Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aad Abdomen Worksheet
Uploaded by
AchOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aad Abdomen Worksheet
Uploaded by
AchCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
AAD abdomen worksheet
Regional Anatomy (University of Birmingham)
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
SurgSoc’s Annual Anatomy Away Day 2022
Anatomical Region: Abdomen
Key Learning Objectives
• Identify the important landmarks defining the boundaries of the abdominal
cavity
• Describe the descriptive regions and quadrants of the abdomen and identify
the organs and viscera underlying these regions
• Recall the muscular layers of the anterolateral abdominal wall
• Describe the structure of the peritoneum, mesentery and omentum.
• Understand the gross anatomy and neurovascular supply of oesophagus, stomach, intestines, liver,
gallbladder, biliary tree and pancreas
Abdominal Anatomy
Abdominal Cavity
• Superiorly bounded by the inferior thoracic aperture and the diaphragm
• Inferiorly bounded at the pelvic inlet (continuous with pelvic cavity)
• Antero-posteriorly bounded by the abdominal wall
Surface Anatomy
1. Four quadrants: intersection of two planes
a. Horizontal trans-umbilical plane
b. Vertical median plane
2. Nine regions: intersection of two horizontal and two vertical planes
a. Subcostal plane (Horizontal at level L3)
b. Intertubercular plane (Horizontal at level L5 and iliac crest)
c. Two midclavicular planes (Vertical from mid-clavicle to anterior-superior iliac spine)
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Regions of the Digestive Tract
1. Foregut
• Distal oesophagus à proximal part of
duodenum
• Includes liver, pancreas and gallbladder
• Arterial supply: Coeliac Trunk
• Venous drainage: Portal and splenic vein
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Greater splanchnic nerve
and coeliac plexus
o Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve
o Referred pain to epigastric region
2. Midgut
• Distal part of duodenum à proximal 2/3 of
transverse colon
• Arterial supply: Superior mesenteric artery
• Venous drainage: Superior mesenteric vein
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Lesser splanchnic nerve
o Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve
o Referred pain to umbilical region
3. Hindgut
• Distal 1/3 of transverse colon à
rectum
• Arterial supply: Inferior
mesenteric artery
• Venous drainage: Inferior
mesenteric vein
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Least
splanchnic nerve and
inferior mesenteric plexus
o Parasympathetic: Pelvic
splanchnic nerves (S2-S4)
o Referred pain to pubic
region
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Abdominal Viscera
Peritoneum
A continuous thin membrane lining the walls of the abdominal cavity and
viscera
• Parietal:
o Lines the innermost lining of the abdominal wall
o Somatic innervation – localised pain
• Visceral:
o Covers the abdominal viscera
o Autonomic innervation – poorly localised pain
• Intraperitoneal organs (A): Suspended in the peritoneal cavity
• Retroperitoneal organs (B): Suspended outside the peritoneal cavity
Peritoneal Cavity
• Potential space between parietal and
visceral peritoneum divided into greater
sac and lesser sac (omental bursa)
• Cavity is closed in men and open in women
• Greater sac:
o Most of the space in peritoneal
cavity
o Diaphragm à pelvic cavity
• Lesser sac (omental bursa):
o Smaller space posterior to stomach
and liver
o Continuous with greater sac via
omental/epiploic foramen
Omenta
• Folded layers of visceral peritoneum
• Greater omentum:
o Four layers of peritoneum
o Greater curvature of stomach à
transverse colon
• Lesser omentum:
o Two layers of peritoneum
o Lesser curvature of stomach/1st part of
duodenum à inferior surface of liver
o Contains hepatogastric and
hepatoduodenal ligament
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Mesenteries
• Peritoneal folds that attach viscera to the posterior abdominal wall
• A channel for vessels, nerves and lymphatics to travel from wall to
viscera
• Mesentery: Connects jejunum and ileum to posterior wall
• Transverse mesocolon: Connects transverse colon to posterior wall
• Sigmoid mesocolon: Connects sigmoid colon to posterior wall
• Intraperitoneal organs suspended my mesentery (stomach, liver,
spleen
• Retroperitoneal organs not suspended (adrenals, aorta, duodenum,
pancreas, ureters, ascending/descending colon, kidneys, oesophagus
