Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question 2
Uploaded by
Irumvamwizerwa Onesme0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
QUESTION 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesQuestion 2
Uploaded by
Irumvamwizerwa OnesmeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
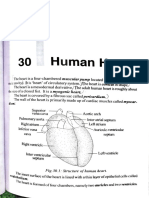
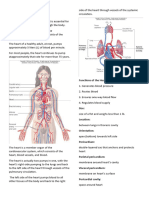
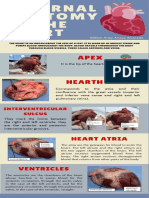
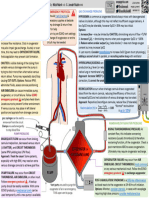
LOOK ON THIS(21.
14 Veins of
the Systemic Circulation)
Major systematic vein and their draining part
They are three systemic veins
I)coronary sinus
II)superior vena cava (SVC)
III)inferior vena cava (IVC)
VEINS DESCRIPTION REGIONS
AND DRAINED
TRIBUTARIES
Coronary sinus Main vein of All tissues of
(KOR-oˉ-Nar-ē; heart; receives heart.
corona = crown) almost all
venous blood
from
myocardium;
located in
coronary sulcus
on posterior
aspect of heart
and opens into
right atrium
between orifice
of inferior vena
cava and
tricuspid valve.
Wide venous
channel into
which three
veins drain.
Receives great
cardiac vein
(from anterior
interventricular
sulcus) into its
left end, and
middle cardiac
vein (from
posterior
interventricular
sulcus) and small
cardiac vein into
its right end.
Several anterior
cardiac veins
drain directly
into right atrium.
Superior vena About 7.5 cm (3 Head, neck,
cava (SVC) (VĒ- in.) long and 2 upper limbs, and
na KĀ-va; vena = cm (1 in.) in thorax.
vein; cava = cave diameter;
like) empties its
blood into
superior part of
right atrium.
Begins posterior
to right first
costal cartilage
by union of right
and left
brachiocephalic
veins and ends
at level of right
third costal
cartilage, where
it enters right
atrium
Inferior vena Largest vein in Abdomen,
cava (IVC) body, about 3.5 pelvis, and lower
cm (1.4 in.) in limbs
diameter. Begins
anterior to fifth
lumbar vertebra
by union of
common iliac
veins, ascends
behind
peritoneum to
right of midline,
pierces caval
opening of
diaphragm at
level of eighth
thoracic
vertebra, and
enters inferior
part of right
atrium.
NB: The inferior vena cava is commonly compressed
during the later stages of pregnancy by the enlarging
uterus, producing edema of the ankles and feet and
temporary varicose veins.
You might also like
- Heart Reviewer 1Document6 pagesHeart Reviewer 1tokzzNo ratings yet
- The Emotion That Breaks Your Heart Is Sometimes The Very One That Heals It!Document4 pagesThe Emotion That Breaks Your Heart Is Sometimes The Very One That Heals It!A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System 1Document66 pagesCardiovascular System 1Mary joy DavidNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument80 pagesHuman HeartYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Sistem KardiovaskulerDocument42 pagesAnatomi Sistem KardiovaskulerNurul Alia FathilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Kardio PDFDocument49 pagesAnatomi Kardio PDFDestrini Anjani LandaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular SystemHira KhanNo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument11 pagesHeart and Neck Vesselsdiana borromeoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy HeartDocument6 pagesAnaphy HeartAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsDocument7 pagesPRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Cardio VasDocument99 pagesCardio VashellerkittyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy CardioDocument6 pagesAnaphy CardioDianne DimaanoNo ratings yet
- ACD 15 - Pericardium & External HeartDocument8 pagesACD 15 - Pericardium & External Heartpranky neyneyNo ratings yet
- Heart: Size, Form, and Location: Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesHeart: Size, Form, and Location: Cardiovascular Systemskyler andradaNo ratings yet
- Heart Tube FormationDocument41 pagesHeart Tube FormationRuchi VatwaniNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument4 pagesThe Heartlilac.poppy.48No ratings yet
- Development of CVSDocument51 pagesDevelopment of CVSalnifeady9No ratings yet
- HeartDocument18 pagesHeartCORONEL, SOPHIANo ratings yet
- Embryology: HeartDocument46 pagesEmbryology: HeartRahul K. JagaNo ratings yet
- Heart & Great Vessels: Structure, Function, DevelopmentDocument57 pagesHeart & Great Vessels: Structure, Function, DevelopmentStefanie GarnerNo ratings yet
- 10th Week Practical LessonsDocument11 pages10th Week Practical LessonstheodorastanerNo ratings yet
- Scan Dec 12, 2022Document6 pagesScan Dec 12, 2022Saktheeswaran VNo ratings yet
- Pig's Heart Post LabDocument2 pagesPig's Heart Post LabMichaella Jane BugayNo ratings yet
- Heart External AnatomyDocument6 pagesHeart External AnatomyKrissia BaasisNo ratings yet
- Brachiocephalic Artery: AnteriorDocument37 pagesBrachiocephalic Artery: AnteriorFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular Systemabdelrhman aboodaNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASDocument3 pagesCARDIOVASFrama Intan MiguelNo ratings yet
- 14 08 11.CV Anatomy Histology - Gundogan.Document6 pages14 08 11.CV Anatomy Histology - Gundogan.allisonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NotesDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NotesChristina Gonez100% (2)
- HEARTDocument8 pagesHEARTSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument36 pagesThe HeartMuskan Bisht100% (3)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Aortic DissectionDocument24 pagesAortic Dissectionsameeha semiNo ratings yet
- Septum Formation in The VentriclesDocument43 pagesSeptum Formation in The VentriclesAhsan IslamNo ratings yet
