Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economics - Money and Credit
Uploaded by
Gg YyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economics - Money and Credit
Uploaded by
Gg YyCopyright:
Available Formats
In the formal sector, loans from banks and In the Informal sector, loans from moneylenders, traders, employers,
aders, employers, relatives and friends are included.
cooperatives are included.
• As we know that major portion of the deposited money is provided to those people who are needy of money for
• In India, the formal sector sources of credit are still economic activities. In India Reserve bank of India is supervised the functioning of loan activities in formal sectors. In India,
only about half of the total credit needs of the rural the rate of interest in informal sector is greater than the rate of interest in formal sector. Rate of interest in formal sector is
people. Thus, it is necessary to the formal sources supervised by the legal authorities.
of credit expand their lending especially in rural
• In the Informal sector, the rate of interest is supervised by moneylenders, traders, employers who are provided money.
areas, so that the dependency on the formal sources
The rate of interest is varying from person to person. There is no organization for supervising loan in informal sector.
of credit is increased, which would benefit the
Lenders can use any method to get back their money from the borrowers. Sometimes, the incomes of the borrowers
development of the country on a wider scale.
become less compare than the amount which has to pay due to the high rate of interest.
Formal sector Informal sector
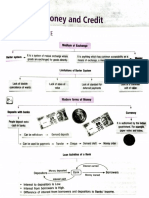
Money as a medium of exchange Loan activities of bank
• Money is an item which is used as a
medium of exchange. In modern economy, • Bank work as mediator between the
money is work as an intermediary. It is depositors and the borrowers. People deposit
used as a medium of exchange for goods
Sources of credit their money in bank and get some rate of
and services. It is also used for payment of interest as extra income. Banks hold only
debts. some percentage of their deposit in bank.
• Introduction of money replaced the
batter system. Before that, Indians used Money • A major portion of the deposited money is
grains and cattle as money. In a barter provided to those people who are needy of
system, selling and purchasing of goods
and services was done with “double
and money for economic activities. In this case,
money is provided as a loan with a higher
coincidence of wants” i.e.by fulfilling
mutual wants without the use of money. In Credit rate of interest. The difference between
interest on borrowing money and the interest
this system goods and services was of deposited money is the income for the
exchanged for another goods and services. Modern form of bank.
money Credit situations
Currency Deposits with two types of Terms of credit
Banks credit situation
• Modern forms of money include currency • Deposits with Banks are also a • In the first situation, a person borrows • The interest rate, collateral and some
— paper notes and coins. The modern coins form of money. A person can money for production activities with the documents fulfill the requirements of
are not made with the precious metals like deposit in the bank by opening an promise to repay the loan at the end of the the terms of credit. Interest rate is
gold, silver. The real values of the modern account on his/her name. People year when production work will be specified when a lender provides loan
coins are less than its face value. Currency need only some money at a point completed. And at the end of the year, to the borrowers. A borrower will have
notes are also used as a medium of of time. So, people can deposit he/she makes a good profit from production to repay the amount taken from the
exchange in modern economy. The currency extra money and earn extra activities and he/she is able to pay the lenders with the amount of interest. In
notes are made with paper. The real values money, which is given on money amount of loan. Therefore, that person some case, lenders may demand
of the currency notes are less than its face already depositing in bank. becomes better off than before. collateral against loans.
value.
• Collateral is an asset of the
borrowers which is given to the
• A facility of payment through • In the second situation, a person borrows
• The currency is authorized by the lenders as security for the specified
cheque is also provided by the money for production activities with the
government of the country. So, it is used as period. A lender can use the assets
bank to their customers. Cheque promise to repay the loan at the end of the
a medium of exchange and accepted by the which are held by him as security until
work as an instrument for year when production work will be
others. In India, Reserve bank of India has the amount of loan is repaid. The
payment which is made by the completed. And at the end of the year,
authority to issue currency notes on behalf lender has right to sell the assets or
paper. A person can directly he/she unable to repay the loan due to loss
of the central government. In India, no collateral when the borrower fails to
transfer money to another in production. For this term, he/she come
individual can legally refuse to accept the repay the amount of loan in a specified
person through cheque rather under the situation of debt trap. Therefore,
rupees issued by the Reserve bank of India. period.
than in cash. that person becomes worse off than before.
Self-help groups for the poor
• Facilities of banks are not available in all rural areas. So, the poor are dependent on informal sector for borrowing loan. The poor have to pay a high rate of interest to the
moneylenders. It is difficult to borrow loan from the bank. Because of the absence of the collateral and documents. And documents and collateral are required for a bank loan.
Informal lenders like, moneylenders are often willing to give a loan without collateral because they personally knew the borrowers.
• An organization constituted to collect the savings of the poor which is known as self-help group. The aim of the organisation is to lend loan at less rate of interest compared to the
rate of interest specified by the moneylenders. A self-help group has 15 – 20 members. Savings vary from member to member i.e., Rs. 25 to Rs. 100 depending on the ability of the
person to save.
• The organization also provides self-employment opportunity for the member by the way of sanctioning the group. For example, small loans are provided to the members for
releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs, for housing materials, for acquiring assets. There is also a group for repayment of loan. In case of any non-repayment
by the one member is followed by the other member of the organisation.
