Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Frequency Bands: General Information
Uploaded by
Karan TyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Frequency Bands: General Information
Uploaded by
Karan TyCopyright:
Available Formats
24 FEB 06
RADIO AIDS GENERAL INFORMATION
11
GENERAL INFORMATION
The general information contained on the following pages is provided for use as quick reference. It has been compiled from a variety of sources. Additional information can be found elsewhere in the Radio Aids section.
FREQUENCY BANDS
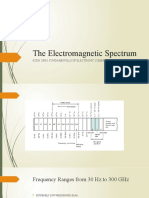
Radio frequencies lie within a relatively narrow range of the electro-magnetic spectrum between approximately 10 kHz and 300 GHz. This range is divided into bands, more or less in accordance with the propagation characteristics of the frequencies. These bands are: VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF SHF EHF Very Low Frequency Low Frequency Medium Frequency High Frequency Very High Frequency Ultra High Frequency Super High Frequency Extremely High Frequency 0 - 30 kHz 30 kHz - 300 kHz 300 kHz - 3 MHz 3 MHz - 30 MHz 30 MHz - 300 MHz* 300 MHz - 3 GHz* 3 GHz - 30 GHz 30 GHz - 300 GHz
108.0 - 111.975 MHz
ILS localizer (on odd-tenths plus twentieth frequencies, 108.1, 108.3 etc.) VOR (even tenths or even tenths plus a twentieth of MHz). VOR (even and odd tenths of MHz). ILS glide slope. DME and TACAN. GPS
108.0 - 111.975 MHz
111.975 - 117.975 MHz 328.6 - 335.4 MHz 960.0 - 1215.0 MHz 1563.42 - 1587.42 MHz
AIRBORNE STATIONS
410 kHz 475 kHz International DF (outside continental USA). Working frequency exclusively for aircraft on sea flights desiring an intermediate frequency. International frequency for aircraft and ships over the seas. Transmission on this frequency (except for urgent and safety messages and signals) must cease twice each hour, for three minute periods beginning at 15 and 45 minutes past each hour. Lighter-than-aircraft.
*200 MHz - 3 GHz is considered UHF in Aviation. All VHF markers (FAN TYPE, OUTER, INNER and ZONE) operate on 75 MHz (75,000 KHz), and are tone modulated as follows: FM LFM MM OM Z Fan Marker (100 Watts) Low-Powered Fan Marker (5 Watts) Middle Marker Outer Marker Station Location Marker 3000 Hz 3000 Hz 1300 Hz 400 Hz 3000 Hz
500 kHz
FREQUENCY ALLOCATION
Frequency allocation is established to provide a clear channeling between the various functions performed by aeronautical navaids and communications facilities. Although a general allocation plan is recognized on a world-wide basis, variations may occur within certain ranges. The listing below is intended to provide that allocation most generally used by civil operators.
3281 kHz
NAVIGATION AIDS
190 - 535 kHz Nondirectional Radio Beacon (low power) and Radio Range (low power). Non-directional Beacon (standard). Marker Beacon. VOR test facility (VOT).
JEPPESEN SANDERSON, INC. 2006. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
190 - 1750 kHz Non-directional Beacon (standard). 108.0 - 117.975 MHz
You might also like
- Radio NavigationDocument176 pagesRadio NavigationOleacov SergiuNo ratings yet
- Radio Spectrum - WikipediaDocument12 pagesRadio Spectrum - WikipediaMubashir AliNo ratings yet
- Radio Aids - Student NotesDocument70 pagesRadio Aids - Student Notesyassir100% (1)
- Topic 4 UHF, VHF, HF and SAT PrinciplesDocument57 pagesTopic 4 UHF, VHF, HF and SAT PrinciplesLikaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Principles of VHF Propagation and The Allocation of FrequenciesDocument3 pagesChapter 2-Principles of VHF Propagation and The Allocation of FrequenciesFahmi PrayogiNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency BandsDocument7 pagesRadio Frequency BandsaceofspadesNo ratings yet
- Scan Nov 14, 17Document17 pagesScan Nov 14, 17Apichai KasamutNo ratings yet
- Information Binary Digit / BitDocument2 pagesInformation Binary Digit / BitJun Alfred AlbaNo ratings yet
- 1 Frequency BandsDocument39 pages1 Frequency BandsRehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Radio Spectrum: ITU Radio Band Numbers ITU Radio Band Symbols NATO Radio Bands IEEE Radar BandsDocument6 pagesRadio Spectrum: ITU Radio Band Numbers ITU Radio Band Symbols NATO Radio Bands IEEE Radar Bandsryoma.lustre5703No ratings yet
- Assignment by Saba-71 and Sabahat-72Document7 pagesAssignment by Saba-71 and Sabahat-72HAJRA khalidNo ratings yet
- Radio Spectrum: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesRadio Spectrum: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Management - A Regulator View & QOS: ELF Extremely Low Frequency 30 HZ - 300 HZDocument4 pagesSpectrum Management - A Regulator View & QOS: ELF Extremely Low Frequency 30 HZ - 300 HZAravind VadaseriNo ratings yet
- Frequency Bands and Applications: International Telecommunication UnionDocument7 pagesFrequency Bands and Applications: International Telecommunication UniongezahegnNo ratings yet
- A Crash Course in Radio Frequency and Frequency ManagementDocument14 pagesA Crash Course in Radio Frequency and Frequency ManagementBashir Hassan MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Propagation 2Document3 pagesPropagation 2Amandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Comsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsDocument3 pagesComsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsNicolasMaregaNo ratings yet