and rectum)
Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
Layers:
1. Skin
2. Superficial fascia
a. Camper’s fascia (fatty)
b. Scarpa’s fascia (thin)
3. 3 flat muscles + 2 vertical muscles
4. Transversalis fascia
5. Extraperitoneal fascia
6. Peritoneum
Rectus Sheath
• Aponeurotic tendinous sheath enclosing vertical muscles
• Tendinous sheath arising form the 3 flat muscles
• Arcuate line: Midway between umbilicus and pubic symphysis
• A: Above arcuate line
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
o Complete enclosure of rectus abdominis
• B: Below arcuate line
o Anterior enclosure of rectus abdominis
Abdominal Oesophagus
• Muscular tube from pharynx to stomach
• Distal 2cm located in abdominal cavity
• Emerges through the right crus of the diaphragm
via oesophageal hiatus at T10
• Arterial supply: Left gastric artery and left inferior phrenic artery
• Venous drainage: Azygos and hemiazygos veins
• Lymphatic drainage: Posterior mediastinal nodes and left gastric nodes
• Innervation:
o Striated muscle: Branchial efferents from Vagus
o Smooth muscle: Parasympathetic from Vagus
o Sensory: Visceral afferents from Vagus, sympathetic trunk and
splanchnic nerves
• Left and right vagus nerve converge to form anterior and posterior vagal
trunk which pass into the abdomen with the oesophagus
Stomach
• Divided into cardia, fundus, body, pyloric part
• Cardial notch where the oesophagus
• A greater curvature to which greater omentum is attached to
• A lesser curvature to which lesser omentum is attached to
• Arterial supply: R+L gastric artery, R+L gastro-omental artery
• Venous drainage: R+L gastric veins, R+L gastro-omental veins
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Greater splanchnic nerve (T6-T9)
o Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Small Intestine
• Pyloric orifice à ileocecal fold
Duodenum
• Widest lumen, 20-25cm long and divided
into four parts
• Superior
o Pyloric orifice à neck of gallbladder
• Descending
o Neck of gallbladder à lower border
of L3
• Inferior
o Inferior duodenal flexure (L3)
o Longest section
• Ascending
o Travels from L3 to L2 and terminates
at duodenojejunal flexure
• Arterial supply: Branches of gastroduodenal artery and superior mesenteric artery
o Supra
• Venous drainage: Pre-pyloric vein and superior/inferior pancreaticoduodenal veins
Jejunum
• Makes up the proximal 2/5 of the rest of the small
intestine
• Located in LUQ
• Compared to ileum:
o Thicker intestinal wall
o Numerous plicae circulares
o Longer vasa recta
o Fewer arterial arcades
• Arterial supply: Superior mesenteric artery
• Venous drainage: Superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Celiac and superior mesenteric plexus
o Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Ileum
• Makes up distal 3/5 of the rest of the small intestine
• Ends at ileocecal junction
• Located in RLQ
• Compared to jejunum:
o Thinner intestinal wall
o Fewer plicae circulares
o Shorter vasa recta
o Numerous arterial arcades
• Arterial supply: Superior mesenteric artery
• Venous drainage: Superior mesenteric vein and
splenic vein
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Celiac and superior mesenteric plexus
o Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve
Large Intestine
• Ileocecal junction à anus
• Absorbs fluids and salts forming faeces
1. Caecum
2. Appendix
3. Colon
a. Ascending
b. Transverse
c. Descending
4. Sigmoid colon
5. Rectum
6. Anal canal
Caecum
• Inferior to ileocecal opening
• Located in RIF
Appendix
• Narrow, hollow, blind-ended tube
• Suspended by mesoappendix
• Contains aggregations of lymphoid tissue
• Location varies
• Arterial supply: Anterior/posterior caecal artery and
appendicular artery
• Venous drainage: Ileocolic vein à superior mesenteric
vein
• Innervation:
o Sympathetic: Superior mesenteric plexus
o Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Colon
• Ascending à R colic flexure à Transverse à L colic flexure à Descending à Sigmoid
• Ascending and descending colon are secondarily retroperitoneal
• Transverse and sigmoid are intraperitoneal
• Sigmoid colon is an S shape from pelvic inlet to S3 vertebrae
Rectum and Anal canal
• Rectum
o Rectosigmoid junction à S3 vertebrae
o Retroperitoneal structure
o Sacral flexure and anorectal flexure
• Anal canal
o Continuation of large intestine inferior to
rectum
o Internal anal sphincter (involuntary control)
o External anal sphincter (voluntary control)
Arterial Supply
