Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout4-Taxonomy-Kendall & Marzano
Handout4-Taxonomy-Kendall & Marzano
Uploaded by
Bruz SundayCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout4-Taxonomy-Kendall & Marzano
Handout4-Taxonomy-Kendall & Marzano
Uploaded by
Bruz SundayCopyright:
Available Formats
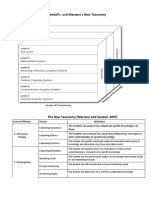
The New Taxonomy (Marzano and Kendall, 2007)
Level of Difficulty Process Useful Verbs, Phrases, Difficulties
6 Examining The student can analyze how important specific knowledge is to them.
Self-System Thinking Importance
Examining The student can examine how much they believe they can improve their understanding
Efficacy of specific knowledge.
Examining The student can identify emotional responses associated with a piece of knowledge and
Emotional determine why those associations exist.
Response
5 Specific Goals The students can set specific goals relative to knowledge and develop a plan for
accomplishing the goal.
Metacognition
Process The student can self-monitor the process of achieving a goal.
Monitoring
Monitoring The student can determine how well they understand knowledge.
Clarify
Monitoring The student can determine how accurate their understanding of knowledge is and
Accuracy defend their judgment.
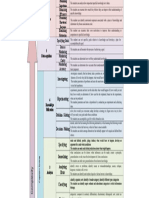
4 Investigate; research; find out about; take a position on; what are the differing features
of; how & why did this happen; what would have happened if;
Knowledge
The student generates a hypothesis and uses the assertions and opinions of others to
C Utilization Investigating
test the hypothesis.
Experiment; generate and test; test the idea that; what would happen if; how would you
O test that; how would you determine if; how can this be explained; based on the
experiment, what can be predicted.
Experimenting
The student generates and tests a hypothesis by conducting an experiment and
M collecting data.
solve; how would you overcome; adapt; develop a strategy to; figure out a way to; how
C
will you reach your goal under these conditions
P O Problem-
Solving The student can accomplish a goal for which obstacle exist.
G
N
L
Decide; select the best among the following alternatives; which among the following
I would be the best; what is the best way; which of these is most suitable
T Decision- The student can select among alternatives that initially appear to be equal and defend
E I
V
Making
their choice.
3 Make and defend; predict; judge; deduce; what would have happen; develop an
E
X Analysis Specifying argument for; under what conditions
The student can make and defend predictions about what might happen.
S Generalizing What conclusions can be drawn; what inferences can be made; create a principle,
I Y
S
generalization or rule; trace the development of; form conclusions
The student can infer new generalization from known knowledge
T Analyzing Identify errors or problems; identify issues or misunderstandings; assess; critique;
T E Errors diagnose; evaluate; edit; revise
M The student can identify and explain logical or factual errors in knowledge.
Y Classifying Classify; organize; sort; identify a broader category; identify different types categories
The student can identify super ordinate and subordinate categories to which information
belongs.
Matching Categorize; compare & contrast; differentiate; discriminate; distinguish; sort; create an
analogy or metaphor
The student can identify similarities and differences in knowledge.
2 Symbolizing Symbolize; depicts; represent; illustrate; draw; show; use models; diagram chart
The student can depict critical aspects of knowledge in pictorial of symbolic form
Comprehension
Integrating Describe how or why; describe the key parts of; describe the effects; describe the
relationship between; explain ways in which; paraphrase; summarize
The student can identify the critical or essential elements of knowledge.
1 Executing Use; demonstrate; show; make; complete; draft
The student can perform procedures without significant errors.
Retrieval
Recalling Exemplify; name; list; label; state; describe; who; what; where; when
The student can produce information on demand.