You might also like
- Mind Map Money and CreditDocument1 pageMind Map Money and CreditMoin Ahmed100% (4)
- Money and Banking, IG - 1Document26 pagesMoney and Banking, IG - 1ANSHIKA CHAUHAN100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Money and CreditDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Money and CreditKiran shukla100% (1)
- Money & Credit - Mind MapDocument2 pagesMoney & Credit - Mind MapMohd RazaNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit One ShotDocument13 pagesMoney and Credit One Shotmrsnightmare76No ratings yet
- Money & CreditDocument9 pagesMoney & CreditGaurav KrishniaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Flow Chat 2Document1 pageClass 10 Flow Chat 2Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument7 pagesMoney and CreditSunil Sharma100% (1)
- Money and Credit - Shobhit NirwanDocument11 pagesMoney and Credit - Shobhit Nirwansannigrahipriyanshu08No ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 3 Handwritten Notes Money and Credit EconomicsDocument11 pagesEconomics Chapter 3 Handwritten Notes Money and Credit EconomicsRenu Yadav100% (1)
- Notes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsDocument9 pagesNotes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money and CreditDocument32 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money and CreditK.SrisudharsanVIII.A K.K.Rohith IV.BNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit NotesDocument4 pagesMoney and Credit Notesadityamanjhi108No ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument7 pagesMoney and Creditraimaali220077No ratings yet
- Economics, Chapter 3 Money and CreditDocument3 pagesEconomics, Chapter 3 Money and CreditshambhaviNo ratings yet
- Money: Slides Are Developed by DG. Do Not Distribute or Duplicate The MaterialDocument54 pagesMoney: Slides Are Developed by DG. Do Not Distribute or Duplicate The MaterialAbbu JNo ratings yet
- MONEY X EconomicsDocument7 pagesMONEY X EconomicsAvika SinghNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 3Document6 pagesEconomics Chapter 3Aavy MishraNo ratings yet
- FinanceDocument7 pagesFinanceFrancine FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Introduction To Bank (Law & Practice)Document9 pagesChapter 01 Introduction To Bank (Law & Practice)Rayyah AminNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit AakashDocument4 pagesMoney and Credit AakashNisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Digital LendingpdfDocument36 pagesDigital Lendingpdflucifer smithNo ratings yet
- PaolaDocument9 pagesPaolalorenaNo ratings yet
- December-10-Eco-Ch-3 Money & Credit-NotesDocument36 pagesDecember-10-Eco-Ch-3 Money & Credit-Notesananyamishra11122007No ratings yet
- 1 Overview Slides Banking v2 SCDocument39 pages1 Overview Slides Banking v2 SCsahilmonga1No ratings yet
- 1.money and CreditDocument18 pages1.money and CreditNandita KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument2 pagesMoney and CreditChris JudeNo ratings yet
- 3 Money and CreditDocument5 pages3 Money and CreditRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingpptDocument19 pagesMoney and BankingpptSania ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Report Text Banking SystemDocument1 pageReport Text Banking Systemchelarisa100% (1)
- HO 1 - Investment EnvironmentDocument24 pagesHO 1 - Investment EnvironmentCora CaramalesNo ratings yet
- Functions of Banks PDFDocument10 pagesFunctions of Banks PDFSumit K SankhlaNo ratings yet
- The Economics of BankingDocument10 pagesThe Economics of Bankingleunice SantyNo ratings yet
- PRINT CC Week 23Document4 pagesPRINT CC Week 23miyanoharuka25No ratings yet
- BANKINGDocument7 pagesBANKINGSalik AfzalNo ratings yet
- Working Capital FinanceDocument5 pagesWorking Capital Financenainaniharshita03No ratings yet
- FIN 121 Quiz1&Quiz2Document2 pagesFIN 121 Quiz1&Quiz2MarkNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Financing: Debts: Financial Management Part IIDocument11 pagesLong-Term Financing: Debts: Financial Management Part IIKisha QuirozNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document98 pagesChapter 1Om Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document3 pagesTopic 5KyNo ratings yet
- Investment Alternatives & Indirect Investment - FIXEDDocument41 pagesInvestment Alternatives & Indirect Investment - FIXEDGulem HealerNo ratings yet
- How Bank WorksDocument3 pagesHow Bank WorksMai Mai VarelaNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit Class 10Document27 pagesMoney and Credit Class 10amritadevi121979No ratings yet
- Money & Credit SlideDocument64 pagesMoney & Credit SlideFREE FIRE SHORT VIDEO'SNo ratings yet
- Credit CollectionLECTURES 1 2Document7 pagesCredit CollectionLECTURES 1 2Efren ChanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Debt ManagementDocument33 pagesModule 3 Debt ManagementJane BañaresNo ratings yet
- 9.banking ServicesDocument26 pages9.banking Servicessaikumar selaNo ratings yet
- Money - Credit Class 10Document1 pageMoney - Credit Class 10Legendary Pokemon Blaster 2406No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Money and Payment System Eco531Document13 pagesChapter 3 Money and Payment System Eco5312022876708No ratings yet
- MONEY & CREDIT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-MapDocument49 pagesMONEY & CREDIT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-Mapnimit jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument10 pagesMoney and BankingIsha KembhaviNo ratings yet
- Pres Money Dec 2021 FinalDocument28 pagesPres Money Dec 2021 FinalandreNo ratings yet
- PPB Module 2Document18 pagesPPB Module 2RAJNo ratings yet
- Modern Banking: Measures of The Money Supply, Functions and Types of Financial Institutions, and Modern E-BankingDocument16 pagesModern Banking: Measures of The Money Supply, Functions and Types of Financial Institutions, and Modern E-BankingnripendunandyNo ratings yet
- Consumer FinanceDocument87 pagesConsumer Financearn01dNo ratings yet
- Finish Line & BeyondDocument5 pagesFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Eco Money & CreitDocument5 pagesClass 10 Eco Money & CreitPrarthna AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Alternate FinanceDocument9 pagesAlternate FinanceAnkita GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Insider's Keys: To The Best Rates And Terms On Your Next Mortgage, #1From EverandInsider's Keys: To The Best Rates And Terms On Your Next Mortgage, #1No ratings yet