- 16 Jul 21 CNS Revision Sem IvDocument7 pages16 Jul 21 CNS Revision Sem Ivkunal chaudharyNo ratings yet
- 1.intro & High Frequency Behavious of ComponentsDocument54 pages1.intro & High Frequency Behavious of Componentspravallika vysyarajuNo ratings yet
- Microwave RadarDocument5 pagesMicrowave Radarrspsm2023No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Principles of Radio CommunicationDocument34 pagesUnit 2 Principles of Radio CommunicationAnonymous j3WOut100% (1)
- L02 1 Aircraft CommunicationDocument40 pagesL02 1 Aircraft Communicationm gopakumarNo ratings yet
- Eten Presentation Group eDocument14 pagesEten Presentation Group eMuhammad AuwalNo ratings yet
- RF Microwave Engineering: Bharath Ganji, RGUKT-NUZVIDDocument54 pagesRF Microwave Engineering: Bharath Ganji, RGUKT-NUZVIDpravallika vysyarajuNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document3 pagesNull 1Kelvin MwitiNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communications Part 1Document104 pagesMicrowave Communications Part 1John Dexter RealizoNo ratings yet
- Frequency PlanningDocument7 pagesFrequency PlanningneerajjangidNo ratings yet
- Table: of The Whole Electromagnetic Spectrum and Usage ExamplesDocument56 pagesTable: of The Whole Electromagnetic Spectrum and Usage ExamplesAd BriceNo ratings yet
- Communication System TC-307: Lecture 5, Week 2 Course Instructor: Nida NasirDocument66 pagesCommunication System TC-307: Lecture 5, Week 2 Course Instructor: Nida NasirUmer farooqNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument10 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumSheena Ann StonehillNo ratings yet
- I. VHF CommunicationsDocument12 pagesI. VHF CommunicationsSamuel OyelowoNo ratings yet
- Radio Is The Technology of Signaling And: A Variety of Radio On Near, New Mexico, USDocument7 pagesRadio Is The Technology of Signaling And: A Variety of Radio On Near, New Mexico, USTrixie MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- RAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010Document45 pagesRAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010zuliana100% (1)
- Lecture 5 CTDocument8 pagesLecture 5 CTSyed Junaid IqbalNo ratings yet
- 1a. Review Radio TheoryDocument46 pages1a. Review Radio TheoryRhonny AlbertoNo ratings yet
- How To Deal With RSL IssuesDocument65 pagesHow To Deal With RSL IssuesMbrn Ali100% (1)
- 1.VHF Propagation, Radio Wave 2 44 SlideDocument44 pages1.VHF Propagation, Radio Wave 2 44 SlidekagancenkNo ratings yet
- Band Frequency Frequency 2 MHZ: DSC RT HFDocument8 pagesBand Frequency Frequency 2 MHZ: DSC RT HFKO KO MinNo ratings yet
- AM Radio Band: Amplitude Modulated CarrierDocument4 pagesAM Radio Band: Amplitude Modulated CarrierSudarshanBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Q1 1) Define Propagation and 3 Components Required For Propagation?Document6 pagesQ1 1) Define Propagation and 3 Components Required For Propagation?Saripuddin MappiasiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledEdson MorenoNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument16 pagesNotesAviatorX JobinNo ratings yet
- Spectrum ChartDocument2 pagesSpectrum ChartMuzacky HadiNo ratings yet
- Radio TechnologyDocument70 pagesRadio TechnologyNikhitaWadhwaNo ratings yet
- 2 Wireless Communications RFDocument79 pages2 Wireless Communications RFCherukuri BharaniNo ratings yet
- NVIS HandbookDocument148 pagesNVIS HandbookRichard PNo ratings yet
- GMDSS2Document65 pagesGMDSS2Cezar M. Barranta Jr.No ratings yet
- 01 ULO2a, KBP, NTCDocument94 pages01 ULO2a, KBP, NTCMelrose LopezNo ratings yet
- Antenna and PropagationDocument43 pagesAntenna and PropagationMeghali Borle100% (1)
- Ata 23Document8 pagesAta 23Dũng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- To Discuss RF, Microwaves and Small Signal Analog Frequencies Along With Applications of EachDocument4 pagesTo Discuss RF, Microwaves and Small Signal Analog Frequencies Along With Applications of Eachdeberjeet ushamNo ratings yet
- Radio Navigation SlidesDocument42 pagesRadio Navigation Slidessegunajayi71No ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE FREQUENCY: Definition: in Communications and Electronic Engineering, An IntermediateDocument9 pagesINTERMEDIATE FREQUENCY: Definition: in Communications and Electronic Engineering, An Intermediatehbueno_1867% (3)
- GMDSS Lection Week 3Document17 pagesGMDSS Lection Week 3George KandelakiNo ratings yet
- RF Training Module PDFDocument56 pagesRF Training Module PDFriskalltowin50% (2)
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument27 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumJacklyn Kate Caballero Garduque100% (2)
- VorDocument11 pagesVorPravin Hande100% (3)
- (Doi 10.1109 - 9780470544662.Ch1) Collin, Robert E. - Foundations For Microwave Engineering Volume 2059 - IntroductionDocument16 pages(Doi 10.1109 - 9780470544662.Ch1) Collin, Robert E. - Foundations For Microwave Engineering Volume 2059 - IntroductionSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tactical Dipole (CHA TD) Operator's Manual: Versatile - Dependable - Stealth - Built To LastDocument22 pagesTactical Dipole (CHA TD) Operator's Manual: Versatile - Dependable - Stealth - Built To LastAsmaa AbduNo ratings yet