Recognizing Recognize (from a list); select form (a list); identify (from a list); determine if the
following statements are true
The student can determine whether provided information is accurate, inaccurate or
unknown
You might also like
- x3B Marzano - New - Taxonomy - Chart - With - Verbs - 3.16.121 PDFDocument1 pagex3B Marzano - New - Taxonomy - Chart - With - Verbs - 3.16.121 PDFSistemas EdutecNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Dear ZooDocument9 pagesLesson Plan - Dear Zooapi-339913298No ratings yet
- Marzano and Kendall 2007 TaxonomyDocument1 pageMarzano and Kendall 2007 TaxonomyCezLuzarraga67% (3)
- Objective - Related Principles of TeachingDocument36 pagesObjective - Related Principles of TeachingQuinie Asperin75% (4)
- Back To Basics Practical NeurologyDocument42 pagesBack To Basics Practical Neurologym2rv110100% (2)
- Badminton Skills Rubric - 7-8Document1 pageBadminton Skills Rubric - 7-8Xyra Ballesteros67% (3)
- 3.7 Kendall's and Marzano's New TaxonomyDocument2 pages3.7 Kendall's and Marzano's New TaxonomyNely Joy YringanNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Learning Techniques: Unlimited Photographic Memory Mastery and Memory ImprovementFrom EverandAccelerated Learning Techniques: Unlimited Photographic Memory Mastery and Memory ImprovementNo ratings yet
- Self Care Deficit Theory of NursingDocument4 pagesSelf Care Deficit Theory of NursingMark Elben100% (1)
- Capstone Artifact Elcc Standard 6Document2 pagesCapstone Artifact Elcc Standard 6api-404096250100% (1)
- The New Taxonomy - PNG SDocument1 pageThe New Taxonomy - PNG SEverly GamayoNo ratings yet
- Fs 5 Episode 4Document25 pagesFs 5 Episode 4Lei-Ann EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Fs 5 Episode 4Document25 pagesFs 5 Episode 4Sheila Mae Lucasan60% (5)
- Fs 5 Episode 4Document24 pagesFs 5 Episode 4JoJo SarionNo ratings yet
- Marzano New Taxonomy Chart With Verbs 3 16 121Document1 pageMarzano New Taxonomy Chart With Verbs 3 16 121api-294667820100% (5)
- 14 Days Quarantine ChallengeDocument10 pages14 Days Quarantine ChallengeRhezty Rhei-vaenNo ratings yet
- Marzano and Kendall 2007 TaxonomyDocument1 pageMarzano and Kendall 2007 TaxonomyFactoran Wilfred100% (1)
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFPatrizzia Ann Rose OcbinaNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFFrancis AbellanaNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFLorenMelegritoNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFMissEu Ferrer MontericzNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFArya Glaine SolNo ratings yet
- Marzano and Kendall 2007 TaxonomyDocument1 pageMarzano and Kendall 2007 TaxonomyCherry Casido - LarenaNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDel PacificoNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFjuanita pardoNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy (A)Document1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy (A)Willyn Nicole Julian MartesanoNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFcandyNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDarwin BalatNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFShine SilvaNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFGail Abby RrestoNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFAnonymous 75TDy2yNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFJuan PabloNo ratings yet
- Marzanoand Kendall 2007 TaxonomyDocument1 pageMarzanoand Kendall 2007 TaxonomyAshley MacarimborNo ratings yet
- Marzanoand Kendall 2007 TaxonomyDocument1 pageMarzanoand Kendall 2007 TaxonomyEmma GhosnNo ratings yet
- MarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFDocument1 pageMarzanoandKendall2007Taxonomy PDFFrancisco BatulanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument1 pageBloom's TaxonomyMutiara AuditaNo ratings yet
- Kendall and Marzano BulletsDocument1 pageKendall and Marzano BulletsElner Dale Jann GarbidaNo ratings yet
- U-CASE: Careful Analysis of Some Enigma Unit: DescriptionDocument2 pagesU-CASE: Careful Analysis of Some Enigma Unit: DescriptionsherrymiNo ratings yet
- Module 11. Research HypothesisDocument13 pagesModule 11. Research Hypothesisvience banzaliNo ratings yet
- Health Educ FinalsDocument12 pagesHealth Educ FinalserythromycinNo ratings yet