Superior Mesenteric Artery
• Ileocolic and right colic artery branches à Ascending colon
• Right and middle colic artery branches à First 2/3 of transverse
colon
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
• Left colic artery branch à Final 1/3 of transverse colon
• Left colic artery à Descending colon
• Sigmoid arteries à Sigmoid colon
• Superior rectal artery à Rectum (above dentate line)
Internal Iliac Artery
• Middle and inferior rectal artery branches à Rectum (Below
dentate line)
Venous Drainage
Superior Mesenteric Vein
• Drains small bowel, cecum, ascending colon and
transverse colon
Inferior Mesenteric Vein
• Drains rectum above dentate line (superior rectal vein),
sigmoid colon, descending colon and splenic flexure
Inferior Vena Cava
• Drains rectum below dentate line (inferior rectal vein)
IMV à SMV and sigmoid colon à Portal vein à Liver à
Inferior Vena Cava
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Innervation
Sympathetic
• Pre-ganglionic neurone
• Paravertebral neurone
• Celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, inferior hypogastric ganglia
• Post-ganglionic neurone
• Abdominal viscera
Parasympathetic
• Vagus Nerve
• Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4)
Liver
• Intraperitoneal
• Located in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region
with extension into left hypochondrium
Surfaces
• Diaphragmatic surface (anterior, superior, posterior)
o Smooth, domed
o Lies against the inferior diaphragm
o Covered with visceral peritoneum (except posterior
aspect)
o Subphrenic recess separates diaphragmatic liver from diaphragm
• Visceral surface (inferior)
o Covered with visceral peritoneum (except gall bladder and porta hepatis)
o Porta hepatis is the entry point for hepatic arteries and portal vein
o Hepatorenal recess separates the visceral liver surface from right kidney and right adrenal
gland
Ligaments
• Connects liver to other structures on the abdomen
• Falciform ligament à Anterior Abdominal Wall
o Free edge contains ligamentum teres
• Hepatogastric ligament à Stomach
• Hepatoduodenal ligament à Duodenum
• Triangular ligaments à Diaphragm
• Coronary ligament à Diaphragm
Lobes
• Divided into right and left lobes anterosuperiorly by:
o Falciform ligament and the ligament teres
• Quadrate Lobe
o Anterior part of visceral surface
o Bound by ligamentum teres and gallbladder fossa
o Structurally appears from right lobe but functionally related to left
• Caudate Lobe
o Posterior part of visceral surface
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
o Bound by ligamentum teres and IVC groove
o Functionally separate to right and left lobe
Neurovascular Supply
Arterial Supply
• Abdominal Aorta à Coeliac trunk à Common Hepatic artery à Hepatic artery proper à R/L
Hepatic Arteries (25%)
• Hepatic portal vein (75%, partially deoxygenated blood)
Venous Drainage
• Hepatic sinusoids à Hepatic vein à IVC
Lymphatic Drainage
• Anterior: Hepatic lymph nodes
• Posterior: Phrenic and posterior mediastinal lymph nodes
Innervation
• Hepatic plexus
• Sympathetic: Coeliac plexus
• Parasympathetic: Vagus Nerve
Gallbladder
• Intraperitoneal on visceral surface of the right love of the liver in a fossa between the right and
quadrate lobes
• Receives, concentrates and stores bile made from the liver
Structure
• Fundus
o Rounded end projecting from inferior liver border
• Visceral
o Located in gallbladder fossa
• Neck
o Mucosal folds forming spiral fold
o Hartmann’s pouch
• Arterial supply: Cystic artery from R Hepatic artery
• Venous drainage:
o Cystic vein à Portal vein
o Hepatic sinusoids
• Lymphatic drainage: Cystic lymph nodes
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Duct System
• Drains bile formed in liver into duodenum
• Liver à R/L hepatic duct à Common hepatic duct (joins with cystic duct) à Bile duct (joins with
pancreatic duct) à Hepatopancreatic ampulla à Descending part of duodenum (major duodenal
papilla)
Pancreas
• Extends across posterior abdominal wall within epigastric and left hypochondrium
• Retroperitoneal structure (except small part of tail)
Structure
• Head
o Lies within C-shaped part of duodenum
• Uncinate process
o Projects from lower head posterior to superior
mesenteric vessels
• Neck
o Anterior to superior mesenteric vessels
• Body
o Elongated area from neck to tail
• Tail
o Passes between layers of splenorenal ligament
Pancreatic Duct System
• Main pancreatic duct runs from tail à body à
head.
