDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Integration of Rational FunctionsKhemme Lapor Chu UbialNo ratings yet
- Rearranging FormulaeDocument6 pagesRearranging FormulaeJimei TanNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous, Quadrilaterals and InequalitiesDocument1 pageSimultaneous, Quadrilaterals and InequalitiesJess KongNo ratings yet
- Rearranging The FormulaeDocument14 pagesRearranging The FormulaeKhin Myat MawNo ratings yet
- Paper III - EnglishDocument4 pagesPaper III - EnglishHarshanaNuwanNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Derivatives of Trigono 4.6 Implicit Differentiation 4.7 Parametric DifferentiationDocument8 pages4.5 Derivatives of Trigono 4.6 Implicit Differentiation 4.7 Parametric Differentiationzarfan sabriNo ratings yet
- P3 May 21 Revision Worksheet CH, 1, 2, 3 & 6Document3 pagesP3 May 21 Revision Worksheet CH, 1, 2, 3 & 6Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Iteration Iterative Processes and Iteration With Growth and Decay 1ma1 Higher Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesIteration Iterative Processes and Iteration With Growth and Decay 1ma1 Higher Exam Questions4cpzx7fp52No ratings yet
- W2 Ex 5D 5E 5F 5G LogarithmsDocument3 pagesW2 Ex 5D 5E 5F 5G LogarithmsJessicaNo ratings yet
- BOHOL MATHSHS GENMATH Q1 PLP2DAY2 v.01Document2 pagesBOHOL MATHSHS GENMATH Q1 PLP2DAY2 v.01Angelica CamaraoNo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod7 - Exponential Functions Equations and Inequalities - Version FinalDocument15 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod7 - Exponential Functions Equations and Inequalities - Version FinalJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Finding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsDocument9 pagesFinding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsParikNo ratings yet
- Nulpmss 42.105.101.57BSCHMTMC101Document2 pagesNulpmss 42.105.101.57BSCHMTMC101sohad99783No ratings yet
- Solving Rational Equations and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesSolving Rational Equations and Inequalitiestishvill18No ratings yet
- 1 Speaking MathematicallyDocument33 pages1 Speaking MathematicallyJessaNo ratings yet
- Genmath Long ExamDocument3 pagesGenmath Long ExamJessa BarberoNo ratings yet
- 12H Binomial TheoremDocument2 pages12H Binomial TheoremPaul ThompsonNo ratings yet
- s4 ch3 Quadratic Equations Ex1 EngDocument4 pagess4 ch3 Quadratic Equations Ex1 EngDon LiaoNo ratings yet
- Math Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandMath Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ch.6 Projectile MotionDocument1 pageCh.6 Projectile MotionAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.7 Trigonometry and ModellingDocument1 pageCh.7 Trigonometry and ModellingAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 ProbabilityDocument1 pageCh.5 ProbabilityAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 Straight Line GraphsDocument1 pageCh.5 Straight Line GraphsAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Measures of Location and SpreadDocument1 pageCh.2 Measures of Location and SpreadAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Permutation CombinationDocument8 pagesPermutation CombinationReina Alliyah GonzalesNo ratings yet
- If You Don't Learn From Your Mistakes, There's No Sense of Making ThemDocument58 pagesIf You Don't Learn From Your Mistakes, There's No Sense of Making ThemCayetano, Tara Leigh MartinezNo ratings yet
- A Neighborhood of Infinity - You Could Have Invented Monads! (And Maybe You Already Have PDFDocument30 pagesA Neighborhood of Infinity - You Could Have Invented Monads! (And Maybe You Already Have PDFsigfpeNo ratings yet
- Texto de Algebra Lineal U de Harvard PDFDocument47 pagesTexto de Algebra Lineal U de Harvard PDFJohn J Gomes EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Homework Solutions - Unit 4: Chapter 23: Exercise 23.1-2Document1 pageHomework Solutions - Unit 4: Chapter 23: Exercise 23.1-2AceNo ratings yet
- Winmeen VAO Mission 100: Number SeriesDocument6 pagesWinmeen VAO Mission 100: Number SeriesarunturboNo ratings yet
- Pseudo Code of Mpi ProgramsDocument22 pagesPseudo Code of Mpi ProgramsAshfaq MirNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Functional AnalysisDocument23 pagesA Brief History of Functional Analysistrashumante10100% (1)
- Essential Mathematics For Computational Design 4th Edition - Table of ContentsDocument7 pagesEssential Mathematics For Computational Design 4th Edition - Table of ContentsdramachinesNo ratings yet
- Document From صابر گڑھیDocument31 pagesDocument From صابر گڑھیTheDisastrousDuckNo ratings yet
- Solution Real Analysis Folland Ch6Document24 pagesSolution Real Analysis Folland Ch6ks0% (1)
- How To Parametrize A CurveDocument3 pagesHow To Parametrize A CurveKhalid AlmuteriNo ratings yet
- Sage FourierDocument8 pagesSage FourierWilliam PeñaNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- MA103 Lecture NotesDocument130 pagesMA103 Lecture NotesAnthony TuyenNo ratings yet
- Beginning and Intermediate Algebra 5th Edition by Martin Gay ISN Solution ManualDocument100 pagesBeginning and Intermediate Algebra 5th Edition by Martin Gay ISN Solution Manualjames100% (28)
- Math 8 LAW Q4docxDocument19 pagesMath 8 LAW Q4docxGirlie Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- CLO3 Exercises CLO3 With AnswersDocument5 pagesCLO3 Exercises CLO3 With AnswersmaryamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Biomedical PhysicsDocument242 pagesMathematics For Biomedical PhysicsSagenxNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Solving Linear Equation MathDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 5 Solving Linear Equation MathSyira ShahimiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9: Supplementary Material Quadratic Equations Week 1Document7 pagesMathematics 9: Supplementary Material Quadratic Equations Week 1Christian PejiNo ratings yet
- DS Chapter 04Document63 pagesDS Chapter 04Asim AliNo ratings yet
- LSU MATH 7311 Qual QuestionsDocument39 pagesLSU MATH 7311 Qual QuestionsHunter PattonNo ratings yet
- Verlet Algoritma PDFDocument15 pagesVerlet Algoritma PDFDwi NurcahyoNo ratings yet
- Rational NumbersDocument26 pagesRational Numbersthinkiit100% (1)
- Elective 4 The Mathematics of GraphsDocument108 pagesElective 4 The Mathematics of GraphsGwen Fedilus Fabrero100% (1)
- Inverse FunctionsDocument50 pagesInverse FunctionsRoszelan MajidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document18 pagesUnit 1Andrea MillerNo ratings yet
- Running TimeDocument1 pageRunning Timeapi-288619706No ratings yet
- Mahima Ranjan Adhikari - Basic Algebraic Topology and Its Applications-Springer (2016)Document628 pagesMahima Ranjan Adhikari - Basic Algebraic Topology and Its Applications-Springer (2016)Walter Castañeda Diaz100% (3)