- Scordo Writing ObjectivesDocument3 pagesScordo Writing ObjectivesSharmane SantiagoNo ratings yet
- PCK3.6 Module10Document5 pagesPCK3.6 Module10Fort FortNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - UBDDocument12 pagesModule 3 - UBDJBM 0531100% (1)
- Science 7 Q1 W1 PDFDocument12 pagesScience 7 Q1 W1 PDFJanezzhel AntivoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Understanding The DesignDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Understanding The DesignDiane HamorNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Chapter 1 Dan 2Document6 pagesUnit Plan Chapter 1 Dan 2Sendi WijayaNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document2 pagesActivity 4Emily DegumaNo ratings yet
- Aiou Assignment 1Document20 pagesAiou Assignment 1Mrs SaadNo ratings yet
- 9th Module Do Not Just Dream Make It HappenDocument4 pages9th Module Do Not Just Dream Make It Happenalexa dawatNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Philo 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan Philo 1Maricar Narag SalvaNo ratings yet
- Module - For Acvity - YbanezDocument10 pagesModule - For Acvity - YbanezRomeo Betache Jr.No ratings yet
- Undertaking Reflection - Jan RaeDocument9 pagesUndertaking Reflection - Jan RaeSahnaz Gohor JahanNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Skills Survey by WKDocument7 pages21st Century Skills Survey by WKwolayatkhanNo ratings yet
- Inquiry (5E) Lesson Plan Template: Evidence of Mastery (Measurable)Document2 pagesInquiry (5E) Lesson Plan Template: Evidence of Mastery (Measurable)api-433583771No ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 2: Week 2Document8 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2: Week 2Abegail Panang100% (2)
- Lesson 2 Learning Targets For Performance AssessmentDocument12 pagesLesson 2 Learning Targets For Performance AssessmentKATE VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Forward Bloom's Taxonomy and Webb's DOKDocument13 pagesForward Bloom's Taxonomy and Webb's DOKEman MostafaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan VTFT Internship 2021 Credible VsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan VTFT Internship 2021 Credible Vsapi-553134523No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 March 3 2021 Conceptualizing The Research Title and SOPDocument7 pagesLesson 4 March 3 2021 Conceptualizing The Research Title and SOPCharlton Benedict BernabeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of LearningDocument28 pagesEvaluation of LearningBrix Augstheer MacarayaNo ratings yet
- Competency Map Chapter 1 The Nature of Science Grade 5 Santa Laurensia Primary SchoolDocument6 pagesCompetency Map Chapter 1 The Nature of Science Grade 5 Santa Laurensia Primary SchoolSendi WijayaNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH 1 Q2 Module 4Document12 pagesRESEARCH 1 Q2 Module 4lyndebdafNo ratings yet
- Minggu 13-14Document147 pagesMinggu 13-14Lyana RahmatNo ratings yet
- English Analysing Themes and Ideas Presentation Beige Pink Lined Style - 20240116 - 200217 - 0000Document18 pagesEnglish Analysing Themes and Ideas Presentation Beige Pink Lined Style - 20240116 - 200217 - 0000socamokingNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Students’ Learning Skills: Education and LearningFrom EverandThe Importance of Students’ Learning Skills: Education and LearningNo ratings yet
- IM NO.: IM-PROFED8-2NDSEM-2020-2021 College of Teacher Education Bayombong CampusDocument9 pagesIM NO.: IM-PROFED8-2NDSEM-2020-2021 College of Teacher Education Bayombong CampusXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- AL2-IM (1) - Review of Principles of AssessmentDocument8 pagesAL2-IM (1) - Review of Principles of AssessmentXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- AL2 Taxonomy Bloom Krathwohl SimpsonDocument7 pagesAL2 Taxonomy Bloom Krathwohl SimpsonXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- AL2-Module7-Grading and ReportingDocument7 pagesAL2-Module7-Grading and ReportingXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- AL2-Module4-Assessment in The Affective DomainDocument9 pagesAL2-Module4-Assessment in The Affective DomainXyra Ballesteros100% (2)