• Joins bile duct to form hepatopancreatic ampulla
before entering descending duodenum via major
duodenal papilla
• Sphincter of ampulla (Oddi) surrounds the ampulla
• Accessory pancreatic duct empties into duodenum
via minor duodenal papilla
• Arterial supply:
o Head and neck: Superior/inferior pancreaticoduodenal branches
o Body and tail: Dorsal and greater pancreatic artery from splenic artery
• Venous drainage:
o Head and neck: Pancreatic veins à SMV à Portal vein
o Body and tail: Pancreatic veins à Splenic vein à Portal vein
• Lymphatic drainage: Coeliac, superior mesenteric and splenic nodes
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
Worksheet Exercises
2)
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
3) Label the abdominal regions:
4) Label the abdominal muscles and related structures:
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|18099120
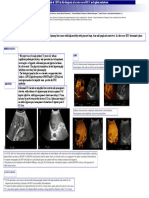
5) Label as many structures as you can from this CT:
6) Label the following structures:
Downloaded by Pre Ten (abionateniola828@gmail.com)
You might also like
- GasterDocument179 pagesGasterAraka Patriota100% (1)
- Anatomy of the Stomach and DuodenumDocument179 pagesAnatomy of the Stomach and DuodenumHaraka NabdaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal CavityDocument78 pagesAbdominal Cavitytanishapatel1005No ratings yet
- ANATOMI SISTEM PENCERNAAN by Dr. RifalDocument97 pagesANATOMI SISTEM PENCERNAAN by Dr. RifalSusi ErawatiNo ratings yet
- Stomach Anatomy in 40 CharactersDocument29 pagesStomach Anatomy in 40 CharactersSupriti Verma Bhatnagar100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Abdomen (6) : - Abdominal Esophagus - Stomach - Small Intestine - Large IntestineDocument34 pagesAnatomy of The Abdomen (6) : - Abdominal Esophagus - Stomach - Small Intestine - Large IntestineBilal YimamNo ratings yet
- Amboss - GITDocument16 pagesAmboss - GITAllysahNo ratings yet
- 4 The Stomach and The Abdominal EsophagusDocument43 pages4 The Stomach and The Abdominal EsophagusAbdullah HaroonNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AnatomyDocument39 pagesAbdominal AnatomyRahul MandhanNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINEDocument38 pagesANATOMY OF SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINERakaNo ratings yet
- Abdomen & Pelvis Anatomy GuideDocument35 pagesAbdomen & Pelvis Anatomy GuidenostavimleNo ratings yet
- GIT Cont 071628Document51 pagesGIT Cont 071628Olatomide OlaniranNo ratings yet
- Small IntestineDocument34 pagesSmall IntestineIAMSANWAR019170100% (1)
- Gross Anatomy of The Small IntestineDocument27 pagesGross Anatomy of The Small IntestineEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Duodenum and PancreaslectureDocument35 pagesDuodenum and PancreaslectureChigozie GeraldNo ratings yet
- LI, Pancreas, Liver, GallbladderDocument106 pagesLI, Pancreas, Liver, GallbladderSuhayb CumarNo ratings yet
- 1.esophagus IntroDocument32 pages1.esophagus Introrobel derejeNo ratings yet
- Abdomen - Esophagus To ColonDocument42 pagesAbdomen - Esophagus To ColonBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Large Intestine Functions and AnatomyDocument34 pagesLarge Intestine Functions and AnatomySastiy MutiadesieNo ratings yet
- 1 Abdominal VisceraDocument45 pages1 Abdominal VisceraMero HamedNo ratings yet
- StomachDocument24 pagesStomachHarini KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- ORG10Document23 pagesORG10TodesengelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of OesophagusDocument22 pagesAnatomy of OesophagusFatima SalahNo ratings yet
- 13b.blood Vessels of AbdomenDocument71 pages13b.blood Vessels of AbdomenIshimwe TheotimeNo ratings yet