- Case 2: David Marsden Case Summary: Ostia TrigonesDocument15 pagesCase 2: David Marsden Case Summary: Ostia TrigonesHuiLinn LeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes CVSDocument8 pagesLecture Notes CVSlubnaNo ratings yet
- PHUS NoteDocument6 pagesPHUS NotelightwhisperNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ProblemsDocument15 pagesCardiovascular ProblemsMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyapi-560921597No ratings yet
- External Anatomy of The HeartDocument2 pagesExternal Anatomy of The HeartAndres LarrottaNo ratings yet
- DOMICINDocument2 pagesDOMICINKaryll AguilaNo ratings yet
- Subdivisions of The MediastinumDocument4 pagesSubdivisions of The MediastinumVin CustodioNo ratings yet
- Cardiac VeinDocument5 pagesCardiac VeinFajar MujibNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument8 pagesHEARTJoyce OmegaNo ratings yet
- Four Chambers of The HeartDocument7 pagesFour Chambers of The HeartJohn TecsonNo ratings yet
- Whitaker 2010Document3 pagesWhitaker 2010Gabriel Jose CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, LudhianaDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, Ludhianapreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Kuliah-23 Sistem Koroner - InervasiDocument27 pagesKuliah-23 Sistem Koroner - InervasiAinun Marwah DaulayNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Heart PDFDocument5 pagesMammalian Heart PDFKhaled TurkNo ratings yet
- Echo HOG - 02.anatomyDocument9 pagesEcho HOG - 02.anatomyakidodjieNo ratings yet
- Development of HeartDocument21 pagesDevelopment of Heartvigneshmmc02No ratings yet
- HeartDocument33 pagesHeartYesh kumarNo ratings yet
- CARDIOLOGYDocument15 pagesCARDIOLOGYPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemadnanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument114 pagesThe Circulatory SystemKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemTasmiah HossainNo ratings yet
- CVS Final 2 (Heart Chambers and Valves)Document9 pagesCVS Final 2 (Heart Chambers and Valves)Muneeb AnjumNo ratings yet
- Four Chambers of The HeartDocument7 pagesFour Chambers of The HeartJohn TecsonNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology (2) - 1Document248 pagesGeneral Pharmacology (2) - 1Irumvamwizerwa OnesmeNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Viral InfectionsDocument33 pagesGroup 4 Viral InfectionsIrumvamwizerwa OnesmeNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument22 pagesTuberculosisIrumvamwizerwa OnesmeNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument50 pagesImmunityIrumvamwizerwa OnesmeNo ratings yet
- RudrakshDocument3 pagesRudrakshAmartyaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument19 pagesBloodToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesUnit 2 - Nervous SystemzulieyanaNo ratings yet
- Echo Report : (Abridged)Document4 pagesEcho Report : (Abridged)Ajay KarolNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (SHS) : The Two Shades of GreenDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (SHS) : The Two Shades of GreenLAN soajasNo ratings yet
- NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decreased Cardiac OutputYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Respiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Document24 pagesRespiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Banu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Energy Expenditure and FatigueDocument49 pagesEnergy Expenditure and FatigueAh Zhang100% (1)
- VVIR Vs DDDRDocument2 pagesVVIR Vs DDDRNITACORDEIRONo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument32 pagesExerciseDibya Ranjan SahuNo ratings yet
- Sgarbossa CrtiteriaDocument4 pagesSgarbossa Crtiteriaanisah astiraniNo ratings yet
- History Form IntroductoryDocument6 pagesHistory Form Introductoryrawan.abujodahNo ratings yet
- Perinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in ManagementDocument31 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in Managementokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- Thermoregulation-Pure PPT BasedDocument12 pagesThermoregulation-Pure PPT BasedMonesa Christy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gap Co2 Cocc 2018Document9 pagesGap Co2 Cocc 2018Cesar Rivas CamposNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsidipusDocument2 pagesDiabetes InsidipusLena RoweNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DiseasesDocument8 pagesCardiac DiseasesTJ NgNo ratings yet
- Ecmo TroubleshootingDocument1 pageEcmo TroubleshootingMitch ConnerNo ratings yet
- Eov PDFDocument2 pagesEov PDFabhishekmla007No ratings yet
- Final Exam - Modern Views of Animals and Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesFinal Exam - Modern Views of Animals and Plant Anatomy and Physiologyrhomelyn malanaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Medullary HormonesDocument19 pagesAdrenal Medullary Hormonesasmara khanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Road TripDocument7 pagesRespiratory Road Tripapi-235944649No ratings yet
- (Hematology) Chapter 7: Hematopoiesis: BloodDocument5 pages(Hematology) Chapter 7: Hematopoiesis: BloodJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Penetrating Abdominal Trauma (Stab Wound)Document1 pagePenetrating Abdominal Trauma (Stab Wound)P BNo ratings yet
- CH 15 Respiratory Practice Exam: StudentDocument10 pagesCH 15 Respiratory Practice Exam: StudentSevilla ErnestdonNo ratings yet
- Fisio1 Exc6 Act1Document5 pagesFisio1 Exc6 Act1Fadli Nurul HanifNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytestentenNo ratings yet
- Congenital Diaphragmatic HerniaDocument40 pagesCongenital Diaphragmatic HerniaPothina Sree HariNo ratings yet
- Test Gaming AddictionDocument3 pagesTest Gaming AddictionAriunjargal RagchaabazarNo ratings yet