- AL2-Module3-Product-oriented-Performance-based AssessmentDocument5 pagesAL2-Module3-Product-oriented-Performance-based AssessmentXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- AL2-Handout5-Assessment Tools in The Affective DomainDocument10 pagesAL2-Handout5-Assessment Tools in The Affective DomainXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 (Lesson 3) - Prof Ed 9ADocument5 pagesMODULE 4 (Lesson 3) - Prof Ed 9AXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Insights As Regards The ArticleDocument2 pagesInsights As Regards The ArticleXyra BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Doctex 1Document2 pagesDoctex 1nwahlian5270No ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology: Dr. Dina Youssri Afifi Dr. Nehal Mostafa Ahmed Lecturers of PsychiatryDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Psychology: Dr. Dina Youssri Afifi Dr. Nehal Mostafa Ahmed Lecturers of Psychiatrynada abdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Comparison and SuperlatifDocument2 pagesComparison and Superlatifsudeepa pathiranaNo ratings yet
- Interviewing at Google Zurich PGMDocument7 pagesInterviewing at Google Zurich PGMSilviu TrebuianNo ratings yet
- Robust Vocabulary InstructionDocument4 pagesRobust Vocabulary Instructionmadhu_gopinathanNo ratings yet
- Indicative Verb Endings TableDocument2 pagesIndicative Verb Endings TableKateNo ratings yet
- Perspectives On The History of Mathematical Logic PDFDocument218 pagesPerspectives On The History of Mathematical Logic PDFPallab Chakraborty100% (1)
- Year 7 English Portfolio AboveDocument31 pagesYear 7 English Portfolio AboveRomeo AvilesNo ratings yet
- The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative ResearchDocument59 pagesThe Oxford Handbook of Qualitative ResearchCINDY DAZANo ratings yet
- Automatic Writing As An Indicator...Document22 pagesAutomatic Writing As An Indicator...Eduardo AramayoNo ratings yet
- Paper FixDocument53 pagesPaper FixayuniNo ratings yet
- Business Model Flexibility: Detecting Weak Signals by Internet-Based Environmental ScanningDocument12 pagesBusiness Model Flexibility: Detecting Weak Signals by Internet-Based Environmental Scanningdco123No ratings yet
- Helping Students Cope With Loss:: Incorporating Art Into Group CounselingDocument13 pagesHelping Students Cope With Loss:: Incorporating Art Into Group Counselingapi-268625907100% (1)
- Implementation of Story Mapping and Mind Mapping Toward Students' Reading Comprehension Enhancement: A Comparative StudyDocument8 pagesImplementation of Story Mapping and Mind Mapping Toward Students' Reading Comprehension Enhancement: A Comparative StudyFlrc29No ratings yet
- Rhs Science Lab Report GuidelinesDocument2 pagesRhs Science Lab Report Guidelinesapi-268599570No ratings yet
- Force Field TheoryDocument15 pagesForce Field TheoryFrancis MaluntagNo ratings yet
- Leadership and StorytellingDocument8 pagesLeadership and StorytellingSmitha DileepNo ratings yet
- David Hume - Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion (1779)Document276 pagesDavid Hume - Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion (1779)WaterwindNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document20 pagesWa0004.Albatross ArtemisiaNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns Possessive Adjectives Possessive PronounsDocument1 pagePersonal Pronouns Possessive Adjectives Possessive PronounsTeh ban lengNo ratings yet
- Brain Imaging Techniques and HemisphereDocument4 pagesBrain Imaging Techniques and HemisphereYour MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Role of Literature Review in Formulation of ResearchDocument8 pagesRole of Literature Review in Formulation of Researchsaraprathap100% (1)
- DLL Acp 09 6 7Document2 pagesDLL Acp 09 6 7eileen omictinNo ratings yet
- Collocation: Make Tea - I Made A Cup of Tea For Lunch. Do Homework - I Did All of My Homework YesterdayDocument8 pagesCollocation: Make Tea - I Made A Cup of Tea For Lunch. Do Homework - I Did All of My Homework YesterdayhanifNo ratings yet
- Educ 360 Fieldwork Action Research Project 1Document12 pagesEduc 360 Fieldwork Action Research Project 1api-584365435No ratings yet
- How To Write A Scientific PaperDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Scientific PaperNguyễn Ngọc TrâmNo ratings yet