- EsopagusstomachDocument20 pagesEsopagusstomachTodesengelNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument64 pagesDigestive SystemAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- PeritoneumDocument39 pagesPeritoneumtuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels of Abdomen-PIMSR DR - Gosai 2022Document32 pagesBlood Vessels of Abdomen-PIMSR DR - Gosai 2022Dr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Ana SGD 15Document67 pagesAna SGD 15Bea ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Abdomen AnatomyDocument22 pagesAbdomen AnatomyJim RohnNo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument26 pagesAbdomenOlivia Chandra DeviNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument32 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyRiza MuttaqinNo ratings yet
- Pancreas 2017Document53 pagesPancreas 2017yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 2 GIDocument123 pagesPemicu 2 GIDessy DsyNo ratings yet
- Anterior Abdominal WallDocument20 pagesAnterior Abdominal WallewijayapalaNo ratings yet
- ANAT 221 - PeritoneumDocument22 pagesANAT 221 - PeritoneumWisdom IkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of DuodenumDocument23 pagesAnatomy of DuodenumEngki AdityaNo ratings yet
- ESOPHAGUSDocument29 pagesESOPHAGUSNasasira CosmasNo ratings yet
- The artery most likely to be eroded in perforation of the posterior wall of the first part of the duodenum is the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. It is a branch of the gastroduodenal arteryDocument33 pagesThe artery most likely to be eroded in perforation of the posterior wall of the first part of the duodenum is the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. It is a branch of the gastroduodenal arteryWahida Amalin Ab RazakNo ratings yet
- 7) Anatomy of OMENTUMDocument22 pages7) Anatomy of OMENTUMGoodone OneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Stomach & Duodenum: by Mekonnen.A (R1)Document46 pagesAnatomy Stomach & Duodenum: by Mekonnen.A (R1)Tsega WesenNo ratings yet
- IvorDocument21 pagesIvorLia AuliantiNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum, Peritoneal Cavity, and Diaphragm 11-6-15-1Document67 pagesPeritoneum, Peritoneal Cavity, and Diaphragm 11-6-15-1Deny ShajiniNo ratings yet
- Anat 221-Large IntestineDocument21 pagesAnat 221-Large IntestineWisdom IkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Small IntestineDocument16 pagesSmall IntestineShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine MMCDocument65 pagesSmall Intestine MMCWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument38 pagesColon CancerUsmle GuyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PeritoneumDocument61 pagesAnatomy of PeritoneumFirdaus SeptiawanNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine Anatomy GuideDocument18 pagesSmall Intestine Anatomy Guideseidevi sankar100% (1)
- Peritoneum: General FeaturesDocument92 pagesPeritoneum: General FeaturestuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Abdomen FinalDocument31 pagesAnatomy Abdomen FinalShakthivel ManiNo ratings yet
- Anal PathologyDocument28 pagesAnal PathologyHaashveeni Jayan KumarNo ratings yet
- Large Intestine (Part 2)Document59 pagesLarge Intestine (Part 2)paranoea911No ratings yet
- Abdomen.: Moore, Keith. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Seventh Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Baltimore. 2014Document58 pagesAbdomen.: Moore, Keith. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Seventh Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Baltimore. 2014Paola Solarte ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EsophagusDocument14 pagesAnatomy of The EsophagusroselynroukayaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Drainage of Abdomen: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLymphatic Drainage of Abdomen: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Anatomi AbdomenDocument36 pagesAnatomi Abdomenari naNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Abdomen: Samara University Biomedical Sciences DepartmentDocument142 pagesAnatomy of The Abdomen: Samara University Biomedical Sciences Departmentfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lower GI TractDocument180 pagesPhysiology of Lower GI TractIcarus WingsNo ratings yet
- SECTION 6: Spleen: and OverviewDocument38 pagesSECTION 6: Spleen: and Overviewtudoranluciana1No ratings yet
- 4 Jama - Leung - 2023 - Gs - 230007 - 1697225319.65814Document2 pages4 Jama - Leung - 2023 - Gs - 230007 - 1697225319.65814Nazly ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Logarajah, 2021Document6 pagesLogarajah, 2021Aze Andrea PutraNo ratings yet
- Pathology Clinical Pathological CaseDocument4 pagesPathology Clinical Pathological CaseJulienne DelfinNo ratings yet
- The Doctrine of SignaturesDocument5 pagesThe Doctrine of SignaturesJoko RinantoNo ratings yet
- Heme Degradation & HyperbilirubinemiasDocument27 pagesHeme Degradation & HyperbilirubinemiasIMDCBiochemNo ratings yet
- RPA Newborn Care Guidelines: Royal Prince Alfred Hospital Umbilical Venous CatheterisationDocument16 pagesRPA Newborn Care Guidelines: Royal Prince Alfred Hospital Umbilical Venous CatheterisationsalamredNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Ascites and Its Etiology Using Ultrasonography JRD 119 PDFDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Ascites and Its Etiology Using Ultrasonography JRD 119 PDFEstu Paramadina PratamaNo ratings yet
- CHS Physical Assessment GuideDocument4 pagesCHS Physical Assessment GuideJosal SinonNo ratings yet
- Digestion AND Absorption: - 1 - HSE Zoology BlogDocument88 pagesDigestion AND Absorption: - 1 - HSE Zoology BlogMahir AfranNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of MushroomDocument22 pagesHealth Benefits of MushroomMeenuNo ratings yet
- Melatonin From Plant Products: Regulation of Immunity and General Physiology in Indian Goat C. HircusDocument18 pagesMelatonin From Plant Products: Regulation of Immunity and General Physiology in Indian Goat C. HircusajmrdNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and NutritionDocument6 pagesDigestive System and NutritionAthena HuynhNo ratings yet
- General Surgical Technique in HepatectomyDocument40 pagesGeneral Surgical Technique in HepatectomyKeam PisethsapheareachNo ratings yet
- Detoxification and Chelation Protocols GuideDocument213 pagesDetoxification and Chelation Protocols Guidedoggydog100% (3)
- Mbbs Pathology QuestionsDocument11 pagesMbbs Pathology QuestionsAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Bile Duct Injury NCBI Stat PearlsDocument6 pagesBile Duct Injury NCBI Stat PearlsDeni Marie GomonidNo ratings yet
- ABDOMEN ANATOMYDocument25 pagesABDOMEN ANATOMYAshraf Alamin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ammonia IntoxicationDocument31 pagesAmmonia IntoxicationClare DucutNo ratings yet
- MCLD 2020 - Poster Board NumberDocument3 pagesMCLD 2020 - Poster Board NumberArdianto SucintaNo ratings yet
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular Diseases of The Liver Q PDFDocument24 pagesEASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular Diseases of The Liver Q PDFMihaela PăvăleanNo ratings yet
- Catálogo+Document21 pagesCatálogo+huanarpoNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument35 pagesCholelithiasisHetty PoendeiNo ratings yet
- Khanna 2018Document20 pagesKhanna 2018wahid akbarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S209636022030048X Main PDFDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S209636022030048X Main PDFsebastiangomez4No ratings yet
- Chapter 61 LiverDocument1 pageChapter 61 LiverDayane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Acute Liver Failure: ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2022Document5 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Pediatric Acute Liver Failure: ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2022Tushar AmbedareNo ratings yet
- Organs in The Body Quadrants and RegionsDocument3 pagesOrgans in The Body Quadrants and RegionsDavid HosamNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis 2018 08 23 18 13 33 319 PDFDocument69 pagesFinal Thesis 2018 08 23 18 13 33 319 PDFPriyanka KanodiaNo ratings yet
- CEUS Role in Rare HCC, Spleen Metastases CaseDocument1 pageCEUS Role in Rare HCC, Spleen Metastases CaseRoxana BaranNo ratings yet